BIOLOGY
FORM 4
END TERM EXAMS
TERM 1 2021
PAPER 2
(THEORY)
TIME 2 hrs
INSTRUCTIONS
- This paper has 2 sections: A and B
- Answer all questions in Section A
- In Section B, Answer ONLY 2 Questions.
SECTION A: (40 MARKS)
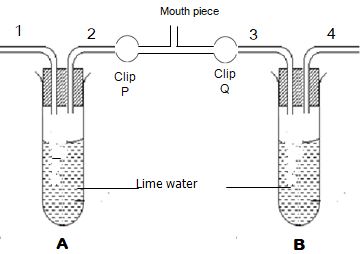
- The following set up was set for the form two class to study a certain concept.
- Point out one mistake in the set-up and correct the mistake on diagram. (2mks)
- State the aim of the experiment. (1mk)
- Explain how the apparatus is used to achieve the aim of the experiment. (5mks)
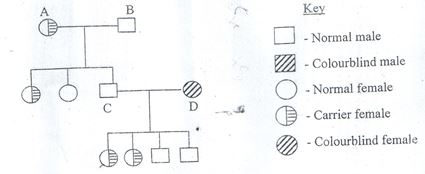
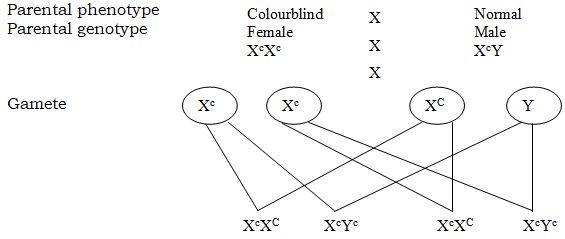
- The following pedigree shows how the gene for colourblindness was passed in a family for three generations. The gene for colour blindness is sex linked.|
- Define the term sex linkage. (1mk)
- Write down the genotype of the parents A and B. (2mk)
- Write down the phenotypic ratios of the 2nd generation from parents A and B. Show how you arrived at your answer. (5mks)
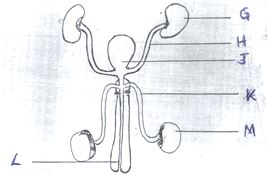
- The diagram below represents the urinogenital system of a human being.
- Name the parts labeled H and K
- State the functions of the parts labeled G and L
-
- Give the letter of the structure in which meiosis occurs(1mk)
- State how the structure identified in (c) (i) is modified to enhance the survival of products of meiosis. (1mk)
-
- Name the hormone secreted by the part labeled M
- What is the function of the hormone named in (d) (i) above. (1mk)
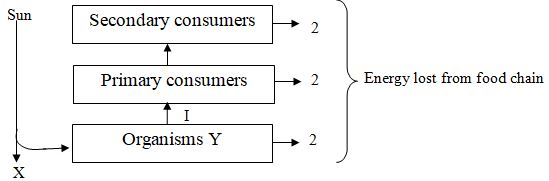
- The scheme below shows how energy is transmitted from the sun into the ecosystem.
- Name; (2mks)
- Organisms
- Process I
- Suggest two ways through which energy is lost from one trophic level to the next. (2mks)
- What is the importance of decomposers in an ecosystem? (1mk)
- Define the term Eutrophication. (1mk)
- Which trophic level has the least number of organisms? Explain why. (2mks)
- Name; (2mks)
- An animal had the following teeth; on the upper jaw, no incisors, no canines, six premolars and six molars. On the lower jaw, 6 incisors, no canines, six premolars and six molars.
- Write down it’s dental formula. (1mk)
-
- Suggest the mode of nutrition of this animal(1mk)
- Give a reason for your answer in (b) (i) above. (1mk)
- State two adaptations of the animal whose dental formula you have written in (a) above. (2mks)
- Name one dental disease in humans. (1mk)
- What is the role of teeth in digestion? (2mks)
SECTION B: (40 MARKS)
This section consist of three questions 6, 7 and 8. Answer question 6 (COMPULSORY) and either question 7 or 8 in the spaces provided.
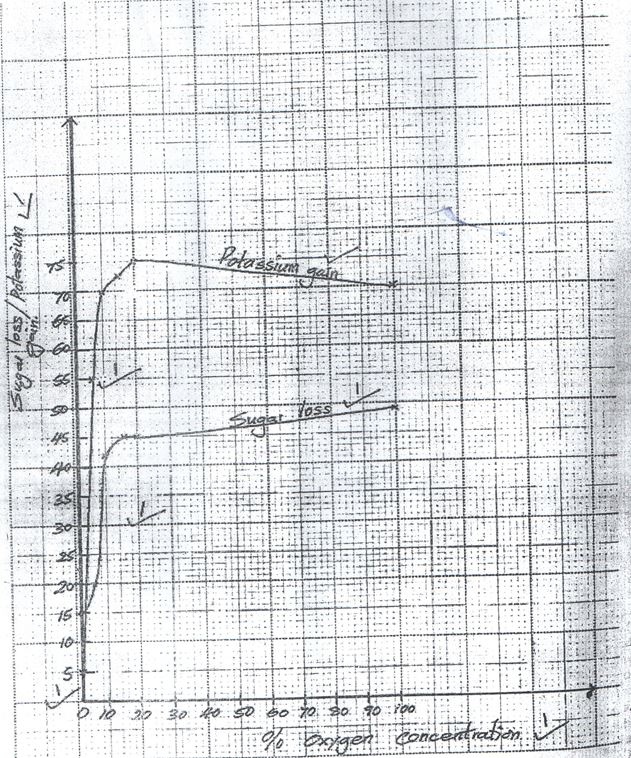
- The relationship between oxygen concentration, potassium gain and sugar loss in isolated barley root was determined. The results obtained are given in the table below. (The sugar loss and potassium gain are expressed in arbitrary units).
Percentage oxygen concentration 0 5 10 15 20 100 Sugar loss 15 20 42 45 45 48 Potassium gain 5 55 70 73 75 70 - Plot on the same axes graphs of sugar loss and potassium gain against oxygen concentrations. (8mks)
-
- Suggest the process by which potassium is taken in by the roots. (1mk)
- Give reasons for your answer. (2mks)
- Account for the sugar loss and potassium gain at;
- 0% oxygen concentration. (2mks)
- Between 5% and 20% oxygen concentration. (2mks)
- Apart from oxygen concentration, suggest two other factors that affect the above process. (2mks)
- State two ways in which you can stop the above process from taking place. (2mks)
- Name one part in human body where the process named in b(i) above take place. (1mk)
-
- What is meant by the term natural selection? (2mks)
- Describe how natural selection brings about the adaptations of a species to its environment. (8mks)
- Distinguish between convergent and divergent evolution. (2mks)
- Discuss four evidences to show that evolution has taken place. (8mks)
- Explain five abiotic factors that affect living organisms in an ecosystem. (20mks)

MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A: (40 MARKS)
- The following set up was set for the form two class to study a certain concept.
- Point out one mistake in the set-up and correct the mistake on diagram. (2mks)
- Tube 3 is hanging instead of being dipped into the lime water in test tube B;
- Tube 3 is hanging instead of being dipped into the lime water in test tube B;
- State the aim of the experiment. (1mk)
- To compare the amount of carbon (II) oxide in inhaled and exhaled air.
- To compare the amount of carbon (II) oxide in inhaled and exhaled air.
- Explain how the apparatus is used to achieve the aim of the experiment. (5mks)
- Close clip Q and open clip P; suck in air into the lungs through the mouth piece inserted into mouth; Hold the air in the lungs; close clip P and open clip Q; breath out through the mouth piece into tube 3 and into the lime water in test tube B; (5mks)
- Close clip Q and open clip P; suck in air into the lungs through the mouth piece inserted into mouth; Hold the air in the lungs; close clip P and open clip Q; breath out through the mouth piece into tube 3 and into the lime water in test tube B; (5mks)
- Point out one mistake in the set-up and correct the mistake on diagram. (2mks)
- The following pedigree shows how the gene for colourblindness was passed in a family for three generations. The gene for colour blindness is sex linked.|
- Define the term sex linkage. (1mk)
- Phenomenon where genes controlling other traits are carried in the sex chromosomes with the sex gene and are transmitted together. (1mk)
- Phenomenon where genes controlling other traits are carried in the sex chromosomes with the sex gene and are transmitted together. (1mk)
- Write down the genotype of the parents A and B. (2mk)
- - XcXc
- - XcY
- Write down the phenotypic ratios of the 2nd generation from parents A and B. Show how you arrived at your answer. (5mks)
Genotype of 2nd generation
Phenotypic ratio/Normal: 1 colourblind.
- Define the term sex linkage. (1mk)
- The diagram below represents the urinogenital system of a human being.
- Name the parts labeled H and K
- H – Ureter
- K – Sperm duct/vas deferens
- State the functions of the parts labeled G and L
- G- Helps to remove impurities from the blood, medicines etc
- L- To remove waste product from the body in form of urine
-
- Give the letter of the structure in which meiosis occurs(1mk)
- M
- State how the structure identified in (c) (i) is modified to enhance the survival of products of meiosis. (1mk)
- Hang outside the body to attain optimum temperature for formation and survival of sperms.
- Give the letter of the structure in which meiosis occurs(1mk)
-
- Name the hormone secreted by the part labeled M
- Testosterone.
- Testosterone.
- What is the function of the hormone named in (d) (i) above. (1mk)
- Development of secondary sexual characteristics;
- Development of secondary sexual characteristics;
- Name the hormone secreted by the part labeled M
- Name the parts labeled H and K
- The scheme below shows how energy is transmitted from the sun into the ecosystem.
- Name; (2mks)
- Organisms - Plants.
- Process I - Eating/Feeding
- Suggest two ways through which energy is lost from one trophic level to the next. (2mks)
- Absorbed into atmosphere.
- Respiration, excretion, faeces, unedible material.
- What is the importance of decomposers in an ecosystem? (1mk)
- Helps to recyle nutrients into the ecosystem.
- Helps to recyle nutrients into the ecosystem.
- Define the term Eutrophication. (1mk)
- Uncontrolled growth of water plants due to increased nutrients.
- Uncontrolled growth of water plants due to increased nutrients.
- Which trophic level has the least number of organisms? Explain why. (2mks)
- 3rd trophic level; contains least energy;
- 3rd trophic level; contains least energy;
- Name; (2mks)
- An animal had the following teeth; on the upper jaw, no incisors, no canines, six premolars and six molars. On the lower jaw, 6 incisors, no canines, six premolars and six molars.
- Write down it’s dental formula. (1mk)
I 0 , C 0, pm 3, m 3
0 0 3 3 -
- Suggest the mode of nutrition of this animal(1mk)
- Herbivorous.
- Herbivorous.
- Give a reason for your answer in (b) (i) above. (1mk)
- Lacks incisors on upper jaw.
- Lacks canines on both jaws/ has diastema.
- Suggest the mode of nutrition of this animal(1mk)
- State two adaptations of the animal whose dental formula you have written in (a) above. (2mks)
- Enamel open at the top crown to allow continuous growth.
- Has diastema to create space for manipulation of food by tongue during chewing.
- Presence of horny pad on upper jaw against which incisors on lower jaw cut off vegetation.
- Jaws joined to allow sideways movement of the jaws during chewing.
- Name one dental disease in humans. (1mk)
- Dental carries; periodontal disease; any 1
- Dental carries; periodontal disease; any 1
- What is the role of teeth in digestion? (2mks)
- Break down and grind food into small chunks for swallowing.
- Write down it’s dental formula. (1mk)
SECTION B: (40 MARKS)
This section consist of three questions 6, 7 and 8. Answer question 6 (COMPULSORY) and either question 7 or 8 in the spaces provided.
- The relationship between oxygen concentration, potassium gain and sugar loss in isolated barley root was determined. The results obtained are given in the table below. (The sugar loss and potassium gain are expressed in arbitrary units).
Percentage oxygen concentration 0 5 10 15 20 100 Sugar loss 15 20 42 45 45 48 Potassium gain 5 55 70 73 75 70 - Plot on the same axes graphs of sugar loss and potassium gain against oxygen concentrations. (8mks)
-
- Suggest the process by which potassium is taken in by the roots. (1mk)
- Active transport;
- Active transport;
- Give reasons for your answer. (2mks)
- An increase in sugar loss results to an increase in potassium gain/used during respiration to produce energy; Energy used during active transport to gain potassium ions;
- An increase in sugar loss results to an increase in potassium gain/used during respiration to produce energy; Energy used during active transport to gain potassium ions;
- Suggest the process by which potassium is taken in by the roots. (1mk)
- Account for the sugar loss and potassium gain at;
- 0% oxygen concentration. (2mks)
- Low/no oxygen concentration; less energy produced hence less potassium gain/ uptake;
- Low/no oxygen concentration; less energy produced hence less potassium gain/ uptake;
- Between 5% and 20% oxygen concentration. (2mks)
- An increase in oxygen concentration; result to an increase in energy production hence an increase in potassium gain/uptake;
- An increase in oxygen concentration; result to an increase in energy production hence an increase in potassium gain/uptake;
- 0% oxygen concentration. (2mks)
- Apart from oxygen concentration, suggest two other factors that affect the above process. (2mks)
- Temperature; pH; Protein carriers;
- Temperature; pH; Protein carriers;
- State two ways in which you can stop the above process from taking place. (2mks)
- Depriving the plant of oxygen supply; Treating roots with metabolic poisons; subjecting roots to very high temperature; provision of unfavourable pH; (2mks)
- Depriving the plant of oxygen supply; Treating roots with metabolic poisons; subjecting roots to very high temperature; provision of unfavourable pH; (2mks)
- Name one part in human body where the process named in b(i) above take place. (1mk)
- Kidney tubeles;/small intestines;/neurons. (1mk)
- Plot on the same axes graphs of sugar loss and potassium gain against oxygen concentrations. (8mks)
-
- What is meant by the term natural selection? (2mks)
- Nature or the environment selects those individuals that are sufficiently adapted; and rejects those that are not well adapted; (2mks)
- Nature or the environment selects those individuals that are sufficiently adapted; and rejects those that are not well adapted; (2mks)
- Describe how natural selection brings about the adaptations of a species to its environment. (8mks)
- Individuals of the same species show variations. The variations are caused by genes that can be passed on from parents to the offsprings (inherited);
- Some of these variation become more suitable or favourable or advantageous in the prevailing environmental conditions;
- Because organisms usually produce more off springs than the environment can support; competition for resources sets in;
- This leads to struggle for existence;
- Individuals with more favourable characteristics/adaptations/gene mutation have better chance of survival in the struggle;
- Hence they reach reproductive age, reproduce and pass on favourable characteristics to the offspring;
- Those with less favourable characteristics or adaptations fail to reach sexual maturity; they die young;
- Examples of natural selection include – malarial parasite/plasmodium which has developed strains that are resistant to anti-malarial drugs;
- Sickle cell trait; the homozygous die young and the heterozygous are resistant to malaria.
- Distinguish between convergent and divergent evolution. (2mks)
- Convergent evolution. - This is a phenomenon where structures from different embryonic origins are modified to perform the same function. E.g. wings of birds and those insects, eyes of human beings and those of octopus;
- Divergent evolution. - This is a phenomenon where one basic structural form is modified to give rise to various different forms which perform different functions. E.g. pentadactyl limbs of vertebrates, shapes of beaks in birds;
- Discuss four evidences to show that evolution has taken place. (8mks)
- Fossil records.
Fossils are remains of dead organisms preserved naturally. They indicate that organisms have evolved from simple life forms to most complex forms. Fossils of human beings indicate that the modern human being has a highly developed brain and uses speech for communication unlike the early human being. Fossils of horses show that the modern horse is 1.5m high, lives in dry grassland, teeth are adapted for chewing and it stands on one digit whose distal end is converted into hoof. - Comparative anatomy.
This involves comparing the form and structure of different organisms. Some groups of organisms show basic structural similarities suggesting common or related ancestry showing divergent evolution. Other groups of organisms show morphological similarities but are found to have different ancestry showing convergent evolution; - Comparative embryology.
Studies show that embryos of fish, birds, amphibians, reptiles and mammals are morphologically similar during the early stages of development but with time they develop and change to look like their parents; - Geographical distribution (continental drift)
Its believed that long ago and the land was one mass which later drifted apart to form the current continents. This is called the continental drift.
Regions with similar climatic conditions and lie in the same latitude have flora and fauna that are not identical. This indicates that they have evolved differently; e.g Amazon forest of South America has long tailed monkeys, panthers and jaguars while similar African forests have short tailed monkeys, leopards and cheetahs. - Vestigial organs.
- Cell biology.
-Cells of higher organisms show basic similarities in their structure and function; e.g. the presence of cell membranes and organelles such as mitochondria, ribosomes and golgi bodies.
-Higher plant cells have cellulose cell walls, chloroplasts and starch showing evolution from a common ancestry.
-The blood pigment, haemoglobin is common in vertebrates and invertebrates.
- Fossil records.
- What is meant by the term natural selection? (2mks)
- Explain five abiotic factors that affect living organisms in an ecosystem. (20mks)
- Water – The availability of adequate amounts of water lead to plant growth which provides food for animals. In aquatic environment, water is a medium in which gametes are released thus lead to continuity in procreation.
- Temperature – influences the rate of enzyme catalysed reactions. Therefore, it exerts an influence on almost all activities of plants and animals such as respiration, photosynthesis, growth, transport e.t.c.
- Light – is necessary in plants for photosynthesis as it influences flowering of a wide variety of plants, affecting opening and closing of stomata, affects the rate of transpiration.
- Salinity – is the salt content of eater. It varies in aquatic habitat. Fresh water organisms suffer the risk of loosing water.
- Humidity – determines the amount of water loss from a bodies animals and organs of plants; high humidity means high rate of evaporation and transpirations;
- pH – it determines if water habitat is acidic or alkaline; pH has a great influence on physiological function of organisms affects enzyme controlled reactions since enzymes operate within a narrow pH ranges.
Download Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Form 4 End Term 1 Exams 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students