Stella
Business and Its Environment - Grade 7 Business Studies Revision Notes
- Business Activities
- Goods and Services
- Economic Resources
- Business Communication
- Production of Goods and Services
- Marketing of Goods and Services
Business Activities
Needs And Wants
| BASIS FOR COMPARISON | NEEDS | WANTS |
| Meaning | Needs refers to an individual's basic requirement that must be fulfilled, in order to survive. | Wants are described as the goods and services, which an individual like to have, as a part of his caprices. |
| Nature | Limited | Unlimited |
| What is it? | Something you must have | Something you wish to have |
| Represents | Necessity | Desire |
| Survival | Essential | Inessential |
| Change | May remain constant over time. | May change over time. |
| Non-fulfillment | May result in onset of disease or even death. | May result in disappointment |
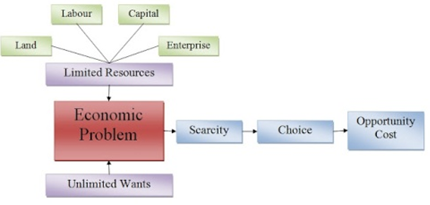
Scarcity, Choice, Scale of preference and opportunity cost
The basic concept or elements of economics are:
- wants,
- scarcity,
- scale of preference,
- choice and
- opportunity cost.
WANTS
Wants simply means the desire or wish to own goods or services that give satisfaction. Goods include things such as cars, radios, food, houses, books, etc., (that is tangible commodities), while services includes hair dressing, the services of an actor, etc(that is intangible commodities). Want s are also called ENDS.
As these basic needs are satisfied, other needs will arise. That is why we say that human wants are insatiable. This is because human wants are unlimited while resources used in satisfying them are limited.
SCARCITY
Scarcity refers to the limited available resources used in satisfying the unlimited human wants.
These resources are scarce relative to their demand. It is as a result of scarcity of resources that needs the study of economics very essential in order to find alternative uses of these scarce resources. The available resources cannot satisfy all human wants. Since human wants are unlimited or insatiable relative to the available resources, we have to choose the most pressing ones and leave others that are less important because resources are scare.
As a student you will need to buy school materials, e.g exercise books worth #100.00 but you have only #50.00. it can be seen that the money you have (#50.00), which is your resources, will not be sufficient to buy all you need. The available resources within the environment can never at any time be in abundance to satisfy all human wants.
If resources were to be unlimited or abundant, no economics problem would arises and there would be no need for a study of economics. Scarcity is the central or basic economic problems
SCALE OF PREFERENCE
Scale of preference refers to a list of unsatisfied wants arranged in order of their relative importance.
A scale of preference refers to a list of unsatisfied wants arranged in order of priority or importance. This aids decision-making. The most pressing needs are ranked first followed by the less pressing ones. In other words, it is a list showing the order in which we want to satisfy our wants arrange in order of priority.
The drawing of scale of preference will make it easier for choice to be made. In order to achieve maximum satisfaction with limited resources at their disposal, an individual, firm and unsatisfied wants in order of priority.
Each individual is assumed to have a scale of preference. This is because economics theory assumes that people always behave rationally and would satisfy their most pressing want first.
For example, a student might rank his wants in following order according to their level of importance:
- Pair of school uniform
- Exercise books
- Wrist watch
- Dictionary
- Scientific calculator
- An arm chair
If he is to choose between items 1 and 4, he chooses the first. Scale of preference of individuals, firms and the government differ from time to time.
IMPORTANCE OF SCALE OF PREFERENCE
- Ranking of needs
- Financial prudence
- Identification of highest priority
- Rational choice
- Efficient utilization of limited resources
- Optimum allocation of resources
- Maximization of satisfaction
The importance of scale of preference can be paraphrased this way also:
- It helps individuals to rank their needs in order of importance.
- It helps us to manage our resources properly.
- It helps both individuals and government to identify the most important needs.
- It enhances optimum allocation of resources.
- It helps individuals, firms and government in the efficient utilization of resources.
- It helps economic agents to maximize their satisfaction.
- It helps individuals to make rational decision.
CHOICE
Choice can be defined as a system of selecting or choosing one out of a number of alternatives. Human wants are many and we cannot satisfy all of them because of our limited resources.
We therefore, decide which of the wants we can satisfy first. Choice arises as a result of numerous human wants and the scarcity of the resources used in satisfying these wants.
OPPORTUNITY COST
Opportunity cost is also known as a real cost or time cost.
The concept of opportunity cost is used in economics to express cost in terms of foregone or sacrificed alternatives. Opportunity cost means the alternative foregone or sacrifice made in order to satisfy another want. It is the satisfaction of one’s want at the expense of another want.
Types Of Business Activities
People carry out different business activities in order to earn income.
Business activities are activities which involve the provision of goods or services with an aim of earning a profit.
Activities done without the intention of making profit are referred to as
non-business activities. Business activities may be grouped into the following seven categories:
- Extraction
This involves obtaining goods from their natural setting e.g. mining, farming, lumbering, fishing, quarrying e.t.c - Processing
This involves the conversion of raw materials into more useful products without combining it with other goods. Examples here
include milling/grinding flour, refining oil, tanning of skins and hides, conversion of iron into steel e.t.c - Manufacturing
This involves combining different raw materials to come up with one final product. Such activities include bread baking, making a table e.t.c - Construction
This involves building of structures such as bridges, ships, aeroplanes, houses, roads, railways e.t.c - Distribution of goods
This refers to the activities involved in moving goods from where they are produced to where they are needed. People
who carry out distribution are called distributors. Examples of distributors are wholesalers and retailers. - Trade-Activities in this category involve the buying and selling of goods with a view of making a profit. People involved in trade are called traders.
- Provisions of Services-Activities in this category involve human acts which could be mental or physical. These include activities such as haircutting, hair styling, car-washing, nursing, teaching, driving, and entertaining e.t.c.
Purpose of Business activity
- Provides goods and services from limited resources to satisfy unlimited wants
- Scarcity is the result of the economic problem – limited resources and unlimited wants
- Choice is necessary for scarce resources. This leads to opportunity costs
- Specialization is required to make the most out of sources
Business activity
- Combines factors of production to create goods and services
- Goods and services satisfy peoples’ wants
- Employs people and pays them wages so they can consume other products
Business Objectives
All businesses have objectives or aims to achieve. Their objectives may vary depending on the type of business and the situation the business is in. The most common objectives are:
- Profit: Profit is what keeps a company going and is the main objective of most businesses. Normally a business will try to obtain a satisfactory level of profits so they do not have to work long hours to pay too much tax.
- Increase added value: Value added is the difference between the price and material costs of a product. E.g.: If the price when selling a pen is Ksh. 3 and it costs Ksh.1 in material, the value added would be Ksh.2. However, this does not take in account overheads and taxes. Added value could be increased by working on products so that they become more expensive finished products. One easy example of this is a mobile phone with a camera would sell for much more than one without it. Of course, you will need to pay for the extra camera but as long as prices rise more than costs, you get more profit.
- Growth: Growth can only be achieved when customers are satisfied with a business. When businesses grow they create more jobs and make them more secure when a business is larger. The status and salary of managers are increased. Growth also means that a business is able to spread risks by moving to other markets, or it is gaining a larger market share. Bigger businesses also gain cost advantages, called economies of scale.
- Survival: If a business do not survive, its owners lose everything. Therefore, businesses need to focus on his objective the most when they are: starting up, competing with other businesses, or in an economic recession.
- Service to the community: This is the primary goal for most government owned businesses. They plan to produce essential products to everybody who need them.
These business objectives or aims can conflict because different people in a business want different things at different times.
Goods And Services
Types Of Goods And Services
We desire to have all the things to satisfy our present and future wants. Thus, our desire is for all those things that satisfy our wants.
All these things are either material goods or services. If something is not wanted by anybody it will not be called a good or service.
Therefore, we can divide the things that we wants into two categories:
- Goods and
- Services.
Goods are material things wanted by human beings. They can be seen or touched. Services are non-material things. These cannot be seen or touched only their effects are felt. When we are hungry, we take food. When we fall sick, we take medicines. When we study, we use book, notebook, pen, paper etc. All these are examples of goods which satisfy some of our wants. All the things which satisfy human wants are good.
However, wants for haircut, washing of cloths, mending of shoes, stitching of cloths, studying in a school or a college etc. are not satisfied by goods. These are satisfied by the services performed by a barber, washer man, cobbler, tailor and teacher etc. So some of our wants are satisfied by goods and some by services. Hence, all the human wants can be satisfied by goods and services.
Classification of Goods and Services:
Goods and services are of many types. However, these can be classified into some broad groups.
These are discussed below:
- Free Goods and Economic goods:
The goods which have unlimited supply and are provided as free gift of nature. The goods which are not man-made and do not have to pay anything to get them. These goods are known as ‘Free Goods’. For example, air, sea, water, sunlight, sand in the desert etc. On the other hand, goods like vegetables, grains, minerals, fruits, fishes etc. which are neither man-made nor unlimited supply of nature are known as ‘Economic Goods’ All these goods are sold and purchased in the market only. - Free Services and Economic Services:
Services which cannot be bought in the market and which are only rendered out of love, affection etc. are known as ‘Free Services’. For example, all services given by the parents to their children are free services. However, all the services that can be bought in the market are ‘Economic Services’. Services rendered by doctors, teachers, lawyers, barbers, cobblers etc. are the example of economic services. - Consumer Goods and Capital Goods:
The goods which are directly used by the consumer for the purposes of consumption are known as ‘Consumer Goods’ The example of consumer goods are bread, biscuit, butter, jam, rice, fish, egg, shoes, shirts, fan, book, pen, cooking gas etc. On the other hand, all the goods which are not directly used to satisfy consumption but which are used in further production are called ‘Producer Goods’ or ‘Capital Goods’. The examples are seeds, fertilizers, tools, machines, raw materials etc. - Consumer Services and Producer Services:
When services are used directly by consumers to satisfy their wants, they are called consumer services. When services are used by producers to produce other goods and services, they are called producer services. When the tailor stitches our shirt, it is a consumer service However when the tailor stitches a shirt for a readymade garments shop, the service rendered by him is a producer service. - Single Use and Durable Use Goods:
Goods (both consumer goods and producer goods) which are only used or consumed for single time or only once are known as single use goods. Bread, milk, fruits, vegetables etc. are the example of single use consumer goods. On the other hand, seeds, fertilizers, raw materials etc. are the example of single use producer goods.
Some goods (both consumer goods and producer goods) can be used for a considerable period, that is, they can be used again and again. They are called durable use goods. For example, table, chair, cloths, shoes etc. are the durable use consumer goods. On the other hand, tube wells, tractors, pump-sets etc. are the example of durable use producer goods, - Private Goods and Public Goods:
On the basics of ownership goods can be classified into two groups. All the goods which are owned by private bodies are called private goods. For example, a car, a house, a motorbike, a mobile phone, books, a television set etc. are the private goods.
There are large number of goods which are collectively owned by the society, the public or the government. These are called public or government goods. For example, roads, bridges, hospitals, government schools etc. are the public goods or the social goods or the government goods.
Economic Resources
Characteristics Of Economic Resources
- Have utility - they have ability to be used
- Have money value - They have a value at which they can be exchanged for ownership
- Have alternative use - They can be put into different uses.
- Scarce in supply - They are not available in sufficient quantities
- Can be combined - They can be combined so as to produce different goods and services
- Can change ownership - Differennt resources can be used together.
- They are distributed - they are available in varying quantities at different places.
Types Of Economic Resources In Kenya
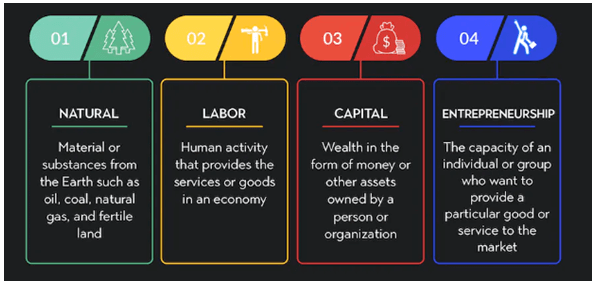
What Are Economic Resources?
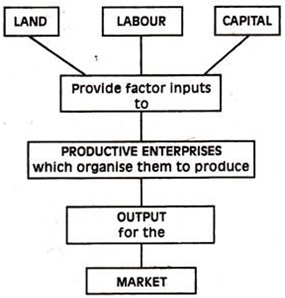
Economic resources are the different factors of production used to produce all goods and services in the economy. Economic theory is primarily concerned with allocating these resources so that the production of goods and services is done most efficiently and effectively.
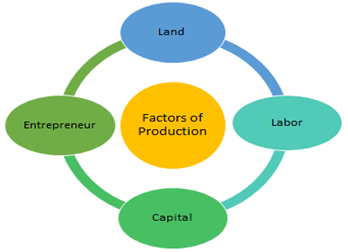
There are four general types of economic resources:
- Land or natural resources
- Labor
- Capital
- Entrepreneurial ability
Sustainable Ways Of Using Economic Resources
Economic sustainability is the practice of conserving natural and financial resources to create long-term financial stability. A system that's sustainable can last far into the future with minimal negative impacts.
In finance, this can mean reducing the worldwide consumption of valuable resources to ensure they're available to future generations to create financial stability and wealth. For example, by reducing the usage of fossil fuels and focusing on alternative fuel sources, companies, governments and consumers can help reduce the global impact of emissions and pollution from fossil fuels.
Here are some examples of economic stability:
Alternative energy
Alternative energy sources, such as wind power, solar power and hydropower, can offer a more sustainable, clean and affordable solution to energy needs. Much of the world depends on fossil fuels like coal, oil and gasoline, which have a limited supply and create greenhouse gas emissions.
Alternative energy sources depend on infinite natural processes or resources, which may make them more sustainable and affordable in the long term. Reducing fossil fuel consumption can help reduce tax burdens for consumers, decrease the costs of environmental impacts and create more energy equity among low-income populations, which can increase economic productivity.
Sustainable agriculture
Many farms are adopting sustainable agricultural practices to reduce soil degradation, which occurs from over-farming, and to reduce animal product consumption. Reducing food consumption and focusing on regenerative farming can help improve soil health, crop yields and the quality of farmed food and resources.
Regenerative farming is a practice farmers use to rotate crops for better soil health, instead of farming the same crops, like corn, all year. Improving soil health and reducing animal product consumption can help keep food costs low, reduce carbon emissions and environmental damage and encourage better habits.
Recycling and pollution reduction
Recycling and reducing pollution is a common economic and environmental stability practice that can help increase the value of materials. For example, a company producing aluminum cans can sustain operations by recycling used cans and creating molten aluminum for recasting, instead of mining for aluminum ore.
This practice can reduce the company's environmental impact, saving the region both cleanup and restoration costs and reducing the organization's mining costs. Reducing pollution can also help reduce worldwide cleanup and restoration costs and the costs of climate change.
Sustainable fisheries
Creating more sustainable fisheries can help reduce the environmental and economic impact of overfishing the oceans. Side effects of overfishing can include population declination, bycatch, or catching other species along with fish, and fishing equipment made of plastics and other materials discarded in waterways.
Adopting more sustainable practices, like reducing fish consumption worldwide and reducing bycatch and fishing pollution, could create a more sustainable fishing environment, resulting in more stable profits and economic health for the fishing industry. It can also help ocean populations recover, which is crucial for ecosystems across the globe.
Resource Mapping
Resource mapping is a strategy for identifying and analyzing the programs, people, services, and other resources that currently exist in the country. This information can help leaders better assess the needs of the country and to make informed decisions about where to focus change efforts.
Mapping Steps
- Reach consensus on the parameters of the map—select a goal to map.
- Select the data to be collected based on these parameters—determine what types of resources you would like to collect.
- Develop tools to collect your data.
- Collect data with help from stakeholders.
- Conduct a community (or environmental) scan.
- Synthesize, analyze, and interpret your data.
- Communicate your findings.
- Set priorities.
- Develop related products.
Importance Of Economic Resources
Resources are significant because:
- They satisfy human wants both individual and social,
- They are a source or possibility of assistance,
- They are a means of development and support,
- They are an expedient,
- They have capacity to take advantage of opportunities, and
- One relies on them for aid, support and supply.
Business Communication
Communication is an essential element in the success of any business. The process of transferring information from one person to another, within and outside the business environment, is termed as ‘Business Communication.’ The term ‘Business Communication’ is derived from general communication which is associated with business activities. In other terms, communication between business parties or people for business-related tasks is considered as ‘Business Communication.’
Business Communication includes different aspects like marketing, public relations, customer relations, corporate and interpersonal communication, etc.
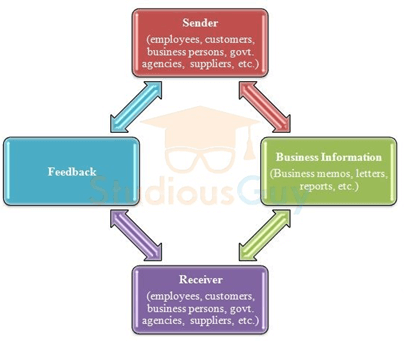
Basic elements of Business communication:
- Sender
- Business information
- Receiver
- Feedback
Importance Of Business Communication
- Helps in increasing productivity: Effective business communication increases the productivity of staff by boosting up teamwork. It creates a trustworthy and understanding environment among employers and employees. Effective communication is related to cooperating with employees and understanding their needs and desires. By doing so, employees are able to accomplish their tasks more effectively and efficiently. Also, the scope of doing mistakes or errors during their work minimizes due to effective communication.
- Helps in increasing customers: Customers are an important part of any business and effective business communication can facilitate in attracting new customers and retain the current customers. A well-defined marketing strategy and public relations campaign run by an organization generates the interest of customers in its goods or services and helps in building the corporate image in customers.
- Enhances business partnerships: Business Communication also improves partnerships in business. It plays a significant role in dealing with external business clients or vendors. Vendors may be required to communicate on products regularly for improvements. Also, an effective and harmonious relationship with other businesses determines the further success of an organization. A business unit that has developed its image as an entity for easy partnership through its effective communication can attract other business units for forming business relationships with them.
- Facilitates innovations in business: Effective business communication helps in business innovations as well as it facilitates employees to convey their ideas and suggestions openly. Similarly, at the time of launching any new product in the market, effective communication ensures the performance of the sales team, market acceptance of the product, fast delivery of products in the market, etc.
- Information exchange: Business communication is required by an organization for exchanging information with internal and external stakeholders. This helps in achieving its goals effectively.
- Preparation of plans and policies: Through effective business communication, organizations can make their plans and policies properly. Relevant information is required for preparing these plans and policies. Through communication, different managers source information through reliable channels.
- Helps in solving problems or issues: Through different communication channels, managers get information about different routine and non-routine issues and based upon that they can take required actions to sort out those issues.
- Facilitates decision-making: Effective decisions require up-to-date information. Using effective communication, managers can acquire information from different sources and can utilize it for making correct decisions.
- Reduces chances of conflicts: Through effective communication different business parties can exchange information in a smooth way. This results in fewer conflicts, controversies, arguments between them.
Business Communication Methods
Different methods of communicating in a business are as below:
- In-person (Face-to-Face) Business Communication: In-person communication is the most common and preferred method of business communication. As it is generally in the form of meetings or conferences which is face to face communication format. This requires refined in-person skills. This method also includes non-verbal communication i.e. body language. While having a conversation between two or more people in business, body language like gestures, facial expression, etc. also play a vital role in communicating a person’s attitude towards others.
- Communication by email system: An e-mail has become the most widely used communication system in any business. Due to its feature of sending and receiving mass or multiple messages at a time, email is considered as one of the preferred methods in business communication. It also increases efficiency as emails can be sent and responded in fast mode. The conversation through email can be among two or more than two people and is the best substitute for formal face to face meetings as discussions can be done in an email system.
- Web conferencing: In the web conferencing method of business communication, the internet is being used for communication in meetings, conferences, presentations, seminars, and imparting training. It includes features like sharing of files, screens, real-time chatting, recording, etc. This can be considered as the most effective way of interacting with people sitting at different locations. Web conferencing is done by using the phone (teleconferencing) or video equipment (videoconferencing).
- Written communication: Written business communication is a formal and detailed form of communication than other methods. Different written communication tools include formal letters, brochures, posters, etc.
- Other methods: There are other business communication methods like an instant messaging system. This technology is easy to use as one can easily connect with people while working offsite and have conversations without waiting so long. They also include WhatsApp, phone calls.
Production Of Goods And Services
Production: Refers to the creation of goods and services or increasing their usefulness through activities such as transporting them to where they are required. People who are involved in production of goods and services are referred to as producers.
Importance of Production
- To produce is independence.
If you don’t produce, you will have to consume what has been produced.
In this case, you have no choice but to the available options. People choose to be free and independent. - The need for various goods
- Availability of goods and services: Production helps to ensure that goods and services are made
- Increase in wealth of people: Production assists people to accumulate wealth as a result of continuous employment. importance of production
- Increase in export potential: Production also assists a state or nation to boost her export of goods and services to other nations.
- Acquisition of skills: The engagement of people in production leads them to acquire special skills
Characteristics of Factors of Production
Fig 5.1. The organization of Production
Meaning: Factors of production refer to agents, components or resources which are combined together to produce goods and services. There are four factors of production. These are:
Labour
Labour - is skillful: Labour becomes skillful through education and training.
- Labour is a human factor: Labour is a human factor hence its supply can easily be controlled== importance of production
- Labour requires motivation: For labour to perform efficiently and increase its productivity, it must be motivated in one way or the other. importance of production
- Labour is not predictable: Labour as a factor of production cannot be easily predicted.
- Labour is not fixed: The supply of labour, unlike land, is not fixed as it varies in quantity and quality.
- Labour is perishable: Knowledge can diminish overtime as a result of continued unemployment, under-employment, age and death.
- Labour controls other factors of production: Labour controls and combines all other factors of production to make them more meaningful to the society.
- Labour has initiative: Labour can act on its own initiative.
Types of labour
- Unskilled
- Semi-skilled
- Skilled
- professional
Classification Of Factors Of Production
| Name | Nature | Reward |
| Land | Any natural resources | Rent |
| Labour | Toil and/or skills | Wage |
| Capital | man-made resource | Interest |
| Enterprise | Risk taking and organising | Profit |
Characteristics Of Land As A Factors Of Production
Types of land
- Residential
- Commercial
- Recreation
- Cultivation
- Extraction
- Uninhabitable
- Fixed supply: The total land area of earth (in the sense of the surface area available to men) is fixed. Therefore, the supply of lands is strictly limited. It is, no doubt, possible to increase the supply of land in a particular region to some extent through reclamation of land from sea areas or deforestation.
- No cost of production: Since land is a gift of nature, it has no cost of production. Since land is already in existence, no costs are to be incurred in creating it. In this sense, land differs from both labour (which has to be reared, educated and trained) and capital (which has to be created by using labour and other scarce resources or by spending money).
- Differences in fertility: Another important feature of land is that it is not homogeneous. All grades (plots) of land are not equally productive or fertile. Some grades of land are more productive than others. And Ricardo argued that rent arises not only due to scarcity of land as a factor but also due to differences in the fertility of the soil.
- Mobility:Land is not geographically mobile. But, it is occupationally mobile. In most parts of India, for example, land has many alternative uses. It might be used for farmland, roads, railways, airlines, public parks, playgrounds, residential housing, office buildings, shopping complex, and so on. Some of the land, for example, in hill area, of say, Shillong, or Darjeeling, has an extremely limited degree of occupational mobility, being useful perhaps for sheep grazing, golf course or as a centre of tourism.
- Return: The income received by the owner of land is known as rent. It may be noted that rent is usually paid for something more than the use of land or another natural resource, but includes also an element of payment for another factor which is involved in making the resource available in a usable form.
Characteristics of Capital as a factor of production
- Capital is manmade factor of production
- Its mobile
- It’s a passive factor of production
Types of capital
- Fixed
- Working
- venture
Characteristics of an entrepreneur
An entrepreneur is a person who brings factors of production in one place. He uses them for the production process. he is the person who decides:
- What to produce
- Where to produce
- How to produce
A person who takes these decisions along with the associated risk is an entrepreneur.
X-tics of an entrepreneur
- He has imagination
- He has great administrative power
- An entrepreneur must be a man of action
- An entrepreneur must have the ability to organize
- He should be a knowledgeable person
- he must have a professional approach
Consumer concerns addressed in the production of goods and services
Learners to check on this
Marketing of Goods and Services
- A market can be defined as a place where buyers and sellers meet to exchange goods, services and other relevant information is called a market. Both these parties can meet in a city, state, province, country and region. The market may be a physical or virtual.
- The one party (seller) sells a product or service to a buyer for money benefits. Most of the time there are more than single buyers and seller in the marketplace. The value and prices of product and service are based on the law demand and supply in the market.
Types of Markets
Physical Markets. Any physical market is a place where buyers and sellers physically meet that involve both parties in a transaction in exchange for money. Few good examples are departmental stores, shopping malls and retail stores
Virtual Markets / Internet Markets. Todays’ business environment such type of markets are increasing on a fast track. It is a place where the seller offers goods and services via online platform i.e. internet. Buyers and sellers are not required to physically meet or interact. Examples are Freelancer.com, Amazon.com.
Auction Market. An auction market is a place where sellers and buyers indicate the lowest and highest prices they are willing to exchange. This exchange takes place when both the sellers and buyers agree on a price. A good example is the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE).
What is Market Size
Market size refers to the total number of people in a specific market who has the potential to buy and sell products and services. Whenever companies launch a new product they are very interested to know the market size. For any market, two factors are very important:
- Total number of buyers and sellers
- Total money in the market on the annual basis
Marketing
Marketing is a process by which a product or service is introduced and promoted to potential customers. Without marketing, your business may offer the best products or services in your industry, but none of your potential customers would know about it. Without marketing, sales may crash and companies may have to close.
Types of Marketing
Where your marketing campaigns live depends entirely on where your customers spend their time. It's up to you to conduct market research that determines which types of marketing -- and which mix of tools within each type -- is best for building your brand. Here are several types of marketing that are relevant today, some of which have stood the test of time:
- Internet marketing: Inspired by an Excedrin product campaign that took place online, the very idea of having a presence on the internet for business reasons is a type of marketing in and of itself.
- Search engine optimization: Abbreviated "SEO," this is the process of optimizing content on a website so that it appears in search engine results. It's used by marketers to attract people who perform searches that imply they're interested in learning about a particular industry.
- Blog marketing: Blogs are no longer exclusive to the individual writer. Brands now publish blogs to write about their industry and nurture the interest of potential customers who browse the internet for information.
- Social media marketing: Businesses can use Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, LinkedIn, and similar social networks to create impressions on their audience over time.
- Print marketing: As newspapers and magazines get better at understanding who subscribes to their print material, businesses continue to sponsor articles, photography, and similar content in the publications their customers are reading.
- Search engine marketing: This type of marketing is a bit different than SEO, which is described above. Businesses can now pay a search engine to place links on pages of its index that get high exposure to their audience. (It's a concept called "pay-per-click" -- I'll show you an example of this in the next section).
- Video marketing: While there were once just commercials, marketers now put money into creating and publishing all kinds of videos that entertain and educate their core customers.
The 4 Ps of Marketing
Essentially, these 4 Ps explain how marketing interacts with each stage of the business.

Consumers
A consumer is any individual or group that uses goods or services. Generally, this means an individual who pays for goods or services, although sometimes the good or service is not paid for, but is instead received as a gift or favor. Usually, the term is used when referring to the demand side of the market. For example, in economics, it is often said that consumers are influenced by price when they make their buying decisions.
Following are the things that customers look at for before buying a product.
- Price: The price of the product is the first thing that almost 80% of the customers look at before buying a product. Because every customer has their own budget and they usually tend to spend within the budget unless they get some extraordinary quality.
- Experience: Nowadays, everyone is busy and they want to buy things which are easily available and also there are so many alternatives available in the market for a certain product. Therefore, it is important to make the shopping experience as well as the quality of the product excellent. So, they don’t move to some other product.
- Design: Design of the product should be attractive.
- Functionality: The product should have all the functionalities that a customer expects while buying a product.
- Convenience: The product and services should be convenient for the customer, otherwise, he/she will not buy the product.
- Reliability: The product should be reliable and it should meet the customer’s needs every single time.
- Compatibility: The product should be compatible with the other products that the customer is already using.
Following is a list of different types of customers.
- Need-based customers :

These customers shop for only specific products when they need them. They already know the section they are heading to when they enter a store. They usually don’t require an assistant to choose a product because they usually have knowledge about the product they want to buy. Therefore, it is very important to approach them with a planned strategy. - Loyal customers :

These types of customers are very important for a business. This segment of the customers should be kept satisfied. They not only stay loyal to the company but also praise and recommend the product to their family and friends. Therefore, they also help the company to market its product by “word -of – mouth” free of cost. Usually, this segment of customers is small and they hardly make 20% of the total customers, but they are responsible for generating the maximum part of the total revenue of the company. - Discount customers :
These are the types of customers who never buy a product on full price. They always look for a discount on the product they want to buy. Such customers never shop for anything off-sale. These types of customers make the biggest portion of total customers of a company. Discount customers are the least loyal customers and they easily move on when getting better offers by some other company. - Impulsive customers :

Impulsive customers’ segment is a bonus segment for any business, as these customers don’t shop as per their need or because of ongoing sale. The shopping of these types of customers is highly influenced by their current mood. They usually tend to buy a product, if, at the time of shopping, they find it useful and good at that point in time. - Potential customers:
Potential customers are not your customer yet, but they just need a little bit of convincing and assistance to make a purchase. These types of customers need a little bit of encouragement and attention before buying your product. To deal with such customers, you should show them some value and assist them by providing information about the products they are interested in.
Factors to consider when selecting a suitable market for goods and services
- The product to be sold or produced
- Personnel to manage the business
- Amount of finance and other resources required
- The market to be served (customers)
- Types of employees required
- Projection (level of achievement in future in terms of profit)
- The name for the business
An attractive market has the following characteristics:
- It is sizeable (large) enough to be profitable given your operating cost. Only a tiny fraction of the consumers in China can afford to buy cars. However, because the country’s population is so large (nearly 1.5 billion people), more cars are sold in China than in Europe (and in the United States, depending on the month). Three billion people in the world own cell phones. But that still leaves three billion who don’t (Corbett, 2008).
- It is growing. The middle class of India is growing rapidly, making it a very attractive market for consumer products companies. People under thirty make up the majority of the Indian population, fueling the demand for “Bollywood” (Indian-made) films.
- It is not already swamped by competitors, or you have found a way to stand out in a crowd. IBM used to make PCs. However, after the marketplace became crowded with competitors, IBM sold the product line to a Chinese company called Lenovo.
- Either it is accessible or you can find a way to reach it. Accessibility, or the lack of it, could include geographic accessibility, political and legal barriers, technological barriers, or social barriers. For example, to overcome geographic barriers, the consumer products company Unilever hires women in third-world countries to distribute the company’s products to rural consumers who lack access to stores.
- The company has the resources to compete in it. You might have a great idea to compete in the wind-power market. However, it is a business that is capital intensive. What this means is that you will either need a lot of money or must be able to raise it. You might also have to compete with the likes of T. Boone Pickens, an oil tycoon who is attempting to develop and profit from the wind-power market. Does your organization have the resources to do this?
- It “fits in” with your firm’s mission and objectives. Consider TerraCycle, which has made its mark by selling organic products in recycled packages. Fertilizer made from worm excrement and sold in discarded plastic beverage bottles is just one of its products. It wouldn’t be a good idea for TerraCycle to open up a polluting, coal-fired power plant, no matter how profitable the market for the service might be.
ICT platforms for marketing Goods and services
They include:
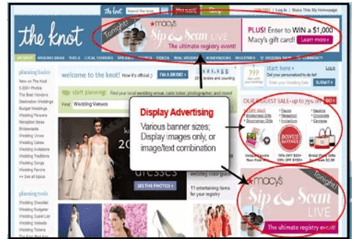
- Online advertising – many businesses advertise through banners on websites. It provides to the customers quickly and easy response.
- Email marketing – it’s a form of direct marketing. It’s very fast and less expensive.
- Social media marketing – it’s a collection of online communication channels. It’s a community based input, interaction, content sharing and collaboration. Examples include: Facebook, Twitter, WhatsApp, Tiktok
- Blogging –

- Target marketing- it’s about attracting a customer who will buy what you are selling.

Advantages
- Anywhere, anytime marketing
- Cost effective
- Fast
By using ICT, we can market anywhere, anytime in the world without being their physically.
- Marketing products on the internet costs less than marketing them through a physical retail outlet.
- The internet provides an important platform for building relationships with customers and increasing retention levels
- It is very fast
- User can get easily information about product.
Business and Money Management Skills - Grade 7 Business Studies Revision Notes
Introduction to Business Studies
- Business: Any activity that is carried out by an individual or an organization concerning provision of goods and services with a view to making profit.
- Business studies: Is the study/examination of the business activities in society. These activities are related to the production of goods and provision of services.
- It can also be defined as the study of activities that are carried out in and around production, distribution and consumption of goods and services.
Components of Business Studies
Business studies consist of the following disciplines
- Commerce
- Accounting
- Economics
- Office practice
- Entrepreneurship
- Commerce
This is the study of trade and aids to trade. Trade refers to the exchange of goods and services for other goods and services or money. Aids to trade are human activities (services) that assist trade to take place. - Economics
This is the study of how human beings strive to satisfy their endless wants using the available scarce resources. - Accounting
This refers to a systematic way of recording business activities which all used for decision making. - Office practice
This refers to all activities that are carried out in an office e.g. communication, filling, clerical work, reproduction of documents etc. - Entrepreneurship
This is the study of activities involved in the process of identifying a business opportunity and acquiring the necessary resources to start and run a business. The person who carries out these activities is referred to as an entrepreneur.
Importance Of Business Studies
Some of the benefits of learning business studies include:
- Assists the learners/members of the society to acquire knowledge and awareness of business terminologies which are necessary when discussing business issues such as profit and loss.
- Assists the individuals in appreciating the role of business in society/in provision of goods and services.
- It enables the learners to acquire basic knowledge, skills and attitudes necessary for the development of self and the nation by starting and operating business.
- Equips the members of society with knowledge and skills necessary to start and run a business comfortably.
- Makes the members of society to appreciate the need for good business management practices
- Assists individual to acquire self-discipline and positive attitude towards work
- Equips individual with abilities to promote co-operation in society through trade
- Enables the individual to understand the role of government in business activities
- Equips individuals with abilities to understand the role of communication and information technology in modern business management
- Helps the individuals to develop positive attitudes towards the environment
- Equips the individual with knowledge and skills required to evaluate business performance
- It helps individual to develop various intellectual abilities such as inquiry, critical thinking, analysis, interpretation, rational judgement, innovation and creativity.
- It enables learners to acquire skills for wise buying and selling.
- It creates a firm foundation for further education and training in business and other related fields.
- It enables one to understand and appreciate the basic economic issues that affect the society such as increase in prices of goods and services.
Career Opportunities In The Field Of Business Studies
- Auditor.
- Logistics analyst.
- Human resources specialist.
- Accountant.
- Operations analyst.
- Marketing manager.
- Financial advisor.
- Financial analyst
- Entrepreneur
Money
- whatever serves society in four functions: as a medium of exchange, a store of value, a unit of account, and a standard of deferred payment.
- Money is power if you utilize it with knowledge. Money is dangerous if you are greedy for money and utilize it without thought. – Vijay Sharma
Uses Of Money In Daily Life
- First, money serves as a medium of exchange, which means that money acts as an intermediary between the buyer and the seller. Instead of exchanging accounting services for shoes, the accountant now exchanges accounting services for money. This money is then used to buy shoes. To serve as a medium of exchange, money must be very widely accepted as a method of payment in the markets for goods, labor, and financial capital.
- Second, money must serve as a store of value. In a barter system, we saw the example of the shoemaker trading shoes for accounting services. But she risks having her shoes go out of style, especially if she keeps them in a warehouse for future use—their value will decrease with each season. Shoes are not a good store of value. Holding money is a much easier way of storing value. You know that you do not need to spend it immediately because it will still hold its value the next day, or the next year. This function of money does not require that money is a perfect store of value. In an economy with inflation, money loses some buying power each year, but it remains money.
- Third, money serves as a unit of account, which means that it is the ruler by which other values are measured.
- Money fulfills your personal and family needs and desires:
Money has the power to buy goods and services. With money, a person can fulfill his daily living needs and desires. With money, you can buy food, clothes, a home, a car, holiday tour packages, and gifts. With money, you can buy a high-speed internet connection and good quality equipment for work and business.
Key security features of the Kenyan Currency
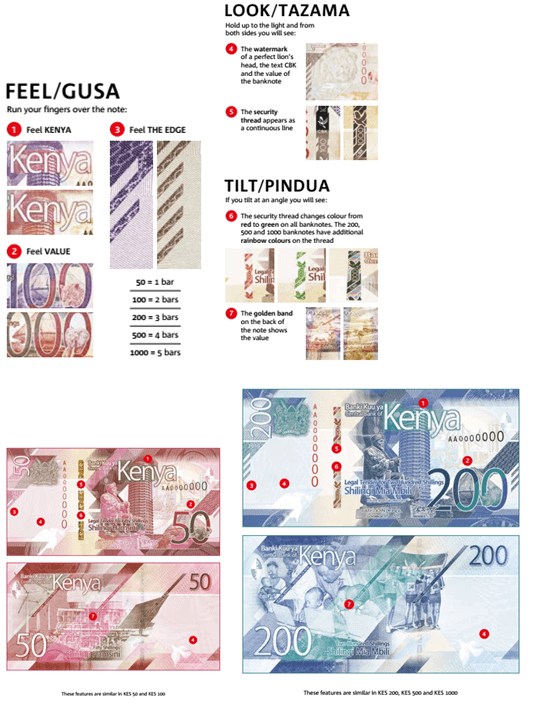
Themes And Symbols In The Kenyan Currency


Personal Goals
- Goals are defined as the desired states that people seek to obtain, maintain, or avoid. Personal goals are goals related to your work, relationship, finances, and other aspects of life.
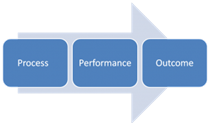
There are three types of goals- process, performance, and outcome goals.
- Process goals are specific actions or ‘processes’ of performing. For example, aiming to study for 2 hours after dinner every day. Process goals are 100% controllable by the individual.
- Performance goals are based on personal standard. For example, aiming to achieve a 3.5 GPA. Personal goals are mostly controllable.
- Outcome goals are based on winning. For a college student, this could look like landing a job in your field or landing job at a particular place of employment you wanted. Outcome goals are very difficult to control because of other outside influences.
Process, performance, and outcome goals have a linear relationship. This is important because if you achieve your process goals, you give yourself a good chance to achieve your performance goals. Similarly, when you achieve your performance goals, you have a better chance of achieving your outcome goal.
General Goal Setting Tips
- set both short- and long-term goals
- set SMART goals
- set goals that motivate you
- write your goals down and put them in a place you can see
- adjust your goals as necessary
- Recognize and reward yourself when you meet a goal
Set all three types of goals- process, performance, and outcome – but focus on executing your smaller process goals to give you the best chance for success!
- specific – highly detailed statement on what you want to accomplish (use who, what, where, how etc.)
- Measurable- how will you demonstrate and evaluate how your goal has been met?
- Attainable- they can be achieved by your own hard work and dedication- make sure your goals are within your ability to achieve
- Relevant- how do your goals align with your objectives?
- Time based- set 1 or more target dates- these are the “by whens” to guide your goal to successful and timely completion (include deadlines, frequency and dates)
Be Clear About Your Purpose in Life
First, be clear about your purpose in life. Having a clear vision in life gives you direction. You know where you are coming from and where you are going. The destination is definite, and this gives you a foundation for your goal setting.
Why These Goals?
Having a foundation for goal setting gives you a destination. The next step is to look at the goals you have in mind and ask yourself why these goals in specific. Let’s say you want to get from Nairobi to Mombasa. You can walk, run, hire a taxi, take a bus, take a train or take a flight.
In the end, you will have to choose one means of transport to get you to Mombasa. If you take a bus, ask yourself why the bus? Why not walk or take a flight? If you can answer the why in your goals. And hopefully, your answer will not be because everyone is doing it, then you are on the right path.
Do The Goals Motivate You?
Do you get motivated when you look at your goals? Remember your why. If the answer to your why is because everyone is doing it, the motivation is going to low. When challenges set in and everyone gives up, you will give up with them or give up when others are still on the move.
Set goals that motivate you. Motivation has to come from the heart. Remember, this is a journey. It is not a destination in itself. Your inner drive will keep you moving when the going gets tough.
You Goals Must Be Specific To You
Your goals have to be specific to you. Do not set random goals just because that is what is expected from you. Let’s say you have a target to meet at the end of the month set by your company. The targets are not specific to you. In most cases, they are distinct to your department but general to you and your colleagues.
A successful person will take the targets set and personalize them. What is it you want to achieve at the end of the month as far as the goals set for your team are concerned? Do you want to meet the exceptions, or do you want to exceed them? Set your weekly and daily goals to reflect what you want to achieve as an individual.
Goals Have To Be Relevant To Your Higher Purpose In Life
Your goals must be relevant to your higher purpose in life. If not, you will deviate from your purpose or vision. Set goals to reflect, and feed your cause. The danger in working on plans that don’t align with your purpose or mission, you end up working for other people.
Proverbs 16:3 New International Version (NIV)
Commit to the Lord whatever you do, and he will establish your plans.
Starting to Set Personal Goals
You set your goals on a number of levels:
- First you create your "big picture" of what you want to do with your life (or over, say, the next 10 years), and identify the large-scale goals that you want to achieve.
- Then, you break these down into the smaller and smaller targets that you must hit to reach your lifetime goals.
- Finally, once you have your plan, you start working on it to achieve these goals.
This is why we start the process of setting goals by looking at your lifetime goals. Then, we work down to the things that you can do in, say, the next five years, then next year, next month, next week, and today, to start moving towards them.
Step 1: Setting Lifetime Goals
The first step in setting personal goals is to consider what you want to achieve in your lifetime (or at least, by a significant and distant age in the future). Setting lifetime goals gives you the overall perspective that shapes all other aspects of your decision making.
To give a broad, balanced coverage of all important areas in your life, try to set goals in some of the following categories (or in other categories of your own, where these are important to you):
- Career – What level do you want to reach in your career, or what do you want to achieve?
- Financial – How much do you want to earn, by what stage? How is this related to your career goals?
- Education – Is there any knowledge you want to acquire in particular? What information and skills will you need to have in order to achieve other goals?
- Family – Do you want to be a parent? If so, how are you going to be a good parent? How do you want to be seen by a partner or by members of your extended family?
- Artistic – Do you want to achieve any artistic goals?
- Attitude – Is any part of your mindset holding you back? Is there any part of the way that you behave that upsets you? (If so, set a goal to improve your behavior or find a solution to the problem.)
- Physical – Are there any athletic goals that you want to achieve, or do you want good health deep into old age? What steps are you going to take to achieve this?
- Pleasure – How do you want to enjoy yourself? (You should ensure that some of your life is for you!)
- Public Service – Do you want to make the world a better place? If so, how?
Spend some time brainstorming these things, and then select one or more goals in each category that best reflect what you want to do. Then consider trimming again so that you have a small number of really significant goals that you can focus on.
Talents and Abilities
For many people, the words “talent” and “ability” are interchangeable. Understanding the difference between them can make all the difference in how we live and work. Here at Pro/spur, one of the first lessons we share with our players is recognizing their talent vs. their ability. So what is the difference?
Talent is what you’ve been given.
Ability is how you grow the talent you’ve been given.
Right now, there are more than 8,000 pro players in Minor League baseball. Do you know how many of those players have enough talent alone to make it to the Big Leagues and stay there? The answer: not that many.
Ways Of Nurturing Talents
Create an Open Culture
Firms are a product of multiple people’s contributions. Each worker should feel like their words have weight and that their input is valued.
Everything starts with the workplace culture, which gives new starters the confidence to stick around and keeps more experienced personnel grounded and loyal. Encourage employees to speak up if they have any concerns or thoughtful ideas.
Develop Mentoring Schemes
Mentoring is an enormous part of nurturing talent. However, finesse is required in how your company approaches it. Vague instances of encouragement aren’t enough to keep workers motivated and performing well.
Introduce Automation
Workers with many responsibilities can soon become overwhelmed. The most overworked staff members may find little time to focus on their own professional development.
Automation can ease these burdens somewhat. These technologies can assume many of the admin tasks a worker needs to do. Signing paperwork, scheduling updates, responses to routine emails – these are all tasks automation can oversee instead of the employee. Work-related stress can be reduced as a result.
Offer Flexibility
Nurturing talent can’t be done under overly rigid work practices. Employees need to grow both personally and professionally and to do so effectively, they need a level of control.
Keep Innovating
Your business needs to aspire to be greater constantly. Only then can you expect your workers to adopt a similar attitude.
Of course, your business may be more concerned about surviving rather than thriving these days. Irrespective of your circumstances or the economic conditions you’re facing, your company must keep pushing to innovate and excel within its industry.
Personal Talents and Abilities
- Communication.
- Interpersonal skills.
- Leadership.
- Problem-solving.
- Time management.
- Adaptability.
- Critical thinking.
- Organization.
Five kinds of talent categories:
- Self-conceptual talents – like self-awareness, self-regulation, self-motivation, and self-confidence.
- Social talents – like social awareness, communication, relationship management, collaboration, and influence.
- General talents – like language skills, mathematical abilities, reasoning, visual-spatial processing, and learning abilities.
- Specific expertise – like strategic thinking, arts, writing, research, sports, design, storytelling, and kinesthetic abilities.
- Fun talents – any cool talents such as exceptional taste, ventriloquism (ability to make your voice appear from somewhere else or with delay), and hypermobility, to name a few.
Ethical Issues Related To Use Of Talents And Abilities In Business
Ethical issues in business occur when a decision, activity or scenario conflicts with the organization’s or society's ethical standards. Both organizations and individuals can become involved in ethical issues since others may question their actions from a moral viewpoint.
- Discrimination and harassment
Two of the most significant ethical issues that HR professionals and managers face are discrimination and harassment. The consequences of discrimination and harassment in the workplace can negatively impact the finances and reputation of the organization. Many countries have anti-discrimination laws to protect employees from unfair treatment. Some anti-discrimination areas include:
- Age: Organizations and internal policies cannot discriminate against employees who are older.
- Disability: To prevent disability discrimination, it's important to accommodate and provide equal treatment for employees with mental or physical disabilities.
- Equal pay: Equal pay focuses on ensuring that all employees receive equal compensation for similar work, regardless of religion, gender or race.
- Pregnancy: Pregnant employees have a right not to be discriminated against on account of their pregnancy.
- Race: Employees should receive equal treatment, regardless of ethnicity or race.
- Religion: Employees' religious beliefs should not affect how anyone within the organization treats them.
- Sex and gender: An employee's sex and gender identity should not influence their treatment while working at an organization.
- Ethics in accounting practices
Laws require organizations to maintain accurate bookkeeping practices. Unethical accounting practices are a serious issue, especially for publicly traded companies. The legislation specifies financial report requirements aimed at protecting shareholders and consumers. All organizations have to keep accurate financial records and pay taxes to attract investment and business partners regardless of the size of the company. - Nepotism or favoritism
As a hiring manager or HR professional, you may want to employ an acquaintance or family member because of your connection to them. Even if you adhere to recruitment policies to ensure a fair process, some employees may still consider this as nepotism or favoritism. Favoritism occurs when managers treat some employees better than others for no professional reason. This can reduce productivity and job satisfaction in other employees, which may negatively impact the entire organization. - Workplace health and safety
All employees have a right to a safe working environment and work conditions.
Importance Of Nurturing Talents And Abilities
Nurturing internal talent can benefit your business in many ways:
Facilitate success. Nurturing the talent you already have allows you to facilitate opportunities for cross-training, career development and networking.
Create a culture of innovation and empowerment. Nurturing your existing talent creates a culture of innovation and empowerment, in which employees know they are valued and they are motivated to strive for excellence
Open leadership opportunities. Nurturing the talent of your teams enables you to foster a culture in which leadership opportunities abound.
Early Civilization in Africa - Grade 7 Social Studies Revision Notes
- Meaning Of State, Kingdom And Empire
- Social Organisation Of Selected African Communities Up To 1900
- Human Diversity And Inclusion
Meaning Of State, Kingdom And Empire
State
A territory is considered as an organised political community under one government
Empire
An extensive group of semi autonomous states ruled by one ruler
Kingdom
A state or territory ruled by a king or queen
The Ancient Egypt
Factors that led to growth of Ancient Egypt Civilization
- Presence of river nile
It the annual flood of river nile and the use of shadoof method of irrigation boosted agriculture - Early technology
It ushered in the bronze stage where copper and tin were used to make simple tools such as chisels and needles
Artisans also made pots for storage and cookery purposes using potter’s wheel - Population
High population in Ancient Egypt provided ready manpower and market - Strong military and leadership
They ensured growth of the kingdom through conquests and assimilation of conquered neighbours into the empire - Use of hieroglyphic
The formal writing helped keep reliable and accurate records in religion, government and history - Use of the calendar
Tracking of days and monitoring events such as annual flooding of the nile, planting and harvesting period - Specialised workers
They worked in various institutions. They helped in keeping recods in the Egyptian empire.
They recorded harvest, finances and history
The Great Zimbabwe
Great Zimbabwe was a city near Masvingo in the central part of the modern day Zimabwe, Mozambique and Botstwana.
It existed between 1000BC to 1500BC
Zimbabwe is a shone word meaning “stone houses”
Great Zimbabwe had a centralized government with hereditary kings. This system of government led to the rise and growth of the kingdom
Factors that led to the growth of the Great Zimbabwe civilization
- Strong agricultural economy
- Existence of several minerals deposits such as gold, copper
- Trade
- Strong leadership
- Acquisition of firearms in exchange of goods
- Strong army
- Religious beliefs brought them together
The Kingdom Of Kongo
Factors that led to the growth of kingdom of Kongo
- Strategic location of the kingdom
- Favourable climate and the kingdom its closeness to congo river which supported agriculture throughout the year
- Arrival of Portuguese
- Religion
- Trade
- Christianity
Locating ancient kingdoms on a map of Africa
Pupil’s activity
Page 77-78
Contributions Of Early African Civilisation To The Modern World
- Modern civilisation owes ts current development to the ancient civilization.
- Ancient Egypt was the beginning of building designs and construction of permanent buildings we have today.
- The hieroglyphics form of writing in Egypt used to keep records developed into the modern writing and education
- The knowledge of planning and prediction of seasons based on calendar started in the early civilisation. Today it is has been developed further to include weather forecasting in predicting accurate changes.
- The industrial development in the ancient kingdoms was based on simple skill. Copper and tin were used in ancient Egypt to make items. Today most of the industries use metals and alloys to make construction and infrastructural equipment.
- The modern irrigation technology barrows a lot from the ancient irrigation techniques such as shadoof. This has been applied in the agricultural sector
- Tools such as jembes/hoes used in farming today were developed in the ancient civilisation
- The political structure of modern government resembles the early civilisation goverment
Social Organisation Of Selected African Communities Up To 1900
Locating areas by the Ogiek, Zulu and Asante communities in Africa
PUPILS’ ACTIVITY
PAGE 81
Social Organisation Of The Ogiek Community Up To 1900
Ogiek are southern nilotic speakers
Most of them live in the county of nakuru, mau and mt elgon forests
- Family was the basic unit among the ogiek community
- The lineage was responsible for enforcing traditional law and order
- Father was head of the family
- The ogiek were polygamous
- There was division of labour among the ogiek community
Men provide for the family needs, provide leadership and security
Women worked in homestead, bear children and do household chores
Children helped with household chores, cultivating in farms and artisanship - The ogiek were a patriarchal society- men owned property and passed it to their sons
- The ogiek believed in one supreme being called Tororet
- They believed also in the existence of ancestral spirits called Oiik
- They had diviners who could foretell the future using supernatural powers
- Both boys and girls were initiated
Boys ceremony was called tumdo op went
Girls ceremony was called tumbo op tiipik - Intiated boys of the same age group sets known as ipinda
- The ogiek used plants and herbs from forest for treating diseases
Social Organisation Of The Zulu Community Up To 1900
Zulu are Ngni people, bantu speaking
They occupy Kwazulu natal province in South africa
In the Ngumi languages izulu means heaven or weather
The zulu clans referred to as the isizwe
The zulu society was organised into parilineal sibs. The sibs were further divide into lineages which were composed of descendants of a common ancestor
Most households comprised extended families who lived in one household called kraal
Men inherited everything. Inheritance was patrilineal
The zulu people were polygamous. Men married many wives and lived with them with the extended family in the kraal.
Men paid dowry in terms of cows and gifts during the weeding day umabo
The zulu community believed in Umhlanga or reeds dance ceremony
Beadwork was a prominent wttire that worn at the Umahlanga
Beadworks was a sign of communication
It also symbolised wealth status of a person
Zulu believed in one God called uNkulunkulu
The controlled day to day human life of the Zulu community
The zulu had traditional mediceine men who treated the sick
Social Organisation Of The Asante Community Up To 1900
Asante are Akan speaking people
They live in the central part of the Modern day Ghana
Are organsised into clans whch is headed by a chief
Each clan speaks its own dialect of the Aken language
They believe in one supreme creator called Nyame
Ancestors were believed to connect people to Nyame
Asante empire leader was called Asatehene
He also acted as a spiritual leader
Omamhene and chiefs were all religious leaders who presided over religious ceremonies
Golden stool was th symbol of national unity in the Aasnte empire
It symboised ones and authority from the Asantehene
It was based in Kumasi, the capital of Asant empire
Odwira festival was an annual ceremony
They believed in the spirits of the departed rulers
Asante were socially stratified into 5 main divions
1st division – king and those close to the king
- Lived in the capital of Kumasi
- Were wealthy and lived in luxury
2nd division – consisted of the chiefs and top officials who assisted the king in enforcing law and order
3rd division – those who had acquired a lot of wealth hence respect in the society
4th division – comprised of ordinary farmers, traders and fishermen
5th division – the lowest class was for the slaves
Asante families were extebded and matrilineal – mother’s brother was the legal guardian of her children
Asante were experts in form of decoration, logos, arts, sculture and pottery
These were known as Adinkra symbols
Comparing the social organisation of thr Ogiek, Zulu, and Asante community up to 1900
| Aspect of social organisation | The Ogiek | The Zulu | The Asante |
| Marriage | Polygamous | Polygamous | |
| Art and Clothing | |||
| Family set up | |||
| Name of their God | Tororet | believed in one God called uNkulunkulu | supreme creator called Nyame |
| Inheritance | The ogiek were a patriarchal society- men owned property and passed it to their son | Men inherited everything. Inheritance was patrilineal | |
| Circumcision | Both boys and girls were initiated |
Human Diversity And Inclusion
Personality Attributes Which Make Individuals Different From Others
Personality attributes are qualities or characteristics that differentiate the character, action and attitude of a person from one another
| Personality attribute | Description |
| Openness to experience | |
| Introversion | |
| Extroversion | |
| Agreeableness | |
Desirable and undesirable personality attributes in a multicultural society
Peace and Conflict Resolution
Peace
A state of calmness when there is no war
Conflict resolution
This is the process or act of solving or settling a disagreement.
Peace and conflict for personal well being
People and Population - Grade 7 Social Studies Revision Notes
Human Origin
Traditional Stories On Human Origin
This is an attempt by communities of people to explain their origin.
It is given through Oral Traditions, myths and legends.
It mainly states that the first people were created by God
- Kikuyu community
According to the Agikuyu, God (Ngai) appeared and created their ancestors (Gikuyu and Mumbi) at Mukurwe Wa Gathanga near present day Muranga
Gikuyu and Mumbi gave birth to 9 daughters who later formed the nine class - Bukusu
The bukusu of wetern Kenya belives that the fist man was called Mwambu.
He was made from mud by WELE KHAKABA (God the creator) at a place called Mumbo which means west.
God created a wife for him. Mwambu and his wife moved from Mumbo to the foothills of Mt. Masaba-mt elgon- where their descendants grew in numbers to become the Abaluhya community - Maasai
Once upon a time Enkai (God) owned all the cattle in the world. One day he opened the sky and replaced all the cattle he owned from heaven to earth using a long rope.
Enkai created 3 communities on earth
The Torrobo(also the Ogiek) , the gikuyu whom God bless with seed and grain and the Maasai whom God blessed with all the cattle of the world - Akamba community
The akamba community believes that God was called Mulungu. He created the first man MUNDU and woman KIVETI.
They were then placed on top of Nzaui Hill in makueni.
He blessed them with children and livestock - Nandi community
According to the Nandi, the first two people came from the knees of a giant man, which began to swell until they burst. A man came from one knee and a woman from the other. These became the ancestors of the Nandi-speaking people of Kenya. This is an example of myths in certain communities that do not directly refer to God‟s creation.
Religious Stories On Human Origin
This presents man and everything else as having been created by God.
It is contained mainly in
- The Bible (used by Christians)
God created the heaven and earth according to Genesis chapter 2 - The Quran (used by Muslims).
Islam believes that all living and non living things were created by Allah - Hindu
The universe was created by Brahma. He is regarded as the hindu god of creation
Factors Proving That Africa Is The Cradle Of Humankind
- African Savannas were ideal for primates.
- The moist, warm and varied climate supported animal and plant life.
- Archaeological sites were discovered in the Great Lakes region of eastern Africa and along the Great Rift Valley. This confirms that hominids were living in this region by the time the rift valley was being formed.
- The earliest apes and various animals may have first lived around what is now Lake Victoria and the rift valley, then some went northwards into Europe and Asia. This was because, at that time, areas along the Equator (especially central and west Africa) were covered in thick forest. Around the Great lakes of East Africa was the Savannah (grassland with scattered trees and bushes). It was in this environment that man had his first home.
- Due to earth quakes and volcanic eruptions during the formation of the great rift valley, allot of dust was brought up, which covered places where hominids had left their weapons, tools, their own bones, and those of other animals. These became archaeological sites in east Africa
- Remains found in Africa especially Eastern Africa are evidence that Africa is the cradle of mankind.
Evolution
Evolution is a natural process of gradual and continuous change of living organisms from a lower (simpler) state to a better-adapted (complex) and superior one.
Archaeological site or prehistoric site
Is a place where human remains were found
Archaeologists
Are scientists who excavated the human remains for study
Fossils
Human remains
Stages Of Man’s Evolution
- Ramapithecus also called kenyapithecus
The 15-12 million year-old remains of Ramapithecus were found by Mary and Louis Leakey at Fort Ternan near kericho and also at Samburu hills and in the Lakes Turkana and Baringo basins. Ramapithecus and other manlike creatures were also discovered in Europe, India and China.
Characteristics of Ramapithecus
- He was manlike.
- He had small canines.
- He was quadrapedal (he moved on his four limbs), though he occasionally walked on two legs
- Australopithecus/southern ape/zinjathropus
Remains of Australopithecus were found at Taung in Botswana in 1924 by Raymond Dart, at Olduvai Gorge in Tanzania by Mary Leakey in 1959 and throughout eastern Africa e.g. regions around Lake Natron in Tanzania, Lake Turkana in Kenya and Omo River valley in Ethiopia.
Characteristics of Australopithecus- He was the earliest most manlike hominid.
- He had a pelvis and leg that were similar to modern man‟s.
- He was bipedal (walked on two limbs).
- Could defend themselves.
- Could attack their enemies.
- Could see or sense impending danger from a distance.
- Could grasp objects with ease.
- May have been hairy, short and strong.
- Had a large face and low forehead.
- Had stereoscopic vision.
- Had much larger teeth, skull and jaws.
- His brain was smaller than modern man‟s, but larger than that of the most intelligent ape: the Gorilla.
- Homo habilis (Practical man).
This was the first species of the genus Homo. His two and a half to one and a half million- year old remains were found at Olduvai Gorge by Jonathan Leakey in 1964, Hadar and Omo River valley in Ethiopia and Koobi-For a in the lake Turkana area in 1972.
Characteristics of Homohabilis- He was five feet tall.
- He had a skull similar to modern man‟s in shape.
- He was omnivorous.
- He could grasp objects.
- He made and used tools.
- HOMOERECTUS (upright man).
Homoerectus lived between two million to two hundred thousand years ago.- He was five and a half feet tall.
- He was bipedal (walked on two legs).
- He made and used tools, such as hand-axes, crude spears and arrowheads from stone, bone and wood.
- Homo sapiens (Thinking/Intelligent man).
Homo sapien appeared between two hundred thousand and a hundred and fifty thousand years ago.
Characteristics of Homosapien- He was under six feet tall
- He had small teeth.
- He had a steep and well-rounded forehead.
- He had long straight legs.
- He made a variety of more refined tools i.e. microliths.
- He was a fisherman and hunter-gatherer.
- He domesticated plants and animals.
- Remains of Homosapien were found at:
- Eliye springs near Lake Turkana,
- Kanjera and Kanam in Kenya,
- Bodo and Omo river valley in Ethiopia,
- Ngaloba in Tanzania.
Weather - Grade 7 Social Studies Revision Notes
Weather
Weather is the daily atmospheric conditions of a place at a particular time.
Elements Of Weather
- Temperature
- Measure or degree of hotness or coldness of a place
- Humidity
- The amount of water vapour or moisture in the atmosphere
- Precipitation
- All forms of moisture which fall from the atmosphere to the earth’s surface
- Rainfall is a form of precipitation formed from clouds that in form of water droplets
- Atmospheric pressure
- Wind
- Moving air on the surface of the earth
- Sunshine
- Direct rays of sunlight on the surface of the earth
- Cloud cover
- Mass of tiny droplets of water or ice formed through condensation
Analysis and interpretation of weather conditions
Diurnal/daily Temperature range
-Difference between the maximum and minimum temperature for any one day.
Mean Daily Temperature
-Average of the maximum and the minimum daily temperatures.
Mean Monthly temperature
-Sum of mean daily temperatures in a month divided by the number of days in that month.
Mean Monthly minimum Temperature
-Sum of daily minimum temperatures divided by the number of days in that month.
Mean Monthly Maximum Temperature
-Sum of daily maximum temperatures divided by the number of days in that month.
Mean Annual Temperature
-Sum of mean monthly temperatures divided by 12.
Mean Annual Temperature Range
-Difference between the highest and the lowest mean monthly temperatures in a year.
Monthly Rainfall Total
-Sum of rainfall recorded in a month.
Annual Rainfall Total
-Sum of monthly rainfall totals for 12 months.
Mean Monthly Rainfall
-Sum of rainfall totals for a particular month over several years divided by the number of the years of observation.
Mean Annual Rainfall
-Sum of mean monthly rainfall for 12 months of the year.
Factors To Consider When Siting A Weather Station
Weather Station
- A place where observation, measuring and recording of weather elements is done
Factors to Be Taken Into Account When Sitting a Weather Station
- Open space
- An open place where there is little obstruction of weather elements.
- Accessible place
- Accessible place so that recording can be done easily.
- Gently sloping land
- A fairly level or gently sloping ground (5◦) so that it’s easy to position weather instruments.
- Security
- The place should have security
- The place should provide a wide view of the surrounding landscape and the sky.
- The site should be free from flooding.
Constructing Selected Instruments For Measuring Elements Of Weather
Instruments for Measuring Elements of Weather
- Thermometer- measures temperature
- Hygrometer- measures humidity
- Rain gauge-measures rainfall
- Barometer-measures air pressure
- Sunshine recorder-measures sunshine duration and intensity
- Wind vane –measures wind direction
- Anemometer-measures wind speed
- Constructing a wind stock
PUPIL’S ACTIVITY
PAGE 52
Materials needed- A paper cup
- Clay and plasticine
- A pin
- Drinking straw
- Marker pen
- A white circular cardboard
- Square and triangular paper cuttings
- A pencil with a rubber head
- Constructing a rain gauge
PUPIL’S ACTIVITY
PAGE 53
Materials needed- A 2-litre plastic bottle
- Ruler
- A ballpoint pen
- Masking tape
- A scalpel or pair of scissors
- Constructing a Windsock
PUPIL’S ACTIVITY
PAGE 53-54
Materials needed- Cylindrical bag
- String
- A scalpel
- Water paints
- An empty plastic fat/magarine tin
- Masking tape or cellotape
- A pole with a pointed end
- Painting brushes or chewed sticks
Significance of weather to human
- Helps us to be aware of natural calamities related to weather before they occur so as to take precautionary measures.
- Guiding tourists on when to visit national parks.
- Helps farmers to plan their activities such as planting, harvesting, etc.
- Ensures air and water transport is carried out safely.
- Helps sporting people to plan their training and competition schedules.
- Helps people to plan many other activities such as mining, electricity generation, holiday events, etc.
- Helps fishing communities to plan their activities
Historical Information
Sources of historical information in the society
- Monuments
- Caves
- Historical pictures
- Folk songs
- Old coins
- Recorded folk stories
- Archaeological sites
- Textbooks
- Articles
- Myths
- Artefacts,
- Fossils
Primary and secondary sources of information
Primary source is historical information that are created during the time period studied or were created at a later age by participant in even being practised
Secondary source is historical information that interprets or analyses a historical phenomenon
| Primary sources of historical information | Secondary sources of historical information |
Ways of preserving historical information
Significance of historical information in providing evidence of past accounts
| Sources of historical information | Significance of sources of information | How did it provide evidence of past accounts |
| Primary source | Provide cultural values of the society | They are preserved in museums and cultural centres for viewing |
| Secondary Sources | Provide knowledge to students of history | They are stocked in libraries and archives |
The Earth and the Solar System - Grade 7 Social Studies Revision Notes
- The Earth And The Solar System
- Rotation Of The Earth
- Revolution of the Earth
- The Internal Structure Of The Earth
The Earth And The Solar System
Solar system is the group of heavenly bodies comprising the sun and the planets.
The Origin Of The Solar System
- The passing star theory
A star with a greater gravitational pull passed near the sun
It attracted large quantities of gaseous materials from the sun
The materials split, cooled and condensed to form planets
The planets were set in orbit by the passing star - The nebula cloud theory
There was a slowly rotating cloud of dust and gas called Nebula
It cooled and began to contact
Rotation speed increased and successive rings of gaseous materials were formed.
The rings condensed to form planets
The central gaseous material remained as the sun
Size of the earth
Equatorial diameter-12756km
Equatorial circumference-40085km
Polar diameter-39995km
Surface area of the earth-510×106 km2
Water surface - 73%.
Mercury
Nearest from the sun
Its 58m km from the sun
Has no satellites
Takes approximately 88 earth days to revolve around the sun
Venus
2nd planet from the sun
It’s 108m km from the sun
One of the brightest planets
Can be seen clearly with naked eyes
Takes approximately 225 earth days to revolve around the sun
Slightly smaller than the earth
Has no satellites
Together with the earth they are called twin planets due to having many similarities
Mars
Also called The Red Planet because when it’s observed through a telescope it appears reddish.
The 4th from the sun
Slightly smaller than the earth
Approximately 228m km from the sun
Takes 687 earth days to revolve around the sun
Between Mass and Jupiter there are small celestial bodies called planetoids.
Has no satellite.
Jupiter
5th planet from the sun
Approximately 778m km from the sun
Largest in the universe
Rotates on its own axis at very fast speed
Has flattened poles due to its fast speed of rotation
Has very thick layers of ice on its surface
takes 12 earth years to revolve around the sun
Has 16 satellites
Saturn
6th planet from the sun
Second largest planet
Approximately 1427m km from the sun
Takes 29 ½ earth years to revolve around the sun
Has a ring around it
Has 18 satellites
Uranus
7th planet from the sun
About 4 times bigger than the earth
Approximately 2870m km from the sun
Also rotates very fast
Also has flattened poles due to fast speed of rotation
It appears greenish foe being surrounded by methane gas
Has 8 satellites
Takes 84 earth years to revolve around the sun
Neptune
One of the farthest from the sun
8th planet from the sun
Approximately 4497m km from the sun
Has 8 satellites
Takes 165 earth years to revolve around the sun
Very similar in size, colour and character with Uranus
The shape of the earth
The shape of the earth is called geoid/ovoid/oblate spheroid due to being an imperfect sphere by being wide at the equator and flat at the poles.
The Position Of The Earth In The Solar System
The 3rd planet from the sun
The earth and the heavenly bodies make the universe
The only planet that supports life
The home of man
Approximately 149m km from the sun
Takes 365 ¼ days to revolve around the sun
Has one satellite, the moon
Rotation Of The Earth
Movement of the earth on its own axis (imaginary line through the centre from N pole to S pole
Rotates through 360º
Takes 24 hours (day) to complete 1 rotation
Rotates in an anticlockwise direction (west to east)
Effects of Rotation of the Earth
- Creates day and night because at any one time one side of the earth faces the sun (day) and the other remains in darkness (night).
- Causes deflection of winds and ocean currents in the N hemisphere to the left and in the S hemisphere to the right.
- It causes rising and falling of ocean tides.
- Causes time difference between longitudes
Effects of Rotation of the Earth on human activities
| Effects of Rotation | How rotation affects human activities |
| Day and night | Planning day and night activities |
| High and low tides | Helps in fishing activities Sea transport - |
| Deflection of winds and ocean currents |
|
| Time difference |
|
Revolution Of The Earth
- Movement of the earth in its orbit around the sun.
- It’s in anticlockwise direction.
- The orbit of the earth’s revolution is elliptical.
- Takes 365 ¼ days in a year or 366 days in a leap year (every 4 years).
- The sun moves from the tropic of cancer to the equator and then towards tropic of Capricorn and back to the tropic of cancer.
- 21st march and 23rd September are called equinoxes because the length of day and night is equal. The sun is vertically overhead at noon at the equator.
- 21st June is called summer solstice because its summer in the N hemisphere. The sun is vertically overhead at noon at the tropic of cancer.
- 22nd December is called winter solstice because its winter in the S. hemisphere. The sun is vertically overhead at noon at noon at the tropic of Capricorn.
- Solstice is the period of maximum tilting of the earth towards the sun.
Effects Of The Revolution Of The Earth
- Causes the four seasons summer, autumn, winter and spring due to the movement of overhead sun causing changes in the heat belt.
- Causes variation of day and night’s lengths due to the earth’s axis being inclined to the path of revolution at an angle of 60◦.
- Equinoxes have equal lengths of day and night.
- Summers have longer days and shorter nights.
- Winters have longer nights and shorter days.
- Causes changes in the altitude of the midday sun due to the earth’s orbit being elliptical.
- Highest altitude during equinox
- Lowest altitude during solstices
- Causes lunar eclipse due to revolution bringing the earth in line with the sun and the moon.
Effects of the Revolution of the earth on human activities
| Effects of Revolution | How revolution affects human activities |
| Changes in the position of midday sun at different times of the year | |
| Varying length of day and night at different times of the day | |
| Seasons |
The Internal Structure Of The Earth
- Crust/Lithosphere
- Outermost layer of the earth
- Made of soils and other loose deposits of sand
- The dominant rocks are granites.
- Extends 0-50km
- Has 2 layers
- Sial
- Also called continental crust
- Made of light coloured rocks
- Called sial because it’s made up of silica and aluminium.
- Sima
- Also called oceanic crust
- Mainly made of basaltic rocks which are brittle.
- Called sima because it is made of silica magnesium and iron.
- Sial
- Mohorovicic Discontinuity (Moho)
- A definite zone of discontinuity between the crust and the mantle.
- Was discovered by Dr. Andrija Mohorovicic in 1909.
- The Mantle/Asthenosphere
- Layer lying between the crust and the core
- Made of iron and magnesium
- Has two layers
- Upper mantle
- Rocks are more elastic than those of sima.
- Temperature is about 1000°c.
- lower mantle
- Rocks are like very viscous liquid.
- Temperature ranges between 1000°c to 3000°c.
- Upper mantle
- Gutenberg Discontinuity
A definite zone of discontinuity between mantle and core. - Core/barysphere/Centrosphere
- The innermost/central layer of the earth.
- Has 2 layers
- Outer Core
- Composed of very dense rocks
- Made up of nickel and iron
- Temperatures are up to 3700°c.
- Inner Core
- A solid mass of mainly iron
- Temperatures are estimated to be 4500°c to 5000°c.
- Outer Core
- The Atmosphere
Layer of gases surrounding the earth.
The earth revolves with it because its held onto it by gravity
It’s about 330km thick.
Composition of the Atmosphere- Gases-exist as a mixture
- Smoke particles
- Dust particles
- Water vapour
- hydrosphere
Ocean and seas
Natural and Historic Built Environment in Africa - Grade 7 Social Studies Revision Notes
Maps And Mapwork
A map is a representation of the earth or part of it on a flat surface.
Position of Africa
- Africa lies between latitude 37ºN and 35ºS and on longitude 18ºW and 52ºE.
- Separated by water from all other continent except at the point where it joins Asia.
- Mostly Easterly point is called ras hafun(cape guardafui)
- Mostly westerly is cape verde
- Mostly northerly is cape bon
- Mostly southerly is cape agulhas
- Africa is connected to sinai peninsula by suez canal
- Separated from Spain by strait of gibraltar
- Separated from Arabia by strait of bab el-mandeb
Shape of Africa
The northern half is very wide while the southern is much narrower
At the cape guardafui extends outwards in the shape of a horn therefore the horn of Africa
Size of Africa
Africa is the second largest continent in the world
Has an area of about 30.3 million square kilometres (20% of the total land surface)
It measures 8000 km from north to south and 7400km from east to west
Other continents
- Asia – 43608000km2
- Africa – 30335000km2
- North America – 25349000km2
- South America – 17611000km2
- Antarctica – 13340000km2
- Europe – 10498000km2
- Australia – 8923000km2
Countries That Makes Up The Africa Continent
Africa has the largest number of countries in the world making o total of 55 countries
- Algeria 2381741km2
- Angola 1246700km2
- Benin 115773km2
- Botswana 600372km2
- Burkina faso 274200km2
- Burundi 28490km2
- Cameroon 475900km2
- Cape verde 7275km2
- Central africa republic 622984km2
- Chad 1284000km2
- Comoros 2117km2
- Congo 34965km2
- Cόte d’ ivoire 322463km2
- Djibouti 23310km2
- DR congo 2345409km2
- Egypt 1101449km2
- Equatorial guinea 28051km2
- Eritrea 124320km2
- Ethiopia 1221900km2
- Gabon 267667km2
- Gambia 11369km2
- Ghana 238537km2
- Guinea 245957km2
- Guinea bisau 36125km2
- Kenya 582648km2
- Lesotho 30460km2
- Liberia 111369km2
- Libya 1775000km2
- Madagascar 592900km2
- Malawi 118484km2
- Mali 1240192km2
- Mauritania 1030700km2
- Mauritius 2040km2
- Morocco 724730km2
- Mozambique 802000km2
- Niger 1267000km2
- Namibia 824295km2
- Nigeria 923773km2
- Rwanda 26338km2
- Sӑo Tome & principe 964km2
- Senegal 196192km2
- Seychelles 453km2
- Sierra leone 72325km2
- Somalia 626541km2
- South africa 1221037km2
- South sudan 644329km2
- Sudan 1886068km2
- Eswatini 17368km2
- Tanzania 947419km2
- Togo 56785km2
- Tunisia 164154km2
- Uganda 236036km2
- Western sahara 252120km2
- Zambia 752618km2
- Zimbabwe 390759km2
The largest country in Africa is Algeria while the smallest is Seychelles.
Offshore island also form part of Africa;
- Seychelles
- Sao Tome and principe
- Mauritius
- Comoros
- Madagascar
- Cape verde
Locating Places And Features On A Map Using Latitudes And Longitudes
- When giving the position of a place or features we with start with the latitude and then longitude
Major latitudes and longitudes - Major longitude is called prime meridian also called Greenwich meridian
- In Africa it passes through:
- Ghana(Accra)
- Algeria
- Burkina faso
- Mali
- All other longitudes are measured and named from prime meridian up to 180 ̊ on both sides
- Major latitude are 3 passing through Africa
- Equator 0 ̊ - divides Africa into two parts
It passes through;- Gabon
- Congo
- DR congo
- Uganda
- Kenya
- Somalia
- Tropic of cancer 23½ ̊ north of equator
It passes through;- Western sahara
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Algeria
- Libya
- Egypt
- Tropic of capricorn 23½ ̊ south of equator
It passes through:- Namibia
- Botswana
- South africa
- Mozambique
- Madagascar
- Other important lines of latitude are far from africa are:
- Arctic circle 66½ ̊N
- Antarctic circle 66½S
| Place | Degrees North | Degrees South | Degree East | Degree West |
| Kenya | 5°N | 4½°S | Between 34°W and 42°E | |
| Algeria | ||||
| Abidjan | ||||
| Eswatini | ||||
| Cairo | ||||
| Capetown | ||||
| Freetown |
| Physical feature | Degrees North | Degress South | Degree East | Degrees West |
| Lake Turkana | ||||
| Namid desert | ||||
| Mt. Kilimanjaro | ||||
| River Zambezi | ||||
| Jos Plateau |
Calculating the time of different places in the world using longitudes
- Rotation of the earth- This is movement of earth on its own axis
- Distance between longitudes is measured in degrees
- There are 360 meridians or longitudes
- One complete rotation is 360 ̊
- The direction of the rotation is from west to east i.e. anticlockwise direction.
- One complete rotation takes 24 hours
- All places found in the east of the Greenwich meridian will see sunrise first and therefore they are one hour ahead of those to the west
Effects of rotation of the earth
- Differences in time along different longitudes
- Occurrence of day and night
24hrs = 360 ̊
1hr = ?
360×1 ÷24 =15
Therefore 1hr =15 ̊ or 360 ̊ = (24×60)minutes=1440min
̊= 1440÷360 ×1=4min
I Hr the earth covers 15º and 1º it covers 4 minutes
Calculating time of places found to the east of Greenwich Meridian
Example 1
The time in Accra 0° is 7.00am.calculate time in bermbera 45°E
1hr =15°
? = 45° = 45÷15×1 =3hrs
So 3hrs is equivalent to 45° then add 3hrs to 7.00am to get 10.00am
Example 2
Suppose the time at GWM is 12 noon what is the local time at Watamu 40°E?
Time gained=40×4=160min=2 hours 40min
Local time at Watamu is 12.00+2.40=14.40-1200=2.40pm.
Example 3
At Dar-es-Salaam 40°E time is 12pm what is the time at Ecuador 40°E?
40°+20°=60°
60×4=240min=4hours
Ecuador is behind in time =12.00-4=8 am.
NB
- When calculating time to the east of Greenwich meridian, we add the time difference to the local time.
Calculating time of places found to the west of Greenwich Meridian
- When calculating time to the west of Greenwich meridian we subtract the time difference to the local time
Example 1
A plane leaves off in New York, 74ºW at 7 am local time. What is the local time in Stockholm 18ºE
NB
- If the places are on the same side subtract the degrees to get the difference and add or subtract from the reference time depending on which side the place is.
Pictures, Plan And Maps
| Picture | Plan | Maps |
| Image of a real object | Outline of something drawn to scale | Representation of the whole or part of the earth’s surface drawn to scale |
| Gives details in their visible shapes and sizes | Also drawn as if a person was directly above the ground | Shows outline of objects on the ground |
| Can be inform of free hand, drawing, painting or a photograph | It represents a very small place | Drawn as if the drawer was above the ground |
| Not drawn to scale | The scale is large to show details e.g. house plan | It shows details |
| Gives specific information | Most of the features are indicated by symbols. |
Types Of Maps
- Topographical maps
This shows selected natural physical features on a small portion of a country. - Atlas map this is a collection of maps in one volume
- Sketch map maps which are roughly drawn.
A good sketch map should have the following characteristics:
- Neat and clear
- Title
- Frame
- Key
- Compass direction
Importance of maps in day to day lives
- Sketch maps are used to summarise information for easy reference.
- Used for locating other countries.
- Used for comparing sizes of countries.
- For locating climatic regions of different parts of the world.
- Give information on distribution of geographical phenomena e.g. vegetation on the earth’s surface.
- Help travellers to find their way.
- Used to calculate distance of a certain place.
- Used to locate physical features like landforms.
Career and Entrepreneurial Opportunities in Social Studies - Grade 7 Social Studies Revision Notes
- Career And Entrepreneurial Opportunities In Social Studies
- Gender Stereotypes Associated With Career Choices And Entrepreneurial Opportunities In Social Studies
Career And Entrepreneurial Opportunities In Social Studies
- Social studies is a learning area that includes History, Geography and Citizenship
- The study of social studies provides us with career and entrepreneurial opportunities in different fields.
- Careers are occupations undertaken for a significant period of a person’s life and with opportunities for progress in life
- Entrepreneurship is the activity of setting up a business or taking on financial risks with hope of making a profit
Importance Of Social Studies For Personal Development And Service To Humanity
- Social studies prepares learners to join various career pathways
- Learners are able to utilise available resources to come up with entrepreneurial projects which help them meet their needs.
- By learning political development and governance learners are exposed to different styles of leadership
- By understanding systems of government, learners are able to make informed decisions once they take up leadership roles in future for the benefit of the community
- The historical understanding of some prominent people in the past is key in shaping learners future
- Social studies encourages learners to appreciate different cultures, values and traditions from national and global perspective which can be adopted in our locality
- learners are able to integrate key aspects of the constitution such as integrity when making decision about governance
- Learning of key aspects on democracy, rule of law, responsible citizenry helps learners living harmoniously in the society.
- Skills and knowledge in personality, human identity and personal well being in promoting inner peace are all meant to enhance understanding of personal growth and development
- Research skills in field work equip learners with data collection, analysis and presentation skills that will help in solving problems affecting our society
| Importance of Social Studies | ||
| Personal development | Service to humanity | |
| 1. | Helps one to understand the real world around us | Helps us to utilize the available resources to serve humanity |
| 2. | Helps us to become good citizens | Helps us to appreciate and relate well with other people |
| 3. | Helps us to know the current affairs | |
| 4. | ||
| 5. | ||
| 6. | ||
Career opportunities related to social studies
- Law -Advocate -Lawyer
- Geology –
- Museology –
- Cartography
- Urban planning
- Meteorology and climatology
- Aviation
- Archaeology
- Medicine
- Teaching
- Survey
- Engineering
| Geography | History | Citizenship |
| Land economics | Archaeology | Public administrator |
Entrepreneurial opportunities for social studies
Some of the entrepreneurial opportunities for social studies in our socisty include
- Pottery
- Basketry
- Ecotourism
- Horticulture
- Agro forestry
- Fishing
- Dairy farming
Gender Stereotypes Associated With Career Choices And Entrepreneurial Opportunities In Social Studies
Gender is the state of being male or female in relation to social and cultural roles.
Stereotypes are fixed general ideas or images that assume that a person behaves in a particular way.
Stereotypes limit aspirations and development of talents.
They create gender differences.
These gender differences ought to be addressed using appropriate strategies.
A strategy is a careful plan or method of dealing with an issue
We can address gender stereotypes in career and entrepreneurial opportunities related to social studies through the following strategies
- Committing and encouraging both males and females to take a full range of careers and business opportunities
- Ensuring representation of both genders in leadership
- Treating both males and females equally by using texts and circular that does not promote gender bias
- Develop policies, law and decision making process that represent both males and females
Recognising Biological Difference Devoid Of Stereotypes In Career Choices And Entrepreneurial Opportunities In Social Studies
- There are biological differences between male and female people.
- Biological difference should never be a hindrance to one’s career choice and entrepreneurial opportunities
- Both male and female should be given equal opportunities to pursue their dreams
Demonstrating respect for one’s gender identity in pursuit of social studies careers and entrepreneurial opportunities
The Life and Ministry of Jesus Christ - CRE CBC Grade 7 Notes
- Background To The Birth Of Jesus Christ
- The annunciation and the birth of John the Baptist
- The Birth And Childhood Of Jesus Christ
Background To The Birth Of Jesus Christ
Prophecies About The Coming Of Jesus Christ
- The coming of Jesus Christ was predicted by many prophets such as Isaiah and Jeremiah.
- A prophecy is a prediction of what will happen in the future.
- It is declared by a prophet who is inspired by the spirit of God.
- Prophets communicate God’s message, condemns evils in the society, give hope to people, anoint kings and teach people the ways of God
Isaiah’s prophecy about the coming of Jesus Christ
Isaiah 9:6-7
Isaiah prophesied that
- The messiah shall be called
- Wonderful counsellor
- Mighty God
- Eternal father
- Prince of peace
- The messiah shall sit upon the throne of David and shall rule with justice and righteousness forever
Jeremiah prophecy about the coming of Jesus Christ
Jeremiah 23:5-6
Jeremiah prophesied that
- The messiah would be a righteous king from the house of David
- The messiah shall execute justice and righteous in the land
- He shall guarantee security and safety in the land of Israel.
- He shall be called “the lord of righteousness”
- He would bring salvation upon Judah
- He would reign as a king
- He would rule wisely
Fulfilment of the Old Testament prophecies about the coming of Jesus Christ
Mathew 1:18-23, Jeremiah 23:5-6, Isaiah 9:6-7
| Old testament prophecies | How they were fulfilled |
| The Messiah would be a descendant of David | Jesus established an everlasting kingdom of God |
| He would bring salvation upon Judah | Mary conceived as a virgin |
| The messiah would rule on the throne of David forever | Joseph, the father of Jesus was descendant of king David |
| A virgin will become pregnant and have a son and He will be called Immanuel | Jesus brought salvation to the whole world |
The annunciation and the birth of John the Baptist
Luke 1:5-25
- To announce means to make known.
- The old testaments said that John the Baptist was to prepare the way for the Messiah.
- Angel Gabriel announced the birth of John the Baptist during the reign of king Herod.
- Angel Gabriel appeared to Zechariah, who was a priest in the temple.
- Both Zechariah and his wife Elizabeth were advanced in age and did not have children , Elizabeth was barren.
- Zechariah, the priest was burning incense at the temple when Angel Gabriel appeared to him
- The angel told him that his wife Elizabeth would bear him a son. His name would be John.
- The angel said the following about the child that would be born
- The child would bring joy and gladness to many
- He will be great before the Lord
- He will not drink wine or strong drink
- He will be filled with the Holy Spirit
- He will bring back many of the people of Israel to the lord their God
- He would be source of joy to his parents
- He will go ahead of the lord strong and mighty
- He will prepare people for the Lord
- Zechariah, due to his old age, could not believe the Angel’s message. The angel told him that he would be dump until all was fulfilled. His wife conceived after five months.
Relating the Birth of John the Baptist to the coming of Jesus Christ
Luke 3:16, John 1:29-30
- Jesus was the son of God whom John the Baptist had come to prepare the way for.
- John the Baptist introduced Jesus as the lamb of God who takes away the sins of the world.
- John acknowledged Jesus as one before him
- Jesus was greater than John the Baptist
| John the Baptist | Jesus Christ |
| John baptized people with water but said Jesus would be greater | Jesus Christ was greater than John the Baptist |
| John introduced Jesus as the lamb of God | Jesus Christ came to where John was batising as the lamb of God |
| John said Jesus came to forgive sins | Jesus Christ came to forgive sins |
| John baptized people with water | Jesus Christ would baptize people with the holy spirit and fire |
How Christians apply the message of John the Baptist
| Teaching | How Christians apply the teaching |
| The warning of people on God’s punishment | Christians repent their sins |
| Urging people to repent their sins | |
| Share clothes and food with the needy | |
| Do not collect more tax then what is allowed by the law | |
| Do not take money from any one by force | |
| Do not accuse anyone falsely | |
| Be happy with whatever amount of money you are paid |
Skills that Christians need to avoid evils condemned by John the Baptist
- Creative thinking
- Enables one to have ideas on how to avoid evil
- Critical thinking
- Enables one to make an informed judgement not to commit sin
- Decision making
- Helps us to make moral decisions that are appropriate
- Self esteem
- Have a feeling of self worth
- Assertiveness
- Express one’s actions with confidence
Appreciating the fulfilment of the Old TESTAMENT Prophecies
Pupil’s activity
Page 86-87
The Birth And Childhood Of Jesus Christ
Events that took place during the annunciation and the birth of Jesus Christ
Luke 1:26-38
- An event is something that takes place and it is of importance.
- The annunciation of the birth of Jesus Christ was important
- During the sixth month of Elizabeth’s pregnancy . angel Gabriel was sent to a virgin woman named Mary, who was engaged to Joseph, a descendant of King David.
- Mary was troubled and he (the angel) told her not to be afraid for she had found favour in the Lord
- The angel announced the following concerning Jesus to mary
- He shall bear a son
- He shall be called Jesus
- He will be great
- He will be called the son of the Most High God.
- He will rule over the house of Jacob forever.
- The Lord would give Him the throne of his Father, David
- His kingdom would last forever
- He will be conceived through the power of the Holy Spirit
Events that took place during the Birth of Jesus Christ
Luke 2:1-20
The Bible - CRE CBC Grade 7 Notes
FUNCTION OF THE BIBLE
The Bible is the inspired word of God.
How the Bible is used in different places and occasions
- The Bible is used when taking oaths in courts of law.
- It is used in schools and colleges for learning, during graduation ceremonies, prayers and research.
- It is used in statehouse or during state functions, during the swearing in ceremonies and prayers.
- It is used in churches and during crusades for preaching.
- It is used at home for personal use during prayer time and home study
- In hospitals when praying for the sick
- Some Christians use the Bible before travelling to pray for journey mercies
Importance of Bible
John 1:1-2, Proverbs 30:5-6
- It contains the word of God
- It gives hope to Christians
- It helps us to understand biblical truths
- The Bible helps a person to discover the will of God
- God speaks to people through the scriptures
- The Bible corrects people when they are wrong and teaches them to do right. Christians should used exemplary lives.
- God protects those whose seek his protection and rebukes liars
- The Bible is the word of God and it was written by people who inspired by the spirit of God.
- The Bible unites people of God, strengthens the faith of the belivers and outlines values for quality Christian living.
How the Bible is used to spread the word of God
The Bible is used in spreading the word of God in the following ways:
- Christians songs are composed using Bible messages
- The Bible is distributed to individuals to read the word of God
- It is used for instructing and teaching new converts of Christian doctrine
- It is used to take oaths therefore, increasing the faith of those who participate
- Christians translate the Bible to vernacular so that many people can read and understand.
The role of the Bible for holistic growth
Holistic growth involves physical, emotional, social, intellectual and spiritual growth.
The Bible helps Christians to grow holistically
How the Bible promotes spiritual growth
Spiritual growth includes
- Increasing your knowledge and understanding of the word of God
- Increase in faith and trust in God
- Developing Christ-like qualities
Role of the Bible in promoting physical growth
Pupil’s activity
Page 51
Role of the Bible in promoting moral growth
Moral growth is the process of developing proper attitudes and behaviuour towards other people based on cultural norms and love
Pupil’s activity
Page 51
Role of the Bible in promoting social, emotional and intellectual growth
Social growth
The Bible tells us that everyone is created in God’s image. Therefore we should not discriminate against others.
We should help those in need, respect and love our neighbour as we love ourselves
Emotional growth
The Bible builds our emotions. When facing sad and difficult situations. It brings us close to God. God provides everything for our enjoyment and we should express our joy to him.
Intellectual growth
As we grow in strength, the Bible helps us to grow in wisdom. God gives us the ability to comprehend, think, reason and remember. The Bible helps us to make correct decisions for quality Christian living.
How God’s word inspires different services among Christians
Christian service is demonstration of who we are in Christ.
- The Bible teaches people to love God and humankind. Helping the needy in the society improves a person’s relationship with God
- Service offered to others is part of Christian living and makes the world a better place to live. Serving others makes one happy and enriches other people’s lives.
- The word of God has inspired different services among Christians. For example, Christians visit the orphans, give them food, clothes and even take them to school.
- Christians donate food, money and medicine to help people suffering when disasters like floods, accidents earthquakes, drought and famine occur
- Christians support refugees by counselling, educating and giving medical care. They also offer shelter, food and sometimes employment.
- For people who are unable to attend church service, the gospel is taken to them through crusades and public rallies.
Divisions of the Bible
The Bible has 2 divisions
- Old testaments - 39 books
- New testaments – 27 books
Why are there two divisions of the Bible
- The two divisions were written at different times in human history
- The two divisions were addressed to different people and individuals
- The messages contained in the two testaments address different issues that were of specific concern to the people addressed.
Importance of the two divisions of the Bible to Christians
- The old testaments talks about how the world was created, the Exodus of Israelites and Ten Commandments given to Moses by God.
The testaments also includes real life stories
The function of this testament is to teach Christians through the experiences of other people throughout history.
Several books also foretell the arrival of the Messiah and the end of the world. - The New Testament focuses more on the life and teachings of Jesus and the early church.
The stories are narrated through gospels and emphasise the importance of the sacrifices of Jesus.
The function of the New testaments is to lead people to follow the example of Jesus more closely. The other books, written by various authors also talk about the end of the world.
The books of the old testaments according to classification
OLD TESTAMENT
It was originally written in Hebrew.
It was written before Jesus Christ came to exist physically.
It was later translated to Greek and other languages.
The following are groups of books in the Old Testament respective of their appearance.
- Torah/Pentateuch/law/mosaic.
- Historical books.
- Major Prophets Books.
- Minor prophet books.
Torah/Pentateuch/law/mosaic.
They were written by Moses.
- Genesis
- Exodus
- Leviticus
- Numbers
- Deuteronomy
Genesis means origin or beginning
Exodus means coming out or departure
Numbers means census
Leviticus explains rules and regulation of priests.
The Ten Commandments (Decalogue) are found in the book of exodus and Deuteronomy.
Historical books.
Contains the history of what happened to the Israelites and its neighbours.
| BOOK | WRITER |
| Joshua | Joshua |
| Judges | Samuel |
| Ruth | Samuel |
| 1 Samuel | Samuel, Gad, Nathan |
| 2 Samuel | Gad and Nathan |
| 1 Kings | Jeremiah |
| 2 Kings | Jeremiah |
| 1 Chronicles | Ezra |
| 2 Chronicles | Ezra |
| Ezra | Ezra |
| Nehemiah | Nehemiah |
| Esther | Mordecai |
Poetic/wisdom books
| BOOK | WRITER |
| Job | Moses |
| Psalms | David |
| Proverbs | Solomon |
| Ecclesiastes | Solomon |
| Song of Solomon | Solomon |
Major prophetic books
| BOOK | WRITER |
| Isaiah | Isaiah |
| Jeremiah | Jeremiah |
| Lamentation | Jeremiah |
| Ezekiel | Ezekiel |
| Daniel | Daniel |
Minor prophetic books
| BOOK | WRITER |
| Hosea | Hosea |
| Joel | Joel |
| Amos | Amos |
| Obadiah | Obadiah |
| Jonah | Jonah |
| Micah | Micah |
| Nahum | Nahum |
| Habakkuk | Habakkuk |
| Zechariah | Zechariah |
| Malachi | Malachi |
NB:
Genesis is the first book of the Bible and the Old Testament.
Malachi is the last book of the Old Testament.
The books of the New testaments according to classification
The New Testament is the period after Christ is born, it is the fulfilment of tthe old testament prophecies of Jesus.
NEW TESTAMENT
- It was originally written in Greek.
- Written after Christ.
- The groups of books found in the new testament are:
- Gospel books.
- Historical books.
- Pauline epistles.
- General epistles.
- Prophetic book
Gospel books
They explain the events in life of Jesus from birth to his ascension in Bethany.
| BOOK | WRITER |
| Matthew | Matthew |
| Mark | Mark |
| Luke | Luke |
| John | John |
Gospel books are divided into two groups:
- Synoptic books
- Non- synoptic book.
Synoptic Books
They explain full life history of Jesus
They are: Matthew, mark and Luke.
Non- Synoptic Book.
It does not explain full history of Jesus.
It is the book of John.
Historical book
- Acts of apostle
The writer of acts of apostle was Luke.
It explains the life of believers in the early church.
Pauline epistles
These are letters which were written by Paul while he was in prison.
They are
- Romans
- 1 Corinthians
- 2 Corinthians
- Galatians
- Ephesians
- Philippians
- Colossians
- 1 Thessalonians
- 2 Thessalonians
- 1 timothy
- 2 Timothy
- Titus
- Philemon
General epistles
Written by different writers who were inspired by God.
| BOOK | WRITER |
| Hebrews | Unknown |
| James | James the brother of Jesus |
| 1 Peter | Apostle Peter |
| 2 Peter | Apostle peter |
| 1 John | John |
| 2 John | John |
| 3 John | John |
| Jude | Jude the brother of Jesus |
Prophetic books
Revelation/apocalypse/disclosure
It was written by John after having a vision on Patmos Island.
Revelation contains the writings about the last days.
NB;
Matthew is the first book of the New Testament.
Revelation is the last book of the Bible and the New Testament.
Bible Translation
To translate means to express spoken or written words in a language that is different from one that was initially used.
How People Benefited From Different Translations Of The Bible
- Spread of the word of God and the general growth of the church.
- Higher demand for formal education in Africa so as to read the Bible.
- It increased the number of Africans in church leadership.
- Unity of mankind, especially through ecumenism.
- It made African Christians more active than passive.
- Africans leaned foreign languages e.g. English.
- Many missionaries were able to learn African languages.
- African languages developed from oral to written form.
- Introduction of new concepts and terms into local languages.
- Development of African theology.
- Many employment opportunities. For instance, people are employed to work for the Bible Society of Kenya.
- Emergence of African indigenous churches.
- Africans rediscovered their culture and developed confidence in it.
- Fast growth of the printing industry.
- Establishment of Bible societies in Africa e.g. the Bible society of Kenya
Reasons that led to the translations of the Bible into local languages
- To enable the word of God to reach more people
- To train local people to take leadership skills
- To facilitate the expansion of the church
- To indigenise Christianity
- To establish local translation society for example Kenya’s Bible society
The Different Translations Of The Bible
- When missionaries began to evangilise in African there was a need to translate the Bible into local languages of the local people to have the scripture in a language they could understand
- Today the Bible has been translated into local languages
- In Kenya, the Bible society of Kenya is the main body mandated to translate the Bible
- Some of the translated Bibles include Kamba, Swahili, kikuyu, Kimiiru/kimeru, Somali, Samburu, Borana, Luhyia Bibles
The Different Versions Of The Bible
A version is the construction of the languages that a translator of the Bible uses in their work
- The Revised Standard Version;
- Good News;
- King James Bible;
- The Living Bible;
- The Jerusalem Bible;
- The New International Version;
- The Gideon International Bible;
- The Holy Bible;
- The New English Bible;
- The Jerome Bible;
- The African Bible;
- The Common Bible;
- The New Life Version;
- The Authorised Bible;
- The New King James Version
Social effects of the translation of the Holy Bible into local languages
- People can now read the Bible in their local languags and understand it better
- It has led to the development of African independent churches
- It has led to the development of local languages which have ben put down in written form
- Africans have become leaders in their established churches as catechists, priests , pastors and deacons
Economic effects of the translation of the holy Bible into local languages
- It has led to the establishment of BIBLE translations societies. The societies offer employment opportunities
- It has led to the development of the Christian printing press and bookshops.
Leadership in the Bible: Moses
Exodus 2:11-13, exodus 3:1-2, Exodus 6:12
During the call of Moses, god told Moses that he had heard the cry of his people (Israelites) God wanted to send Moses to the king of Egypt so that he could lead his people out of the country
Characteristics Of A Good Leader
- God fearing.
- Ready to serve
- Hardworking
- Good decision maker
- Gentle
- Have respect
- Honest
- Humble
- Loyal
- Loving
- Peaceful
- Be a role model
- Have integrity
How God prepared Moses for Leadership
Exodus 2:11-13, Exodus 3:1-2, Exodus 6:12
- In the society leaders are prepared to take up their position in different ways, for example through training
- Like today leaders, God prepared Moses for leadership in different ways
- Speaking from a miraculously burning bush, God says he will send Moses to lead His people from Egyptian slavery
- This mission was overwhelming to Moses. He responded to Gods call with doubt. He did not see himself as the best person to free the jews or an appropriate leader for the task. However God often calls the most unlikely people to accomplish his greatest tasks
- God prepare Moses for leadership by making him witness the suffering of the Hebrews under the Egyptians
- God prepare Moses to solve conflicts among his people and the Israelites
- Life in the desert made Moses bold and ready to face hardship
- As a shepherd, Moses learnt to be keen and responsible in leading Israelites
Roles performed by Moses during the Exodus
- Moses was the prophet who led Israelites out of slavery in Egypt and brought them to the edge of the promised land
- Moses played various roles during the exodus
- He asked Israelites to trust in god and not to be afraid
- He interceded on behalf of the Israelites
- He led the people of Israel away from the red sea. The seas waters separated when Moses lifted his rod and held it over the sea.
- Moses sought for providences for the people of Israel when they were in the wilderness. God responded to his prayer and made bitter water fit to drink.
- Moses received the laws God had given the people of Israel. the laws would help to safeguard their relationship with God and among themselves
- Moses also appointed judges to help him administering justice among israelites . he taught the Israelites the ten commandments and advertised them to obey
Qualities of Moses that Christians can emulate
- Responsibility
- Obedience
- Honesty
- Justice
Advantages of choosing good leaders in the society
- A good leader, among other qualities should be God fearing, trustworthy, a team player, obedient, responsible, and humble.
- Good leadership promotes peace, love, unity and development of many nation
- Leaders should follow the example of Moses.
Pupil’s activity
Page 75