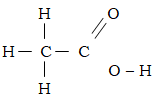Instructions
- Answer All questions in the spaces provided.
-
- Hydrogen gas is one of the lightest gases known. Explain why it is not preferred in weather balloons. (1mk)
- Give any two large scale uses of hydrogen gas. (2mks)
- A compound with a general formula X(OH)3 reacts as shown by the equations below.
X(OH)3(s) + OH−(aq) → [X(OH)4]−(aq)
X(OH)3(s) + 3H+(aq) → X3+(aq) + 3H2O(l)- What name is given to compounds which react like X (OH)3? (1mk)
- State any two elements whose hydroxides behave like that of X. (1mk)
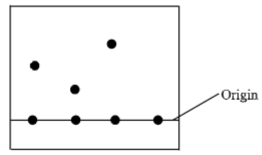
- The diagram below represents a paper chromatogram of pure substances R, P and Q. A mixture S contains R and Q only. Indicate on the diagram the chromatogram of S. (2mks)
-
- State Graham’s Law of diffusion. (1mk)
- 100cm3 of Carbon (IV) oxide diffuses through a porous plate in 30 seconds. How long will it take 150cm3 of nitrogen (IV) oxide to diffuse across the same plate under similar conditions? (C=12, N=14, O=16) (3mks)
- Starting with solid Zinc oxide, describe how a pure sample of zinc carbonate can be prepared. (3mks)
-
- The structure of ethanoic acid is;
State the number of electrons used in bonding in a molecule of ethanoic acid. (1mk) - Give the name of the following organic compounds. (2mks)
-
- CH3C(CH3)(Br) CH2CH3
-
- The structure of ethanoic acid is;
- A current of 0.5A was passed for 64.33 minutes to deposit 1.2g of metal Q. Calcualte the number of Faradays required to deposit one mole of Q. (RAM of Q=120, 1F=96,500C) (3mks)
-
- Name the type of artificial radioactivity represented by each of the following nuclear equations. (2mks)
-
- Complete the diagram below to show how alpha particles and gamma rays can be distinguished. (2mks)
- Name the type of artificial radioactivity represented by each of the following nuclear equations. (2mks)
- A white solid M was heated. It produced a brown gas A and a colourless gas B. The residue left was yellow after cooling.
- Name gases A and B. (2mks)
- Write a balanced chemical equation for the decomposition of solid M.(1mk)
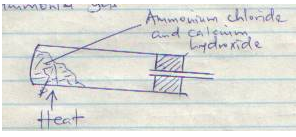
- Below is a set-up for laboratory preparation of ammonia gas.
- Complete the set-up to show how a sample of dry ammonia gas can be collected. (2mks)
- Write an equation for the reaction. (1mk)
- Elements X and Y have atomic numbers of 12 and 16 respectively. Using dots (.) and crosses (x), show how bonding takes place. (2mks)
- Aqueous ammonia solution is passed through a colourless solution Y. A white precipitate which dissolves in excess ammonia to form a colourless P solution is formed.
- Identify the cation present. (1mk)
- Write down the formula of;
- White precipitate. (1mk)
- Complex ion in solution P. )1mk)
- The table below shows pH values of solutions A, B, C and D. The solutions tested were sodium chloride, soap solution, potassium hydroxide and aluminium chloride. Complete the table by identifying the solution tested. (2mks)
Solution pH Name of solution A 8.5 B 3.0 C 7.0 D 13.0 - When 0.6g of element M was completely burned in oxygen, all the heat evolved was used to heat 500cm3 of water, the temperature of the water rose from 23.0°C to 32°C. Calculate the relative atomic mass of element M given that the specific heat capacity of water is 4.2Jg-1K-1, density of water is 1.0gcm-3 and molar heat of combustion of M is 380KJ/mol. (3mks)
-
- What is an electrolyte? (1mk)
- State how the following substances conduct electricity.
- Molten sodium chloride. (1mk)
- Copper metal. (1mk)
- Hydrogen and bromine react according to the equation.
H2(g) + Br2(g) → 2HBr(g)
Use the bond energies given below to calculate the heat of formation of hydrogen bromide. (3mks)
Bond Energy (KJ/mol)
H – H 436
Br – Br 192
H – Br 368 - Solid A forms a mixture with liquid B. State two properties of substance A that would make decantation the method of choice for separating the mixture. (2mks)
- Sulphur (IV) oxide gas was bubbled through a solution of water and litmus solution.
- State what was observed. (1mk)
- Write an equation for the reaction. (1mk)
-
- What causes water hardness? (1mk)
- State two methods that can be used to remove permanent hardness in water. (2mks)
- State one advantage of drinking hard water. (1mk)
- Graphite is one of the allotropes of carbon.
- Name one other element which exhibits allotropy. (1mk)
- Explain why graphite is used to make pencil leads. (2mks)
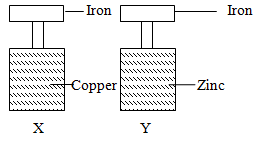
- A form four student in an attempt to prevent rusting, put copper and zinc in contact with iron as shown below.
- State what would happen in set up X and Y after one week. (2mks)
- Explain your answer in diagram Y. (1mk)
- What name is given to the above method? (1mk)
- Urea, (NH2)2CO, is prepared by the reaction between ammonia and carbon (IV) oxide.
2NH3(g) + CO2(g) → (NH2)2CO(aq) + H2O(l)
In one process, 680kg of ammonia were reacted with excess carbon (IV) oxide. Calculate the mass of urea that was formed. (H=1.0, C=12.0, N=14.0, O=16.0 and R.M.M of ammonia = 17) (3mks) - Aqueous hydrogen chloride reacts with potassium manganate (VII) to produce chlorine gas, while a solution of hydrogen chloride in methylbenzene has no effect on potassium manganate (VII). Explain this observation. (2mks)
- Explain the following:
- Aluminium carbonate does not exist. (2mks)
- Hydrochloric acid is not used to acidify potassium manganate(VII). (2mks)
- Naturally occurring magnesium consists of three isotopes: 78.6% 24Mg, 10% 25Mg and 26Mg. calculate to one decimal place, the relative atomic mass of magnesium. (3mks)
- Under certain conditions, carbon (IV) oxide reacts with water to form methanol (CH3OH) and oxygen as shown below
2CO2(g) + 4H2O(l)2CH3OH(l) + 3O2(g) ∆H=+1452KJ
What would be effect on the yield of methanol if the temperature of the reaction mixture is increased? Explain. (2mks) - Use the cell representation below to answer the questions that follow.
Cr(s) |Cr3+(aq) || Fe2+(aq) |Fe(s)- Write the equation for the cell reaction. (1mk)
- If the e.m.f of the cell is 0.30volts and the Eθ value for Fe2+(aq) | Fe(s) is -0.44 volts, calculate the Eθ value for Cr3+(aq)|Cr(s). (2mks)
- Explain why the boiling point of ethanol is higher than that of hexane. (Relative molecular mass of ethanol is 46 while that of hexane is 86) (2mks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Hydrogen gas is one of the lightest gases known. Explain why it is not preferred in weather balloons. (1mk)
- Hydrogen is highly flammable.
- Give any two large scale uses of hydrogen gas. (2mks)
- Making oxy-hydrogen flame used in welding.
- Propelling of rockets.
- Manufacture of margarine
- Haber process to manufacture ammonia.
- Hydrogen gas is one of the lightest gases known. Explain why it is not preferred in weather balloons. (1mk)
- A compound with a general formula X(OH)3 reacts as shown by the equations below.
X(OH)3(s) + OH−(aq) → [X(OH)4]−(aq)
X(OH)3(s) + 3H+(aq) → X3+(aq) + 3H2O(l)- What name is given to compounds which react like X (OH)3? (1mk)
- Amphoteric hydroxides
- State any two elements whose hydroxides behave like that of X. (1mk)
- Aluminium
- Zinc
- Lead
- What name is given to compounds which react like X (OH)3? (1mk)
- The diagram below represents a paper chromatogram of pure substances R, P and Q. A mixture S contains R and Q only. Indicate on the diagram the chromatogram of S. (2mks)
-
- State Graham’s Law of diffusion. (1mk)
- For a given volume of a gas, the rate of diffusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its density, temp and pressure being constant.
- 100cm3 of Carbon (IV) oxide diffuses through a porous plate in 30 seconds. How long will it take 150cm3 of nitrogen (IV) oxide to diffuse across the same plate under similar conditions? (C=12, N=14, O=16) (3mks)
100cm3 of CO2 diffuse in 30 sec.
150cm3 of CO2 diffuse in (150×30) = 45 sec
100
tNO2 = √MNO2 = D tNO2 = √46
tNO2 √MCO2 45 √44
tNO2 = (45×√46) = 46.01 seconds
√44
- State Graham’s Law of diffusion. (1mk)
- Starting with solid Zinc oxide, describe how a pure sample of zinc carbonate can be prepared. (3mks)
- Add excess zinc oxide to dilute HNO3
- Filter to obtain zinc nitrate solution
- Add Na2CO3(aq) / K2CO3(aq)
- Filter to obtain zinc carbonate residue
- Dry between filter papers to obtain ZnCO3 crystals.
-
- The structure of ethanoic acid is;
State the number of electrons used in bonding in a molecule of ethanoic acid. (1mk)
8 X 2 = 16e- - Give the name of the following organic compounds. (2mks)
- 2,3-Dimethylpentane
- 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane.
- The structure of ethanoic acid is;
- A current of 0.5A was passed for 64.33 minutes to deposit 1.2g of metal Q. Calculate the number of Faradays required to deposit one mole of Q. (RAM of Q=120, 1F=96,500C) (3mks)
Q = It
= 0.5 X 64.33 X 60
= 1929.9C
1.2g is deposited by 1929.9C
120g deposited by 120×1929.9 = 192990
1.2
No. of Faradays = 192990 = 1.9998
96500
= 2 Faradays. -
- Name the type of artificial radioactivity represented by each of the following nuclear equations. (2mks)
- Nuclear fission
- Nuclear fusion
- Complete the diagram below to show how alpha particles and gamma rays can be distinguished. (2mks)
- Name the type of artificial radioactivity represented by each of the following nuclear equations. (2mks)
-
- A white solid M was heated. It produced a brown gas A and a colourless gas B. The residue left was yellow after cooling.
- Name gases A and B. (2mks)
- A – Nitrogen (IV) oxide
- B – Oxygen gas
- Write a balanced chemical equation for the decomposition of solid M. (1mk)
2Pb(NO3)2(s) → 2PbO(s) + 4NO2(g) + O2(g)
- Name gases A and B. (2mks)
- A white solid M was heated. It produced a brown gas A and a colourless gas B. The residue left was yellow after cooling.
- Below is a set-up for laboratory preparation of ammonia gas.
- Complete the set-up to show how a sample of dry ammonia gas can be collected. (2mks)
- Write an equation for the reaction. (1mk)
Ca(OH)2(s) + NH4Cl(s) → CaCl2(s) + 2H2O(l) + 2NH3(g)
- Elements X and Y have atomic numbers of 12 and 16 respectively. Using dots (.) and crosses (x), show how bonding takes place. (2mks)
- Aqueous ammonia solution is passed through a colourless solution Y. A white precipitate which dissolves in excess ammonia to form a colourless P solution is formed.
- Identify the cation present. (1mk)
Zn2+ - Write down the formula of;
- White precipitate. (1mk)
Zn(OH)2 - Complex ion in solution P. )1mk)
[Zn(NH3)4]2+
- White precipitate. (1mk)
- Identify the cation present. (1mk)
- The table below shows pH values of solutions A, B, C and D. The solutions tested were sodium chloride, soap solution, potassium hydroxide and aluminium chloride. Complete the table by identifying the solution tested. (2mks)
Solution pH Name of solution A 8.5 Soap solution B 3.0 Aluminium chloride C 7.0 Sodium chloride D 13.0 Potassium hydroxide - When 0.6g of element M was completely burned in oxygen, all the heat evolved was used to heat 500cm3 of water, the temperature of the water rose from 23.0°C to 32°C. Calculate the relative atomic mass of element M given that the specific heat capacity of water is 4.2Jg-1K-1, density of water is 1.0gcm-3 and molar heat of combustion of M is 380KJ/mol. (3mks)
∆H = mc∆T
= 500g X 4.2Jg-1K-1 X 9K
= 18900 J
= 18.9 KJ
0.6g → 18.9KJ
? → 380 KJ
0.6×380
18.9
= 12.06g
= 12 -
- What is an electrolyte? (1mk)
- Is a substance that conducts electricity/ electric current in molten or aqueous form/ state.
- State how the following substances conduct electricity.
- Molten sodium chloride. (1mk)
- Use of mobile/free ions
- Copper metal. (1mk)
- Use of delocalized electrons.
- Molten sodium chloride. (1mk)
- What is an electrolyte? (1mk)
- Hydrogen and bromine react according to the equation.
H2(g) + Br2(g) → 2HBr(g)
Use the bond energies given below to calculate the heat of formation of hydrogen bromide. (3mks)
Bond Energy (KJ/mol)
H – H 436
Br – Br 192
H – Br 368
H – H + Br – Br → 2 H – Br
436 + 192 −368 X 2
Heat of formation = HBB + HBF
= 436 + 192 – 368 X 2
= −108KJ/mol. - Solid A forms a mixture with liquid B. State two properties of substance A that would make decantation the method of choice for separating the mixture. (2mks)
- Solid A is insoluble in water.
- Solid A has/is made of large particles.
- Sulphur (IV) oxide gas was bubbled through a solution of water and litmus solution.
- State what was observed. (1mk)
- The solution turned red
- Write an equation for the reaction. (1mk)
- SO2(g) + H2O(l) → H2SO3(aq)
- State what was observed. (1mk)
-
- What causes water hardness? (1mk)
- Presence of dissolved salts of Ca2+ and Mg2+
- State two methods that can be used to remove permanent hardness in water. (2mks)
- addition of sodium
- permutit softener
- distillation
- State one advantage of drinking hard water. (1mk)
- Hard water has Ca2+ for strong bones and teeth.
- What causes water hardness? (1mk)
- Graphite is one of the allotropes of carbon.
- Name one other element which exhibits allotropy. (1mk)
- Sulphur
- Explain why graphite is used to make pencil leads. (2mks)
- Its soft and black hence easy to write on a paper.
- Name one other element which exhibits allotropy. (1mk)
- A form four student in an attempt to prevent rusting, put copper and zinc in contact with iron as shown below.
- State what would happen in set up X and Y after one week. (2mks)
- In set-up X iron turned red-brown while in set up Y, iron remained unchanged.
- Explain your answer in diagram Y. (1mk)
- Iron is more reactive than copper hence combines with the moist atmospheric air while zinc is more reactive than iron hence will combine with oxygen.
- What name is given to the above method? (1mk)
- Sacrificial protection.
- State what would happen in set up X and Y after one week. (2mks)
- Urea, (NH2)2CO, is prepared by the reaction between ammonia and carbon (IV) oxide.
2NH3(g) + CO2(g) → (NH2)2CO(aq) + H2O(l)
In one process, 680kg of ammonia were reacted with excess carbon (IV) oxide. Calculate the mass of urea that was formed. (H=1.0, C=12.0, N=14.0, O=16.0 and R.M.M of ammonia = 17) (3mks)
No. of moles of NH3 = 680 = 40 moles
17
M.R NH3 : (NH2)2CO
2 : 1
Moles of (NH2)2CO = 20 moles
Mass = Molar mass X Moles
= 60 X 20
= 1200 kg - Aqueous hydrogen chloride reacts with potassium manganate (VII) to produce chlorine gas, while a solution of hydrogen chloride in methylbenzene has no effect on potassium manganate (VII). Explain this observation. (2mks)
- HCl(g) in water ionizes to form H+ and Cl− hence showing acidic properties. In methylbenzene however it remains in molecular form and does not display acidic properties.
- Explain the following:
- Aluminium carbonate does not exist. (2mks)
- Aluminium hydrolyses in water to give H+ which react with
to liberate CO2(g) and water.
- Aluminium hydrolyses in water to give H+ which react with
- Hydrochloric acid is not used to acidify potassium manganate(VII). (2mks)
- HCl reacts with potassium manganate (VII) to produce chlorine gas.
- Aluminium carbonate does not exist. (2mks)
- Naturally occurring magnesium consists of three isotopes: 78.6% 24Mg, 10% 25Mg and 26Mg. calculate to one decimal place, the relative atomic mass of magnesium. (3mks)
RAM = 24 × 78.6 + 25 ×10+ 26×11.4
100
= 2432.8
100
= 24.328
= 24.3 - Under certain conditions, carbon (IV) oxide reacts with water to form methanol (CH3OH) and oxygen as shown below
2CO2(g) + 4H2O(l)2CH3OH(l) + 3O2(g) ∆H =+1452KJ
What would be effect on the yield of methanol if the temperature of the reaction mixture is increased? Explain. (2mks)- The yield of methanol will increase. The forward reaction is endothermic and increase in temperature favours endothermic process.
- Use the cell representation below to answer the questions that follow.
Cr(s) |Cr3+(aq) || Fe2+(aq) |Fe(s)- Write the equation for the cell reaction. (1mk)
2Cr(s) + 3Fe2+(aq) →2Cr3+(aq) + 3(s) - If the e.m.f of the cell is 0.30volts and the Eθ value for Fe2+(aq) | Fe(s) is −0.44 volts, calculate the Eθ value for Cr3+(aq)|Cr(s). (2mks)
E.m.f = –0.44 – x
0.30 = –0.44 – x
X = –0.44 – 0.30 = –0.74V.
- Write the equation for the cell reaction. (1mk)
- Explain why the boiling point of ethanol is higher than that of hexane. (Relative molecular mass of ethanol is 46 while that of hexane is 86) (2mks)
- In addition to van der waals forces, strong hydrogen bonds exist in ethanol. These bonds require more energy to break.
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Form 4 End Term 1 Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students