- Business Activities
- Goods and Services
- Economic Resources
- Business Communication
- Production of Goods and Services
- Marketing of Goods and Services

Business Activities
Needs And Wants
| BASIS FOR COMPARISON | NEEDS | WANTS |
| Meaning | Needs refers to an individual's basic requirement that must be fulfilled, in order to survive. | Wants are described as the goods and services, which an individual like to have, as a part of his caprices. |
| Nature | Limited | Unlimited |
| What is it? | Something you must have | Something you wish to have |
| Represents | Necessity | Desire |
| Survival | Essential | Inessential |
| Change | May remain constant over time. | May change over time. |
| Non-fulfillment | May result in onset of disease or even death. | May result in disappointment |
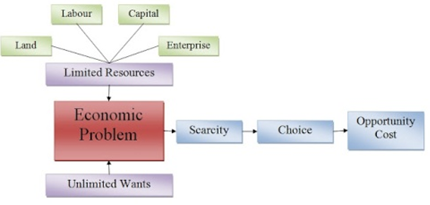
Scarcity, Choice, Scale of preference and opportunity cost
The basic concept or elements of economics are:
- wants,
- scarcity,
- scale of preference,
- choice and
- opportunity cost.
WANTS
Wants simply means the desire or wish to own goods or services that give satisfaction. Goods include things such as cars, radios, food, houses, books, etc., (that is tangible commodities), while services includes hair dressing, the services of an actor, etc(that is intangible commodities). Want s are also called ENDS.
As these basic needs are satisfied, other needs will arise. That is why we say that human wants are insatiable. This is because human wants are unlimited while resources used in satisfying them are limited.
SCARCITY
Scarcity refers to the limited available resources used in satisfying the unlimited human wants.
These resources are scarce relative to their demand. It is as a result of scarcity of resources that needs the study of economics very essential in order to find alternative uses of these scarce resources. The available resources cannot satisfy all human wants. Since human wants are unlimited or insatiable relative to the available resources, we have to choose the most pressing ones and leave others that are less important because resources are scare.
As a student you will need to buy school materials, e.g exercise books worth #100.00 but you have only #50.00. it can be seen that the money you have (#50.00), which is your resources, will not be sufficient to buy all you need. The available resources within the environment can never at any time be in abundance to satisfy all human wants.
If resources were to be unlimited or abundant, no economics problem would arises and there would be no need for a study of economics. Scarcity is the central or basic economic problems
SCALE OF PREFERENCE
Scale of preference refers to a list of unsatisfied wants arranged in order of their relative importance.
A scale of preference refers to a list of unsatisfied wants arranged in order of priority or importance. This aids decision-making. The most pressing needs are ranked first followed by the less pressing ones. In other words, it is a list showing the order in which we want to satisfy our wants arrange in order of priority.
The drawing of scale of preference will make it easier for choice to be made. In order to achieve maximum satisfaction with limited resources at their disposal, an individual, firm and unsatisfied wants in order of priority.
Each individual is assumed to have a scale of preference. This is because economics theory assumes that people always behave rationally and would satisfy their most pressing want first.
For example, a student might rank his wants in following order according to their level of importance:
- Pair of school uniform
- Exercise books
- Wrist watch
- Dictionary
- Scientific calculator
- An arm chair
If he is to choose between items 1 and 4, he chooses the first. Scale of preference of individuals, firms and the government differ from time to time.
IMPORTANCE OF SCALE OF PREFERENCE
- Ranking of needs
- Financial prudence
- Identification of highest priority
- Rational choice
- Efficient utilization of limited resources
- Optimum allocation of resources
- Maximization of satisfaction
The importance of scale of preference can be paraphrased this way also:
- It helps individuals to rank their needs in order of importance.
- It helps us to manage our resources properly.
- It helps both individuals and government to identify the most important needs.
- It enhances optimum allocation of resources.
- It helps individuals, firms and government in the efficient utilization of resources.
- It helps economic agents to maximize their satisfaction.
- It helps individuals to make rational decision.
CHOICE
Choice can be defined as a system of selecting or choosing one out of a number of alternatives. Human wants are many and we cannot satisfy all of them because of our limited resources.
We therefore, decide which of the wants we can satisfy first. Choice arises as a result of numerous human wants and the scarcity of the resources used in satisfying these wants.
OPPORTUNITY COST
Opportunity cost is also known as a real cost or time cost.
The concept of opportunity cost is used in economics to express cost in terms of foregone or sacrificed alternatives. Opportunity cost means the alternative foregone or sacrifice made in order to satisfy another want. It is the satisfaction of one’s want at the expense of another want.
Types Of Business Activities
People carry out different business activities in order to earn income.
Business activities are activities which involve the provision of goods or services with an aim of earning a profit.
Activities done without the intention of making profit are referred to as
non-business activities. Business activities may be grouped into the following seven categories:
- Extraction
This involves obtaining goods from their natural setting e.g. mining, farming, lumbering, fishing, quarrying e.t.c - Processing
This involves the conversion of raw materials into more useful products without combining it with other goods. Examples here
include milling/grinding flour, refining oil, tanning of skins and hides, conversion of iron into steel e.t.c - Manufacturing
This involves combining different raw materials to come up with one final product. Such activities include bread baking, making a table e.t.c - Construction
This involves building of structures such as bridges, ships, aeroplanes, houses, roads, railways e.t.c - Distribution of goods
This refers to the activities involved in moving goods from where they are produced to where they are needed. People
who carry out distribution are called distributors. Examples of distributors are wholesalers and retailers. - Trade-Activities in this category involve the buying and selling of goods with a view of making a profit. People involved in trade are called traders.
- Provisions of Services-Activities in this category involve human acts which could be mental or physical. These include activities such as haircutting, hair styling, car-washing, nursing, teaching, driving, and entertaining e.t.c.
Purpose of Business activity
- Provides goods and services from limited resources to satisfy unlimited wants
- Scarcity is the result of the economic problem – limited resources and unlimited wants
- Choice is necessary for scarce resources. This leads to opportunity costs
- Specialization is required to make the most out of sources
Business activity
- Combines factors of production to create goods and services
- Goods and services satisfy peoples’ wants
- Employs people and pays them wages so they can consume other products
Business Objectives
All businesses have objectives or aims to achieve. Their objectives may vary depending on the type of business and the situation the business is in. The most common objectives are:
- Profit: Profit is what keeps a company going and is the main objective of most businesses. Normally a business will try to obtain a satisfactory level of profits so they do not have to work long hours to pay too much tax.
- Increase added value: Value added is the difference between the price and material costs of a product. E.g.: If the price when selling a pen is Ksh. 3 and it costs Ksh.1 in material, the value added would be Ksh.2. However, this does not take in account overheads and taxes. Added value could be increased by working on products so that they become more expensive finished products. One easy example of this is a mobile phone with a camera would sell for much more than one without it. Of course, you will need to pay for the extra camera but as long as prices rise more than costs, you get more profit.
- Growth: Growth can only be achieved when customers are satisfied with a business. When businesses grow they create more jobs and make them more secure when a business is larger. The status and salary of managers are increased. Growth also means that a business is able to spread risks by moving to other markets, or it is gaining a larger market share. Bigger businesses also gain cost advantages, called economies of scale.
- Survival: If a business do not survive, its owners lose everything. Therefore, businesses need to focus on his objective the most when they are: starting up, competing with other businesses, or in an economic recession.
- Service to the community: This is the primary goal for most government owned businesses. They plan to produce essential products to everybody who need them.
These business objectives or aims can conflict because different people in a business want different things at different times.

Goods And Services
Types Of Goods And Services
We desire to have all the things to satisfy our present and future wants. Thus, our desire is for all those things that satisfy our wants.
All these things are either material goods or services. If something is not wanted by anybody it will not be called a good or service.
Therefore, we can divide the things that we wants into two categories:
- Goods and
- Services.
Goods are material things wanted by human beings. They can be seen or touched. Services are non-material things. These cannot be seen or touched only their effects are felt. When we are hungry, we take food. When we fall sick, we take medicines. When we study, we use book, notebook, pen, paper etc. All these are examples of goods which satisfy some of our wants. All the things which satisfy human wants are good.
However, wants for haircut, washing of cloths, mending of shoes, stitching of cloths, studying in a school or a college etc. are not satisfied by goods. These are satisfied by the services performed by a barber, washer man, cobbler, tailor and teacher etc. So some of our wants are satisfied by goods and some by services. Hence, all the human wants can be satisfied by goods and services.
Classification of Goods and Services:
Goods and services are of many types. However, these can be classified into some broad groups.
These are discussed below:
- Free Goods and Economic goods:
The goods which have unlimited supply and are provided as free gift of nature. The goods which are not man-made and do not have to pay anything to get them. These goods are known as ‘Free Goods’. For example, air, sea, water, sunlight, sand in the desert etc. On the other hand, goods like vegetables, grains, minerals, fruits, fishes etc. which are neither man-made nor unlimited supply of nature are known as ‘Economic Goods’ All these goods are sold and purchased in the market only. - Free Services and Economic Services:
Services which cannot be bought in the market and which are only rendered out of love, affection etc. are known as ‘Free Services’. For example, all services given by the parents to their children are free services. However, all the services that can be bought in the market are ‘Economic Services’. Services rendered by doctors, teachers, lawyers, barbers, cobblers etc. are the example of economic services. - Consumer Goods and Capital Goods:
The goods which are directly used by the consumer for the purposes of consumption are known as ‘Consumer Goods’ The example of consumer goods are bread, biscuit, butter, jam, rice, fish, egg, shoes, shirts, fan, book, pen, cooking gas etc. On the other hand, all the goods which are not directly used to satisfy consumption but which are used in further production are called ‘Producer Goods’ or ‘Capital Goods’. The examples are seeds, fertilizers, tools, machines, raw materials etc. - Consumer Services and Producer Services:
When services are used directly by consumers to satisfy their wants, they are called consumer services. When services are used by producers to produce other goods and services, they are called producer services. When the tailor stitches our shirt, it is a consumer service However when the tailor stitches a shirt for a readymade garments shop, the service rendered by him is a producer service. - Single Use and Durable Use Goods:
Goods (both consumer goods and producer goods) which are only used or consumed for single time or only once are known as single use goods. Bread, milk, fruits, vegetables etc. are the example of single use consumer goods. On the other hand, seeds, fertilizers, raw materials etc. are the example of single use producer goods.
Some goods (both consumer goods and producer goods) can be used for a considerable period, that is, they can be used again and again. They are called durable use goods. For example, table, chair, cloths, shoes etc. are the durable use consumer goods. On the other hand, tube wells, tractors, pump-sets etc. are the example of durable use producer goods, - Private Goods and Public Goods:
On the basics of ownership goods can be classified into two groups. All the goods which are owned by private bodies are called private goods. For example, a car, a house, a motorbike, a mobile phone, books, a television set etc. are the private goods.
There are large number of goods which are collectively owned by the society, the public or the government. These are called public or government goods. For example, roads, bridges, hospitals, government schools etc. are the public goods or the social goods or the government goods.

Economic Resources
Characteristics Of Economic Resources
- Have utility - they have ability to be used
- Have money value - They have a value at which they can be exchanged for ownership
- Have alternative use - They can be put into different uses.
- Scarce in supply - They are not available in sufficient quantities
- Can be combined - They can be combined so as to produce different goods and services
- Can change ownership - Differennt resources can be used together.
- They are distributed - they are available in varying quantities at different places.
Types Of Economic Resources In Kenya
What Are Economic Resources?
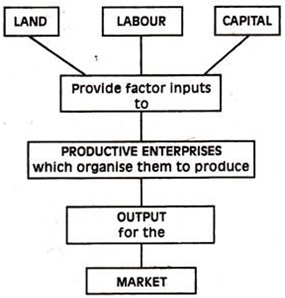
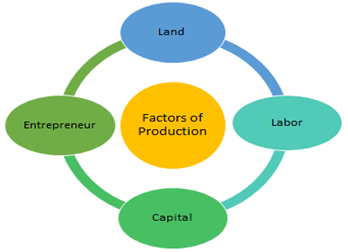
Economic resources are the different factors of production used to produce all goods and services in the economy. Economic theory is primarily concerned with allocating these resources so that the production of goods and services is done most efficiently and effectively.
There are four general types of economic resources:
- Land or natural resources
- Labor
- Capital
- Entrepreneurial ability
Sustainable Ways Of Using Economic Resources
Economic sustainability is the practice of conserving natural and financial resources to create long-term financial stability. A system that's sustainable can last far into the future with minimal negative impacts.
In finance, this can mean reducing the worldwide consumption of valuable resources to ensure they're available to future generations to create financial stability and wealth. For example, by reducing the usage of fossil fuels and focusing on alternative fuel sources, companies, governments and consumers can help reduce the global impact of emissions and pollution from fossil fuels.
Here are some examples of economic stability:
Alternative energy
Alternative energy sources, such as wind power, solar power and hydropower, can offer a more sustainable, clean and affordable solution to energy needs. Much of the world depends on fossil fuels like coal, oil and gasoline, which have a limited supply and create greenhouse gas emissions.
Alternative energy sources depend on infinite natural processes or resources, which may make them more sustainable and affordable in the long term. Reducing fossil fuel consumption can help reduce tax burdens for consumers, decrease the costs of environmental impacts and create more energy equity among low-income populations, which can increase economic productivity.
Sustainable agriculture
Many farms are adopting sustainable agricultural practices to reduce soil degradation, which occurs from over-farming, and to reduce animal product consumption. Reducing food consumption and focusing on regenerative farming can help improve soil health, crop yields and the quality of farmed food and resources.
Regenerative farming is a practice farmers use to rotate crops for better soil health, instead of farming the same crops, like corn, all year. Improving soil health and reducing animal product consumption can help keep food costs low, reduce carbon emissions and environmental damage and encourage better habits.
Recycling and pollution reduction
Recycling and reducing pollution is a common economic and environmental stability practice that can help increase the value of materials. For example, a company producing aluminum cans can sustain operations by recycling used cans and creating molten aluminum for recasting, instead of mining for aluminum ore.
This practice can reduce the company's environmental impact, saving the region both cleanup and restoration costs and reducing the organization's mining costs. Reducing pollution can also help reduce worldwide cleanup and restoration costs and the costs of climate change.
Sustainable fisheries
Creating more sustainable fisheries can help reduce the environmental and economic impact of overfishing the oceans. Side effects of overfishing can include population declination, bycatch, or catching other species along with fish, and fishing equipment made of plastics and other materials discarded in waterways.
Adopting more sustainable practices, like reducing fish consumption worldwide and reducing bycatch and fishing pollution, could create a more sustainable fishing environment, resulting in more stable profits and economic health for the fishing industry. It can also help ocean populations recover, which is crucial for ecosystems across the globe.
Resource Mapping
Resource mapping is a strategy for identifying and analyzing the programs, people, services, and other resources that currently exist in the country. This information can help leaders better assess the needs of the country and to make informed decisions about where to focus change efforts.
Mapping Steps
- Reach consensus on the parameters of the map—select a goal to map.
- Select the data to be collected based on these parameters—determine what types of resources you would like to collect.
- Develop tools to collect your data.
- Collect data with help from stakeholders.
- Conduct a community (or environmental) scan.
- Synthesize, analyze, and interpret your data.
- Communicate your findings.
- Set priorities.
- Develop related products.
Importance Of Economic Resources
Resources are significant because:
- They satisfy human wants both individual and social,
- They are a source or possibility of assistance,
- They are a means of development and support,
- They are an expedient,
- They have capacity to take advantage of opportunities, and
- One relies on them for aid, support and supply.

Business Communication
Communication is an essential element in the success of any business. The process of transferring information from one person to another, within and outside the business environment, is termed as ‘Business Communication.’ The term ‘Business Communication’ is derived from general communication which is associated with business activities. In other terms, communication between business parties or people for business-related tasks is considered as ‘Business Communication.’
Business Communication includes different aspects like marketing, public relations, customer relations, corporate and interpersonal communication, etc.
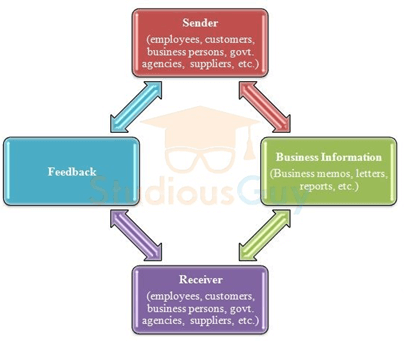
Basic elements of Business communication:
- Sender
- Business information
- Receiver
- Feedback
Importance Of Business Communication
- Helps in increasing productivity: Effective business communication increases the productivity of staff by boosting up teamwork. It creates a trustworthy and understanding environment among employers and employees. Effective communication is related to cooperating with employees and understanding their needs and desires. By doing so, employees are able to accomplish their tasks more effectively and efficiently. Also, the scope of doing mistakes or errors during their work minimizes due to effective communication.
- Helps in increasing customers: Customers are an important part of any business and effective business communication can facilitate in attracting new customers and retain the current customers. A well-defined marketing strategy and public relations campaign run by an organization generates the interest of customers in its goods or services and helps in building the corporate image in customers.
- Enhances business partnerships: Business Communication also improves partnerships in business. It plays a significant role in dealing with external business clients or vendors. Vendors may be required to communicate on products regularly for improvements. Also, an effective and harmonious relationship with other businesses determines the further success of an organization. A business unit that has developed its image as an entity for easy partnership through its effective communication can attract other business units for forming business relationships with them.
- Facilitates innovations in business: Effective business communication helps in business innovations as well as it facilitates employees to convey their ideas and suggestions openly. Similarly, at the time of launching any new product in the market, effective communication ensures the performance of the sales team, market acceptance of the product, fast delivery of products in the market, etc.
- Information exchange: Business communication is required by an organization for exchanging information with internal and external stakeholders. This helps in achieving its goals effectively.
- Preparation of plans and policies: Through effective business communication, organizations can make their plans and policies properly. Relevant information is required for preparing these plans and policies. Through communication, different managers source information through reliable channels.
- Helps in solving problems or issues: Through different communication channels, managers get information about different routine and non-routine issues and based upon that they can take required actions to sort out those issues.
- Facilitates decision-making: Effective decisions require up-to-date information. Using effective communication, managers can acquire information from different sources and can utilize it for making correct decisions.
- Reduces chances of conflicts: Through effective communication different business parties can exchange information in a smooth way. This results in fewer conflicts, controversies, arguments between them.
Business Communication Methods
Different methods of communicating in a business are as below:
- In-person (Face-to-Face) Business Communication: In-person communication is the most common and preferred method of business communication. As it is generally in the form of meetings or conferences which is face to face communication format. This requires refined in-person skills. This method also includes non-verbal communication i.e. body language. While having a conversation between two or more people in business, body language like gestures, facial expression, etc. also play a vital role in communicating a person’s attitude towards others.
- Communication by email system: An e-mail has become the most widely used communication system in any business. Due to its feature of sending and receiving mass or multiple messages at a time, email is considered as one of the preferred methods in business communication. It also increases efficiency as emails can be sent and responded in fast mode. The conversation through email can be among two or more than two people and is the best substitute for formal face to face meetings as discussions can be done in an email system.
- Web conferencing: In the web conferencing method of business communication, the internet is being used for communication in meetings, conferences, presentations, seminars, and imparting training. It includes features like sharing of files, screens, real-time chatting, recording, etc. This can be considered as the most effective way of interacting with people sitting at different locations. Web conferencing is done by using the phone (teleconferencing) or video equipment (videoconferencing).
- Written communication: Written business communication is a formal and detailed form of communication than other methods. Different written communication tools include formal letters, brochures, posters, etc.
- Other methods: There are other business communication methods like an instant messaging system. This technology is easy to use as one can easily connect with people while working offsite and have conversations without waiting so long. They also include WhatsApp, phone calls.

Production Of Goods And Services
Production: Refers to the creation of goods and services or increasing their usefulness through activities such as transporting them to where they are required. People who are involved in production of goods and services are referred to as producers.
Importance of Production
- To produce is independence.
If you don’t produce, you will have to consume what has been produced.
In this case, you have no choice but to the available options. People choose to be free and independent. - The need for various goods
- Availability of goods and services: Production helps to ensure that goods and services are made
- Increase in wealth of people: Production assists people to accumulate wealth as a result of continuous employment. importance of production
- Increase in export potential: Production also assists a state or nation to boost her export of goods and services to other nations.
- Acquisition of skills: The engagement of people in production leads them to acquire special skills
Characteristics of Factors of Production
Fig 5.1. The organization of Production
Meaning: Factors of production refer to agents, components or resources which are combined together to produce goods and services. There are four factors of production. These are:
Labour
Labour - is skillful: Labour becomes skillful through education and training.
- Labour is a human factor: Labour is a human factor hence its supply can easily be controlled== importance of production
- Labour requires motivation: For labour to perform efficiently and increase its productivity, it must be motivated in one way or the other. importance of production
- Labour is not predictable: Labour as a factor of production cannot be easily predicted.
- Labour is not fixed: The supply of labour, unlike land, is not fixed as it varies in quantity and quality.
- Labour is perishable: Knowledge can diminish overtime as a result of continued unemployment, under-employment, age and death.
- Labour controls other factors of production: Labour controls and combines all other factors of production to make them more meaningful to the society.
- Labour has initiative: Labour can act on its own initiative.
Types of labour
- Unskilled
- Semi-skilled
- Skilled
- professional
Classification Of Factors Of Production
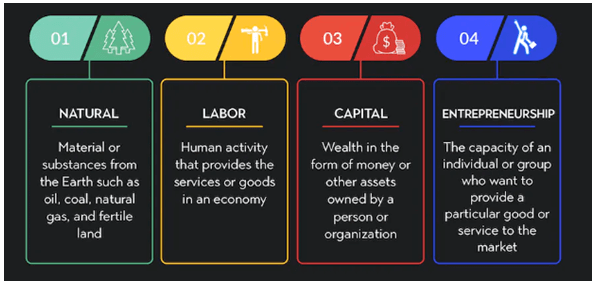
| Name | Nature | Reward |
| Land | Any natural resources | Rent |
| Labour | Toil and/or skills | Wage |
| Capital | man-made resource | Interest |
| Enterprise | Risk taking and organising | Profit |
Characteristics Of Land As A Factors Of Production
Types of land
- Residential
- Commercial
- Recreation
- Cultivation
- Extraction
- Uninhabitable
- Fixed supply: The total land area of earth (in the sense of the surface area available to men) is fixed. Therefore, the supply of lands is strictly limited. It is, no doubt, possible to increase the supply of land in a particular region to some extent through reclamation of land from sea areas or deforestation.
- No cost of production: Since land is a gift of nature, it has no cost of production. Since land is already in existence, no costs are to be incurred in creating it. In this sense, land differs from both labour (which has to be reared, educated and trained) and capital (which has to be created by using labour and other scarce resources or by spending money).
- Differences in fertility: Another important feature of land is that it is not homogeneous. All grades (plots) of land are not equally productive or fertile. Some grades of land are more productive than others. And Ricardo argued that rent arises not only due to scarcity of land as a factor but also due to differences in the fertility of the soil.
- Mobility:Land is not geographically mobile. But, it is occupationally mobile. In most parts of India, for example, land has many alternative uses. It might be used for farmland, roads, railways, airlines, public parks, playgrounds, residential housing, office buildings, shopping complex, and so on. Some of the land, for example, in hill area, of say, Shillong, or Darjeeling, has an extremely limited degree of occupational mobility, being useful perhaps for sheep grazing, golf course or as a centre of tourism.
- Return: The income received by the owner of land is known as rent. It may be noted that rent is usually paid for something more than the use of land or another natural resource, but includes also an element of payment for another factor which is involved in making the resource available in a usable form.
Characteristics of Capital as a factor of production
- Capital is manmade factor of production
- Its mobile
- It’s a passive factor of production
Types of capital
- Fixed
- Working
- venture
Characteristics of an entrepreneur
An entrepreneur is a person who brings factors of production in one place. He uses them for the production process. he is the person who decides:
- What to produce
- Where to produce
- How to produce
A person who takes these decisions along with the associated risk is an entrepreneur.
X-tics of an entrepreneur
- He has imagination
- He has great administrative power
- An entrepreneur must be a man of action
- An entrepreneur must have the ability to organize
- He should be a knowledgeable person
- he must have a professional approach
Consumer concerns addressed in the production of goods and services
Learners to check on this

Marketing of Goods and Services
- A market can be defined as a place where buyers and sellers meet to exchange goods, services and other relevant information is called a market. Both these parties can meet in a city, state, province, country and region. The market may be a physical or virtual.
- The one party (seller) sells a product or service to a buyer for money benefits. Most of the time there are more than single buyers and seller in the marketplace. The value and prices of product and service are based on the law demand and supply in the market.
Types of Markets
Physical Markets. Any physical market is a place where buyers and sellers physically meet that involve both parties in a transaction in exchange for money. Few good examples are departmental stores, shopping malls and retail stores
Virtual Markets / Internet Markets. Todays’ business environment such type of markets are increasing on a fast track. It is a place where the seller offers goods and services via online platform i.e. internet. Buyers and sellers are not required to physically meet or interact. Examples are Freelancer.com, Amazon.com.
Auction Market. An auction market is a place where sellers and buyers indicate the lowest and highest prices they are willing to exchange. This exchange takes place when both the sellers and buyers agree on a price. A good example is the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE).
What is Market Size
Market size refers to the total number of people in a specific market who has the potential to buy and sell products and services. Whenever companies launch a new product they are very interested to know the market size. For any market, two factors are very important:
- Total number of buyers and sellers
- Total money in the market on the annual basis
Marketing
Marketing is a process by which a product or service is introduced and promoted to potential customers. Without marketing, your business may offer the best products or services in your industry, but none of your potential customers would know about it. Without marketing, sales may crash and companies may have to close.
Types of Marketing
Where your marketing campaigns live depends entirely on where your customers spend their time. It's up to you to conduct market research that determines which types of marketing -- and which mix of tools within each type -- is best for building your brand. Here are several types of marketing that are relevant today, some of which have stood the test of time:
- Internet marketing: Inspired by an Excedrin product campaign that took place online, the very idea of having a presence on the internet for business reasons is a type of marketing in and of itself.
- Search engine optimization: Abbreviated "SEO," this is the process of optimizing content on a website so that it appears in search engine results. It's used by marketers to attract people who perform searches that imply they're interested in learning about a particular industry.
- Blog marketing: Blogs are no longer exclusive to the individual writer. Brands now publish blogs to write about their industry and nurture the interest of potential customers who browse the internet for information.
- Social media marketing: Businesses can use Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, LinkedIn, and similar social networks to create impressions on their audience over time.
- Print marketing: As newspapers and magazines get better at understanding who subscribes to their print material, businesses continue to sponsor articles, photography, and similar content in the publications their customers are reading.
- Search engine marketing: This type of marketing is a bit different than SEO, which is described above. Businesses can now pay a search engine to place links on pages of its index that get high exposure to their audience. (It's a concept called "pay-per-click" -- I'll show you an example of this in the next section).
- Video marketing: While there were once just commercials, marketers now put money into creating and publishing all kinds of videos that entertain and educate their core customers.
The 4 Ps of Marketing
Essentially, these 4 Ps explain how marketing interacts with each stage of the business.

Consumers
A consumer is any individual or group that uses goods or services. Generally, this means an individual who pays for goods or services, although sometimes the good or service is not paid for, but is instead received as a gift or favor. Usually, the term is used when referring to the demand side of the market. For example, in economics, it is often said that consumers are influenced by price when they make their buying decisions.
Following are the things that customers look at for before buying a product.
- Price: The price of the product is the first thing that almost 80% of the customers look at before buying a product. Because every customer has their own budget and they usually tend to spend within the budget unless they get some extraordinary quality.
- Experience: Nowadays, everyone is busy and they want to buy things which are easily available and also there are so many alternatives available in the market for a certain product. Therefore, it is important to make the shopping experience as well as the quality of the product excellent. So, they don’t move to some other product.
- Design: Design of the product should be attractive.
- Functionality: The product should have all the functionalities that a customer expects while buying a product.
- Convenience: The product and services should be convenient for the customer, otherwise, he/she will not buy the product.
- Reliability: The product should be reliable and it should meet the customer’s needs every single time.
- Compatibility: The product should be compatible with the other products that the customer is already using.
Following is a list of different types of customers.
- Need-based customers :

These customers shop for only specific products when they need them. They already know the section they are heading to when they enter a store. They usually don’t require an assistant to choose a product because they usually have knowledge about the product they want to buy. Therefore, it is very important to approach them with a planned strategy. - Loyal customers :

These types of customers are very important for a business. This segment of the customers should be kept satisfied. They not only stay loyal to the company but also praise and recommend the product to their family and friends. Therefore, they also help the company to market its product by “word -of – mouth” free of cost. Usually, this segment of customers is small and they hardly make 20% of the total customers, but they are responsible for generating the maximum part of the total revenue of the company. - Discount customers :
These are the types of customers who never buy a product on full price. They always look for a discount on the product they want to buy. Such customers never shop for anything off-sale. These types of customers make the biggest portion of total customers of a company. Discount customers are the least loyal customers and they easily move on when getting better offers by some other company. - Impulsive customers :

Impulsive customers’ segment is a bonus segment for any business, as these customers don’t shop as per their need or because of ongoing sale. The shopping of these types of customers is highly influenced by their current mood. They usually tend to buy a product, if, at the time of shopping, they find it useful and good at that point in time. - Potential customers:
Potential customers are not your customer yet, but they just need a little bit of convincing and assistance to make a purchase. These types of customers need a little bit of encouragement and attention before buying your product. To deal with such customers, you should show them some value and assist them by providing information about the products they are interested in.
Factors to consider when selecting a suitable market for goods and services
- The product to be sold or produced
- Personnel to manage the business
- Amount of finance and other resources required
- The market to be served (customers)
- Types of employees required
- Projection (level of achievement in future in terms of profit)
- The name for the business
An attractive market has the following characteristics:
- It is sizeable (large) enough to be profitable given your operating cost. Only a tiny fraction of the consumers in China can afford to buy cars. However, because the country’s population is so large (nearly 1.5 billion people), more cars are sold in China than in Europe (and in the United States, depending on the month). Three billion people in the world own cell phones. But that still leaves three billion who don’t (Corbett, 2008).
- It is growing. The middle class of India is growing rapidly, making it a very attractive market for consumer products companies. People under thirty make up the majority of the Indian population, fueling the demand for “Bollywood” (Indian-made) films.
- It is not already swamped by competitors, or you have found a way to stand out in a crowd. IBM used to make PCs. However, after the marketplace became crowded with competitors, IBM sold the product line to a Chinese company called Lenovo.
- Either it is accessible or you can find a way to reach it. Accessibility, or the lack of it, could include geographic accessibility, political and legal barriers, technological barriers, or social barriers. For example, to overcome geographic barriers, the consumer products company Unilever hires women in third-world countries to distribute the company’s products to rural consumers who lack access to stores.
- The company has the resources to compete in it. You might have a great idea to compete in the wind-power market. However, it is a business that is capital intensive. What this means is that you will either need a lot of money or must be able to raise it. You might also have to compete with the likes of T. Boone Pickens, an oil tycoon who is attempting to develop and profit from the wind-power market. Does your organization have the resources to do this?
- It “fits in” with your firm’s mission and objectives. Consider TerraCycle, which has made its mark by selling organic products in recycled packages. Fertilizer made from worm excrement and sold in discarded plastic beverage bottles is just one of its products. It wouldn’t be a good idea for TerraCycle to open up a polluting, coal-fired power plant, no matter how profitable the market for the service might be.
ICT platforms for marketing Goods and services
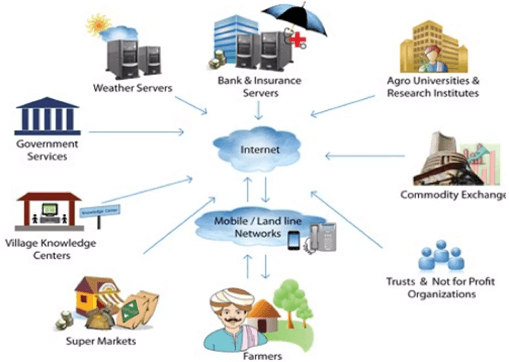
They include:
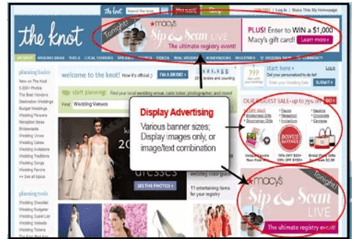
- Online advertising – many businesses advertise through banners on websites. It provides to the customers quickly and easy response.
- Email marketing – it’s a form of direct marketing. It’s very fast and less expensive.
- Social media marketing – it’s a collection of online communication channels. It’s a community based input, interaction, content sharing and collaboration. Examples include: Facebook, Twitter, WhatsApp, Tiktok
- Blogging –

- Target marketing- it’s about attracting a customer who will buy what you are selling.

Advantages
- Anywhere, anytime marketing
- Cost effective
- Fast
By using ICT, we can market anywhere, anytime in the world without being their physically.
- Marketing products on the internet costs less than marketing them through a physical retail outlet.
- The internet provides an important platform for building relationships with customers and increasing retention levels
- It is very fast
- User can get easily information about product.
Download Business and Its Environment - Grade 7 Business Studies Revision Notes.
Tap Here to Download for 30/-
Get on WhatsApp for 30/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students