Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Mathioya Mock 2021 Exams
Get the complete Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Mathioya Mock 2021 Exams PDF on WhatsApp by tapping on the button
QUESTIONS
- Name the branch of Biology that deals with the study of fish. (1mk)
- State one advantage of metamorphosis in the life of insects (1mk)
- Name the phylum whose members possess notochord. (1mk)
- The diagram below represents a bread mould.
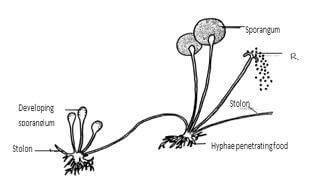
-
- Name the Kingdom to which bread mould belongs. (1mk)
- Give two distinguishing characteristics of the Kingdom named in (a)(i) above. (2mk)
- State the function of the part labeled R. (1mk)
-
- Explain why the following processes are important during the preparation of temporary slides:-
- Staining (1mk)....................................
- Use of a sharp cutting blade (1mk) .
- In a laboratory exercise, a student observing a drop of pond water under a microscope saw and drew a spirogyra. If the magnification of the eye-piece was x5 and that of the objective lens was x100, what was the magnification of the spirogyra? (2mks)
- Identify the structures of the cells that perform the following functions:-
- Synthesize ribosomes. (1mk)
- Regulate exchange of substances in and out of the nucleus. (1mk)
- What are the functions of the following parts of a light microscope?
- Condenser (1mk)
- Diaphragm (1mk)
- Potato cylinders were weighed and kept in distilled water evernight. They were then reweighed.
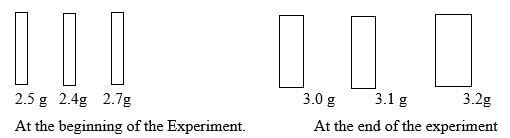
- Calculate the average mass of potato cylinders after reweighing. Show your working. (2mks)
- Explain why mass of the cylinders hand increased. (2mks)
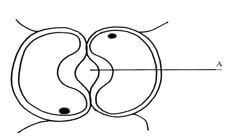
- The diagram below represents a cell at a certain stage in meiotic cell division

- Name the stage at which the cell drawn above represents (1mk)
- Give a distinguishing reason for your answer in 10(a) above .(1mk)
- The chemical equation below represents a physiological process that takes place in living organisms:
R
C6H12O6 + C6H12O6 → C12H22O11 + Q- Name the process R (1mk)
- Name the substance Q (1mk)
- The diagram below shows cells in plants:-
- Identify the cells shown above (1mk)
- Explain how the cells are adapted to their function (2mks)
- Explain how accumulation of carbon (IV) Oxide in the cells above would lead to the closure of structure A. (2mks)
- Below is a process that takes place along the mammalian digestive system:
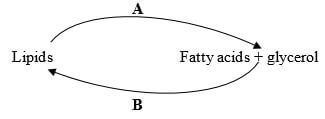
- Name the processes represented by A and B. (2mks)
A............................................
B............................................ - Name part of the alimentary canal where the process B takes place (1mk)
- Name the processes represented by A and B. (2mks)
- In an experiment to investigate an aspect of digestion, two tubes A and B were set up as shown in the diagram below.
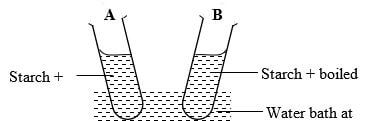
The test tubes were left in the water bath for 30 minutes. The content of each tube was then tested for starch using iodine solution.- What was the aim of the experiment? (1mk)
- Explain the expected results in the tube. (2mks)
A.................................
B.................................
- Name the blood vessel that nourishes the heart (1mk).
-
- In which form is oxygen transported in the blood. (1mk)
- Why do plants not take in oxygen during the day although they need it for respiration. (2mks)
- The diagram below represents a transverse section of a young stem.
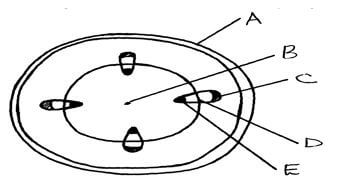
- State the functions of the parts labeled C and E . (2mks)
C.....................................................
D.....................................................
- State the functions of the parts labeled C and E . (2mks)
- Give a reason for each of the following on mammalian Red blood cells (2mks)
- Absence of the nucleus
- Biconcave shape
- Name the nitrogenous wastes excreted by the following organisms:- (3mks)
Animal Nitrogenous Waste- Desert mole .
- Marine fish ..
- Tilapia .
- Study the homeostatic scheme below:
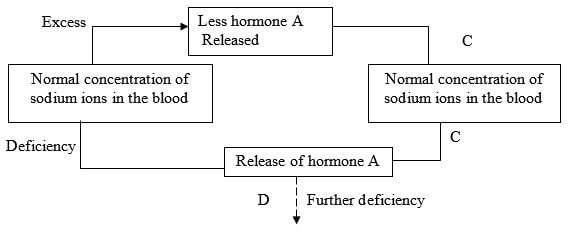
- Identify the hormone labeled A. (1mk) ..
- Name the site of action of hormone A (1mk) ..
- Identify the feedback labeled D (1mk) ..
- A student wanted to estimate the number of grasshoppers in 5km2 grass field near the school compound. Using a sweep net he captured 36 grasshoppers. He used a red felt pen to mark the thorax of each insect before releasing it back into the field. Three days later he made another catch of grasshoppers. He collected 45 grasshoppers of which only 4 had been marked with red mark.
- Name the above method used in the population estimation (1mk)
- Calculate the population of grasshoppers using the above data (3mks) .
- The figure represents a feeding relationship in an ecosystem
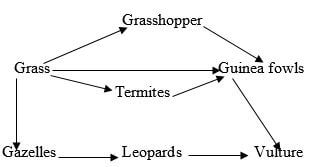
- Write down the food chain in which the Guinea Fowls are secondary consumers. (2mks)
- What would be the short term effects on the ecosystem if lions invaded the area. (2mks)
- Name the organism through which energy from the sun enters the food web. (1mk)
- The diagram below represents a mature embryo sac. Study it carefully and answer the questionsthat follow:
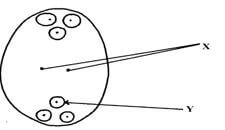
- Identify structures X and Y (2mks)
X....................................
Y.................................... - Why is cross pollination more advantageous to a plant species than self pollination? (2mks)
- Identify structures X and Y (2mks)
- Explain why menstrual periods stop immediately after conception? (2mks)
- The diagrams below represent two gynoecia A and B obtained from two different plants.
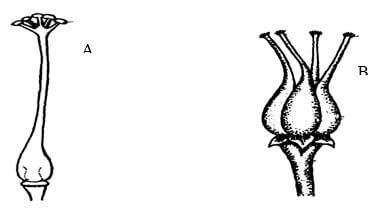
- What name is given to;
Gynoecium A? .(2mks)
Gynoecium B? . - State the observable difference between the gynoecia A and B (1mk)
- State the role played by Heterostyly in plants. (1mk)
- What name is given to;
- State the difference between the sperm cell and the ovum. (3mks)
- State two sources of variation (2mks)
- The table below is a representation of a chromatid with genes along its length. It undergoes mutation to appear as shown below:
Before mutation
L
M
N
O
P
Q
After mutation
L
O
N
M
P
Q
- Name the type of chromosomal mutation represented (1mk).
- Name one mutagenic agent (1mk)
-
- Distinguish between homologous and analogous structures in evolution. (1mk)
- Name one vestigial structure in mammals. (1mk)
-
- What is meant by the term natural selection (1mk)
- A response exhibited by a certain plant tendril is illustrated below:
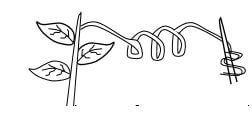
- Name the type of response. (1mk)
- Explain how the response named in (i) above occurs (2mks)
MARKING SCHEME
- Name the branch of Biology that deals with the study of fish. (1mk)
Icththyology; - State one advantage of metamorphosis in the life of insects (1mk)
- Reduce competition between the young ones (larvae) ;
- Avoid predation of the young ones as they are different ;
- The pupa stage can withstand harsh environment by being inactive;
(mark first one) - Name the phylum whose members possess notochord. (1mk)
Chordata; (first letter must be capital) - The diagram below represents a bread mould.

-
- Name the Kingdom to which bread mould belongs. (1mk)
Fungi; - Give two distinguishing characteristics of the Kingdom named in (a)(i) above. (2mk)
- Non— green/ lacks chlorophyll;
- Body made up of hyphae/ mycelia;
- Name the Kingdom to which bread mould belongs. (1mk)
- State the function of the part labeled R. (1mk)
Asexual reproduction; OW TTE
-
- Explain why the following processes are important during the preparation of temporary slides:-
- Staining (1mk).Make cells visible;
- Use of a sharp cutting blade (1mk) .Prevent distortion of cells;
- In a laboratory exercise, a student observing a drop of pond water under a microscope saw and drew a spirogyra. If the magnification of the eye-piece was x5 and that of the objective lens was x100, what was the magnification of the spirogyra? (2mks)
O.L.M x E.L.M;
= 100 x 5
= x500; - Identify the structures of the cells that perform the following functions:-
- Synthesize ribosomes. (1mk)
nucleolus; - Regulate exchange of substances in and out of the nucleus. (1mk)
nuclear membrane/pore;
- Synthesize ribosomes. (1mk)
- What are the functions of the following parts of a light microscope?
- Condenser (1mk)
Concentrates light onto the object; - Diaphragm (1mk)
Controls amount of light illuminating the object;
- Condenser (1mk)
- Potato cylinders were weighed and kept in distilled water evernight. They were then reweighed.

- Calculate the average mass of potato cylinders after reweighing. Show your working. (2mks)
3.0 + 3.1 + 3.2 = 9.3 g;
Average = 9.3 = 3.1g/3g - Explain why mass of the cylinders hand increased. (2mks)
The cell sap had a higher concentration of solutes than distilled water;
water therefore moves from the environment to the cell by osmosis;
- Calculate the average mass of potato cylinders after reweighing. Show your working. (2mks)
- The diagram below represents a cell at a certain stage in meiotic cell division

- Name the stage at which the cell drawn above represents (1mk)
Prophase I ;Reject prophase alone - Give a distinguishing reason for your answer in 10(a) above .(1mk)
Homologous Chromosomes side by side or Bivalency
- Name the stage at which the cell drawn above represents (1mk)
- The chemical equation below represents a physiological process that takes place in living organisms:
R
C6H12O6 + C6H12O6 → C12H22O11 + Q- Name the process R (1mk)
Condensation; - Name the substance Q (1mk)
water;
- Name the process R (1mk)
- The diagram below shows cells in plants:-

- Identify the cells shown above (1mk)
Guard cells; - Explain how the cells are adapted to their function (2mks)
Cells walls are thicker on the inner side then the outer side; which enables them to pull inwards when the cells are turgid; /
contains chloroplasts that are able to phosynthesize and produce sugars which enable them to absorb water; (any two points) - Explain how accumulation of carbon (IV) Oxide in the cells above would lead to the closure of structure A. (2mks)
Accumulation of carbon (IV) oxide in the leaf forms a weak carbonic acid; lowering the pH
which favours conversion of sugar to starch; causing the guard wells to lose turgidity; and close;
- Identify the cells shown above (1mk)
- Below is a process that takes place along the mammalian digestive system:

- Name the processes represented by A and B. (2mks)
A.condensation;
B.; hydrolysis; - Name part of the alimentary canal where the process B takes place (1mk)
Duodenum; (any correct Rj .wrong spelling)
-ileum;
- Name the processes represented by A and B. (2mks)
- In an experiment to investigate an aspect of digestion, two tubes A and B were set up as shown in the diagram below.

The test tubes were left in the water bath for 30 minutes. The content of each tube was then tested for starch using iodine solution.- What was the aim of the experiment? (1mk)
To investigate the effect of heat on salivary amylase; - Explain the expected results in the tube. (2mks)
A – The brown colour of iodine was retained because the starch was digested by enzyme amylase in the saliva;
B – The colour changed to blue black/black; because amylase in the saliva was denatureby heat;
- What was the aim of the experiment? (1mk)
- Name the blood vessel that nourishes the heart (1mk).
Coronary Artery; -
- In which form is oxygen transported in the blood. (1mk)
Oxyhaemoglobin; - Why do plants not take in oxygen during the day although they need it for respiration. (2mks)
During the day plant carry out photosynthesis, they release oxygen as one of their by-products
Oxygen released from photosynthesis process is used in respiration;
- In which form is oxygen transported in the blood. (1mk)
- The diagram below represents a transverse section of a young stem.

- State the functions of the parts labeled C and E . (2mks)
C secondary phloem;
D cambium;
- State the functions of the parts labeled C and E . (2mks)
- Give a reason for each of the following on mammalian Red blood cells (2mks)
- Absence of the nucleus
Create more room/space for packing of more haemoglobin; - Biconcave shape
To provide a large surface area for diffusion of a lot of respiratory gases;
- Absence of the nucleus
- Name the nitrogenous wastes excreted by the following organisms:- (3mks)
Animal Nitrogenous Waste- Desert mole . urea;
- Marine fish .. Triethylamine;
- Tilapia . Ammonia;
- Study the homeostatic scheme below:

- Identify the hormone labeled A. (1mk) ..
Aldosterone; - Name the site of action of hormone A (1mk) ..
Loop of Henle; - Identify the feedback labeled D (1mk) ..
Positive feed back;
- Identify the hormone labeled A. (1mk) ..
- A student wanted to estimate the number of grasshoppers in 5km2 grass field near the school compound. Using a sweep net he captured 36 grasshoppers. He used a red felt pen to mark the thorax of each insect before releasing it back into the field. Three days later he made another catch of grasshoppers. He collected 45 grasshoppers of which only 4 had been marked with red mark.
- Name the above method used in the population estimation (1mk)
Capture –recapture method; - Calculate the population of grasshoppers using the above data (3mks) .
FM x SC = 36 x 45; = 405;
MR = 4
- Name the above method used in the population estimation (1mk)
- The figure represents a feeding relationship in an ecosystem

- Write down the food chain in which the Guinea Fowls are secondary consumers. (2mks)
Grass → Grasshopper → Guinea Fowl;
Grass → Termites → Guinea Fowl; - What would be the short term effects on the ecosystem if lions invaded the area. (2mks)
- Leopards will decrease;
- Gazelles will also decrease; - Name the organism through which energy from the sun enters the food web. (1mk)
Grass;
- Write down the food chain in which the Guinea Fowls are secondary consumers. (2mks)
- The diagram below represents a mature embryo sac. Study it carefully and answer the questionsthat follow:

- Identify structures X and Y (2mks)
X – Polar nuclei; reject polar nucleus Y – Egg cell; - Why is cross pollination more advantageous to a plant species than self pollination? (2mks)
Results to variation; that makes the plant to be adapted for survival;
- Identify structures X and Y (2mks)
- Explain why menstrual periods stop immediately after conception? (2mks)
Production of the hormones progesterone and oestrogene continues;
These hormones inhibit the production of Stimulating hormone (FSH) and lutenising hormone (LH); This inhibits the maturation of more follicles, - The diagrams below represent two gynoecia A and B obtained from two different plants.

- What name is given to;
Gynoecium A? Syncarpous:….(2mks)
. Rj: Wrong spellings
Gynoecium B? …. Apocarpous; - State the observable difference between the gynoecia A and B (1mk)
A fused ovaries
B — separate ovaries - State the role played by Heterostyly in plants. (1mk)
Hinder self pollination? fertilization:
- What name is given to;
- State the difference between the sperm cell and the ovum. (3mks)
Sperm
Ovum
- Spear shaped.
- Posses a tail.
- Has acrosome .
No vitelline membrane.
Spherical shaped
No tail
No acrosome
Has vitelline membrane.
- State two sources of variation (2mks)
Genetic recombination’s of alleles reading to variations;
Independent assortment of chromosomes;
Random fusion of gametes; mutations; - The table below is a representation of a chromatid with genes along its length. It undergoes mutation to appear as shown below:
Before mutation
L
M
N
O
P
Q
After mutation
L
O
N
M
P
Q
- Name the type of chromosomal mutation represented (1mk).
Inversion ; - Name one mutagenic agent (1mk)
- mustard gas;
Exposure to
- ionizing radiation;
- gamma rays;
- X- rays
- Name the type of chromosomal mutation represented (1mk).
-
- Distinguish between homologous and analogous structures in evolution. (1mk)
Homologous structures have a common embryonic origin but are modified to Perform different functions; while analogous structures have different embryonic origin but are modified to perform similar functions; - Name one vestigial structure in mammals. (1mk)
Nictitating membrane;
- Distinguish between homologous and analogous structures in evolution. (1mk)
-
- What is meant by the term natural selection (1mk)
Nature or the environment selects those individuals that are sufficiently adapted; and rejects
those that are not adapted
- What is meant by the term natural selection (1mk)
- A response exhibited by a certain plant tendril is illustrated below:

- Name the type of response. (1mk)
Thigmotropism / haptotropism - Explain how the response named in (i) above occurs (2mks)
High concentration of auxin on side away from contact surface; promotes faster growth of this side; causing tendril to curl round the object.
- Name the type of response. (1mk)