QUESTIONS
SECTION A (50MKS)
-
- Give two reasons why most laboratory apparatus are made of glass. (1 mark)
- The diagrams below are some common laboratory apparatus. Name each apparatus and state its use. (2mks)
- Two immiscible liquids P and U were found to have densities 1.65g/cm3 and 0.52g/cm3 respectively. Using the most suitable set of apparatus, describe how one can separate them. (2 marks)
- When hydrogen chloride gas dissolves in pure ethanoic acid the following equilibrium is established.
CH3COOH(l) + HCl(g) ⇌ CH3COOH+2(aq) + Cl–(aq)- Identify the acid in the forward reaction. (1 mark)
- Identify its conjugate base. (1 mark)
- Metals J, K, L and M and their respective oxides were reacted. Metal M reduced the oxides of K and L. Metal L reduced the oxide of K and metal J reduced the oxide of M.
- Arrange the metals in order of reactivity starting with the least reactive. (2 marks)
- Which of the above metals can be used as a sacrificial metal in electroplating of metal M. (1 mark)
-
- State two observations made when a small piece of potassium metal is put in a trough full of water (2 marks)
- Write a chemical equation for the reaction. (1 mark)
- The atomic number of element Q is 15 and that of R is 9.
- Write the electronic arrangement of element Q and R (1 mark)
- Using dots (•) and crosses (x) to represent electrons, draw a diagram to show bonding in the compound formed. (2 marks)
- Give the chemical family to which element R belongs. (1 mark)
- Study the table below and answer the questions that follow.
Identify with reasons the substances that haveSubstance A B C D E F Melting point (°C) 801 113 or 119 -39 5 -101 1356 Boiling point (°C) 1410 445 457 54 -36 2860 Electrical conductivity solid poor poor good poor poor poor liquid good poor good poor poor poor - a metallic structure (1 mark)
- a molecular structure (1 mark)
- Substances A and C conduct electric current in liquid state. State how the two substances differ as conductors of electric current. (2 marks)
- Describe how a sample of calcium carbonate can be prepared in the laboratory starting with calcium oxide. (3 marks)
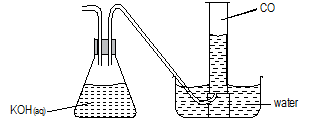
- Carbon (II) oxide CO is prepared by passing carbon (IV) oxide over red hot charcoal.
- Complete the diagram below showing how pure carbon (II) oxide can be collected. (2 marks)
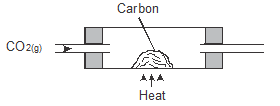
- Write chemical formulae of two other gases which can be similarly collected. (1mark)
- Complete the diagram below showing how pure carbon (II) oxide can be collected. (2 marks)
- Nitric (V) acid may be prepared in the laboratory by the reaction of concentrated sulphuric acid on a suitable nitrate and distilling off nitric (V) acid. This reaction is carried out in an all glass apparatus.
- Explain why the apparatus consisting of glass is only desirable for this preparation (2 marks)
- Pure nitric (V) acid is a colourless liquid but the product in this preparation is pale yellow. Explain. (2 marks)
- The diagram below represents pipes used in the Frasch pump for the extraction of sulphur.
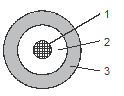
Which substances pass through the tubes?(3mks) - The diagram below shows a set up for large scale manufacture of hydrochloric acid.
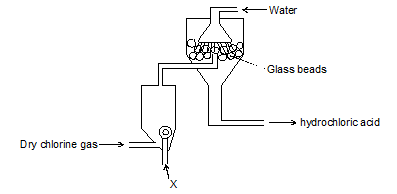
- Name substance X (1 mark)
- What is the purpose of the glass beads? (1 mark)
- Give one use of hydrochloric acid (1 mark)
- The graph below shows the behaviour of a fixed mass of a gas at constant temperature.
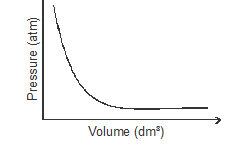
- What is the relationship between the volume and pressure of the gas? (1 mark)
- A fixed mass of a gas at 750mmHg pressure and -23ºC temperature occupies a volume of 600cm3 What volume will it occupy at 33ºC and 900mmHg? (2 marks)
- 10 molecules of an unknown gas have a mass of 1.0667 x 10-21g. Determine the relative molecular mass of the gas. (L = 6.0 x 1023) (2 marks)
- 10cm3 of a gaseous hydrocarbon was mixed with 90cm3 of oxygen and sparked. The resulting volume at r.t.p was 70cm3 which was reduced by 30cm3 on shaking with sodium hydroxide. Find the empirical formula of the hydrocarbon. (3 marks)
-
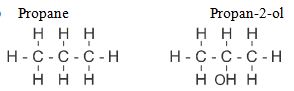
- Draw the structural formulae of propane and propan-2-ol (1/2 mark)
Propane
Propan-2-ol (1/2 mark) - Give the chemical test for distinguishing propane from propene. (1 mark)
- Draw the structural formulae of propane and propan-2-ol (1/2 mark)
- Some average bond energies are given below.
Calculate the energy change for the reaction belowBond Energy in kJmol-1 C-C 348 C_H 414 Cl-Cl 243 H-Cl 340 C-Cl 432
C2H6 + Cl2(g) → CH3CH2Cl(g) + HClg (3 marks)
SECTION B (50MKS)
- The table below shows the atomic numbers and boiling points of element U, V, W, X and Y (not their actual symbols). Study it and answer the questions that follow.
Element Atomic number Boiling point (°C) U 3 1330 V 13 2470 W 16 445 X 18 -186 Y 19 774 - Select the elements which belong to the same
- Group (1 mark)
- Period (1 mark)
- Which element :
- Is gaseous at room temperature ? Explain (room temperature = 298K) (2 marks)
- Does not form an oxide (1 mark)
- Write the
- Formula of the sulphate of element (1 mark)
- Equation for the reaction between Y and W(1 mark)
- What type of bond exists in the compound formed between U and W? Give a reason for your answer. (2 marks)
- An aqueous sulphate of element V was electrolysed using carbon electrodes. Name the products at the:
- Cathode (1 mark)
- Anode (1mrk)
- Select the elements which belong to the same
- Study the set up below which was used by Form Four students to prepare a gas in the laboratory.
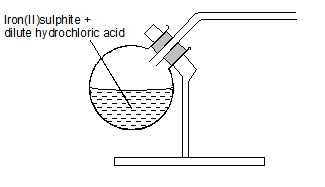
- Write the equation for the reaction in the flask. (1 mark)
- State a chemical test for the gas prepared. (1 mark)
- When hydrogen sulphide gas was bubbled into an aqueous solution of iron (II) chloride a yellow precipitate was deposited.
- State the other observation that was made. (1 mark)
- Write the reaction equation for c (i) above. (1 mark)
- When sugar crystals were reacted with concentrated sulphuric (IV) acid, a black substance T was formed which when dried burnt in excess air to form a colourless gas U only. While when concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid is reacted with liquid D at temperature of 170ºC, a colourless gas W is formed this turns brown bromine water to colourless and also turns colour of substance Y from purple to colourless.
- Identify substances (5 marks)
- Which property of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid is being demonstrated by formation of a black mass? (1 mark)
- The flow chart below shows some chemical reactions. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
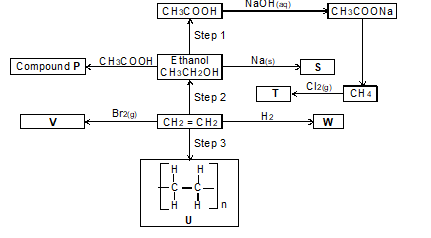
- Write the name and formula of the organic compounds P, V and W
- Name P (½ mark)
Formula (½ mark) - Name V (½ mark)
Formula (½ mark) - Name W (½ mark)
Formula (½ mark)
- Name P (½ mark)
- Write the name of the process that leads to the formation of substance(s) (11/2mks)
- Give one necessary condition for the formation of compound P (1/2mark)
- If the relative molecular mass of compound U is 84,000 units, determine the value of n.
(c = 12, O = 1.0) (2 marks) - Write an equation for the reaction leading to the formation of substance S (1 mark)
- State and explain the observation made when substance ‘W’ and C2H4 are burnt in excess air. (2 marks)
- Write the name and formula of the organic compounds P, V and W
- In an experiment to determine the molar heat of neutralisation of hydrochloric acid with sodium hydroxide, students of Kima Secondary school reacted 100cm3 of 1M hydrochloric acid with 50cm3 of 2M sodium hydroxide solution. They obtained the following results :
Initial temperature of acid = 25.0ºC
Initial temperature of base = 25.0ºC
Highest temperature reached with the acid - alkali mixture = 34.0ºC- Define the term molar heat of neutralization. (1 mark)
- Write an ionic equation for the neutralization reaction between hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide. (1 mark)
- Calculate:
- The amount of heat produced during the reaction. (S.h.c of solution = 4.2kJkg-1k-1) (2 marks)
- The molar heat of neutralization of sodium hydroxide. (1 mark)
- Explain why molar heat of neutralization of 1M NaOH is higher than that of 1M NH4OH when reacted with 2M HCl. (2 marks)
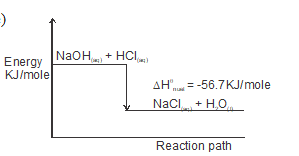
- Write the thermochemical equation for the reaction involving neutralization of 1M hydrochloric acid with 2M sodium hydroxide. (1mk)
- Draw an energy level diagram for the reaction in (d) above. (2 marks
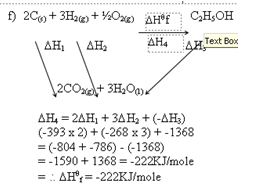
- Below are heats of combustion of carbon, hydrogen gas and ethanol.
- Hc(carbon)H = -393kJ/mol
- Hc(hydrogen)H = -268kJ/mol
- Hc(ethanol)H = -1368kJ/mol
Calculate the heat of formation of ethanol (3 marks)
-
- Name the chief ore from which iron is extracted. (1 mark)
- Name the two impurities found in iron ores. (2 marks)
- Iron rusts in the presence of moist air. Give the chemical name of rust. (1 mark)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- glass does not react with most chemicals
It is transparent one can see when the reaction is taking place or it is easy to clean - Name: Desicator
Use : Drying or keeping substance from moisture crystals
Name: evaporating dish
Use: evaporating liquids to obtain crystals
- glass does not react with most chemicals
 Working diagram
Working diagram
- Place the mixture into the separating funnel and let it settle
- On separating into layers open the tap
- Allow the first layer to drain the close the tap
-
- Hydrogen chloride gas donates hydrogen chloride
- Level of ionisation / dissociation
-
- K, L, M, J
- J
-
-
- Bursts into lilac flame
- Darts on the surface of the water
- Produces a hissing sound
- Floats
- 2K(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2KOH(aq) + H2(g)
-
-
- Q = 2.8.5
R = 2.7 -
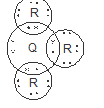
- Halogens
- Q = 2.8.5
-
- C good conductor of electricity in both solid and liquid state due to delocalised electrons
- D or E are poor conductor in both solid / liquid state
Have relatively low Mpt and Bpt due to molecular structure - A - mobile / free ions
B - delocalised electrons
- Add excess dilute nitric (V) acid to the given calcium oxide.
Calcium nitrate is formed
Add sodium carbonate solution / K2CO3 //
(NH4)2CO3(aq) to the calcium nitrate solution formed, filter obtain CaCO3 as residue -
-
- Glass apparatus withstand the high temperatures used in this experiment and are corrosion resistant
- Nitric (V) acid prepaid has dissolved NO2
- 1 - Compressed hot air in
2 - Molten froth of sulphur water mixture out
3 - superheated water-in -
- X - hydrogen gas
- To increase the surface area of absorption of hydrogen chloride gas in water
- Manufacture of dyes, drugs, photographic materials. A commonly laboratory reagent used in schools and in researched institutions
-
- Volume is inversely proportional to pressure (P 1/V)
- P1V1 = P2V2
T1 T2
P1 = 750mmHg
V1 = 600cm3
T1 = 273 - 23 = 250K
P2 = 900mmHg
V2 = ?
V2 = 750 x 600 x 306 = 612cm3
250 x 900
- 10 molecules = 1.0667 x 10-21
6.0 x 1023 = ?
= 6.0 x 1023 x 1.0667 x 10-21
10
= 64.002g - CxHy(g) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + H2O(g)
10cm3 90cm3 30cm3
Excess volume of = 70 - 30 = 40cm3
oxygen
volume of O2 reacted = 90 - 40 = 50cm3
CxHy(g) + 5O2(g) → 3CO2(g) + 4H2O(g)
empirical formula = C3H8 -
- Bubble the two gases separately through acidified potassium manganate (VII)
Propene decolourises it but not propane
Or Bubble the two gases separately through bromine (liquid or water) in the dark propene decolourises but not propane
ΔH = 3075 - 2850Reactants Products C-C = 348 x 1 = 348
C-H = 6 x 414 = 2484
Cl-Cl = 243 x 1 = 243
+3075KJ/molC-C= 348 x 1 = 348
C-H = 5 x 414 = 2070
C-Cl = 432 x 1 = 432
-2850KJ/mol
= + 225KJmol-1
SECTION B (50MKS)
-
-
- Same group : U and Y
- Same period: V, W and X
-
- X, Bpt = (-186 + 273)
= 87K below room temp. - X
- X, Bpt = (-186 + 273)
-
- V3(SO4)2
= V2(SO4)3 - Y(s) + W2 → 2Y2W(s)
- V3(SO4)2
- Ionic bond
U loses electrons the electrons gained by W -
- Cathode
Hydrogen gas - Anode: oxygen gas
- Cathode
-
-
- FeS(s) + 2HCl(aq) → FeCl2(aq) + H2S(g)
- Blackens wet lead ethanoate powder
(any other possible test) -
- A green solution is formed
- 2FeCl3(aq) + H2S(s) → 2FeCl2(aq) + 2HCl(aq)
-
- T - carbon
U - carbon (IV) oxide
D - ethanol
W - ethene
Y - acidified potassium manganate (VII) - Dehydration
- T - carbon
-
-
- P – ethylethanoate formula
- 1, 2, dibromo-ethane
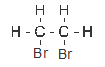
- ethane
- reaction process
V –Addition halogenation
T - Substitution
P - Esterification - Concentrated H2SO4
- 28n = 84000
n = 3000 - 2CH3CH2OH(l) + 2Na(s) → 2CH3CH2ONa(s) + H2(g)
- W burns with a blue flame
C2H4 burns with a yellow sooty flame
-
-
- The enthalpy change that occurs when one mole of H+ ion react with one mole of OH ion forming one mole of water
- H+(aq) + OH–(aq) H2O(l)
-
- The volume of mixture = (100 + 50)cm3
= 150cm3
Mass of mixture = 150
1000
= 0.15kg
Average initial temp. = 25 + 25 = 50 = 25ºC
2 2
Change in temp.
= 34 - 25 = 9ºC
H = MCT
= 0.15 x 4.2 x 9
= 5.67KJ - Moles of NaOH
If 1000cm3 contains 2 moles
Then 50cm3 contains 50 x 2 = 0.1 moles
1000
If 0.1 moles evolve 5.67KJ
Then 1 moles evolve 5.67 = 56.7kJ
0.1
Hnuet = -56.7kJ/mole - NH4OH is a weak base that dissociates
partially while NaOH is a strong base that dissociates completely. Some heat is absorbed before neutralisation takes place for NH4OH
- The volume of mixture = (100 + 50)cm3
- NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) Hnuet = -56.7KJ/mole
-
-
-
- Haemitite Fe2O3 or magnetite Fe3O4
- Silicon (IV) oxide (silica) / Aluminium oxide
- Hydrated iron (III) oxide
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Questions and Answers - Form 4 Mid Term 2 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

