Chemistry Questions and Answers - Form 2 Term 1 Opener Exams 2023
Get the complete Chemistry Questions and Answers - Form 2 Term 1 Opener Exams 2023 PDF on WhatsApp by tapping on the button
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Write your name and admission number.
- Answer all the questions in the spaces provided after every question.
- All working for numerical questions must be clearly shown.
-
- A form one girl slipped a wooden splint at the innermost part of non-luminous flame as shown.
- Using a well labeled diagram, explain the observations made when the wooden splint is removed. (2mks)
- Name another type of flame produced by Bunsen burner. (1mk)
- State three differences between the two types of flames (3mks)
- A form one girl slipped a wooden splint at the innermost part of non-luminous flame as shown.
-
- What is drug abuse? (1mk)
- State two effects of drug abuse in the society
- What are over the counter drugs? State two such drugs (2mks)
- State four safety precautions or safety rules in the laboratory to control accidents (4mks)
- Four solutions A,B,C and D had their pH values measured and recorded as follows:
Solution PH Value A 8.5 B 1.5 C 6.0 D 13.0 - Identify from the list the solution which is:
- Strong acid (1mk)
- Weak base (1mk)
- Strong base (1mk)
- Which solution can react readily with magnesium ribbon to produce hydrogen gas (1mk)
- Which solution could be the solution of lemon juice? (1mk)
- Identify from the list the solution which is:
- State two advantages of non- luminous flame over the luminous flame (2mks)
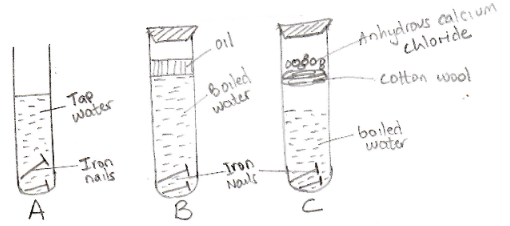
- The following set-up of three test tubes was used to investigate rusting of iron nails. Study it and answer the questions that follows:
- State the set-up in which rusting did not occur. Explain (2mks)
- State one disadvantage of rusting (1mk)
- State two factors or conditions which accelerate rusting (2mks)
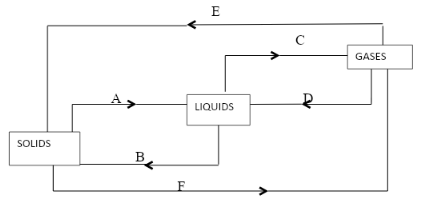
- The following diagram shows the effects of heat on the physical states of substances
- Identify the processes represented by the letters A,B,C,D,E and F. (3mks)
- Name two substances that undergo the process labeled E and F (2mks)
- Name the best method that can be used to separate the following
- common salt from salt solution (1mk)
- paraffin from crude oil (1mk)
- iron filings in sulphur powder (1mk)
- Describe two different experiments which can be used to show the presence of moisture in the atmosphere (4mks)
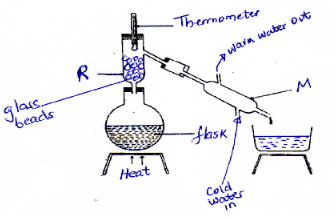
- A student separated liquid P (Bpt= 78°C) and liquid Q (Bpt= 100°C) using the apparatus below
- Name the apparatus labeled (2mks)
- M –
- R –
- State one function of the glass beads in apparatus labeled R. (1mk)
- What is the reading on the thermometer when the first drops of the distillate appeared in the beaker (1mk)
- Which of the solutions remains in the flask? (1mk)
- Name the apparatus labeled (2mks)
-
- What would be observed when the following substances are heated and cooled in a crucible
- Wax (1mk)
- Zinc oxide (1mk)
- Give the name for the type of change that takes place (1mk)
- State two characteristics of this type of change (2mks)
- State what is observed when copper (II) nitrate crystals are heated (2mks)
- What would be observed when the following substances are heated and cooled in a crucible
- Complete the following table(4mks)
Element Symbol Element Symbol Silver Cu K Mercury Sodium Iron Sn Co - Write word equations for the following reactions between hydrochloric acid and the following
- Zinc (1mk)
- Magnesium oxide (1mk)
- Calcium carbonate (1mk)
-
- Candle wax is a compound consisting of two elements. Name the two elements (2mks)
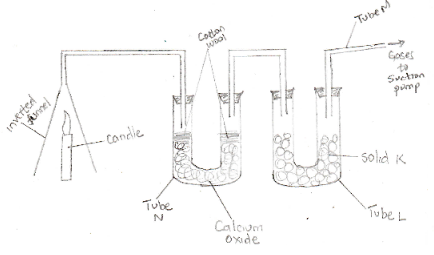
- The set-up below was used to investigate the burning of a candle. Study it and answer the questions that follow:
- What would happen to the candle if the pump was turned off? (2mks)
- State and explain the changes in mass that are likely to take place in tube N by the end of the experiment (2mks)
- Name two gases that comes out through tube M. (1mk)
- State two industrial uses of oxygen (2mks)
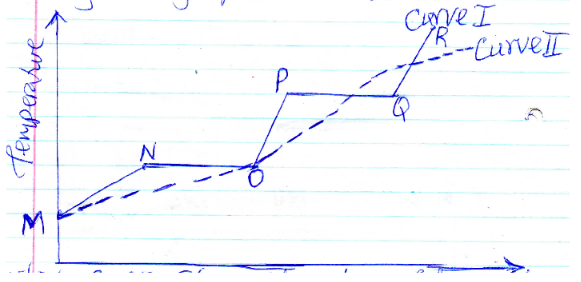
- Study the graph on heat curves shown below
- Which curve shows variation of temperature for a pure sample of solid? Explain (2mks)
- Explain in terms of kinetic energy what happens at the following regions during heating
- MN
- NO (3mks)
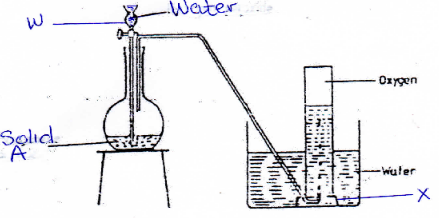
- Study the diagram below used to prepare oxygen gas
- Name the apparatus labeled (2mks)
- W –
- X –
- Name solid A (1mk)
- Write a word equation for the reaction in the flask (2mks)
- State the test for oxygen gas (1mk)
- Name the apparatus labeled (2mks)
-
- List down two sources of water (1mk)
- State three uses of water other than domestic use like cooking (3mks)
- List down three causes of water pollution (3mks)
- Study the diagram below and use it to answer the question that follows:
- State the property of hydrogen gas tested in the experiment (1mk)
- State and explain what would happen to the copper(II) oxide in the experiment (2mks)
- Write word equation for the reaction in the combustion tube (2mks)
- State the test of hydrogen gas (1mk)
- State two uses of hydrogen gas (2mks)
-
- Define the term indicators as used in chemistry (1mk)
- Explain briefly how one can make simple flowers indicator in the laboratory (3mks)
- A student was stung by bee in the laboratory. The laboratory technician used a certain solution X to wash the student. Name the solution X used to bring relief (1mk)
- Sodium chloride (common salt) is contaminated with copper (II) oxide. Explain how pure sodium chloride can be obtained from the mixture (2mks)
MARKING SCHEME
-
-
- Luminous flame
-
Luminous flame Non- luminous flame Yellow Blue Not hot Very hot Four zones Three zones Quiet Noisy/Roars
-
-
- Any usage of drug for a reason not intended for overdose of a type of a drug or under dose.
-
- Cause disease like liver cirrhosis/ cancer
- Brings poverty in the society
- Can cause marriage breakages
- Drugs which can be bought without doctor’s prescription instructions. Eg Actal, piriton, mara moja.
-
- Label chemicals in use to avoid confusion
- Clean benches after use
- Wear shoes to avoid cut by broken glasses
- Do not do practical without teacher assistant
- Never hold hot test tubes with bare hands.
-
-
- B
- A
- D
- B
- C
-
-
- Its very hot
- It does not produce soot so apparatus remains clean
-
- B or C – oil blocks oxygen entering the water. Boiled water has no oxygen
- Tear and wear of equipment or disfigures surfaces of equipment
-
- Salty condition
- Acidic condition
- Basic condition
-
-
- A- melting
- B – Freezing
- C – Evaporating/ boiling
- D- Condensation
- E- Deposition/sublimation
- F- Sublimation
-
- Iodine NH4Cl
- Benzoic acid Dry ice (solid CO2 )
-
- Evaporating/ simple distillation
- Fractional distillation
- Use magnet
-
-
- Use anhydrous CuSO4 which turns blue due to water which makes it hydrated.
- Use anhydrous CoCl2 which is blue and it will turn to pink to slow presence of water.
-
-
- M – Liebig condenser
- R – Fractionating column
- Increase surface area for condensation
- 78°
- Q
-
-
-
- Wax melts on heating. It turns back to solid wax on cooling.
- White zinc oxide changes to yellow zinc oxide on heating. On cooling the yellow solid turns to white ZnO.
- physical/Temporary change
-
- No change in mass
- No new substance formed
- Are reversible.
- Brown gas nitrogen (IV) oxide gas evolved, a colourless gas which rekindles a glowing splint formed and black solid of copper (II) oxide solid remains in the test tube.
-
-
Element Symbol Element Symbol Silver Ag Copper Cu Potassium K Mercury Hg Sodium Na Iron Fe Tin Sn Cobalt Co -
- Zinc + hydrochloric → Zinc Chloride + hydrogen gas
- Magnesium oxide + hydrochloric acid → magnesium chloride + water
- Calcium carbonate + hydrochloric acid → calcium chloride + water + carbon (IV) oxide
-
- Carbon and hydrogen
-
-
- It will go off. CO2 gas formed accumulated and it does not support combustion
- CO2 gas formed does not support combustion
- Mass increases. Due to calcium oxide reacting with carbon (IV) oxide to form calcium carbonate.
- Rare gases eg Argon, Neon
-
- welding
- Sea divers
- Metal extraction
- Mountain climbers
- Stainless steel making
-
-
- curve I has sharp variation for boiling points or change of state
-
- Solid absorbs heat energy. Kinetic energy of particles increases
- Heat absorbed is used to break the forces of attraction in the solid as it melts.
-
-
- W – dropping funnel
- X – Bee- hive shelf
- Sodium peroxide
- Sodium peroxide + water → sodium hydroxide + oxygen gas
- Use glowing splint which rekindles
-
-
- Rivers, streams, oceans, lakes, dams
-
- Recreational – Boating, Swimming
- In industries – cool engines
- Agricultural (irrigation of plants)
- Habitat for marine animals
-
- industrial effluents
- Man’s activities bathing in water sources
- Agricultural activities herbicides, pesticides
- Sewage breakages/ leakages
-
- Reducing agent
-
- Black copper (II) oxide turns to brown
- Reduction of the oxide takes place
- Copper (II) + hydrogen gas → copper + water
- Use a burning splint which gives a pop- sound
-
- Hardening oils to fat
- Manufacture of HCl acid or ammonia gas
- In rocket fuel
-
- Substance with one colour in alkalne solution and a different colour in acidic solution.
- Place flower petals in a crucible. Crush well and add little water. Continue to crush and add suitable solvent eg. Propanone filter and filtrate is required indicator
- Any base/alkaline(NaOH) or potassium hydroxide .
- Add water to the mixture and stir well. Filter to obtain copper (II) oxide as residue. Evaporate the filtrate to dryness to recover the sodium chloride crystals.