Instructions to the candidates.
- Choose any five questions. All questions carry equal marks.
-
- Highlight five characteristics of an efficient tax system. (10mks)
- Differentiate between a public limited company and a public corporation. (10mks)
-
- Explain clearly the malpractices by traders against which consumers may need protection by the government. (10mks)
- Explain clearly with the aid of a diagram the change in equilibrium as a result of a change in demand of a commodity. (10mks)
-
- Discuss five benefits that a customer may get by using Automated Teller Machine (ATM) for financial transactions. (8 mks)
- The following trial balance related to Kimani’s business as at 31st December 2012
DR(SHS) CR(SHS)
Stock on 1st January 2003 60,000
Purchases and sales 400,000 580,000
Returns 20,000 50,000
Debtors and Creditors 65,000 40,000
Premises 540,000
Machinery 200,000
Fixtures and fittings 100,000
Carriage outwards 8,000
Wages and salaries 30,000
Discounts 25,000 32,000
Commissions 16,000 14,000
Cash in hand 70,000
Capital _________ 818,000
1,534,000 1,534,000
REQUIRED:
Prepare a trading profit and loss account for the period ended 31st December 2012 and a balance sheet as at that date if the closing stock was worth shs 70,000 (12 mks)
-
- Explain clearly the problems associated with expenditure approach method in measurement of national incomes. (10mks)
- Outline five reasons why ethical practices is necessary in product promotion. (10mks)
-
- Jane,a petty cashier was given Sh ,2000 on 1st June 2005. During the month, she made the following payments:
2005 June
2 Stationery Sh 100, staff tea Sh 80.
5 Telephone bill Sh 50, postage stamps Sh 100.
8 Travelling Sh 200, telephone Sh 100.
10 Stationery Sh 50, staff tea Sh 100.
15 Postage stamps Sh 50, travelling Sh 100.
20 Sundry expenses Sh 100.
23 Stationery Sh 80, telephone Sh 40.
25 Travelling Sh 50, sundry expenses Sh 100.
28 Envelopes Sh 20, staff tea Sh 50.
30 Adhiambo, a creditor, was paid Sh 100.
Use the following analysis columns to prepare a petty cash book:
Stationery, Staff tea, Travelling. Telephone, Sundry expenses. Ledger accounts. (12 mks) - Explain five demerits that a country may suffer when the government becomes a major investor in business. (8 mks)
- Jane,a petty cashier was given Sh ,2000 on 1st June 2005. During the month, she made the following payments:
-
- Explain the role played by insurance industry in promoting the development of Kenyan economy. (10mks)
- Explain clearly the tools of monetary policy used by the central bank to control inflation. (10mks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Highlight five characteristics of an efficient tax system. (10mks)
- Equity — the tax should be fair / just / people should be taxed according to their level of income.
- Economical — ft should be cheap / easy to administer / cost effective / cost of collection should be relatively lower than tax revenue.
- Convenient / method of payment I collection should be convenient to the tax payer — it should be suited! favourable to the needs I activities / programmes of the tax payer.
- Certainity — tax payer / collectors should know what / when / how to pay / collect.
- Flexibility – (Where a tax is used as an instrument of national policy) it should be adaptable to all (economic) circumstances/conditions / subject to revision.
- Simplicity — It should be easily understood/administered.
- Elasticity - Proceeds front taxation should be capable of expanding /contracting with changes in income/population.
- Diversity /wide base there should be a (wide) variety/range of taxes/ net many tax payers.
- Difficult to evade — it should not create a loophole for people to escape / dodge.
- should regulate the economy — by encouraging production/proper allocation of resources.
- Should have (maximum) benefits to taxpayers through provision of quality goods / services /to encourage them to pay.
(any five with explanation = 10mks)
- Differentiate between a public limited company and a public corporation. (10mks)
(five tallying differences = 10 marks)Public Corporation Public Ltd Company a) Formed by shareholders a) Formed by the government. b)Formed through registration under the company’s act. b) Formed by an act of parliament. c) Profit motivated c) Not necessarily profit motivated. d) Financed by the shareholder d) Initially financed by the government. e) Directors are nominated or elected by shareholder. e) Directors are nominated/appointed by the government. f) No political influence except the enacted laws. f) Political influence is eminent due to political appointments by the government. g) Losses may eventually lead to collapse of business/ borne by shareholders. g) Losses occasionally borne by the government.
- Highlight five characteristics of an efficient tax system. (10mks)
-
- Explain clearly the malpractices by traders against which consumers may need protection by the government. (10mks)
- Selling of underweight goods – some traders may sell product that are not of the right quantity and size by tampering with the weighing scales.
- Overcharging of goods – some traders may charge exorbitant prices to customers who are unaware of the actual prices of goods.
- sale of harmful commodities which could adversely affect their health
- Giving false information about a product since consumers are sometimes very ignorant producers may take advantage and persuade them through adverts.
- Hoarding of commodities by traders – producers and businessmen may create artificial shortages.
- Selling of counterfeit or goods to the consumers – some traders might produce goods of law quality or use substandard ingredients in production of goods.
- Breach of contract – producers and traders may fail to honour contracts entered into with consumers in regard to sales of commodities.
(any five with explanation = 10mks)
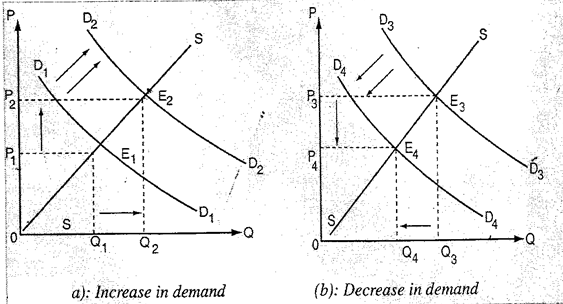
- Explain clearly with the aid of a diagram the change in equilibrium as a result of a change in demand of a commodity. (10mks)
(a) (3marks) (b) (3 marks)
From the above diagram, demand increased from D1D1 to D2D2 with the effect that the equilibrium price and quantity changed fron P1 to P2 and Q1 to Q2 respectively. This change increased the equilibrium point from E1 to E2. On the other hand, a decrease in demand will result into a decrease in the equilibrium price and also the equilibrium quantity as illustrated above. In the diagram, a reduction in demand from D3D3 to D4D4 changed the equilibrium hence shifted from E3 to E4 .
Explanation (4mks)
- Explain clearly the malpractices by traders against which consumers may need protection by the government. (10mks)
-
- Discuss five benefits that a customer may get by using Automated Teller Machine (ATM) for financial transactions.(8 marks)
- Customer can withdraw money at any time/24 hours/7 days/a week.
- Means of payment. Customer can pay utility bills/buy goods/service (through the ATMs)/ Accept examples of payment of bills as explanation.
- fees charged (for withdrawal) is low compared to over the counter/ services/withdrawals hence saving on cost.
- Strategic locations — ATMs can be found even where banks are nonexistent/ accept examples of strategic locations as an explanation.
- security - The customer has a PIN number which guarantees confidentiality/safer to carry card than cash.
- Getting mini statement — Customer can use it to monitor his transactions with the bank (by getting mini statement).
- customers can deposit money/cheque at any time/24 hours/7 days.
- Saves time/faster service due to less paper work/avoidance of long queues in the bank/queues may be shorter at ATMs.
- Use of visa cards to make inter-bank withdrawals.
- probability as it is light to carry ATM card around.
- access to credit through the use of credit cards.
- simple/easy to operate/use as the user is guided by the machine.
- transaction receipts to show current balance/amount withdrawn/for record keeping/ reveal errors.
- Accessibility/unlimited use since it operate throughout the day/24 hours/7 days/a week.
- Funds transfer—facilitates movement of funds/cash from one account to another
(any four with explanation = 8 marks)
- The following trial balance related to Kimani’s business as at 31st December 2012
REQUIRED:
Prepare a trading profit and loss account for the period ended 31st December 2012 and a balance sheet as at that date if the closing stock was worth shs 70,000 (12 mks)
Kimani’s
Trading and profit and loss account,
for the period ended 31st Dec 2012 √
(24 x =8 marks)Dr Cr Shs
opening stock 60,000√
Add: Purchases 400,000√
Less: returns outwards 50,000√ 350,000√
Cost of goods available for sale 410,000√
Less: Closing stock 70,000√
Cost of goods sold 340,000√
Grosss profit c/d 220,000√
560,000√
carriage outwards 8,000√
Wages and salaries 30,000√
Disocunts allowed 25,000√
Commissions allowed 16,000√
Net profit c/d 187,000√
266,000√
Shs
Sales 580,000√
Less returns 20,000√
560,000√
_______
Gross profit b/d 560,000√
220,000√
Disocunts received 32,000√
Commissions received 14,000√
______
266,000√
Net profit b/d 187,000√
Kimani’s
Balance sheet
as at 31st December
(12 x= 8 Marks)Shs
Premises 540,000√
Machinery 200,000√
Fixtures and fittings 100,000√
Stock 70,000√
Debtors 65,000√
Cash 70,000√
1,045,000√Shs
Capital 818,000√
Add: net profit 187,000√
1,005,000√
Creditors 40,000√
________
1,045,000√
- Discuss five benefits that a customer may get by using Automated Teller Machine (ATM) for financial transactions.(8 marks)
-
- Explain clearly the problems associated with expenditure approach method in measurement of national incomes. (10mks)
- No accurate records for expenditure are kept especially in the private sector.
- Expenditure for the subsistence sector can only be mere approximations are due to lack of records in the sector
- Differentiating between final expenditure and intermediate expenditure may be difficult.
- It suffers the problem of double counting
- Fluctuating exchange rates may pose challenges especially in valuation of exports and imports.
(any 5 with explanations 5x2 =10 marks)
- Outline five reasons why an ethical practice is necessary in product promotion. (10mks)
- To safeguard consumers against misleading advertisement.
- To curb environmentally degradation
- To ensure compliance with existing government legislation.
- To curb environmental; degradation since some promotional activities may have adverse effects on the environment.
- To safeguard cultural pactices sometimes product promotion encourages use of foreign products and styles that conflict with the culture of various communities in the country.
- To safeguard competitors in the market by controlling unhealthy competition.
- To encourage selling of quality goods including stating correct ingredients.
(any 5 with explanations 5x2 =10 marks)
- Explain clearly the problems associated with expenditure approach method in measurement of national incomes. (10mks)
-
- Jane,a petty cashier was given Sh ,2000 on 1st June 2005. During the month, she made the following payments:
Use the following analysis columns to prepare a petty cash book:
Stationery, Staff tea, Travelling. Telephone, Sundry expenses. Ledger accounts.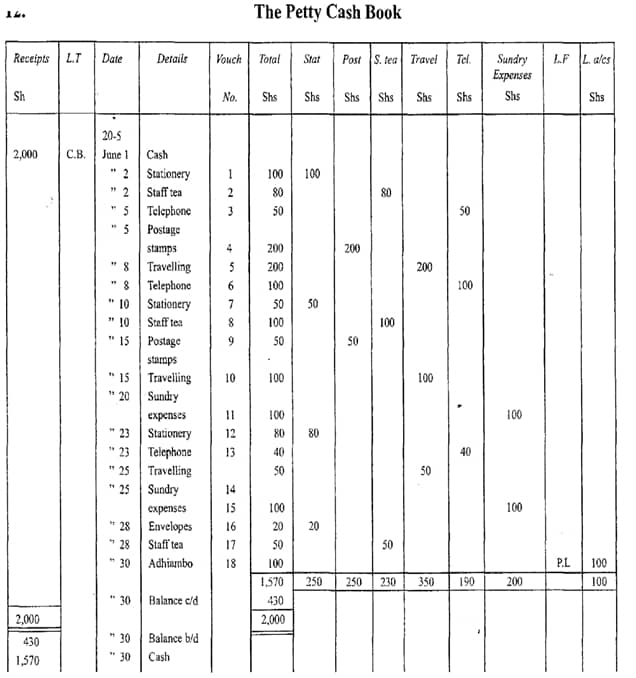
For any correct entry36 x ¼ =9 marks
All correct totals 2 marks
Balance b/d 1 mark
Total 12 Marks+ - Explain four demerits that a country may suffer when the government becomes a major investor in business. (8mks)
- Some of the managerial posts in government-run businesses are filled by political appointees who are kept in such positions even when they are performing very poorly.
- Government involvement in business may scare away investors who would have rendered the same service in a more efficient manner.
- Some state-run organizations continuously make losses thereby failing to sustain themselves. This may force the government to finance them with tax payers’ money.
- Most government projects are expensive enterprises which require heavy investment in terms of personnel training and equipment.
- Corruption and embezzlement of funds are rampant in government enterprises because of poor controls.
(any 4 with explanations 4x2 = 8 marks)
- Jane,a petty cashier was given Sh ,2000 on 1st June 2005. During the month, she made the following payments:
-
- Explain the role played by insurance industry in promoting the development of Kenyan economy. (10 mks)
- Employment creation insurance companies provided employment opportunities either directly or indirectly to individuals who would otherwise be unemployed.
- Insurance companies create confidence for the investors who are able to invest in risky but profitable areas in that they are assured of compensation in case of a loss.
- Insurance companies provide revenue for the government through profits realized and salaries for the employees when taxed.
- The business is continuous even with the occurrence of the risk because the insured is compensated. Thus business people conventure even in risky ventures.
- The amount contributed in the insurance company can be used as a security for a loan
- Some policies in life insurance encourages savings. The amount contribute is owners savings. This money can be invested later once the policies matures.
(any 5 with explanations 5x2 =10 marks)
- Explain clearly the tools of monetary policy unused by the central bank to control inflation. (10mks)
Tools of monetary policy that may be used by government to reduce excess money in circulation include:-- Open market operations — to sell government securities through the central bank.
- Bank rate — raising interest rate on loans to banks.
- Cash / Liquidity ratio can be raised for commercial banks.
- Directives — can be given to commercial banks to reduce money in supply.
- Raising margins requirement — raise the value of assets required as security for loans.
- Selective credit control — freeze lending to some sectors of the economy.
- Moral persuasion to reduce money supply.
- Increase compulsory deposits required.
(any 5 with explanations 5x2 =10 marks)
- Explain the role played by insurance industry in promoting the development of Kenyan economy. (10 mks)
Download Business Studies Paper 2 Questions And Answers - Form 4 Term 2 Opener 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students