INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Answer All questions
- What is meant by the term sex linkage. (1mk)
- Part of one strand of DNA molecule was found to have the following sequence
G-C-C- G – A – T- T – T – A – C – G – G
What is the sequence- of the complimentary DNA strand? (1mk)
- On a m-RNA strand copied from this DNA portion? (1mk)
- State three regions ion a plant where the end products of photosynthesis are translocated to? (3mks )
- With reference to circulatory system only give two reasons why birds and mammals are more active compared to other organisms? (2mks)
-
- What three characteristics are used to divide the phylum arthopoda into classes? (3mks)
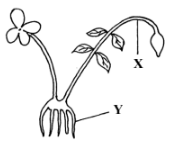
- The diagram below shows an organisms from a division in Kingdom plantae. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the division from which the plant was obtained. (1mk)
- Name the parts labelled X and Z (2mks )
- What is the relationship between a genus and a species? (1mk)
- A drawing of 3 cm was made of a giant spider whose actual length was 7cm. calculate the magnification of the drawing? (3mks)
- Explain why osmosis is described as a special type of diffusion? (1mk)
- The following table shows the estimated number of organisms recorded in a dam.
Organisms Number Small fish 3500 Microscopic algae 12000 Crocodiles 100 Large fish 950 Mosquito larvae 8900 - Construct a possible food chain for the dam? (1mk)
- Construct a pyramid of numbers for the given data? (1mk)
- Explain the shape of pyramid obtained? (2mks)
-
- Explain why leaves of most plants are thin and broad. (2mks)
- State the function of the following enzymes during digestion in the stomach?
- Pepsin (1mk) ………………………………………………………………………………………………….
- Renin (1mk) ………………………………………………………………………………………………….
- Explain the following:
- Respiratory surface must be moist? (1mk) ………………………………………………………………………………………………….
- Respiratory surface must be thin (1mk) ………………………………………………………………………………………………….
- Palisade cells are cylindrical shaped and arranged with long axis perpendicular to the leaf surface. (1mk)
-
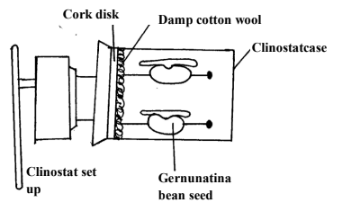
Germinating beans seeds were placed in the clinostat as shown in the diagram and left for three days. (a)- What is a clinostat. (1mk) ………………………………………………………………………………………………….
- The Clinostat was switched on and left to run for the three days. Suggest the direction the seedling will be facing at the end of the three days. (1mk)
- Give a reasons for your answer in (b) above? (1mk)
- Explain why the body temperature of a healthy person rises slightly during humid days? (2mks)
- Nocturnal animals such as owl are capable of seeing fairly at night. What two retinal adaptations have made this possible? (2mks)
- State the function of the following organelles:
- Granulated Endoplasnic reticulum (1mk) ………………………………………………………………………………………………….
- Nucleolus (1mk) ………………………………………………………………………………………………….
- State three gaseous exchange sites in plants? (3mks)
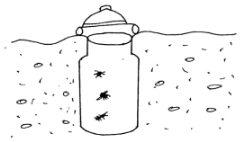
- The diagram below shows an apparatus used during collection of specimen or biological study.
- Identify the apparatus? (1mk) ………………………………………………………………………………………………….
- What is the use of the apparatus named above? (1mk)
- List three limitations of fossil records as an evidence of organic evolution? (3mks)
- Distinguish between enzyme co-factors and co-enzymes? (2mks)
- Give two reasons for the rapid growth during the exponential phase of growth curve? (2mks)
- Give two reasons why Carolus Linneaus preferred the use of latin language in the scientific naming of living organisms. (2mks)
- State three roles played by active transport in living organisms. (3mks)
- List three factors affecting the rate of respiration? (3mks)
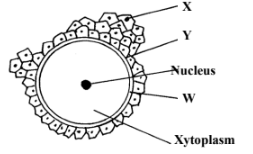
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the cell (1mk)
- Label the parts X,Y and W (3mks)
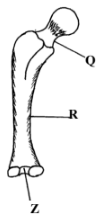
- The diagram below shows a bone of the hind limb. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Name the bone (1mk) ………………………………………………………………………………………………….
- Name the parts labelled Q and R (2mks)
- Name the structure that articlualtes with the part labelled Z and the joint formed? (2mks)
Structure ………………………………………………………………………………………………
Joint …………………………………………………………………………………………………… .
- List two functions of inter-vertebral discs between two adjacent vertebrae. (2mks)
- Explain why it is becoming more difficult to treat malaria using chloroquine? (4mks)
- State four ways by which the ileum is adapted fro absorption of food materials? (4mks)
- Name two processes that contribute to variation during gamete formation? (2mks)

MARKING SCHEME
- These are genes located on the sex chromosomes and are transmitted together with those determine sex. 1mk
-
- C – G – G – C – T – A – A – A – T – G – C – C 1mk
- C – G – G – C – U – A – A – A – U – G – C – C 1mk
-
- The growing and developing regions such as shoots, leaves, flowers, fruits and roots
- Storage organs or tissues such as tubers, corns, bulbs, rhizomes and seeds.
- The secretors organs such as nectar glands in some insect pollinated plants such as bananas
3×1= 3mks
-
- Deoxygenated and oxygenated blood do not mix
- Blood is at a higher pressure once the heart pumps it twice.
2×1= 2mks
-
-
- Number of limbs
- Presence and number of antennae
- Number of body parts
3×1= 3mks
-
- Bryophyta
- X – Seta
Z – Rhizoid rej Rhizoids.
-
- A species is a subset of genus i.e. one genus contains several species. 1×1= 1mk
- Magnification = length of drawing √1
length of real object
= 3cm = 0.429 √1
7cm
X 0.43√1
3×1= 3mks - Because it involves movement of solvent (water) molecules from their region of high concentration to region of low concentration across a semi permeable membrane. 1×1= 1mk
-
- Microscopic algae → mosquito larvae → small fish → large fish → crocodile NB: mark as a whole
1×1= 1mk -
1×1= 1mk
-
- Body size of the organism increase at each trophic level from the base as their numbers decrease.
- At each trophic level much of the energy obtained is lost in respiration thus fewer organisms can be supported at the succeeding level. 2mks
- Microscopic algae → mosquito larvae → small fish → large fish → crocodile NB: mark as a whole
-
-
- Thin
- To reduce distance for diffusion of gases. 1×1= 1mk
- To reduce distance for sunlight to reach the photosynthetic cells. 1×1= 1mk
- Broad – To provide large surface area for maximum light absorption. 1×1= 1mk
- Thin
- Pepsin – Breaks down proteins into peptides. 1×1= 1mk
Renin – Digests protein caseinogens in milk to casein (curd) 1×1= 1mk
-
-
- Moist o dissolve the diffusing gases across the respiratory surface. 2mks
- Thin to reduce distance covered by diffusing gases i.e. for the gases to diffuse through short distance. 1mk
- Many palisade cells in a small area to enable them receive maximum sunlight. 1×1= 1mk
-
- A clinostat is a device which slowly rotates a plant to nullify the effect of unidirectional stimulus.
1×1= 1mk - Horizontal direction as in diagram. 1mk
- The clinostat will nullify the effect of gravity on the seedling hence the seedling continues to grow horizontally. 1×1= 1mk
- A clinostat is a device which slowly rotates a plant to nullify the effect of unidirectional stimulus.
- This is because during humid day, there is low rate of sweating; since less water is lost from the body surface, leading to less heat loss through sweat hence body temperature tend to rise slightly.
1×2= 2mks -
- High concentration of rods in the retina of their eyes.
- There is more rods than cones in the retina.
1x2 = 2mks
-
- Helps in the transport of proteins. 1mk
- Manufacture of ribosomes 1mk
-
- Stomata;
- Lenticels of woody plants
- Cuticles
3×1= 3mks
-
- Pitfall trap
- For catching crawling animals.
-
- Distortion of parts of fossils during sedimentation hence can give wrong impression of the structure; -
- There was several missing links of fossils records as some parts or whole organism decomposed, some scavenged upon and conditions may not be conducive for fossilization (O.W.T.T.E).
- Destruction of fossils by geological activities like earthquakes, faulting and mass movement.
3×1= 3mks
- Enzymes cofactors are non-proteinous substances which activate enzymes; while co-enzymes are organic non protein molecules that work is association with particular enzymes. (Mark as a whole) 2mks
-
- Cells have adjusted to the new environment
- Food and other factors are not limiting hence no competition for resources.
- Rate of cell increase is higher than cell death.
- There is an increase in the number of cells dividing
First two 2×1= 2mks
-
- Latin language was widely spoke and used by scientists during his time;
- Local names used previously could not be understood by everyone thus Latin language enhanced scientific communication worldwide. 2×1= 2mks
-
- Excretion of waste products from the body cells.
- Absorption of digested food from alimentary canal of animals in the blood stream.
- Absorption of some minerals salt from soil by plant roots.
- Accumulation of substances into the body to offset osmotic imbalance in arid and saline environment. - Reabsorption of sugars and some salts by the kidney. 3×1= 3mks
-
- Oxygen concentration
- Presence or absence of hormones
- Substrate concentration
- Surface area to volume ratio/body size of an organism. 3×1= 3mks
-
- Mature human ovum 1mk
- X – follicle cell
Y – viteline membrane 1mk
W – Plasma membrane 1mk
-
- Femurs
- Q – neck
R – Shaft - Structure - patella
Joints – hinge joint
-
- Act as a cushion that absorbs shock thus reducing friction.
- Allows for a certain degree of movement between the vertebrae in the vertebral column.
2×1= 2mks
- Some malaria plasmodium developed resistance; to chloroquine drug; through mutation; those resistant individuals transmit the characteristic to their offspring through reproduction thus establishing a new population of resistant forms. 4mks
-
- It is long to provide large surface area for absorption.
- It is numerous to bring digested food into close contact with walls of the ileum for easier absorption. -
- Highly coiled to slow down movement of food, allowing more time for absorption.
- Higher surface has large number of villi and micro-villi which increase the surface area for absorption of end products of digestion.
- Presence of thin layer of cells through which digested food diffuses.
- Presence of tense network of blood capillaries in villi into which nutrients are absorbed.
- Presence of lacteals in the villi for absorption of fatty acids and glycerol.
4×1= 4mks
-
- Independent assortment
- Crossing over
2×1= 2mks
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Biology Paper 1 Questions And Answers - Form 4 Term 2 Opener 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students