INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- This paper consist of 6 questions
- Answer ANY FIVE questions.
-
- Explain five cannons of effective government expenditure. (10marks)
- Uzima juice enterprises are considering marketing their imported goods direct to consumers. Outline five reasons that may be influencing them to make this decision. (10marks)
-
- Explain four features of direct production. (8marks)
- Record the following transactions in the books of original entry of Tumaini traders as at 15 th June 2010 and post to the relevant ledger accounts and balance them off.
- Bought an office printer for shs. 200,000 from Seals Stationary shop on credit.
- Sales returns by Ouma traders worth 5,000 Credit note number cr.56 issued.
- Sold goods on credit sh. 500,00 to Sargar Traders invoice no. 78
- Sold goods shs. 900,000 cash to Mugo receipt no. 210 was issued
- Paid salaries sh. 50,000 by cheque no. 589 (12marks
-
- Explain the procedure that is used in personal selling. (10marks)
- With the aid of suitable diagrams explain the difference between a movement and a shift in the demand curve. (10marks)
-
- Explain five limitations of a trial balance as a tool of locating bookkeeping errors (10marks)
- Explain five factors that could hasten economic development in Kenya (10marks)
-
- Explain five differences between a public warehouse and a private warehouse (10marks)
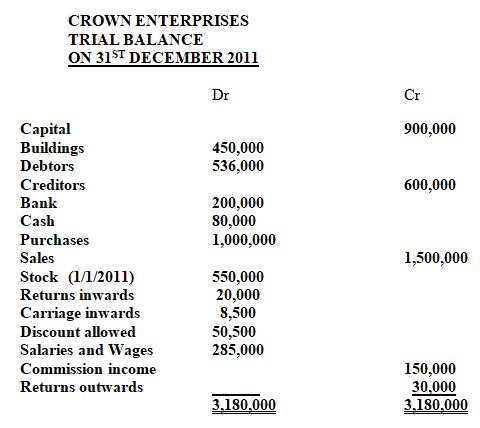
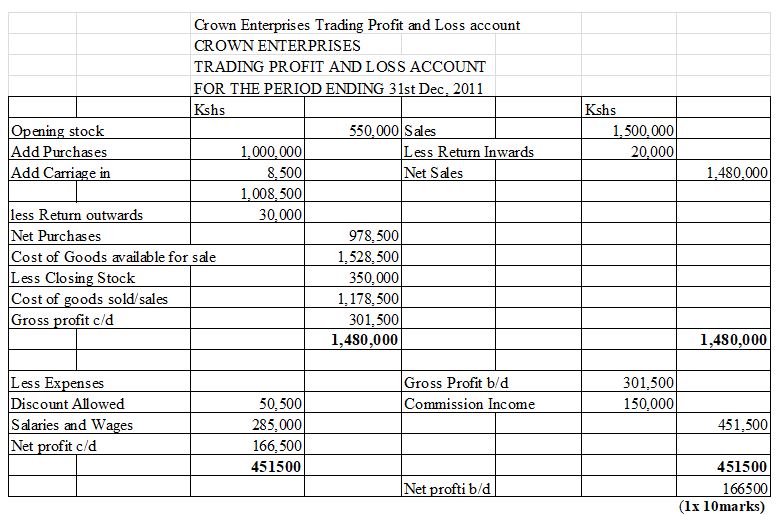
- The trial balance given below relates to Crown Enterprises
Stock on 31 st December 2011 was valued at Sh. 350,000
Required: Crown Enterprises Trading Profit and Loss account (10 marks)
-
- Explain SIX measures that the Government of Kenya may take to control her persistent Balance of payment deficit. (12 marks)
- Outline FOUR differences between endowment policy and whole life policy. (8 marks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Canons of government expenditure
- Maximum social benefit: should aim at benefiting all persons/majority in the society.
- Economy: should avoid wasteful expenditure.
- Equity: should aim at reducing income/wealth inequalities in the society.
- Sanction: proper authorization must be secured before public projects are undertaken/expenditure is incurred.
- Elasticity/flexibility :so as to cope with changing times/accommodate any changes
- Productivity: a major proportion should be spent on development projects in order to increase production in a country.
- Good financial management: proper records should be kept/there should be transparency in spending public funds. (1x 10marks)
- Reasons for marketing products direct to consumers
- It may be that the goods are produced according to customer specifications
- The firm may be having their own retail outlets/distribution facilities.
- The market may be localised[in terms of geographical location]
- The goods may be expensive and middlemen may not be able to stock them.
- The goods may be of technical nature/require after-sales service.
- The goods may be perishable[and the firm may want to deliver them fast to the customers]
- The firm may want to have direct contact with customer/get immediate feedback
- Where government policy requires goods to be sold directly to consumers
- If there are no middlemen.
- Where customers order for goods directly from the trader/firm
- Where goods imported are in small quantities
- Where the firm will maximise profits by selling directly to consumers
- Where there is stiff competition. (1x 10marks)
- Canons of government expenditure
-
- Features of direct production
- Goods/services are produced for own consumption/use and therefore not meant for sale
- Make use of rudimentary/simple technology hence goods are produced in small quantities.
- It involves little division of labour/ specialisation in production which leads to fatigue.
- Goods produced are of low quality goods due to use of simple technology
- Volume of production is very small due to use of little mechanisation.
- Promotes individualism due to less interdependence among producers.
- Limited variety of goods/services thus denying consumers choice
- Poor time management/ waste of time as producers switch from one activity to another. (1x 8marks)
-
Sales Journal
Date
2010
Details
(debtors)
Invoice issued
Folio
Amount
shs
9/06/10 Sargar traders
Total posted to sales a/c (cr)in G.L
78
S.L 500,000
Sales Returns Journal
Date
2010
Details
(debtors)
Credit note issued
Folio
Amount
shs
7/06/10 Oumas traders
Total posted to sales returns a/c (dr.) in G.L
56
S.L
5000
General Journal
Date Details DR (shs) CR(shs) 5/7/10 Office ptinter A/C
seals stationery A/C
Being purchase of an office printer from seal stationery on credit
200,000
20,000
200,000
20,000
Cash Book
Date
2010
Details
Folio
Cash
shs
Bank
sh
Date
2010
Dentals
Folio
Cash
shs
Bank
sh
11/6 Sales G.L 900,000 13/6 Salary N//L 50,000
GENERAL LEDGER
Sales A/C
Date
2010
Details
Folio
Amount
shs
Date
2010
Dental
Folio
Amount
shs
15/6 Total
debtors
G.L 500,000
Sales Returns A/C
Date
2010
Details
Folio
Amount
shs
Date
Details
Folio
Amount
sh
7/6 Total returns G.L 5,000
Office Printer A/C
Cash A/CDate
2010
Details
Folio
Amount
Shs
Date
2010
Details
Folio
Amount
Shs
7/6 Seals
stationary
G.J 200,000
Date
2010
Dental
Folio
Amount
shs
Date
2010
Dental
Folio
Amount
Shs
11/6 Cash receiots
journal
G.L 900,000
Bank A/C
Date
2010
Details
Folio
Amount
shs
Date
2010
Details
Folio
Amount
shs
11/6 Cash payment journal
G.L 50,000
SALES LEDGER
SARGAR TRADERS A/C
Date
2010
Details
Folio
Amount
shs
Date
2010
Dental
Folio
Amount
shs
15/6 Credi sales S.L 500,000
OUMA TRADERS A/C
Date
2010
Dental
Folio
Amount
shs
Date
2010
Details
Folio
Amount
shs
7/6 Sales return S.L 5000
PURCHASES LEDGER
Seal Stationary A/C
(1x 12marks)Date
2010
Dental
Folio
Amount
shs
Date
2010
Dental
Folio
Amount
sh
5/6 Office printer P.L 200,000
- Features of direct production
-
- Procedure for personal selling
- Preparing to meet the customer
This activity involves making a good impression on the potential customer - Locating the potential customer:
The activity involves going out to look for customer - Opening the sale:
This involves holding face to face discussions with the potential customer the products to the potential customer. - Presenting the products:
In this step, the sales person displays the products to the customer - Dealing with objectives:
Objectives properly, tactfully and effectively in order to complete the successfully. - Closing the sale:
In this step the sales person asks the buyer for an order, therefore the sales person should narrow down to the customer’s choice of preferred products (1x 10marks)
- Preparing to meet the customer
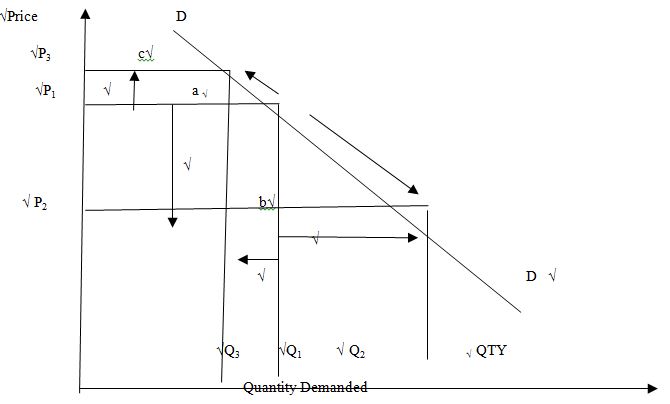
- diagrams on the difference between a movement and a shift in the demand curve Movement along the demand curve
(16 ticks /4= 4marks)
When price increases from P1 to P3 it causes an upward movement on the demand curve from a to c which is a contraction of the demand resulting to a decrease in the demand from Q1 to Q3.√ When price decreases from P1 to P2 it causes a downward movement on the demand curve from a to b which is an expansion of the demand curve resulting to an increase in demand from Q1 to Q2. √ (2 ticks /2 = 1mark)
8 ticks /2 = 4mks
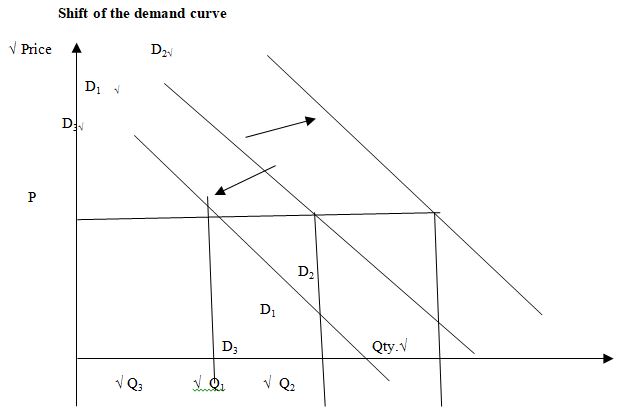
When price is held constant and all the other factors change positively the demand curve will shift to the right D2D2 and quantity demanded increases to Q2 √ and when all the other factors change negatively the demand curve will shift to the left D3D3 and the quantity demanded decreases to Q2√. (2 ticks /2 =1mark.)
Differences between a movement along a demand curve and a shift of the demand curve
(Any 1x 4marks)Movement along the demand curve Shift of a demand curveIt involves only one demand curve It involves two demand curves It is brought about by a change in price of the product Brought about by a change in other factors that influence demand other than the price of the product It involves a change in the quantity demanded It involves a change in demand A different quantity is demanded only at a different price A different quantity is demanded at the same price as before It can be traced up or down along the same curve A shift causes the curve to move either to the right or the left
- Procedure for personal selling
-
- Limitations of a trial balance as a tool of locating bookkeeping errors
- Error of omission: no record or entry of a transaction is made in any of the ledger accounts
- Error of commission: a transaction is recorded in the wrong account but the same class where the entry should have been made eg a sale of good on credit to Anne’s account is debited to Anna’s account.
- Error of principle: where a transaction is recorded in the wrong account of a different class from the correct account in which the entry should have been recorded eg purchase of furniture is debited to purchases account instead of furniture account
- Error of compensation/compensating Error: the effect of this error is such that it cancels out each other. Where two errors of equal amounts, but on opposite sides of the account cancel out each other.
- Complete reversal of entries: this occurs when the account to be originally debited is credited while one that was to be originally credited is debited.eg payment of salaries by cash is debited to cash account and credited to salaries account.
- Error of original entry: when an item is entered but both the debit and credit entries are of the same incorrect amount. (1x 10marks)
- factors that could hasten economic development in Kenya
- Presence of strong entrepreneurial culture
- Industrialisation
- Infrastructure/social amenities.
- Research and development/planning
- Education and training
- Use of modern technology/capital.
- Good medical facilities.
- Good governance/government goodwill
- Economic endowments/natural resources. (1x 10marks)
- Limitations of a trial balance as a tool of locating bookkeeping errors
-
- Differences between a public warehouse and a private warehouse
(1x 10marks)Public warehouse Private warehouse Could be owned by business people who operate warehouses as a business Owned by manufacturers/retailers Usually mainly found in towns, port area or terminals Usually located at traders/manufacturers’ premises Used by members of the public who intends to rent it for storage of goods Used by owners only Usually bigger in size in order to meet the needs of many prospective public users Usually in small size since it is for owner’s use only More documentation involved when handling the goods Less Less documentation is needed in handling the goods Goods must be insured while in this warehouse Insurance of goods is not a must. -
- Differences between a public warehouse and a private warehouse
-
- Explain six measures that the government of Kenya may take to control her persistent Balance of payment deficit (12mks)
- Increase the volume of export i.e. by giving incentives to traders so that they can produce more output.
- Reduce the level of imports i.e. by using restrictive measures such as import total ban etc.
- By diversifying the rate of export of the country so that when some fail others can still sell in the world market.
- Through Devaluation of the country’s currency – this makes the export cheaper and hence more competitive in the market.
- By negotiating for foreign debt reduction- which will off load the debt burden.
- By adding value to the export e.g processing of primary products so as to fetch better prices when exported.
(Any six well explained points @2 =12marks)
- Outline four differences between endowment policy and whole life policy.
(Any four clear differences @2=8mks)Endowment policy Whole life policy i) Benefits go to the insured unless death occurs i) Benefits goes to the beneficiaries. ii) Focuses on financial security of insured and beneficiaries ii) Aims at financial stability of beneficiaries iii) premiums paid only for the agreed period iii) Premium paid throughout one’s life time iv) Compensation paid after the risk or expiry ofperiodiv) Compensation paid only after death of insured v) Can be used as collateral for loan v) Cannot be used as collateral for loans
- Explain six measures that the government of Kenya may take to control her persistent Balance of payment deficit (12mks)
Download Business Studies Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Form 4 End Term 1 Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students