INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Answer ALL the questions in the spaces provided in the question paper.
- You are NOT allowed to start working with the apparatus for the first 15 minutes of the 2¼ hours allowed for this paper. This time is to enable you to read the question paper and make sure you have all the chemicals and apparatus you need.
- Mathematical tables and silent electronic calculators' may be used.
- All working must be clearly shown where necessary.
FOR EXAMINER'S USE ONLY
|
Question |
Maximum marks |
Candidate's score |
|
1 |
22 |
|
|
2 |
10 |
|
|
3 |
08 |
|
|
Total score |
40 |

QUESTIONS
- You are provided with
- 7g of an alkanoic dibasic acid labeled solid P in a boiling tube.
- 0.4M sodium hydroxide solution solution Q.
You are required to- Determine the solubility of solid P at different temperatures.
- Find the molar mass of the alkanoic acid.
Procedure I- Using a burette add 10cm3 of distilled water to solid P in the boiling tube. Heat the mixture while stirring with the thermometer to about 70ºC. when the entire solid has dissolved, allow the solution to cool by dipping the boiling tube in a beaker of cold water, while stirring with the thermometer. Note the temperature at which crystals of solid P first appears. Record this temperature in table 1.
- Using the burette, add 5cm3 of distilled water to the contents of the boiling tube. Warm the mixture while stirring with the thermometer until all the solid dissolves. Allow the mixture to cool using cold water in the beaker, while stirring. Note and record the temperature at which crystals of solid P first appear.
- Repeat the procedure (2) more times and record the temperature in table 1. Retain the contents of the boiling tube for use in procedure II.
Complete table I by calculating the solubility of solid P at the different temperatures. (The solubility of a substance is the mass of that substance that dissolves in 100cm3 (100g) of water at a particular temperature)
TABLE I
|
Volume of water in the boiling tube |
Temperature at which crystals of solid first appear. |
Solubility of solid p (g/100water) |
|
10 |
||
|
15 |
||
|
20 |
||
|
25 |
||
|
30 |
||
|
35 |
(6mks)
ii) On the grid provided, plot a graph of the solubility of solid p (Vertical axis) against temperature. (3mks)

iii) Using your graph, determine the temperature at which 70g of solid P would dissolve in 100cm3 of water. (1mk)
v) 130g of saturated solution above was cooled from 55ºC to 40ºC. Calculate the amount of solid P that will crystallize out. (3mks)
PROCEDURE (II)
- Transfer the contents of the boiling tube in procedure I into a 250ml volumetric flask. Rinse both the boiling tube and the thermometer with distilled water and add to the volumetric flask. Add more distilled water to make up to the mark. Cover the volumetric flask with lid when shaking and lable this solution R.
- Fill the burette with solution R. Using a clean pipette and a pipette filler place 25.0cm3 of solution Q into a 250ml conical flask. Add three drops of phenolphtlanein indicator and titrate with solution R. Record your results in table II. Repeat the titration two more times and complete the table.
|
I |
II |
III |
|
|
Final burette reading (cm3) |
|||
|
Initial burette reading (cm3) |
|||
|
Volume of solution R added (cm3) |
(4mks)
- Calculate the average volume of solution R used. (1mk)
- Calculate the number of moles of solution Q used. (1mk)
- Determine the number of moles of P in solution R used. (1mk)
- How many moles moles of solid P was present in 250cm3 of R? (1mk)
- Calculate the relative formula mass of substance P. (1mk)
2. You are provided with substance E. Carry out the following tests and record your observations and inferences in the space provided.
- Describe the appearance of substabnce E. (1mk)
- Place about one third of substance E in a dry test tube and heat it strongly.
Observations
Inferences
(1mk)
(1mk)
- Place the remaining amount of substance E in bolling tube. Add about 10cm3 of distilled water and shake well retain the mixture for test (d) below.
Observations
Inferences
(1mk)
(1mk)
- Use about 2cm3 portion of the mixture obtained in (c ) above for tests (i) and (ii) below.
- Add two to three drops of aques barium Nitrate to the mixture.
Observations
Inferences
(1mk)
(1mk)
- Add five drops of dilute Nitric (v) acid to the mixture.
Observations
Inferences
(1mk)
(1mk)
- Add to the mixture aqueus sodium hydroxide drop wise till excess.
Observations
Inferences
(1mk)
(1mk)
- Add two to three drops of aques barium Nitrate to the mixture.
3. You are provided with substance F and a wooden splint. Carry out the following tests and record your observations and inferences in the space provided. Use about 2cm3 potion of substance F in the test tube for each of the tests (a), (b), (c) and (d).
- Add 3 drops of bromine water.
Observations
Inferences
(1mk)
(1mk)
- Add about 1cm3 of acidified potassium chromate (VI) warm the mixture.
Observations
Inferences
(1mk)
(1mk)
- Add solid sodium carbonate provided.
Observations
Inferences
(1mk)
(1mk)
- Add the piece of magnesium ribbon provided.
Observations
Inferences
(1mk)
(1mk)

MARKING SCHEME
- You are provided with
- 7g of an alkanoic dibasic acid labeled solid P in a boiling tube.
- 0.4M sodium hydroxide solution solution Q.
You are required to- Determine the solubility of solid P at different temperatures.
- Find the molar mass of the alkanoic acid.
Procedure I- Using a burette add 10cm3 of distilled water to solid P in the boiling tube. Heat the mixture while stirring with the thermometer to about 70ºC. when the entire solid has dissolved, allow the solution to cool by dipping the boiling tube in a beaker of cold water, while stirring with the thermometer. Note the temperature at which crystals of solid P first appears. Record this temperature in table 1.
- Using the burette, add 5cm3 of distilled water to the contents of the boiling tube. Warm the mixture while stirring with the thermometer until all the solid dissolves. Allow the mixture to cool using cold water in the beaker, while stirring. Note and record the temperature at which crystals of solid P first appear.
- Repeat the procedure (2) more times and record the temperature in table 1. Retain the contents of the boiling tube for use in procedure II.
Complete table I by calculating the solubility of solid P at the different temperatures. (The solubility of a substance is the mass of that substance that dissolves in 100cm3 (100g) of water at a particular temperature)
TABLE I
|
Volume of water in the boiling tube |
Temperature at which crystals of solid first appear. |
Solubility of solid p (g/100water) |
|
10 |
60 | 70.00 |
|
15 |
45 | 46.67 |
|
20 |
39 | 35.00 |
|
25 |
35 | 28.00 |
|
30 |
30 | 23.33 |
|
35 |
24 | 20.00 |
(6mks)
ii) On the grid provided, plot a graph of the solubility of solid p (Vertical axis) against temperature. (3mks)
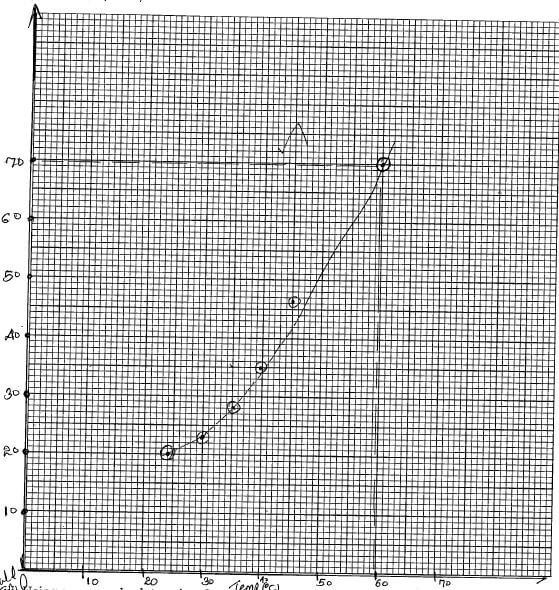
iii) Using your graph, determine the temperature at which 70g of solid P would dissolve in 100cm3 of water. (1mk)
on graph = 60ºC ± 0.2
v) 130g of saturated solution above was cooled from 55ºC to 40ºC. Calculate the amount of solid P that will crystallize out. (3mks)
55 ºC = 62.5g/100g water
40ºC = 35.0g / 100g water
27.5g
mute + solvent → saturated solution
62.5 + 100 → 162.5
PROCEDURE (II)
- Transfer the contents of the boiling tube in procedure I into a 250ml volumetric flask. Rinse both the boiling tube and the thermometer with distilled water and add to the volumetric flask. Add more distilled water to make up to the mark. Cover the volumetric flask with lid when shaking and lable this solution R.
- Fill the burette with solution R. Using a clean pipette and a pipette filler place 25.0cm3 of solution Q into a 250ml conical flask. Add three drops of phenolphtlanein indicator and titrate with solution R. Record your results in table II. Repeat the titration two more times and complete the table.
|
I |
II |
III |
|
|
Final burette reading (cm3) |
22.5 | 44.5 | 32.5 |
|
Initial burette reading (cm3) |
0.0 | 22.5 | 10.0 |
|
Volume of solution R added (cm3) |
22.5 | 22.0 | 22.1 |
(4mks)
- Calculate the average volume of solution R used. (1mk)
22.0 + 22.1 = 22.0 cm3
2 - Calculate the number of moles of solution Q used. (1mk)
0.4 x 25 = 0.01 moles
1000 - Determine the number of moles of P in solution R used. (1mk)
moles ratio 1 : 2
hence 0.01/2 = 0.005 moles - How many moles moles of solid P was present in 250cm3 of R? (1mk)
0.005 moles → titre value
? → 250cm2
0.005 x 250
titre value
titre value = 22
0.005 x 250
22
= 0.0568 Moles - Calculate the relative formula mass of substance P. (1mk)
moles = 7/0.0568
=123
2. You are provided with substance E. Carry out the following tests and record your observations and inferences in the space provided.
- Describe the appearance of substabnce E. (1mk)
white crystalline solid // colourless crystalline solid - Place about one third of substance E in a dry test tube and heat it strongly.
Observations
Inferences
colourless vapour condenses on colour flats
white / colourless crystalline solid turns to powderHydrated salt / compound or contains water of crystallisation
- Place the remaining amount of substance E in bolling tube. Add about 10cm3 of distilled water and shake well retain the mixture for test (d) below.
Observations
Inferences
solid dissolves forming colourless solution
Accept 1/2 mark - colourless solution formedAbsence of Fe2+, Fe3+ and Cu2+
Soluble salt / compound
- Use about 2cm3 portion of the mixture obtained in (c ) above for tests (i) and (ii) below.
- Add two to three drops of aques barium Nitrate to the mixture.
Observations
Inferences
White precipitate formed
Accept white solid formedpresent :
SO42-
SO32-
CO32-
- Add five drops of dilute Nitric (v) acid to the mixture.
Observations
Inferences
No effervescence // No bubbles , no fizzing
Absent
SO32-
CO32-
present
SO42-
- Add to the mixture aqueus sodium hydroxide drop wise till excess.
Observations
Inferences
white precipitate insoluble in excess
Mg2+ present
- Add two to three drops of aques barium Nitrate to the mixture.
3. You are provided with substance F and a wooden splint. Carry out the following tests and record your observations and inferences in the space provided. Use about 2cm3 potion of substance F in the test tube for each of the tests (a), (b), (c) and (d).
- Add 3 drops of bromine water.
Observations
Inferences
Bromine water not decolourised // orange bromine water doesnt change
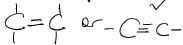
Accept unsaturated compound in words but award 1/2 mark
- Add about 1cm3 of acidified potassium chromate (VI) warm the mixture.
Observations
Inferences
Orange K2Cr2O7 doesnt turn green
Orange colour of K2Cr2O7 persistsR - OH Absent
reject OH absent - Add solid sodium carbonate provided.
Observations
Inferences
effervescence // bubbles / fizzing and colourless gas produced puts off burning splint
H+ / H3O+ / R - COOH present
Accept acidic solution for 1/2 mark - Add the piece of magnesium ribbon provided.
Observations
Inferences
Effervescence // fizing / bubbles of colourless gas produced that produces a pop sound with burning splint
H+ / H3O+ / R - COOH present
Accept in words acidic solution but award 1/2 mark

CONFIDENTIAL
In additional to the fittings and Chemical found in the lab each candidate will require the following.
- Solid P.
- Solution Q 100cm3
- Substance E
- Substance F
- Magnesium ribbon
- Thermometer
- Stopwatch
- Boiling tube
- 6 test tube in a rack
- Burette
- Pipette
- Distilled water in wash bottle
- 2 conical flasks
- 250ml volumetric flask
- About 0.5g solid Na2co3// 0.5gNaHco3
- Test tube holder
- Wooden splint
- Funnel
- Empty plastic beaker (100ml or 200ml)
Access to
- Phenolphthalein indicator and a dropper.
- Bunsen burner
- 0.5mBaCNo3)2 supplied with a dropper Ba(No3)2
- IMHNO3 supplied with a dropper
- 2MNaOH supplied with a dropper
- Bromine water supplied with a dropper
- Acidified potassium Chromate VI
- Solid P is 7g of oxalic acid in a polypot
- Solution Q is 0.4MNaOH.
- Substance E is 0.5g MgSO4H2O
- Substance F is Ethanoic acid = 10cm3 in a test tube
- Mg ribbon about 1cm long.
Download Chemistry Paper 3 Questions and Answers - Form 4 Term 2 Opener Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

