INSTRUCTION TO CANDIDATES
- This paper has two sections A and B
- Answer all questions in section A
- Answer questions 6 and any other questions from section B
SECTION A
Answer all questions in this section
-
- List the disadvantages which are related with the following areas of study of geography.
- Geomorphology (1mk)
- Biogeography. (1mk)
- List three main areas of study of physical /geography (3mks)
- List the disadvantages which are related with the following areas of study of geography.
-
- List any two main areas which make up the external art of the earth.
- List any three discontinuities which are found in the atmosphere (3mks)
-
- What is plate tectonics theory? (2mks)
- Name three main boundaries which develop due to the movement of plate tectonic(3mks)
-
- Define the following terms of the hydrological cycle
- Precipitation (1mk)
- Evaporation (1mk)
- List any three factors that influence the rate of evaporation from the earth’s surface(3mks)
- Define the following terms of the hydrological cycle
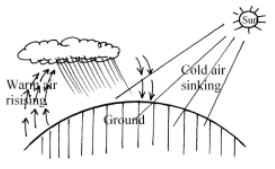
- The diagram below show the formation of some type of rainfall .Use it to answer question(a) and (b)
-
- Name the type of rainfall shown by this diagram (1mk)
- Name the type of cloud marked (a) (1mk)
- List three weather conditions associated with the above name (a) type of rainfall.(3mks)
-
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other two questions from this section
- Study the map of Karatina 1: 50,000(Sheet 121/3)
Provided to answer questions that follow.-
- Identify the feature found in grid reference 967543 (1mk)
- What is the distance of River Sagana found to the South Western area of the area covered by the map from the bridge in grid square 8347 to the Southern edge of the area covered by the map (Give your answer in Kilometres)
- List any two methods that have been used to represent the relief of the area covered by the map (2mks)
-
- Calculate the area covered by the part of Mt. Keya forest East of easting 99 and south of Northing 55(Give your answer in square Kilometres) (3mks)
- Name two district found in the area covered by the map (1mk)
-
- Using a vertical scale of 1cm rep 50m draw a cross section from grid reference 810500 to 870500 (5mks)
- On the cross section drawn mark and name
- All weather roads (loose surface) (1mk)
- River Rithithi (1mk)
- Power line (1mk)
- Calculate vertical exaggeration (VE) for the cross section drawn (2mks)
- Describe drainage in the area covered by the map (6mks)
-
-
-
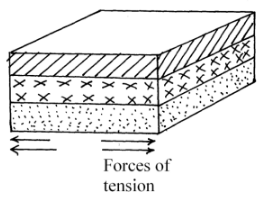
- Define the term faulting (2mks)
- Describe how a normal fault is formed (2mks)
-
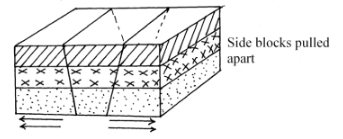
- With the aid of well –labelled diagrams explain how a rift valley is formed by tensional forces. (8mks)
- A part from the Rift valley name any other three features formed by faulting(3mks)
- Mention any five effects of the process of faulting to human environment (5mks)
- Students from Itiero Girls High School intend to carry out a field study of a fault block near their school.
- List any three objectives for their study (3mks)
- List any two secondary sources of information that they would use to collect data (2mks)
-
-
-
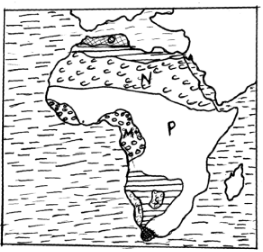
- Name the types of climates marked M,O and P (3mks)
- Name the desert marked T and S (2mks)
- Describe the characteristics of the climate marked N (6mks)
- Explain any four natural factors influencing aridity and desertification. (8mks)
- Explain any six effects of desert features on the human environment. (6mks)
-
-
-
- Define the term sea. (2mks)
- List any three features which occur in the oceans (3mks)
-
- Define the term waves (2mks)
- Differentiate the term swash from backwash (2mks)
-
- Explain any three processes of wave erosion (6mks)
- Explain how a tombolo is formed (4mks)
- Give three conditions necessary force formation of coral reefs (3mks)
- List any three features which develop on submerged highland coasts. (3mks)
-
-
-
- List any three sources of underground water (3mks)
- Differentiate pervious rocks from porous rocks (2mks)
- Explain four factors that influence the occurrence of underground water. (8mks)
-
- Mention any three factors necessary for the formation of karst features. (3mks)
- List any three underground features of karst areas (3mks)
- Explain any three significance as of karst features to man. (6mks)
-

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Disciplines related with the following areas study of geography
- Geomorphology
- Geology
- Biogeography
- Biology
- Geomorphology
- Three main areas of study of physical geography
- The earth and the solar system
- The internal land forming processes
- The external land forming processes
- Weather and climate
- Vegetation
- Soils and rocks
3x1=(3mks)
- Disciplines related with the following areas study of geography
-
- Two main areas which make up the external part of the earth.
- Atmosphere
- Hydrosphere
- SIAL
- Three distributions which are found in the atmosphere
- Tropopause
- Stratopause
- Mesopause
- Two main areas which make up the external part of the earth.
-
- Meaning of plate tectonic theory
- A theory which argues that the earth’s crust is made up of semi- rigid broken blocks called tectonic plates which floats of semi- liquid upper mantle 2x1=(2mks)
- Three boundaries which develop due to movement of plate tectonics
- Extensions boundaries
- Compressed boundaries
- Transform faults
- Meaning of plate tectonic theory
-
- Definition of process.
- precipitation
- All forms of moisture formed when water vapour condenses in the atmosphere
- Evaporation
- Process through which moisture is lost from the surfaces to the atmosphere through air movement and the sun’s heat.
- precipitation
- Three factors influencing the rate of evaporation from the earth’s surface
- Availability of moisture
- Temperature
- Speed of wind
- Hours sunshine
- Characteristics of the water body –salinity and depth.
3x1=(3mk)
- Definition of process.
-
-
- Type of rainfall shown on the diagram
- Conventional 1x1 =(1mk)
- Type of cloud marked (a)
- Comululonimbus clouds 1x1 =(1mk)
- Type of rainfall shown on the diagram
- Three weather conditions associated with the above (a) rainfall
- Thunderstorm and lightening
- Hailstones
- Warm air near surface in the afternoon hours 2x1=(2mks)
-
SECTION B
- Study the map of Karatina 1:50,000 sheet 121/3 provided to the question that follow
-
- Identifying features found in grid reference 967543
- Water intake 1x1 =(1mk)
- Distance of River sagana from the bridge in grid square 8347 to the southern edge of the map
- 5.8, 5.9, 6.0 Km 2x1= (2mks)
- Two methods that have been used to represent relief of the area covered by the map
- Contours
- Trigonometrical stations
- Spot heights
- Use of names of relief features
2x1 = (2mks)
- Identifying features found in grid reference 967543
-
- Calculating the area covered by part of Mt Kenya forest east of easting 99 and south of Northing 55.
- 9Km2 3x1 =(3mks)
- Two districts found in the area covered by the map
- Nyeri
- Kirinyaga
1x2 =(2mks)
- Calculating the area covered by part of Mt Kenya forest east of easting 99 and south of Northing 55.
-
- Using a scale of 1cm rep 5om draw a cross section from grid reference 810500 to 870500 (Refer graph paper)
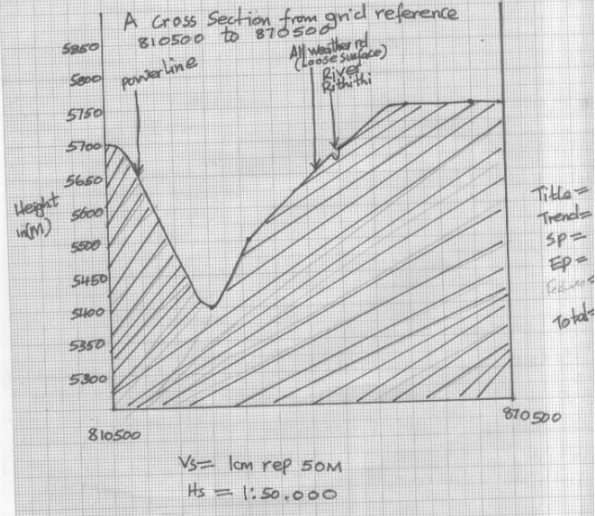
- Cross section drawn mark and name
- All weather road (loose surface)
- River Rithithi
- Power line
- vertical exaggeration
VE = vs
Hs
=1 cm rep 50m
1: 50, 000
=50 times
- Using a scale of 1cm rep 5om draw a cross section from grid reference 810500 to 870500 (Refer graph paper)
- Description of drainage on area covered by the map
- The most dominant drainage features found here are permanent rivers like Sagana,Rithithi etc
- Most rivers found on these areas originate in the Northern part especially from the mount Kenya forests and flow Southwards
- The largest river in the area covered by the map is rive Sagana found to the sw part.
- Most of the rivers found on the map shows some traces of radial drainage pattern because the seem to be originally from the Mt Kenya forests and flow to different directions.
- Some rivers also show dandrific drainage pattern e.g. River Nyanyaga Gathambi etc
- Most of the rivers found here are in their youthfull stages and have the presence of interlocking spurs e.g. Rivers Sagana ,Thego etc
- Drainage features like dams have been developed on the rivers especially along river Sagana in grid square 8348.
- Several other artificial drainage features are found on the map e.g. water reservoir , water intake , Cattle dips ,etc
1x6 =(6ms)
-
-
-
- Definition of faulting
- A process which takes place in rocks of the crust which makes them to fracture or break
- Description of normal fault
- Forces of tension act on rocks of earth’s crust
- Forces pull away from each other
- vertical or inclined faults plane and direction of the down throw are both to the left and or both to the right.
1X2=(2mks)
- Definition of faulting
-
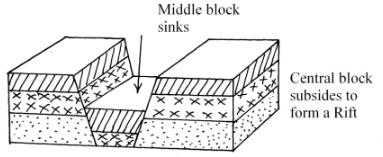
- Explaining formation of Rift valley by tension forces with aid of diagrams.
- The earth’s crust is subjected to forces of tension. Forces pull away from each other
- Lines of weakness develop in the rocks of the earth’s crust leading to thedevelopment of adjacent normal faults which are almost parallel
- The forces pull away the side blocks
- The middle block is formed to sink forming loading to the formation of a long trough between the faults which is called a Rift valley.
- Sometimes the normal faults may be multiple and as middle block sinks the other blocks are displaced unequally forming a rift valley with sides of step faulting.
Text 5
Diagram 3=(8mks)
- The earth’s crust is subjected to forces of tension. Forces pull away from each other
- other features formed by faulting a part from Rift Valleys
- Fault blocks /block Mountains
- Tilt blocks
- Fault scarps
- Tilt block landscape
4x1=(4mks)
- Explaining formation of Rift valley by tension forces with aid of diagrams.
- Mentioning five effects of the process of faulting to man
- Subsidence of land by faulting forms lakes which are rich in minerals which forms hot springs and geysers.
- Fascinating features of faulting like escarpments attract tourists.
- Foot of fault scarps underground water emerges leading to occurrence of springs. -Windward sides of block mountains receives high rainfall becoming sources of rivers. -Faulting may expose mineral that were found underground.
- Faulting disjoints land bringing problems in development of infrastructure. -Fractures and displacement of land by faulting makes rivers change direction of flow or may disappear underground.
- A field study of a fault near Itiero Girls High School
- Three objectives for their study
- To find out the forces that were behind the formation of the fault block
- To investigate the age of the fault block.
- To know the economic importance of the fault block
- To find out the negative impact that the feature has had on the surrounding communities 1x3 = (3mks)
- Two secondary source of information that they would use to collect data -Waiting films and videos.
- Listening to audio tapes.
- Reading published documents like books ,magazines. 1x2 =(2mks)
- Three objectives for their study
-
-
-
- Climate marked
- M- Equitorial
- O-Mediterranean
- P-Savana
- Deserts.
- T-Namib
- S- Kalahari
- Climate marked
- Description of characteristics of climate marked N
- High mean annual temperatures but varies.
- Large diurnal /range of temperature absence of cloud cover
- High annual range of temperature about 260C
- Low rainfall (annual) less 250mm p.a
- winds found here are offshore most of the year.
- Sandstorms common in these places
- High rate of evaporation
- Natural factors influencing aridity and desertification
- A place receiving insufficient rainfall.
- Extremely high temperatures at a place
- A coastal region lying next to cold ocean currents.
- A place lying on leeward side of a mountain.
- A place being found far away from water bodies 2x4 (8mks)
- Explaining five effects of desert features on human environment.
- Less deposits form good place for development of caves providing shelter in winter -Loess deposits form deep and fertile soils which support agriculture.
- Desert features like yardangs, rocks pedestal offer fascinating features which attract tourist.
- Extensive and bare surfaces and sands are suitable for testing of weapons/machines ,military training etc.
- Some defletion hollows contain water providing water for domestic and industrial use. -Salt fluts can be used to provide salts required in salt industries.
- Sand dunes interfere with infrastructure e.g. roads. 1x6 =(6mks)
-
-
-
- Defintion of sea.
- A large body of saline water on margins of continents.
- A large body of saline water enclosed by landmass
- A large body of saline water connected to an ocean by a narrow stretch of water called a strait.
- List any features which occur in the oceans.
- Continental shelf
- Continental slope
- The deep sea plains
- The ocean ridges.
- ocean deeps
- Ocean trenches
- Defintion of sea.
-
- definition of waves
- Ridges of running water developed by oscillationof water particles
- Differentiating swash from backwash
- Swash refers to most of water up the shore as wave breaks while the backwash is backward movement of water to sea after breaking of a wave
- definition of waves
-
- Explain three processes of wave erosion
- Hydroalic action
- Corcasism
- Solution
- Attritium
2x3 =(6mks)
- explaining the formation of a tombolo
- A coastal area happens to have shallow waters
- Not far from this coastal place there is an island.
- Waves approach such a shallow coast and because of shallow depth they are forced to break
- The pebbles and sand the waves are carrying are deposited by the waves.
- As a result a low ridges is formed by these deposit and start developing from the coast
- More deposition of these materials take place and the ridge continues lengthening towards the side of the sea.
- Gradually the ridge joins up with an island on the side of the sea leading to the formation of a tombolo
1x4 =(4mks)
- Giving three conditions necessary for formation of coral reefs.
- Sea temperatures of about 210c /high temperatures.
- Sunlight that penetrates the floor of sea up to a depth of 50m/shallow water
- Plenty ful supply of plant food (planktons)
1x3 =(3mks)
- Explain three processes of wave erosion
- Listing three features which develop on submerged highland coasts.
- Rids
- Fiord
- Dalmatians coast
-
-
-
- Three sources of underground water.
- Rainwater
- Meltwater
- Lake and sea water
- Magmaic water
- Differentiate pervious rocks from porous rocks
- Pervious rocks are rocks that allow water to pass through them through their cracks /.joint fissures while porous ones allow water to pass through them via their spaces.
- Three sources of underground water.
- Explaining four factors influencing the occurrence of underground water. Amount of precipitation in an area.
- The nature of the slope of an area
- Nature of the rocks
- Amount of vegetations cover in an area
- Level of saturation of the ground
- Rate of evaporation –Transportation in an area.
-
- Mentioning three factors necessary for formation of a karst scenery -Thick limestone, chalk or dolomite rock
- Rocks must be hard and well jointed
- Hot and humid climate
- Water table deep below the ground
- Three underground features in karst areas
- Stalactites
- Stalagmites
- Limestone pillars
- Underground caves
- Underground rives
- Mentioning three factors necessary for formation of a karst scenery -Thick limestone, chalk or dolomite rock
- Explain three significant of karst features to man
- Features like stalagmites ,stalactites polijes attract tourist.
- The lime stone block can be used in building houses.
- Limestone rocks are also used as raw materials in the cement making industries.
- The limestone ground are dry and therefore provide good grounds for rearing of sheep.
2x3 =(6mks)
-
Download Geography Paper 1 Questions And Answers - Form 4 Term 2 Opener 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students