Instructions
- This paper has two sections A & B.
- Answer all questions in section A. in section B, answer question 6 and any other two questions.
SECTION A
-
- Name two areas where gold is mined in South Africa (2marks)
- State three uses of gold (3 marks)
-
- What is balance of trade (2marks)
- List two major imports to Kenya from Japan (2marks)
- Study the map of East Africa below and use it to answer question (a)
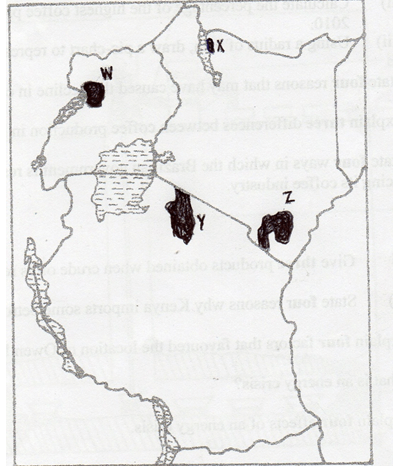
- Name the national parks marked W,X,Y & Z (4marks)
- State two differences between a national park and a game reserve (2mks)
-
- Give three trans -Africa highways (3marks)
- State three ways through which challenges hindering smooth navigation along St. Lawrence water way were overcome (3mks)
- List four main factors that influence population growth (4mks)
SECTION B
- The table below shows world leading producers of heat between 2010 and 2012 in million metric tonnes.
Country 2010 2011 2012 China 115 117 126 India 81 87 95 U.S.A 60 54 62 France 38 38 40 Russia 42 56 37 Canada 23 25 25 -
- What is the difference in wheat production between China and Canada in year 2010 (2mks)
- Calculate the percentage decrease in wheat production in Russia between 2011 and 2012 (2mks)
-
- Draw a divided rectangle 15cm long to present the data for year 2012 (10mks)
- List three suitable methods that can be used to present the data in the table (3mks)
- Explain four problems facing wheat farmers in canada (8mks)
-
-
-
- Differentiate between a forest and a forestry (2mks)
- Give three examples of coastal forests in Kenya (3mks)
- Explain four factors that have favoured the growth of Mau forest (8mks)
-
- Name three main lumbering regions in Canada (3mks)
- State five characteristics of coniferous trees that favour their exploitation (5mks)
- Compare softwood forests in Kenya and in Canada under the following sub-headings
- Distribution of softwoods forests (2mks)
- Marketing of forest products (2mks)
-
-
-
- State five physical conditions that favour tea growing in Kenya (5mks)
- Name three counties within the highlands East of the rift valley where tea is produced (3mks)
- Describe the stages involved in tea processing at the factory (8mks)
-
- Outline three ways through which tea is sold in Kenya (3mks)
- Explain three ways in which KTDA assist tea farmers in Kenya (6mks)
-
-
-
- Differentiate between fishing and fisheries (2mks)
- Give three examples of pelagic fish (3mks)
- The diagram below represents a method of fishing
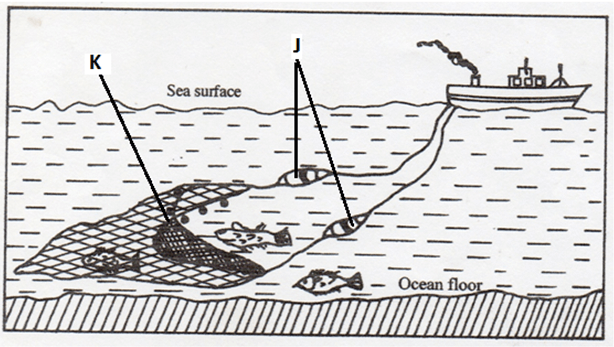
- Name the fishing method represented by the diagram (1mk)
- Identify the parts marked J and K (2mks)
- Describe how fishing is carried out using the basket Method (5mks)
- Explain three measures taken to conserve fisheries in Kenya (6mks)
- Compare fishing in Kenya and in Japan under the following sub-headings
- Ocean currents (2mks)
- Nature of the coastline (2mks)
- Level of technology (2mks)
-
-
-
- Define the term industrialization (2mks)
- State three reasons why some industries are located at the source of raw materials (3mks)
- Explain four problems arising from industrialization in Kenya (8mks)
- State six characteristics of the cottage industry in India (6mks)
- Suppose you were to carry out a field study in a shoe making factory in Kenya.
- State three objectives that you would set for the study (3mks)
- Give three main methods that you would use to collect data at the factory. (3mks)
-

MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A
-
- Name two areas where gold is mined in South Africa (2marks)
- Witwatersrand
- Fareastrand
- Farwestrand
- Orange free state
- Lydenburg
- Klerlsorp
- State three uses of gold (3 marks)
- make ornamental objects and jewels
- as financialbacking for currency
- are used in cell phones and some televisions
- making memory chips and some computer parts
- gold alloys are used in dentistry eg crowns, brigdes and fillings
- to make some surgical instruments
- used in circuitry of some space vehicles
- Name two areas where gold is mined in South Africa (2marks)
-
- What is balance of trade (2marks)
- It’s the difference in value between a countrys visible exports and its visible imports
- List two major imports to Kenya from Japan (2marks)
- motor vehicles/ motor vehicle parts
- electronics
- textiles
- machinery
- What is balance of trade (2marks)
- Study the map of East Africa below and use it to answer question (a)
- Name the national parks marked W,X,Y & Z (4marks)
- W-Murchison falls
- X-Sibiloi
- Y-Serengeti
- Z-Tsavo
- State two differences between a national park and a game reserve (2mks)
- Games reserve are managed by county governments whereas national parks are managed by the national governments.
- In game reserves domestic animals can be accommodated whereas in national parks, domestic animals are prohibited
- Name the national parks marked W,X,Y & Z (4marks)
-
- Give three trans -Africa highways (3marks)
- The Great North Road
- TransAfrican highway
- West African highway
- Trans-saharan highway
- State three ways through which challenges hindering smooth navigation along St. Lawrence water way were overcome (3mks)
- canals were constructed to by pass areas with waterfalls and rapids
- dams were constructed thus drowning some outcrop rocks
- rock shoals in some parts were removed through blasting
- shallow section were deepened through dredging
- locks were constructed where levels of lakes were different
- small islands along rivers were removed
- ice breakers were introduced to improve navigation during winter
- Give three trans -Africa highways (3marks)
- List four main factors that influence population growth (4mks)
- fertility
- mortality
- migration
- cultural beliefs / tradations
- Modernization
- availability of food
- religion
- health services
SECTION B
- The table below shows world leading producers of heat between 2010 and 2012 in million metric tonnes.
-
- What is the difference in wheat production between China and Canada in year 2010 (2mks)
115 million – 23million = 92 million metric tones
Or 92,000,000 metric tonnes - Calculate the percentage decrease in wheat production in Russia between 2011 and 2012 (2mks)
difference: 56-37= 19 million metric tones
19/56 ×100% = 33.93% or 33.9%
- What is the difference in wheat production between China and Canada in year 2010 (2mks)
-
- Draw a divided rectangle 15cm long to present the data for year 2012 (10mks)
Total production in 2012
126 + 95 + 62 + 40 + 37 + 27 = 387 million metric tones
China: 126/387 × 15cm = 4.9cm
India: 95/387 × 15cm = 3.7cm
U.S.A: 62/387 × 15cm = 2.4 cm
France: 40/387 × 15cm = 1.6cm
Russia: 37/387 × 15cm = 1.4cm
Canada: 27/387 × 15cm = 1.0cm - List three suitable methods that can be used to present the data in the table (3mks)
- proportional divided circles
- comparative line graph
- comparative bar graph
- compound bar graph
- Draw a divided rectangle 15cm long to present the data for year 2012 (10mks)
- Explain four problems facing wheat farmers in canada (8mks)
- stiff competition from other wheat exporting countries such as USA and Russia which reduces her market quota.
- exhaustion of soil due to prolonged use which lowers the quality and quantity of wheat produced per hectare.
- occurrence of frost and hail at times destroys the crop in some areas lowering the yield
- Fluctuations in the world prices for wheat at times reduces farmers profits thus lowering their morale
- Occurrence of summer heat waves at times destroys wheat in farms thus leading to lower yields
- Spraying the crop to control weeds, pests and diseases with chemicals has increased the cost of production.
-
-
-
- Differentiate between a forest and a forestry (2mks)
- A forest is a contuinuous growth of trees and undergrowth covering a large tract of land whereas forestry refers to the practice of managing and using forests, trees and their associated resources for human benefits.
- Give three examples of coastal forests in Kenya (3mks)
- Arabuko Sokoke forest
- Shimba hills forest
- Boni forest
- Mangrove forests
- Kaya forests
- Tana river forests
- Differentiate between a forest and a forestry (2mks)
- Explain four actors that have favored the growth of Mau forest (8mks)
- The region receives high rainfall of about 1300mm annually which supports the growth of trees
- Moderate to high temperatures experienced in the area allows the growth of a variety of trees
- presence of deep and well drained volcanic soils which allow tree roots to penetrate deep into the ground.
- Some areas are steep / rugged which discourage settlement and allows the forest to grow
- The area is a gazette forest hence settlement and cultivation are prohibited
- Enforcement of laws especially evicting squatters to allow for the re-establishment of the forest
-
- Name three main lumbering regions in Canada (3mks)
- British –Columbia
- Nova Scotia
- Prince Edward Island
- Quebec
- Ontario
- New Foundland
- New Brunswick
- State five characteristics of coniferous trees that favour their exploitation (5mks)
- trees occur in a place stand thus easy to exploit
- absence of undergrowths favour transportation of cut logs
- trees are lighter in weight compared to tropical hardwoods
- the trees are tall thus a single trunk yields several logs
- trees have straight trunks and very few / short branches
- absence of buttress roots enable easy cutting
- Name three main lumbering regions in Canada (3mks)
- Compare softwood forests in Kenya and in Canada under the following sub-headings
- Distribution of softwoods forests (2mks)
- In Kenya soft woods are found in highlands while in Canada, softwoods are found both in highlands and in lowlands.
- In Keny a soft woods cover a small percentage of total land area whereas in Canada soft woods cover a large percentage of total area
- Marketing of forest products (2mks)
- In Kenya soft wood forests are mainly sold locally with a very small percentage being exported whereas in Canada forests products are also sold locally with a large percentage being exported to USA, Britain and Japan
- Distribution of softwoods forests (2mks)
-
-
-
- State five physical conditions that favour tea growing in Kenya (5mks)
- moderate high temperature between 15oC to 26oC
- High rainfall between 1000mm and 2000mm annually
- well distributed rainfall throughout the year
- high altitude areas between 1500m and 2400metres above sea level
- deep and well drained volcanic soils
- slightly acidic soils of PH between 4 and 6
- tea requires areas that are frost free
- Gently sloping land/ undulating land
- Name three counties within the highlands East of the rift valley where tea is produced (3mks)
- Kiambu
- Kirinyaga
- Nyeri
- Muranga
- Embu
- Meru
- State five physical conditions that favour tea growing in Kenya (5mks)
- Describe the stages involved in tea processing at the factory (8mks)
- at the factory green leaves are spread on long wire trays and withered by blowing hot and cool air through holes
- withered leaves are passed between steel rollers to break the fibre and leaf cells then through a machine that chops them into very small pieces
- tiny chopped leaves are placed in rooms with a high temperature to ferment thus turning brown
- Fermented leaves are dried and roasted by blowing hot air in a drier at 104.4oC for a few minutes
- roasted black leaves are allowed to cool overnight
- cooled tea particles are sieved through a trainer which also grades the tea via different hole sizes
- graded tea particles are winnowed through a machine which blows out unwanted stems and particles
- the tea is tasted and packed ready for sale or export
-
- Outline three ways through which tea is sold in Kenya (3mks)
- Through auction at the port of Mombasa
- Direct sales to local and oversea buyers
- through Kenya Tea packers for the local market
- through factory door sales
- Explain three ways in which KTDA assist tea farmers in Kenya (6mks)
- KTDA establishes and sells tea seedlings mainly to small scale farmers
- KTDA supervises the cultivation of new tea bushes among small scale farmers
- KTDA facilitates the collection of harvested green leaf from farmers through setting up tea collection centres
- KTDA establishes tea processing factories on behalf of farmers
- KTDA facilitates the sale of tea through auction at the port of Mombasa and all other marketing outlets at the highest price
- KTDA is in charge of collecting payments from buyers and disbursement to farmers
- Outline three ways through which tea is sold in Kenya (3mks)
-
-
-
- Differentiate between fishing and fisheries (2mks)
- Fishing is the act of catching fish and other aquatic animals in both seas and inland waters whereas fisheries are watr bodies where fish and other aquatic organisms are naturally found or reared in large numbers.
- Give three examples of pelagic fish (3mks)
- Sardines
- Herrings
- Mackerel
- Pilchard
- capeline
- Differentiate between fishing and fisheries (2mks)
- The diagram below represents a method of fishing
- Name the fishing method represented by the diagram (1mk)
- trawling
- Identify the parts marked J and K (2mks)
- J - otterboards;
- K - Trawl net
- Describe how fishing is carried out using the basket Method (5mks)
- woven baskets with a narrow cone shapep opening are used
- the basket if funnel shaped to allow easy entry of fish
- a no return valve is fitted at the mouth of the basket to prevent the escape of fish
- the basket is lowered in water with the mouth facing the direction where water is flowing from .
- the basket is held with ropes, sticks or stones to prevent it from being swept away
- after some time the basket is removed and the fish are emptied
- Name the fishing method represented by the diagram (1mk)
- Explain three measures taken to conserve fisheries in Kenya (6mks)
- encouraging fish farming to complement the fish caught in natural waters hence reducing overfishing
- restocking overfished waters / areas by introducing fingerings from hatcheries of from overpopulated areas.
- Restricting fishing to specific seasons to allow breeding and maturing of fish
- standardizing the size of nets used by fishermen to ensure that only mature fish are caught
- patrolling a countries waters within the exclusive economic zones to prevent foreign fishing vessels that do fish poaching
- enforcing international conventions in order to protect endangered fish species and marine creatures such as whales
- Compare fishing in Kenya and in Japan under the following sub-headings
- Ocean currents (2mks)
- warm Mozambique ocean current causes Kenyas waters to be too warm thus limiting the growth of planktons which reduces the numbers of fish whereas convergence of warm Kurosiwo and cold Oya Siwo causes upwelling at the Japanese Coast which favours large fish numbers.
- Nature of the coastline (2mks)
- Kenya coastline is almost straight with very few inlets and islands thus limited fish breeding sites whereas Japan has an indented coastline with numerous inlets, bags and islands which favour fish breeding.
- Level of technology (2mks)
- low levels of technological advancements in Kenya results in traditional methods of fishing and preservation which limits fish catch whereas advanced technology in Japan leads to efficient fishing vessels, equipment processing and storage facilities hence a large fish catch
- Ocean currents (2mks)
-
-
-
- Define the term industrialization (2mks)
- Industrialization is the process and pace at which a country sets to establish industries
- State three reasons why some industries are located at the source of raw materials (3mks)
- for a steady supply of raw materials
- to reduce transport cost of bulky raw materials
- some raw materials are perishable thus ought to be processed immediately
- Define the term industrialization (2mks)
- Explain four problems arising from industrialization in Kenya (8mks)
- industries contribute to all forms of environmental pollution such as air water land and noise
- automation and computerization of some industries has led to unemployment especially due to use of cranes, forklift and conveyor belts
- increased rural to urban migration in search for jobs resulting in overcrowding
- displacement of people where a new industry is to be established
- imbalanced regional development as some industrial towns develop and expand while some areas are marginalized
- some industrial products have made some people to adopt a new lifestyle thus abandoning their traditional values
- State six characteristics of the cottage industry in India (6mks)
- cottage industries are spread all over India
- the crafts men and women are highly skilled
- work is done in homes and in simple workshops
- the industry is labour intensive as most operations are done by hand using simple tools
- labour is mainly provided by individuals or by family members
- the industries relies on locally available raw materials
- little capital is invested
- most of the products are consumed locally with a few being exported
- Suppose you were to carry out a field study in a shoe making factory in Kenya.
- State three objectives that you would set for the study (3mks)
- to find out the sources of the raw materials
- to identify the stages involved in shoe manufacture
- to investigate the main market for the shoes made
- to identify various types of shoes made
- to find out the problems that the factory experiences
- Give three main methods that you would use to collect data at the factory. (3mks)
- taking photographs / videos
- interviewing
- State three objectives that you would set for the study (3mks)
-
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Geography Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Form 4 End Term 1 Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students


