-
ANSWER ALL THE QUESTION IN THE SPACES PROVIDED.
Answer all the questions in the spaces provided
-
You are provided with substance L.Carry out food tests on the substance using the reagents provided .Record your procedure , observations and conclusions in the table below.(9mks)
Food substance Procedure Observation conclusions -
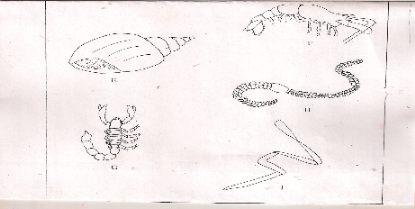
During a visit to a museum, students were shown ten specimens of organisms on display.The teacher provided a dichotomous key (shown in a separate page) to enable them to place each species on display into its taxonomic group. Five of the specimens that were on display are shown in the diagrams provided.
Dichotomous Key.
-
-
Animal with a flattened body….. …………………………………..go to 9.
-
Animal without a flattened body……………………………………. go to 2.
-
-
-
Animal with body in a shell ………………………………………….Mollusca
-
Animal with body in shell………………………………………….. go to 3.
-
-
-
Animal with segmented body….. …………………………………….go to 4.
-
Animal with body not segmented…………………………………….Nematoda.
-
-
-
Animal with jointed appendages go to 6.
-
Animal without jointed appendages to 5.
-
-
-
Animal with long and cyndrical body…………………………………..annelida.
-
Animal with short stout body………………………………………….. Trenada.
-
-
-
Animal with antennae…………………………………………………...go to7.
-
Animal without antennae ….. ………………………………………….go to 8
-
-
-
Animal with one pair of antennae……………………………………… Insecta.
-
Animal with more than one pair of antennae………………………….. crustacean.
-
-
-
Animal with pincer –like mouthparts………………………………….. Arachida.
-
Animal with sucking mouth parts………………………………….….Acarina.
-
-
-
Animal with long ribbon-like body ……………………….…………….cestoda.
-
Animal with circular body………………………………………….. rinoidea).
Use the dichotomous key to identify the taxonomic group of each of the five specimens shown in the drawings.
-
In each case, show in sequence the steps (ef 1a,2a,5a, 7b) in the key that you followed to arrive at the identify of each specimen.(5mks)
Animal Steps followed Identity
E ……………………………… ………………………
F ………………………………. …………………………
G ……………………………… ……………………
H ……………………………… …………………………
J ……………………………… ………………………… -
-
Name the phylum and the class to which specimen M belongs(2mks)
Phylum:
Class: -
Name the observation features that enabled you to place it in the class above.(3mks)
-
-
With the help of a hand lens, examine the body of specimen M.
-
State with a reason in each case he observable features that enable the specimen to be a disease vector.(2mks
-
Name one disease transmitted by specimen M.(1mk)
-
State two methods that can be used to prevent specimen M from spreading diseases.(2mks)
-
-
-
-
-
You are provided with specimens labeled S1 S2 and S3
-
Using a scarpel blade split S1 longitudinally and draw a well labeled diagram to show the internal structures.
State your magnification (4mks) -
With a reason ,state the class to which the plant from specimen S1 belongs to.
Class(1mk)
Reason(1mk) -
Specimen S2 is a germinated seedling of S1.In the table below, name three structures and say which structure in S1developed into the structure in S2.
Structure in S1 Structure in S2 -
-
Using specimens S1 and S3 ,name the type of germination in :-
S1
S3 (1mk) -
Give the difference between the this type of germination in (d) (i) above (2mks)
-
Account for the type of germination in :-
S1 2mks
S3(2mks)
-
-
CONFIDENTIAL
NB/Requirement instruments:
- About 10ml of substance L.
- 4 clean test tubes on a rack.
- A means of heating
- Test tube holder.
- A scalpel.
- A house fly labeled specimen M.
- A dry bean seed labeled S1.
- A bean seedling labeled S2.
- A maize seedling labeled S3.
- 1% copper (II) sulphate solution.
- 10% sodium hydroxide solution.
- Benedictۥs solution.
- Iodine solution.
Note:
- To make substance L,mix egg albumen and starch.
- Specimen S2 and S3 should be ready 1 week before the exams and must have the seeds intact.

MARKING SCHEME
Food substance Procedure Observation conclusions Starch To a little of substance L in a test tube,add a little iodine Blue-blackcolour forms Starch present; Reducing sugar To a little of substance L in a test tube add equal amount of Benedict’s solution and heat to boil. Colour remains blue Reducing sugars absent
Proteins To a little L,add a little sodium hydroxide followed by a little copper(II) sulphate solution and shake the mixture. Purple colour forms Protein present; -
- Animal Steps followed Identity(9mks)
E 1b,2a; Mollusca
F 1b,2b,3a,4a,6a,7b; Crustacea;
G 1b,2b,3a,4a,6b,8a; Arachnida;
H 1b,2b,3a,4b,5a; Annelida;
J 1a,9a; Cestoda; ½mk -
- Phylum: Arthropoda(1mk)
Class:Insecta (1mk) -
- Has three body part;
- Has three pairs of leg;
- Has one pair of wings;
- Has one pair of antennae; max 3mks
- Phylum: Arthropoda(1mk)
-
-
- Presence of legs that walk on contaminated surfaces;
- Presence of wings that facilitate movement to and from contaminated surfaces;
- Hairly body on which disease causing microorganisms attach;
- Has a proboscis to suck /contaminate food; any 2 (2mks)
- Cholera/dysentery(1mk)
-
- Covering food;
- Proper disposal of waste /rubbish;
- Eradication of houseflies using insecticides; any 2 (2mks)
-
- Animal Steps followed Identity(9mks)
-
- Magnification – 1mk.
Each correct label-½ mk.
correct drawing (1mk) - Class: Dicotyledonae;(1mk)
Reason :Has two cotyledons has network veins /has at a tap root system.(1mk)
Max 2Structure in S1 Structure in S2 Plumule
Radicle
CotyledonStem system /shoot
Root system;
Seed leaf-
- S1 – Epigeal (1mk)
S3 – Hypogeal (1mk)
S1 S2 -Cotyledons pushed above the ground
-Hypocotyl elongates
-Cotyledons remain in the soil
-Epicotyl elongates
2mks- S1- has little food store; hence leaves develop early to start photosynthesis ; (2mks) S3- has a lot of food stored; which is enough for early growth, hence no need for early photosynthesis ;( 2mks)
- S1 – Epigeal (1mk)
- Magnification – 1mk.
Download Biology Paper 3 Questions And Answers with Confidential - Form 4 Term 2 Opener 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students