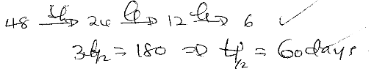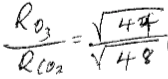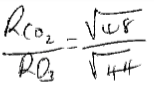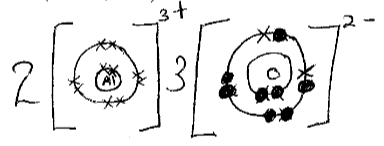INSTRUCTIONS
- Answer all the questions in the spaces provided
- Mathematical tables and silent electronic calculators may be used
- All working must be clearly shown where necessary
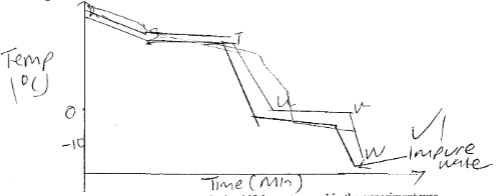
- The figure below shows the cooling curve for water is gaseous state.
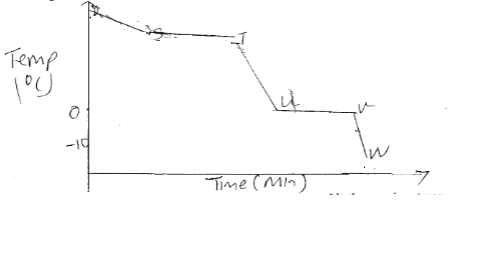
- Using the same axis draw a curve obtained if the water used in the experiment was impure. (1mk)
- Name the process taking place between:
- S and T (1mk)
- U and V (1mk)
- On addition of a few drops of aqeous sodium hydroxide to solution M a white precipitate forms which dissolves on a addition of excess sodium hydroxide. A white precipitate forms when solution M is reacted with sodium chloride solution. Suggest the identity of the cation present and explain. (2mks)
- 1g of sodium hydroxide is added to 30cm3 of 1M HCl. How many cm3 of 0.1M KOH solution will be needed to neutralize the excess acid. ( Na=40, O=16, H=1) (3mks)
- Describe how you can prepare crystals of magnesium chloride starting with 50cm3 of 2M magnesium hydroxide. (3mks)
- Use the following information to answer the questions that follow
∆Hlattice Mgcl2 = -2489 KJ/ mol-1
∆Hhydration Mg2+ = - 1891 kJ/ mol
∆H hydration Cl- = -384 kJ/ mol- Calculate the heat of solution of magnesium chloride. (2mks)
- Draw an energy level diagram for the dissolving of magnesium chloride. (2mks)
- The reaction between hydrochloric acid and potassium dichromate can be used to demonstrate a reversible reaction. The ionic equation is given below
2Cro42-(aq) + 2H+(aq)Cr2O72- (aq) + H20(l)
Yellow orange
Explain the observation that would be made when dilute hydrochloride acid is added to the equilibrium mixture. (2mks) - The table below gives the rate of decay for a sample of a radioactive element P
Mass of P (g) number of days 48 0 18 90 6 180 - Determine its half-life (2mks)
- Complete the following nuclear equation. (1mk)
233 0
Pa + e
91 -1
- Study the following flow chart. Use it to answer the question that follow
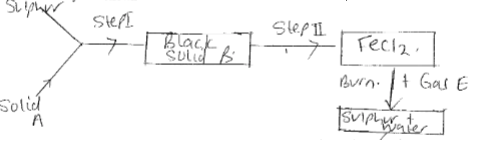
- Identify (3mks)
- Solid A
- Solid B
- Gas E
- Name the reagents used in step (2mks)
- II
- Identify (3mks)
-
- Name two salts responsible for permanent hardness of water. (2mks)
- Explain the precipitation method used to remove water hardness. (1mk)
- When steam was passed over heated charcoal as shown in the diagram, below, hydrogen and carbon (II) oxide gases were formed.
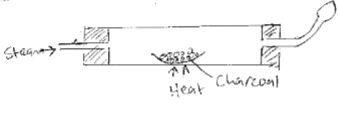
- Write the equation for the reaction which takes place. (1mk)
- Name two uses of carbon (II) oxide gas which are also uses of hydrogen gas. (2mks)
-
- State and explain the observations made when a few drops of concentrated Sulphuric (vi) acid is added to sucrose ( C12, H22,O11) (2mks)
- Using an equation show how the above reaction takes place. (1mk)
- Students from Sunshine Secondary School suspected that some water contained either sulphate or sulphite cons. Explain how the ion present can be determined. (3mks)
- A mixture of ethane, oxygen and nitrogen are ignited. On cooling the residual gas occupied 58cm3 when shaken with aqeous alkali, the volume was reduced to 32cm3. A further 18cm3 of the product was absorbed by alkaline pyrogallo. Calculate the composition of the original mixture. ( C = 12, H = 1, N = 14, O = 16 and molar volume at r.t.p = 24dm3. (4mks)
- 0.24g of a divalent metal x dissolves in 50cm3 of 0.25 M sulphuric acid. The resulting solution required 5.0cm3 of 1.0 M sodium hydroxide solution to neutralize the excess acid. What is the reactive atomic mass of x.
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow.
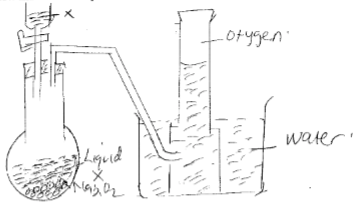
- Identify liquid x (1mk)
- Write an equation for the reaction that occurs in the flask. (1mk)
- Describe the confirmatory test for oxygen gas. (1mk)
- When zinc metal is reacted with a solution of hydrogen chloride gas in water there is effervescence. When the experiment is repeated with a solution of hydrogen chloride gas in methylbenzene there is no observable change. Explain this observations. (3mks)
- Compare the rate of diffusion of carbon dioxide (CO2) & ozone (O3) at the same temperature. (C = 12, O = 16 ) (3mks)
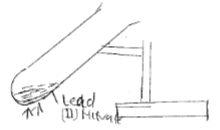
- Starting with Lead metal describe how to prepare a solid sample of Lead (II) Sulphate salt. (3mks)
- Given the following reaction
HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaCNl(aq) + H2O(l)
T1 = initial temperature of solutions before additions = 18.0oC
T2 = final temperature of solution at neutralization = 19.2oC
50cm3 1M HCl
50cm3 1M NaOH
Calculate Molar enthalpy of neutralization of hydrogen cyanide (3mks) - Compound K reacts with sodium hydroxide as shown
- What type of reaction is represented by the equation. (1mk)
- To what class of organic compounds does K belong. (1mk)
- How is M separated from aqueous mixture of L and M. (1mk)
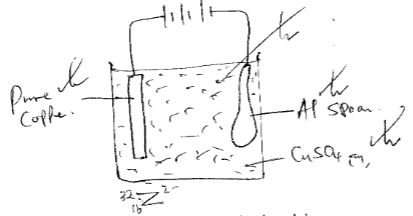
- Draw a diagram to show how an aluminium spoon can be electroplated with pure copper. (2mks)
- An ion of element Z can be represented as shown below,
Use the information to answer the questions that follow- Identify the period in which the element belong. (½mk)
- Write the electron configuration of the ion of Z ( ½mk)
- What would be the nature of the solution of the chloride of Z if dissolved in water. (1mk)
-
- What is PH scale (1mk)
- State whether the values of the following solution are strong or weak acids and bases.
PH = 8 (½mk)
PH = 5 (½ mk)
PH = 2 (½ mk)
PH = 13 (½mk)
- Draw the structure of;
-
- Hydroxonium ion H3O+ (1mk)
- Aluminium oxide (Al = 13, 0 = 8) (1mk)
- Aluminium chloride has a melting point of 120°C while Aluminium oxide has a melting point of 2977°C. In terms of structure and bonding explain how the differences come about. (2mks)
-
- State the use of the following laboratory apparatus
-
(1mk)
-
(1mk)
-
- The diagram below shows heating of Lead nitrate
- State the observations made in the above experiment (2mks)
- Write an equation for the reaction that takes place. (1mk)
- Give two differences between nuclear reactions and chemical reactions. (2mks)
- 3.1 g of an organic compound containing carbon, hydrogen and oxygen only produced 4.4 g of carbon oxide and 2.0 g of water on complete combustion:
- Calculate its empirical formulae (2mks)
- Calculate its molecular formulae if its formulae mass is 62. (2mks)
- Two cleansing agents are represented below
- R – COO−Na+ and
- R – OSO3−Na+
- Name the detergents (2mks)
- Select one of the detergents that would be suitable for washing in water containing magnesium chloride. Explain. (2mks)
- Use the data below to calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction below
CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H20(l) (3mks)
Bond Energy (KJ)
C – H 413
O = O 489
C = O 805
H – O 464

MARKING SCHEME
- The figure below shows the cooling curve for water is gaseous state.

- Using the same axis draw a curve obtained if the water used in the experiment was impure. (1mk)
- Name the process taking place between:
- S and T (1mk)
- Condensation
- U and V (1mk)
- Freezing
- S and T (1mk)
- Using the same axis draw a curve obtained if the water used in the experiment was impure. (1mk)
- On addition of a few drops of aqeous sodium hydroxide to solution M a white precipitate forms which dissolves on a addition of excess sodium hydroxide. A white precipitate forms when solution M is reacted with sodium chloride solution. Suggest the identity of the cation present and explain. (2mks)
- Pb2+
When Pb2+ reacts with NaOH, itforms insoluble lead (II) hydroxide which dissolves in excess to form comlex ions. When reacted with chloride ions there is formation of PbCl.
- Pb2+
- 1g of sodium hydroxide is added to 30cm3 of 1M HCl. How many cm3 of 0.1M KOH solution will be needed to neutralize the excess acid. ( Na=40, O=16, H=1) (3mks)
NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
Moles of NaOH = 1/40 = 0.025moles
Moles of HCl = 1 × 30 = 0.003moles
1000
Moles of HCl to react with KoH
0.003 − 0.025 = 0.005moles
HCl(aq) + KoH(aq) → KCl(aq) + H20(l)
Moles of KoH used = 0.005moles
0.1moles → 1000cm3
0.005moles → ?
1000 × 0.005 = 50cm3
0.1 - Describe how you can prepare crystals of magnesium chloride starting with 50cm3 of 2M magnesium hydroxide. (3mks)
Take 100cm3 of 2M HCl (or 200cm3 of 1M HCl) and add to 50cm3 of 2M MgCl2 in a beaker to form Magnesium sulphate solution. heat the solution to saturation and allow to cool for crystals to form. Filter and dry the crystals between filter papaers - Use the following information to answer the questions that follow
∆Hlattice Mgcl2 = -2489 KJ/ mol-1
∆Hhydration Mg2+ = - 1891 kJ/ mol
∆H hydration Cl- = -384 kJ/ mol- Calculate the heat of solution of magnesium chloride. (2mks)
Heat os solution = ∆Hlattice + ∆Hhydration
= +2489 + (−1891 +( 2×−384))
=+2489 −2659 =−170KJ/mol - Draw an energy level diagram for the dissolving of magnesium chloride. (2mks)
- Calculate the heat of solution of magnesium chloride. (2mks)
- The reaction between hydrochloric acid and potassium dichromate can be used to demonstrate a reversible reaction. The ionic equation is given below
2Cro42-(aq) + 2H+(aq)Cr2O72- (aq) + H20(l)
Yellow orange
Explain the observation that would be made when dilute hydrochloride acid is added to the equilibrium mixture. (2mks)
The orange colour intensifies because the added H+ makes the equilibrium to shift to the right. - The table below gives the rate of decay for a sample of a radioactive element P
Mass of P (g) number of days 48 0 18 90 6 180 - Determine its half-life (2mks)
- Complete the following nuclear equation. (1mk)
233 0 233
Pa + e → y
91 -1 90
- Determine its half-life (2mks)
- Study the following flow chart. Use it to answer the question that follow

- Identify (3mks)
- Solid A - Iron(Fe)
- Solid B - Iron (II) Sulphide (FeS)
- Gas E - Hydrogen sulphide (H2S)
- Name the reagents used in step (2mks)
- II Dilute Hydrochloric acid
- Identify (3mks)
-
- Name two salts responsible for permanent hardness of water. (2mks)
- Calcium sulphate
- Magnesium sulphate
- Explain the precipitation method used to remove water hardness. (1mk)
Sodium Carbonate is added to precipitate Ca2+ or Mg2+ ions
Mg2+ + CO32−→ MgCO3(s)
OR
Ca2+(aq)+ CO32−→MgCO3(s)
- Name two salts responsible for permanent hardness of water. (2mks)
- When steam was passed over heated charcoal as shown in the diagram, below, hydrogen and carbon (II) oxide gases were formed.

- Write the equation for the reaction which takes place. (1mk)
H2O(g) + C(s) → CO(g) + H2(g) - Name two uses of carbon (II) oxide gas which are also uses of hydrogen gas. (2mks)
- As a fuel
- As a redusing agent in hte extraction of metals such as iron fron that ore.
- Write the equation for the reaction which takes place. (1mk)
-
- State and explain the observations made when a few drops of concentrated Sulphuric (vi) acid is added to sucrose ( C12, H22,O11) (2mks)
- Black masss of substance is formed. This is because the concentrated sulphuric (V) acid removes the atom which forms water from the sucrose i.e Hydrogen and oxygen leaving behind Carbon which is black.
- Using an equation show how the above reaction takes place. (1mk)
Conc.H2SO4(l)
C12H22O11(S)12C(s) + 11H2O(l)
- State and explain the observations made when a few drops of concentrated Sulphuric (vi) acid is added to sucrose ( C12, H22,O11) (2mks)
- Students from Sunshine Secondary School suspected that some water contained either sulphate or sulphite cons. Explain how the ion present can be determined. (3mks)
- To a certain sample of water, add a few drops of Barium Nitrate solution followed by drops of dilute nitric(V) acid. If a white precipitate soluble on addition of the acid is formed the water contains sulphite ions and if a white precipitate insoluble on addition of the acid is formed the water contains sulphate.
- A mixture of ethane, oxygen and nitrogen are ignited. On cooling the residual gas occupied 58cm3 when shaken with aqeous alkali, the volume was reduced to 32cm3. A further 18cm3 of the product was absorbed by alkaline pyrogallo. Calculate the composition of the original mixture. ( C = 12, H = 1, N = 14, O = 16 and molar volume at r.t.p = 24dm3. (4mks)
1C2H4 + 2O2 → 2O2(g) + 2H2O(l)
Volume of CO2 = 58 − 32
= 26
Volume of O2 unreacted =18cm3
Mole ratio of CO2 : H2O
2 : 1
26 : ?
26 × 1 =13cm3 volume of C2H4
2
volume of O2 used
Mole ration of O2: CO2
2 : 2
? : 26
26 × 2 =26cm3 of O2 used
2
Total O2 present
26+18 =44cm3
Residual = Nitrogen + CO2 + used O2
58= N + 26 + 18
58 − 44 =14cm3 Nitrogen
Original mixture
44cm3 - oxygen
13cm3 - ethene
14cm3 - Nitrogen - 0.24g of a divalent metal x dissolves in 50cm3 of 0.25 M sulphuric acid. The resulting solution required 5.0cm3 of 1.0 M sodium hydroxide solution to neutralize the excess acid. What is the reactive atomic mass of x.
H2SO4(aq) + 2NaOH(aq) → Na2SO4(aq) + 2H2O(l)
Moles of NaOH = 0.005 × 1 = 0.005moles
Mole ratio of NaOH : H2SO4 =
2 : 1
0.005 0.0025 moles of H2SO4
X(s) + H2SO4(aq) → XSO4(aq) + H2(g)
Available moles of H2SO4 = 0.25 × 0.05 = 0.0125moles
Moles of H2SO4 reacted with X = 0.0125-0.0025 = 0.01
Mole ratio of X : H2SO4
1 : 1
0.01 : 0.01
Moles = mass
RFM
RFM = Mass = 0.24
Moles 0.01
=24 - Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow.

- Identify liquid x (1mk)
- Water
- Write an equation for the reaction that occurs in the flask. (1mk)
2Na2O2(g) + 2H2O(l) → 4NaOH(aq) + O2(g) - Describe the confirmatory test for oxygen gas. (1mk)
- Insert a glowing splint to a gas jar containing the gas, If it relights the gas is confirmed to be Oxygen.
- Identify liquid x (1mk)
- When zinc metal is reacted with a solution of hydrogen chloride gas in water there is effervescence. When the experiment is repeated with a solution of hydrogen chloride gas in methylbenzene there is no observable change. Explain this observations. (3mks)
- Solution of Hydrogen Chloride in water ionizes product hydrogen ions which makes the solution acidic hence reacting with zinc to produce hydrogen gas while a solution of hydrogen chloride in methylbenzene is in molecular form hence no reaction with zinc.
- Compare the rate of diffusion of carbon dioxide (CO2) & ozone (O3) at the same temperature. (C = 12, O = 16 ) (3mks)
CO2 = 12+ 32 =44
O3 = 16 × 3 = 48
=0.957
O3 diffuse 0.957 times fast than CO2
=1.044
CO2 diffuse 1.044 times fast than O3 - Starting with Lead metal describe how to prepare a solid sample of Lead (II) Sulphate salt. (3mks)
- Heat lead in air to form PbO.
- React excess PbO with dilute HNO3.
- Filter the excess PbO to get Pb(NO3)2 as filtrate.
- React Pb(NO3)2 with Na2SO4/K2SO4.
- Filter to get PbSo4 as the precipitate.
- Dry between filter paper.
- Given the following reaction
HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaCNl(aq) + H2O(l)
T1 = initial temperature of solutions before additions = 18.0oC
T2 = final temperature of solution at neutralization = 19.2oC
50cm3 1M HCl
50cm3 1M NaOH
Calculate Molar enthalpy of neutralization of hydrogen cyanide (3mks)
∆H = MC∆T
M = (50+50)cm3 × 1g/cm = 100 = 0.1
1000
C = 4.2
∆T = 19.2 − 18.0 = 1.2
∆H = 0.1 × 4.2 × 1.2
= 0.504KJ
Mole of HCl = 50 × 1 =0.05moles
1000
0.05 = 0.504
1m = ? 0.504
0.05
= − 10.08 KJmol−1 - Compound K reacts with sodium hydroxide as shown
- What type of reaction is represented by the equation. (1mk)
- Saponification/Neutralization
- To what class of organic compounds does K belong. (1mk)
- Carboxylic acid
- How is M separated from aqueous mixture of L and M. (1mk)
- Adding Sodium Chloride, C17H35COONa precipitates
- What type of reaction is represented by the equation. (1mk)
- Draw a diagram to show how an aluminium spoon can be electroplated with pure copper. (2mks)
- An ion of element Z can be represented as shown below,
Use the information to answer the questions that follow- Identify the period in which the element belong. (½mk)
- Period 3
- Write the electron configuration of the ion of Z ( ½mk)
- 2.8.8
- What would be the nature of the solution of the chloride of Z if dissolved in water. (1mk)
- Acidic
- Identify the period in which the element belong. (½mk)
-
- What is PH scale (1mk)
- Range of values running from 0-14 used to distinguish acids from bases and give theri strength/weakness.
- State whether the values of the following solution are strong or weak acids and bases.
PH = 8 weak base (½mk)
PH = 5 weak acid (½ mk)
PH = 2 strong acid (½ mk)
PH = 13 strong base (½mk)
- What is PH scale (1mk)
- Draw the structure of;
-
- Hydroxonium ion H3O+ (1mk)
- Aluminium oxide (Al = 13, 0 = 8) (1mk)
- Hydroxonium ion H3O+ (1mk)
- Aluminium chloride has a melting point of 120°C while Aluminium oxide has a melting point of 2977°C. In terms of structure and bonding explain how the differences come about. (2mks)
- Aluminium Chloride forms a dimer with co-ordinate bonds (covalent) between the molecules which can easily dissociate with minimum heat. Aluminium oxide forms an ionic compound with strong ionic bonds throughout the structure(giant ionic bonds)
-
- State the use of the following laboratory apparatus
-
(1mk)
Used to deliver liquid substances into vessels -
(1mk)
Deliver liquids drop-wise into vessels
-
- The diagram below shows heating of Lead nitrate
- State the observations made in the above experiment (2mks)
- An orange solid left behind which turns to yellow after cooling.
- Brown fumes at the mouth of the boiling tube.
- Write an equation for the reaction that takes place. (1mk)
2Pb(No3)2(s) → 2PbO(s) + 4NO2(g) + O2(g)
- State the observations made in the above experiment (2mks)
- Give two differences between nuclear reactions and chemical reactions. (2mks)
Nuclear Reactions Chemical reactions -Takes place within the nucleus and involves protons and neutrons
-A lot of energy is involved
-Not affected by environmanteal factors-Takes place within the energy levels and involves electrons
-No much energy
-Affected by environmental factors - 3.1 g of an organic compound containing carbon, hydrogen and oxygen only produced 4.4 g of carbon oxide and 2.0 g of water on complete combustion:
- Calculate its empirical formulae (2mks)
Empirical Formulae = CH2O - Calculate its molecular formulae if its formulae mass is 62. (2mks)
n=62/30 = 2
Molecular formulae = 2 (CH2O)
=C2H4O2
- Calculate its empirical formulae (2mks)
- Two cleansing agents are represented below
- R – COO−Na+ and
- R – OSO3−Na+
- Name the detergents (2mks)
- Soap
- Soapless detergents
- Select one of the detergents that would be suitable for washing in water containing magnesium chloride. Explain. (2mks)
R – OSO3−Na+ - Forms a soluble salt of Magnesium
- Name the detergents (2mks)
- Use the data below to calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction below
CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H20(l) (3mks)
Bond Energy (KJ)
C – H 413
O = O 489
C = O 805
H – O 464
Bond Breaking
4 × 413 = 1652
2 × 489 = 978
+2630KJ
Bond Formation
2 × 805 = 1610
4 × 464 = 1856
−3466
2630 − 3466 = −836KJ/mol
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Paper 1 Questions And Answers - Form 4 Term 2 Opener 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students