Stella
Kiswahili Questions and Answers - Class 8 Opener Exams Term 1 2023 Set 3
INSHA
Anzisha insha yako kwa maneno haya:
Siku tuliyosubiri kwa hamu na ghamu iliwadia, hivyo basi sote .........
QUESTIONS
Soma kifungu kifuatacho. Kina nafasi hadi 15. Kwa kila nafasi umepewa majibu manne. Chagua jibu lifaalo zaidi kati ya yale uliyopewa.
Kuoga ni ___1___ shartyi mtu ___2___kila wakati au kila siku. Hasa watoto ___3___kuoga ama kuogeshwa mara kwa mara. Watoto ___4___ jasho ___5___ wanapocheza. Jasho ___6___ huchanganyika na vumbi___7___ mahali ___8___. Nao wanapata ushafu. Baada
ya kupata uchafu ___9___ , ni lazima waoge. Tusipowasaidia watoto kutunza usafi ___10___ mili ___11___hawatakuwa na afya bora. ___12___magonjwa kama vile upele na harara ya ngozi. Usafi si muhimu kwa watoto tu ___13___ pia kwa watu ___14___. Hao ___15___
wasipooga ni hatari zaidi kuliko hata watoto wadogo
| A | B | C | D | |
| 1. | hiari | faradhi | kutaka | ngumu |
| 2. | haogi | kuoga | aoge | anaoga |
| 3. | hupasa | hupasua | hapaswa | hupaswa |
| 4. | hutoa | hutoka | hutia | hutokwa |
| 5. | mingi | nyingi | jingi | mengi |
| 6. | hilo | hiyo | huo | hizo |
| 7. | ya | za | la | vya |
| 8. | wanacheza | wanauchezea | wanapochezea | wanapocheza |
| 9. | huo | hiyo | hilo | hizo |
| 10. | ya | za | wa | la |
| 11. | zao | yao | lao | cha |
| 12. | watungua | wataugua | wataangua | watapungua |
| 13. | mbali | bali | wala | ili |
| 14. | wazima | wazimu | wasafi | yeyote |
| 15 | ndipo | ndiye | ndio | ndivyo |
Kutoka swali la 16 mpaka 30, chagua jibu lililo sahihi.
- "Sabalkheri wanafunzi," Mwalimu aliwasalimia wanafunzi wake. Huo ulikuwa wakati wa
- adhuhuri
- asubuhi
- jioni
- alasiri
- Chagua sentensi yenye kivumishi kiulizi
- Mashubaka haya yalitengenezwa lini?
- Leo wameapishwa wangapi?
- Wasusi, wanaelekea wapi?
- Huyu atavikwa pete gani?
- Andika sentensi hii kwa wingi
Mtume huyo ana tunda hili- watume hawa wana matunda haya
- Mitume hao wana matunda hizi
- Watume hao wana matunda haya
- Mitume hao wana matunda haya
- Miongoni mwa sehemu hizi za mwili ni sehemu ipi iliyo tofauti na zingine?
- Paja
- Kiganja
- Pafu
- Goti
- Methali inayofaa funzo kuwa;
Mtu anaposababisha shida huishia kuwahusisha watu wake au jamaa yake ni- Kikulacho ki nguoni mwako.
- Mwiba wa kujichoma huambiwi pole.
- Mla nawe hafi nawe ila mzaliwa nawe.
- Mchuma janga hula na wa kwao.
- Chagua sentensi iliyoakifishwa vizuri
- Lo? Amefika?
- Viti vyenu ni vipi?
- njoo nikutume!
- "mimi sisemi na mtu"
- Tumia kivumishi '-enye-'kwa njia sahihi
Mbuzi____________madoadoa ni wangu.- lenye
- chenye
- yenye
- mwenye
- Kamilisha methali hii
Hakuna ____________________________________ yasiyo na mbu.- masika
- vuli
- kiangazi
- kipupwe
- 'kazi ya kijungu jiko, 'ni kazi gani?
- kupika jikoni
- kukupatia riziki pekee
- kupika na kupakua
- kupika na jiko moja tu
- Nomino habari iko katika ngeli ya
- U-ZI
- I-I
- U-I
- I-ZI
- Chagua sentensi sahihi
- Viluwiluwi vile vilimezwa na samaki
- Mikebe hizo zimetupwa katika moto
- Ng'ombe hiyo ilikamuliwa maziwa
- mengi
- Wanajeshi wale walikuwa watiifu na wapole
- Wageni walikuja wakati ______________ tuliowangoja
- huu huu
- uo huo
- uu huu
- uo huu
- Ni saa ngapi sasa?
- Saa kumi kasoro robo
- Saa nne kasoro robo
- Saa tisa kasoro robo
- Saa kumi na robo
- Andika kwa maneno tarakimu hii 8,000,001
- Milioni mia nane na elfu moja
- Milioni nane na moja
- Milioni mia nane na moja
- Milioni mi anane na mia moja
- Kipindi cha miaka mia huitwa
- muongo
- majira
- karne
- milenia
Soma kifungu hiki kisha ujibu maswali kutoka 31-40.
Ni jambo la busara kwetu vijana kusikiliza mashauri tunayopewa na watu wazima kama vile wazazi na walimu kwani wametuzidi kwa maarifa. Ama kwa hakika,lolote lile wakuu wetu hutu.unbia yafaa tuzingatie tusije kufikwa na balaa iliyomfika kijana matatizo.
Matatizo alikuwa kijana mwenye sura nzuri na tabasamu ya kuvutia. Kwa nje aliweza kuwavutia wengi hasa wasiomjua. Hata hivyo, hakuna kizuri kisicho na dosari. Matatizo alikuwa na hulka mbaya isiyopendeza kwa watu wengi. Alikuwa mkali kama pilipili na mkaidi mfano wa mkia wa nguruwe. Tabia yake iliwashinda hata wazazi wake ingawa hawakusita kummwagia bahari ya maneno ya busara kwa tamaa ya kumwokoa.
Baadaye alipopelekwa shule angalau apate kisomo cha kumwekea nguzo maishani mwake, Matatizo alipatikana akishiriki visa vya ujeuri na kuwa mtundu. Visa hivi havikupungua, viliuma. Siku moja baba yake kijana huyu alishtuka alipojulishwa kuzidi kwa utundu wa mwanawe shuleni hasa alipoambiwa mtoto wake anapiga mtindi, hakosi sigara mdomoni na anashiriki wizi ili ajipatie pesa za kujitimizia haja zake. Matatizo alifukuzwa shule. Vitendo vya matatizo vilimtahadharisha mzee Toboasiri.
Wakati mmoja siku ya Jumapili alfajiri, mzee Toboasiri alijikuta ameshika mkongojo wake akienda kwake mzee Busara wakiwa na mzee Saidia.
Aliwaalika mkutano wa dharura nyumbani kwake siku iliyofuata. Wazee hawa wawili walipowasili, walimkuta Toboasiri na mtoto wake Matatizo wameketi kimya. "Wazee wenzangu," alianza huku sauti yake ikionyesha masikitiko, "Nimewaita hapa ili mnisaidie kumpa mawaidha kijana wangu. Nimejaribu niwezavyo kumkanya mwanangu dhidi ya matendo maovu lakini nimeshindwa. Nawaomba wazee wenzangu mnifanyie kazi hiyo."
Wazee hawa wawili walimshauri na kumshawishi Matatizo aache ile tabia yake mbaya. Kabla hawajamaliza, Matatizo alisimama huku akipandwa na hasira. Alifoka na kuwakodolea wale wazee macho huku amekunja uso wake na kuonekana kama jitu lililonyimwa chakula mwezi mzima.
Hapo alitoka nje, akawasha sigara kubwa na kupiga mikupuo miwili. Macho yakageuka na kuwa mekundu kami. pilipili. Akarudi na kumkabili mzee Busara. "Kwa vile unaitwa Busara, unadhani unahaki ya kunipa mawaidha, leo utanitambua. "Alimzaba mzee Busara kofi moja pa! Mzee huyu hakushimili kofi hilo na hapo akaanguka chini pu!
- Kulingana na aya ya kwanza, anayezungumza ni
- Toboasiri
- Matatizo
- Busara
- Mwandishi
- "Yafaa tuzingatie ya wakuu wetu tusije tukakumbwa na yaliyomkabili Matatizo" Ni methali gani isiyoambatana na maelezo haya?
- Usipoziba ufa utajenga ukuta
- Asiyesikia la mkuu hupatwa na makuu
- atangaye sana na jua hujua
- sikio la kufa halisikii dawa
- Kulingana na aya ya pili ni ipi si sifa ya matatizo?
- Alitemea mate nasaha za wazazi wake.
- Matatizo alikuwa mtanashati.
- Matatizo alikuwa mkaidi na mjanja.
- Tabia zake ziliambatana na sura yake.
- Lengo la Matatizo kupelekwa shuleni ni
- kupata masomo ili kuboresha maisha yake
- kuwafurahisha wazazi wake
- kuendelea kudumisha hulka yake
- kuelimika ili azidishe hulka yake
- Kulingana na kifungu hiki. Matatizo
- Alibadilika alipoenda shuleni
- Alishiriki katika uvutaji sigara na kunywa pombe
- Alifanya bidii katika masomo yake
- Aliepukana na hulka ya wizi
- Baba yake matatizo ni
- mzee saidia
- mzee Busara
- Mzee Toboasiri
- Mwalimu mkuu
- Ni kweli kusema kuwa
- Baba yake matatizo alikuwa amefika mwisho
- Wazee walipoitwa hawakutoa nasaha
- Mkutano ulipangwa kwa siku nyingi
- Matatizo alitekeleza yote aliyoambiwa
- 'kupiga mtindi' ni maneno yaliyotumiwa. Ni tamathali gani ya lugha?
- Istiari
- Nahau
- Methali
- Tashbihi
- Methali inayomlenga matatizo katika aya ya mwisho ni
- sikio la kufa halisikii dawa
- ushikwapo shikamana
- la leo litende leo
- aliyekalia kigoda mtii
- Neno 'foka' namna ilivyotumiwa katika kifungu hiki halima maana
- kughadhabika
- kuwa na mafutu
- kuwa na huzuni
- kupandwa na mori
Soma kifungu kifuatacho kisha ujibu maswali ya 41-50.
Kulonga dhahiri shahiri Kiswahili ni mojawapo ya lugha za kimataifa zinazozungumzwa ulimwenguni. Hata hivyo inasikitisha sana sisi wenyeji wa eneo la Africa Mashariki ambao ni kitovu cha lugha hii, tumekuwa tukinyonga raslimali hii kwa ukatili mkubwa.
Ni aibu iliyoje kukitumia Kiswahili kiholela bila kuzingatia kanuni zake huku tukijidanganya kuwa sisi ni mahiri tunapokiporomosha Kimombo kwa usanifu mkubwa. Jinsi tunavyokitema kiingereza sawasawa. Kwa nini hali hii tusiizingatie katika lugha yetu tunu? Wageni kutoka nchi za ughaibuni waliopata fursa ya kuzuru eneo la Afrika Mashariki wametambua utamu wa Kiswahili wakajifunza wakajistawisha. Baadhi ya wageni hao wamekuwa walimu wa lugha hii.
Aidha tunazidi kukitia kitanzi Kiswahili kupitia uchapishaji wa magazeti yetu. Bei ya gazeti la kiswahili inaashiria uduni wake. Habari zinazochapishwa katika magazeti ya kiswahsili ni za kiwango cha chini na ni chache mno cha kuudhi zaidi ni kuwa baadhi ya kaifa za magazeti ya kiswahili hujikuta katika masuala ya kijamii kwa kiasi kikubwa na kuyapa kisogo au kugusia gusia tu mambo kuhusu uchumi,siasa na dini. Hakuna mazito kuhusu matangazo ya biashara. Hakuna habari ya vifo. Hakuna habari za ajira na kadhalika. Si ajabu wakati mmoja niliulizwa mtaani, "Hili gazeti ulilo nalo umemnunulia babu yako?" Swali hili lilinijulisha kuwa fikra za waja wengi imejengwa na mtindo wa wakati mrefu wa kuchapisha magazeti kwa njia hii; hivi kwamba magazeti ya kiswahili yanapaswa kusomwa na wazee na labda wale walioshindwa na masomo skulini.
Nawasihi wananchi wa eneo lote la Afrika Mashariki wazinduke na kukiendeleza kiswahili.
- Kulonga dhahiri shahiri ni sawa na;
- kunena ukweli
- kuamba bila hadaa
- kupiga vijembe
- kuongea waziwazi
- Maneno tunavyo kitema kiingereza yamepigiwa mstari. Maana yake ni
- Tunavyokikaia kiswahili
- Tunavyokikata kiingereza
- Tunavyokiongea kimombo barabara
- Tunavyokizungumza kiingereza ovyoovyo
- Neno lipi katika taarifa hii lina maana sawa na kaifa
- picha
- habari
- kurasa
- vichwa
- Kwa mujibu wa taarifa ni kauli gani sahihi?
- Magazeti ya kiswahili yana bei ghali
- Magazeti ya kiswaili huwavutia wengi kuyasoma
- Bei ya magazeti ya kiingereza ni rahisi
- Magazeti ya kiswahili yamedunishwa
- Watu mahiri ni watu
- woga
- wajuzi
- walaghai
- washindani
- Tunazidi kukitia kitanzi kiswahili ni
- kukfrunga kiswahili
- kukipa sifa kiswahili
- kukiharibu kiswahili
- kukienzi kiswahili
- Visawe vya neno waja si pamoja na
- Mahuluki
- Adinasi
- Nswi
- Wanadamu
- Kulingana na taarifa hii asili ya lugha ya kiswahili ni
- nchi ya ughaibuni
- nchi ya Kenya
- Afrika mashariki
- Hatujaambiwa
- Mwandishi anawashauri wakazi wa eneo la Africa mashariki
- wasiitumie kiswahili hadharani
- waache kutumia kimombo
- wakipe kiswahili kipaumbele
- wakididimize kiswahili
- Kichwa kifaacho taarifa hii ni
- Lugha za Afrika-
- Mbinu za kuboresha Kimombo
- Historia za kiswahili na kiingereza
- Kiswahili kitukuzwe
MARKING SCHEME
- B
- C
- D
- A
- B
- B
- A
- C
- A
- C
- B
- B
- B
- A
- C
- B
- D
- D
- C
- D
- B
- D
- A
- B
- D
- D
- B
- A
- B
- C
- D
- C
- D
- A
- B
- C
- A
- B
- A
- B
- D
- C
- B
- D
- B
- C
- C
- C
- C
- D
English Questions and Answers - Class 8 Opener Exams Term 1 2023 Set 3
COMPOSITION
DO NOT JUDGE A BOOOK BY ITS COVER
QUESTIONS
Read the passage below. It contains blank spaces numbered 1-15. For blank spaces choose the best alternative from the choices given
I ___1___to study late ___2___ the night to prepare for my essay. ___3___ in the hall ___4___ everyone also was ___5___, a ___6___ slight noise frightened me. I ___7___ that ___8___ was someone ___9___me.
Every time the curtain ___10___ in the ___11___, my heart missed ___12___. When my ___13___ dog ___14___, I broke ___15___ in goose bumps.
| A | B | C | D | |
| 1. | have | had | ought | get |
| 2. | in | at | on | into |
| 3. | Alone | Lonely | Lonesome | Once |
| 4. | after | while | when | before |
| 5. | asleep | sleepy | dreamy | dreaming |
| 6. | quite | very | too | much |
| 7. | knew | assured | imagined | think |
| 8. | then | their | it | there |
| 9. | in front of | above | below | behind |
| 10. | tossed | fluttered | flattered | teased |
| 11. | wind | rain | gale | moon |
| 12. | a bit | abit | a beat | abeat |
| 13. | neighbouring | neighbour | neighbours' | neighbour's |
| 14. | hissed | barked | yelled | yelped |
| 15. | out | off | up | down |
For questions 16-18, choose the correct form of adjective
- Joy is my ____________________ sister.
- older
- eldest
- more old
- elder
- Of the twins, Tom is the ______________________ one.
- clever
- more cleverer
- cleverer
- cleverest
- Nairobi is the ________________ city in Kenya.
- most populous
- more populous
- most pepulace
- most dense
For questions 19-20, complete appropriately
- Do you prefer coffee______________ tea?
- or
- and
- to
- with
- Scarcely had I walked in, ____________-
A. than he arrived
B. when he arrived
C. as he arrived
D. unitl he arrived
Use the correct form of the verb in the following questions.
- None of my friends __________________ that has been going on.
A. attend
B. are attending
C. attends
D. attending - Either Kay or her friends ___________________ come.
A. have
B. has
C. is
D. were being
For questions 23-25, select the best preposition.
- I told him _____________________ his face that he was a disgrace to our family.
- on
- in
- at
- to
- How much money do you have, __________________ you?
- by
- with
- in
- on
- We congratulated them _____________________________ their incredible performance.
- for
- on
- with
- of
Read the passage below to answer questions 26-38
Is it possible to predict the future? Can we know something before it has taken place? For those of us who do not think it possible, let us look at the case of Janet Henley.
One day, Janet, a colleague of Linda's, a nurse, told Linda that she had dreamt something terrible. Apparently, in her dream, Linda was trapped in a store-room in the hospital and fire was engulfing her. Janet could not remember the ending to the dream. Linda laughed it away as "Overwork!" The dream came again two days later. This time, she saw Linda trying hard to escape but unable to do so because the door was stuck. However, Janet also saw a large hammer in the corner of the room. She related the events to Linda again. Two days later, she dreamt the same thing again. This time she was scared as the number ten kept appearing too.
She got up the next day and felt depressed When she reached the hospital, she realized that the date that day was the tenth. She told Linda, "Please be careful - remember my dream - it's the tenth today." Linda shrugged it off as another crazy dream
At about eleven in the morning, Linda had to get some plasters and bandages for an emergency case from the store-room. As she was rummaging through the shelves for more bandages, she smelt smoke. Before she knew it, there was an explosion and bottles started cracking in the heat. She ran to the door to escape and found it locked. Suddenly, she remembered Janet's dreams. Looking around her frantically, she saw a large hammer leaning against the wall! She grabbed it quickly, broke the lock and scrambled out to safety.
After the firemen had put out the fire and everyone was safe, Linda related what had happened in the store-room to Janet. She added, "I remember you saying there was a hammer in your dream. You know what - that's what saved me. You are psychic!"
It was a scary thought for Janet but she was pleased that her dreams had saved Linda. She never dreamt anything like that again but she could never understand how she knew about the fire.
Was it really a dream or was it a premonition? Was it God's way or just a fantastic coincidence? As you can see, there is no rational explanation — or, at least, I cannot think of one. Can you?
- According to paragraph one, it's true to say that
- It is not possible to predict the future.
- Everyone thinks it's impossible to predict the future.
- Some people believe it's possible to predict the future.
- We always know things before they happen.
- What was Janet's first dream about Linda?
- Linda was killed in a fire.
- Linda was trapped in a lift with fire engulfing her.
- There was a hammer in a corner
- Linda was trapped in a store-room with fire engulfing her.
- What would the meaning of the word colleague be as used in the passage?
- Workmate
- Acquaintance
- Ally
- Antagonist
- According to Linda, Janet's dreams were as a result of
- tension
- anger
- burnout
- exhaustion
- On the night before the actual fire, Janet
- was very depressed
- dreamt about the number ten
- slept well
- dreamt that Linda managed to escape
- What did Janet think the number ten meant in her dream?
- Linda would be trapped at ten O'clock
- It would happen on her tenth birthday
- Linda would be caught in the fire on the tenth
- Ten bottles would explode in the store-room
- Linda went to the storeroom because
- she needed some peace
- there was an explosion
- she had to get some medical items there
- she was to swathe bandages and plasters
- Linda believed in Janet's story when
- Janet said, "I told you!"
- She found herself locked in the storeroom C
- The fireman arrived
- She saw the bottles exploding
- What saved Linda from dying in the fire?
- The broken lock
- The hammer in Janet's dream and its position
- The explosion broke the lock
- The firemen saved her
- Janet was scared when the whole incident was over because
- her friend was safe
- the store-room was on fire
- the firemen arrived late
- her dream became reality
- Was the whole thing a dream?
- It was coincidence
- There was no explanation for what happened
- It was God's way
- It was only a dream
- Who is a psychic?
- A person who sees a hammer in a dream
- A person who can predict a fire
- A person that is able to know what ma happen in future
- A nurse with special power
- What is a suitable title for the passage?
- Premonition
- Friendship
- Crazy dreams
- A fire
Read the passage below to answer questions 39-50
A visit to a healthcare provider is often not a very exciting undertaking. Patients and their family members are in an uneasy state during the time. Many healthcare professioanls that we interact with during such visits do not make it any better.
Most of us have come across cold doctors, harsh nurses, insensitive dentists, slack laboratory assistants, unhelpful pharmacists among other not-so- caring healthcare professionals. Experience with such staff makes patients feel worse about their medical condition.
Why is customer experience in healthcare lagging? Why are our experiences in hospitals, doctors' and dentists' clinics laboratories, pharmacies and other health-service providers frequently below par?
Two to three decades ago, healthcare services in Kenya were mainly public. Growing up, those were our natural choices, locally, we had a renowned health centre for outpatient services, there was the general hospital and a few missionary hospitals not too far away. This may not have been the case for every Kenyan. Today, it is different both public and private healthcare servies in most counties are a stone's throw away and some are next to each other. The number of healthcare providers has soared.
Most patients are spoilt for choice. Despite this, many of our local providers do not seem to have improved their experience considerably. The healthcare industry seems to be trailing in its focus on the customer. Kudos to the few providing an exceptional experience.
In the public sector, healthcare services continue to face a myriad or indequancies. There has been frequent labour unrest. There is also lack of adequate supplies, and facilities are poorly maintained. As a result, most Kenyans continue to experience sloppy public healthcare services. The customer
experience in public heathcare certainly needs improvement.
- According to the paragrah one, a visit to a health care provider
- is a walk in the park
- B. is a tall order
- is a rosy affair
- is a professional one
- Who among the followng is not a healthcare professional?
- Doctors
- Laboratory assistants
- Quacks
- Pharmacists
- The word slack has been underlined. What does it mean according to the passage?
- Loose
- Quiet
- Calm
- Lazy
- According to paragraph four sentence one, it is true to say that
- there were no private hospitals then
- healthcare services were topnotch
- there were few private hospitals
- there were many private hospitals
- Three decades is equivalent to
- thirty years
- three years
- ten years
- three hundred years
- The number of healthcare providers has soared, means that they have
- become better
- gone up
- improved
- stagnated
- Most patients are spoilt for choice means that patients
- have fewer choices
- have spoilt the healthcare provides
- have a wide array of hospitals to choose from
- cannot decide what to do.
- Who is the customer mentioned in paragraph six?
- The doctor
- The patient
- The professional
- The healthcare providers
- Which one of the following is not an inadequacy in the healthcare services?
- Cheap drugs
- Poor maintenance of facilities
- Inadequate medicines
- Strikes by doctors
- The customer care in public healthcare is
- good
- wanting
- impressive
- okay
- A stone's throw away as used in the passage means
- by the road
- near a quarry
- very near
- in the outskirt
- The best title for the passage would be
- A visit to a hospital
- Patients and doctors confidentiality
- Minimising patients pain by healthcare providers
- Private healthcare providers
MARKING SCHEME
- B
- B
- A
- B
- A
- B
- C
- D
- A
- B
- A
- A
- D
- B
- D
- D
- C
- A
- C
- B
- D
- B
- A
- B
- A
- C
- D
- A
- D
- B
- C
- C
- C
- B
- D
- B
- C
- C
- B
- C
- B
- C
- A
- B
- C
- B
- A
- B
- C
- A
Mathematics Questions and Answers - Class 8 Opener Exams Term 1 2023 Set 3
QUESTIONS
- Write 70070007 in words
- Seventy million, seventy thousand and seven
- Seven hundred million seventy thousand and seven
- Seven million seven thousand and seven
- Seven million seventy thousand and seven
- Round off 150956 to the nearest hundred
- 200 000
- 151000
- 150000
- 150900
- Evaluate
20 of ¼ − 1/8 x 4 ÷ ½- 5
- 2¼
- 4¾
- 4
- What is the sixth number in the series
4, 9, 25, 49, _____- 169
- 121
- 225
- 81
- What is the value of
82(62 − 36)
√16- 0
- 8
- 16
- 4
- How many times is the value of digit 3 more than the value of digit 6 in 34769803
- 2000
- 500
- 5000
- 20,000
- What is the sum of the largest and smallest numbers formed by the digits
9, 3, 8, 5 and 1- 112120
- 84942
- 102020
- 102110
- What is 23.1408 correct to three decimal places
- 23.1
- 23.140
- 23.141
- 23.0
- Which of the following statements is not true about a rhombus
- opposites angles are equal
- has two pairs of parallel lines
- diagonals are equal
- all sides are equal
- The figure below represents triangle ABC in which line BC=15cm and line AC is 17cm and angle ABC is a right angle
What is the area of the triangle- 120cm2
- 127.5
- 68cm2
- 60cm2
- Jane deposited sh.2000 in a bank that paid a simple interest of the rate of 12% p.a. How much money was in her account at the end of 2 years
- Sh. 2240
- Sh. 480
- Sh 2480
- Sh.2508.50
- John is.a farmer. He sold milk from January 17th to April 17th 2011. How many days did he sell the milk.
- 92
- 90
- 93
- 91
- How many poles placed 10m apart can be used to fence a rectangular plot measuring 1200m by 800m
- 201
- 200
- 400
- 402
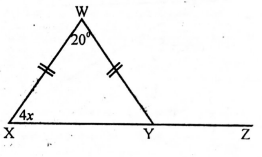
- In the figure below WXY, line WX=WF. Angle WXY=4x and angle XWY is 20°
What is half the value of angle WYZ- 80°
- 50°
- 100°
- 20°
- A printing firm produces 1160470 advertising posters in a month. How many posters will be produced in a year
- 35974570
- 34814100
- 11604700
- 13925640
- Njagi is paid a salary of sh 3800 plus 5% commission for the total sales in one month, he sold goods worth sh 32000. How much did he earn that month?
- Sh 5590
- Sh 5400
- Sh 1600
- Sh 35800
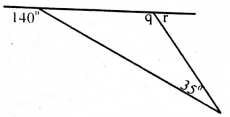
- Find the size of angle Q
- 105°
- 95°
- 40°
- 88°
- Find the radius of a circle whose area is 2464cm2. take pie to be 31/7
- 14cm
- 28cm
- 7cm
- 56cm
- An empty vehicle weighs 1.2 tonnes. When loaded with 30 bags of maize, it weighs 4.2 tonnes. Calculate the mass of each bag
- 100kg
- 180kg
- 540kg
- 280kg
- Simplify the following expression ½x − 12 > 4
- x < 16
- x <36
- x > 32
- x > 16
- Okongo walked from his home to the hospital for 2hrs 30 min at 4km/h. He stayed at the hospital for 30 min. He then returned home at 5km/h for how long was he away from home?
- 2 hours
- 4hours 30 minutes
- 5 hours 30 minutes
- 5 hours
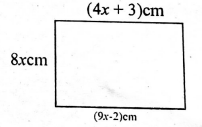
- Work out the perimeter of the figure below
- 15cm
- 30cm.
- 56cm
- 56cm2
- What is the capacity of a container whose volume is 1000,000cm3
- 100litres
- 10litres
- 1000cm
- 1000litres
- Convert 4:5 as a decimal
- 0.9
- 0.4
- 0.8
- 1.25
- In January last year the number of candidate who registered for KCPE in Gucha zone was 4500. This year the number of candidate registered increased 15%. How many candidates were registered this year
- 4900
- 675
- 975
- 5175
- The marked price of a TV flat screen is Sh.38200. Otieno paid Sh.37436 after begaining what was his percentage discount
- .2.5%
- 764
- 20%
- 2%
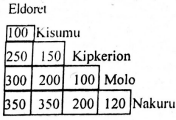
- The table below shows the fares in shillings charged between Eldoret to Nakuru by train
Omollo travelled from Eldoret to Molo through Kipkerion. How much did he pay- Sh. 50
- Sh. 250
- Sh. 150
- Sh. 300-
- Evaluate the following (2/3 ÷ ¾ of 5/6) × (¼ of 1/3 ÷ ½)
- 2/9
- 8/45
- 62/5
- 10/81
- A class has 16 girls and 27 boys. During a mathematics lesson, of the girls and, of the boys were sent home because of school fees. How many pupils were sent home for fees.
- 36
- 7
- 43
- 50
- Kamau bought the following items from a sho
- 6 oranges @sh 20 per an orange
- 3 litres of water @ sh 16 per '/, litres (i
- 4 kg of meat @sh 120 per kg (
- 2kg of onions@sh 45 per kg
- 2kg tins of cooking fat @sh 97 per kg
and 4 bottles of soda sh 27 per bottle
How much balance was he given if he gave two one thousand shillings notes.- Sh 1088
- Sh. 3088
- Sh 912
- Sh. 928
- Omagwa paid sh 1930 for a shirt after being allowed 3½% discount. What was the discount
- Sh 2500
- Sh 70
- Sh 3900
- Sh 2000
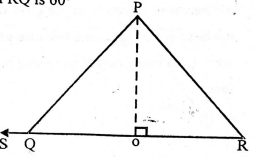
- In the triangle PQR below line PQ=15cm, QR=16cm and RP=10cm. PO is perpendicular to QR. Angle PQS is 145° and PRQ is 60°
Calculate the size of angle RPQ- 150°
- 30°
- 85°
- 95°
- A group of pupils in Kimwera primary school took 2 decilitres of milk each. How many pupils took 0.1m3 of milk
- 100
- 500
- 50
- 5
- Construct an equilateral triangle ABC of sides 5cm. Draw a circle such that points A,B andC are on the circumference. What is the radius of the circle
- 2
- 6
- 3
- 4
- A car travelling at 70km/h takes 3 hours to finish a journey. At what speed must it travel to finish the journey in 2 hours
- 84km/h
- 100km/h
- 105km/h
- 138,km/h
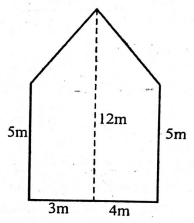
- Korir's flower garden is in the shape shown below
Calculate the area of the garden in ares- 59.5
- 0.0595
- 5.95
- 0.595
- Convert 2/9, to a decimal and give your answer to the nearest whole number
- 2
- 0
- 0.2
- 0.22
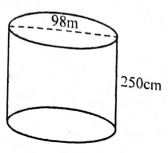
- Calculate the volume of the cylinder drawn below in cubic metres
- 1886500m3
- 18865m2
- 18865m3
- 1886500m2
- The cash price of a radio cassette is 20% less than the hire purchase price. Kimani bought the radio cassette on hire purchase price by paying a deposit of Sh 2000 and five monthly installments of sh 300. How much more than the cash price was the hire purchase price?
- Sh 3500
- Sh 700
- Sh 583.50
- Sh 2800
- The temperature of a room was -18°C. After sometimes of a gradual increase, it read 15°c. What was the temperature increase?
- 33°C
- 30°C
- 15°C
- 0°C
- A river of length 12.5km is represented on map by a distance of 25cm. What was the scale on a map
- 1:50000
- 1:10000
- 1:125000
- 1:25000
- The number of children in a town is twice than that of women. There are 340 more women than men. If there are 6240 children, how many men are there in the town?
- 3120
- 3420
- 2780
- 3460
- Find the value of 2.45 + 0.03 (4 x 3) − 0.54
- 2.55
- 32.46
- 2.36
- 2.27
- Construct triangle RST in which line RS-4cm, ST-6cm and angle RST=100°. Draw a circle touching its edges. What is the diameter of the circle?
- 1.5cm
- 3cm
- 2cm
- 4cm
- Solve the value of x in the equation 5/8 (x − 48) − 24 − 38
- 144
- 76
- 147.2
- 146.2
- The table below shows the types and number of vehicles Njuguna counted along Embu-Meru road on one day
Buses Lorries Nissans Cars
12 45 120 b?
If the mean of all the vehicles counted was 50. How many more Nissans than cars did he count?- 60
- 97
- 23
- 54
- The charges for sending a telegram are sh. 20 for the first ten words of less. Each additional word is charged @ Sh.1.00 A 10% tax is charged on the total. How much did Beatrice pay to send the following telegram ALICE MUTHONI BOX 46933 NAIROBI SEND YOUR CERTIFICATES FOR TEACHER TRAINING RECRUITMENT BEATRICE ACHIENG NAKURU
- Sh.50.50
- Sh.25.00
- Sh.12.50
- Sh 27.50
- The circumference of a circle is 88cm. Calculate the area of the circle in cm2
- 616cm2
- 768cm2
- 308cm2
- 154cm2
- Pauline has 2x sweets. Her sister Mary has 8 more sweets than Pauline. If they all put their sweets together and shared them equally. How many sweets did each of them get?
- 2x + 4
- 2x+8
- 4x+8
- 4x + 4
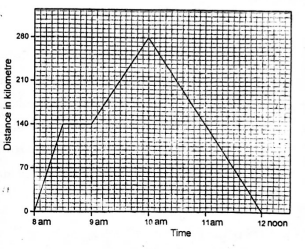
The graph below shows Mr. Ndungu's journey from Nieri to Molo and back. Study it and answer question 50.
- From the graph, calculate Mr. Ndungu's average speed for the whole journey?
A. 93km/h
B. 140km/h
C. 80km/h
D. 70km/h
MARKING SCHEME
- A
- B
- C
- B
- A
- B
- A
- C
- C
- D
- C
- B
- C
- A
- D
- B
- A
- B
- A
- C
- D
- B
- D
- C
- D
- D
- A
- B
- B
- C
- D
- C
- B
- C
- C
- D
- B
- C
- B
- A
- A
- C
- D
- B
- C
- B
- D
- A
- A
- B
Foundation Of Computer Science - Grade 7 Computer Science Revision Notes
- Computer Concepts
- Evolution Of Computers
- Generation Of Computers
- Classification of Computers
- Hands On Skills Concepts
- Computer System Overview
- Computer Hardware Concepts
- Computer Setup
Computer Concepts
Definition
- Computer
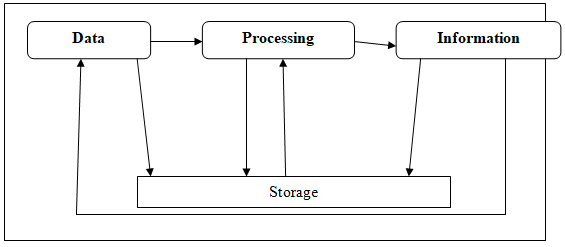
An electronic device that accepts data from a user, Processes the data using given instructions, stores it and presents it in a desired format - Data
Raw facts which include numbers, texts, images, audios or videos that input into a computer - Information
Data that has been processed and made meaningful to the user
Examples Of Computers
- Notebooks
- Smartphones
- Macbook
- PDA
- Desktop computer
- Laptop
- Ipad
- Tablet
- Smartwatch
- Server
- Each examples of computers have different features that enable them to serve different
Characteristics Of A Computer
- Speed
A computer works at a higher speed than human beings - Storage
Computers have storage space that can hold large amounts of data and information - Multitasking
Computers can perform more than one tasks at the same time - Accuracy
Computers give information without errors if given the correct data and instructions - User dependant
Computer cannot work without instructions from the user - Versatility
Computers have ability to perform a variety of task(complex and simple) - Reliability
The electronic components in modern computer have very low failure rate. The modern computer can perform very complicated calculations without creating any problem and produces consistent (reliable) results. - Diligence
Computers, unlike frail human beings, do not become bored or tired or lose concentration when performing highly repetitive work. If a computer has to perform a certain calculation on a million numbers, it will calculate the first and the last with equal diligence. This enables trust to be placed in the results generated by computers, and confidence to be replaced in their ability – neither of which can always be replaced in humans!
Function of a computer
- Stores data and information
- Process data into information using given instructions
- Accepts data from the user
- A computer gives out information to the user
Uses of computers to perform daily activities
- Accessing internet
- Paying online bills
- Home/school tutoring
- Stock taking
Stages of computer processing cycle
Computer processing cycle is the stage or events that takes place from the time data is entered into the computer to the time is given to the user.
Model of a computer
Advantages Of Using A Computer
- Computer process data faster than human beings
- Computers keep data and information secure
- Computers can store a lot of data in a small physical space
- Computer can do the same repeatedly without getting tires or bored
- Computer are able to perform different types of jobs at the same time
- A computer is reliable because it consistently does what it is supposed to do.
- Computers have a very big storage capacity and can store data and information for a very long time
- Information given by computers after processing has no error because they work under instructions and are always accurate
Disadvantages Of Using A Computer
- Use of computer has caused people to lose jobs because computers process data within a shorter time
- Use of computers for long hours leads to health problem like headaches, eye strains
- Computer lack intelligence. They cannot determine what is wrong or right. If given wrong data, they give out wrong information
- People sometimes become too dependent on computers. This affects their creativity and ability to do simple tasks
- Information and data stored in computers is at risk of theft and misuse
- People use the internet to perform online crimes and fraud
- Online threats such as cyber bulling are on the increase with the increased use of computers and the internet
- Electronic waste from computers contains chemicals that destroy the environment
Application Areas Of Computers
- Education
- For online reading
- To maintain class notes and registers
- For research and to do assignments
- Business
- To make payments
- To keep records
- To order for goods
- To sell goods and services online
- Banking
- To facilitate online and internet banking
- To operate ATM machines
- For money transfer from one bank to another
- To keep account and customer information
- Health care
- To conduct research
- To store patient data
- Manufacturing
- To model and design products for example airplane
- To test functionality of machines they are manufactured
- To automatic process in manufacturing companies
- Government
- To offer government services online through platforms such as Nemis and ecitizen
- To store data and information
- Communication
- To send and receive messages
- For making video and voice calls
- Engineering design
- To design houses, roads and buildings.
Engineers and designers use programmes like computer aided design for designing
- To design houses, roads and buildings.
- Marketing
- Marketing of goods and services
- To design and create marketing content
- Insurance
- Computers are used to keep records about customers
- Computers are used to manage money transactions
- Home
- For entertainment like watching movies
- For security purpose like storing and displaying data from CCTV cameras
Evolution Of Computers
Evolution Stages Of Computers
Computers have evolved from the abacus to digital devices
- The Abacus
It is believed to have been invented 4000years ago
It was made of a wooden frame with rods fitted across, with round beeads that slide along the rod - Mechanical devices
Napier’s bones – 1617
Pascaline or pascal’s calculator – 1642
Stepped reckoer 1671-1674
Jacquard loom 1801-1804
Difference engine 1820-1822
Analytical engine 1834-1838 - Electromechanical devices
Tabulating machine 1880-1888
Atanasoff – berry computer ABC 1937-1942
Mark 1 – 1937 1944 - Electronic digital computers
Digital computers are now classified into five generations with each having improved from the previous one
Tasks performed by computers at different evolution stages
| Type | Computer | Task performed |
| Abacus | Abacus | It performed calculations like addition and subtraction |
| Mechanical Devices | Napier’s bones – Pascaline or pascal’s calculator – Stepped reckoer Jacquard loom Difference engine Analytical engine |
They performed arithmetic calculations like addition, subtraction, division and multiplication. They automated tasks The analytical engine had a store processor (mill) and printing components |
| Electromachanical devices | Tabulating machine Atanasoff – berry computer ABC Mark 1 |
They solved fairly complex calculations They complied and analysed statistical information They solved calculations based on instructions given |
| Electronic digital devices | Personal computer Desktop computer Laptops Smartphones |
They performed complex tasks such as mathematical calculations, word processing, data storage and analysis and communications |
Difference Engine And Analytical Engine
- The difference engine and the analytical engine were designed by Charles Babbage.
- The difference engine was a simple calculator
- When he was unable to complete the difference engine, he started on the analytical engine which was advancement of the difference engine
Difference between the difference engine and the analytical engine
| Difference Engine | Analytical engine |
| Could perform only one mathematical operations | Could perform four mathematical operations |
| It had no input component | It had no input component |
| It had no storage component | Had a storage component |
| It had no processing component | Had an arithmetic unit called mill |
| It was a simple mechanical calculator | It was a general purpose computer system that could be fed with instructions to carry out operations automatically |
| It was faster than the analytical engine | It was slower than the difference engine |
Using computer that existed at different evolution stages
Pupil’s activity
Page 17
Contemporary Technology And Sustained Development Of Computers
| Device | Technology used |
| Abacus | Decimal number system where each rod represents a column and each column represents a place value Binary digit system used in computers today where a value is either 0 or 1 |
| Napier's bones | Used rods made of ivory, wood, metal or bones to work out multiplication problems using position of a number on a rod |
| Pascaline or pascal’s calculator | Used gears technology to feed data into the computer Had a display bar where the user could see the number entered and the answer It had no storage |
| Jacquard loom | Used punched cards technology to feed data into the computer Had no storage |
| Stepped rechoer | used stepped drum gear which mechanised addition, subtraction, division and multiplication employed the decimal number system |
| Difference engine | Used a set of cogs levers and punched cards Had a storage for data Was designed to stamp its answer on set metal Used decimal number system where each number from 0-9 was represented by position on toothed wheels |
| Analytical engine | It had a processor called the mill and a store It could be given instructions to make the work automatic using punched cards |
| Tabulating machine | Used punched card technology Used electric current to count data on punched cards |
| ABC | Used binary digits to represent data Performed calculations using electric current Had storage for data Had processor |
| Mark 1 | Used electric circuits Data was fed in using punched sheets or rolls |
| Digital devices | Use the binary number system Have larger processors Have large storage Use electrical components |
Generation Of Computers
Computer technology has been advancing in many ways since the invention of the first electronic digital computer
Identifying Generations Of Computers
- 1ST generation 1940-1956
- 2nd generation 1956-1963
- 3rd generation 1964-1971
- 4th generation 1971-1980
- 5th generation 1980 – present and beyond
Characteristics Of Different Computer Generations
- Characteristics of 1ST generation computers 1940-1956
- Entered data using punched cards, paper tape and magnetic tape
- Produced information in form of print outs
- Were very expensive
- Were very large in size
- Used alot of power
- Produced a lot of heat
- Were very slow
Examples
ENIA, EDVAC, UNIVAC, IBM 701, 1BM 750
- Characteristics of 2ND generation computers
- Increased data processing speed
- Were very expensive to buy
- Were more reliable as compared to the first generation
- Consumed less power
- Were smaller in size compared to the first generation
- Used punched cards to enter data
Examples
IBM 1620, IBM 7094, CDC 1604, CDC 3600, UNIVAC 1108
- Characteristics of 3RD generation computers
- Had faster processing speed than the previous generation
- Consumed less power and emitted less heat as compared to the other generation
- Became relatively cheaper and therefore available for commercial use
- Were smaller in size than the second generation
- Had larger storage for data
- Used a mouse and keyboard to enter data
- Were more accurate
Example
IB 360 SERIES, PDP, IBM 370 SERIES
- Characteristics of 4TH generation computers
- Were vry fast and more reliable
- Were cheap and more easily available
- Were much smaller in size and therefore portable
- Introduced the use of personal computers
- Were able to connect to the internet
- Had very to large storage up to several hundred megabytes
- Used a keyboard and a mouse to enter data
- Used screens and printers to five information
- Produced less heat and could be cooled using a fan
Examples
IBM 308 AND 4300 SERIES, STAR 1000, APPLE II CRAY
- Characteristics of 5TH generation computers
- Have very large storage capacity
- Can use more than one processor at the same time
- Can perform more than one task at the same time
- Are cheaper and readily available even for personal use
- Are much faster than other generation computers
- Led to development of AI artificial intelligence
- Are easier to use
Examples
Desktop
Laptop
Tablets
Applying technologies of different computer generations in daily life
| Computer generation | Computer Technology used | |
| First generation | Vacuum tubes |
These computers used thousands of electronic gadgets called vacuum tubes They were used for storage, calculations and control |
| Second generation | Transistors |
2nd generation computers used smaller components called transistors They allowed the use of words in specifying instructions |
| Third generation | Integhrated circuits |
The 3rd generation used IC technology which is a single device containing many transistors |
| Fourth generation | Very large scale integration |
During the 4th generation LSI and VLSI technology was used to pack thousands or millions of transistors on a single device |
| Fifth generation | Ultra large scale integration |
The 5th generation of computers is based on ULSI. Millions of transistors are packed into one small device This has enabled the rise in the use of AI |
Classification Of Computers
Types Of Computers
There are different types of computers used different purpose
- Mini computers
- Mainframe computers
- Analogue computers
- Hybrid computers
- Special purpose computers
- Micro computers
- Super computers
- Digital computers
- General purpose computers
Analogue Computers:
The word "Analogue" means continuously varying in quantity. The analogue computers accept input data in continuous form and output is obtained in the form of graphs. It means that these computers accept input and give output in the form of analogue signals. The output is measured on a scale. The voltage, current, sound, speed, temperature, pressure etc. values are examples of analogue data. These values continuously increase and decrease. The analogue computers are used to measure the continuous values. The thermometer is an example of analogue device because it measures continuously the length of a mercury column.
Digital Computers:
The word "Digital" means discrete. It refers to binary system, which consists of only two digits, i.e. 0 and 1. Digital data consists of binary data represented by OFF (low) and ON (high) electrical pulses. These pulses are increased and decreased in discontinuous form rather than in continuous form.
Hybrid Computers:
The hybrid computers have best features of both analogue and digital computers. These computers contain both the digital and analogue components. In hybrid computers, the users can process both the continuous (analogue) and discrete (digital) data. These are special purpose computers. These are very fast and accurate. These are used in scientific fields. In
hospitals, these are used to watch patient's health condition in ICU (Intensive Care Unit). These are also used in telemetry, spaceships, missiles etc.
Supercomputer
Is the most powerful and fastest, and also very expensive
Mainframe computer
Are large-scale computers but supercomputers are larger than mainframe.
Mini computer
Are smaller in size, have lower processing speed and also have lower cost than mainframe
Microcomputers
Are known as personal computers or simply PCs
Are meant for personal use by single users eg laptop, PDA
Special purpose computer
Computers designed to carry out specific tasks eg ATM
General purpose computer
Computers that can perform most common tasks eg word processing
Criteria used to classify computers
| Classification of computers | ||
| ,By functionality | By size | By purpose |
| 1. Analogue | 1. Microcomputer | General purpose |
| 2. Digital | 2. Minicomputer | Special purpose |
| 3. Hybrid | 3. Mainframe | |
| 4. Supercomputer | ||
Appropriate computers to use in different situations
Pupil’s activity
Page 33
Use of embedded computers in daily life
An embedded computer is a computer designed to perform a specific function
Embedded computers are used in different devices for example
- ATM machines have a computer that facilitates withdrawal of money, cash deposit and checking bank balance
- Cars have computer system to control the realises of airbags when a sensor detects an accident
Embedded computers also sense when one applies emergency brakes and prevent the wheels of the vehicle from locking and skidding through antilock braking system - Microwaves have a computer that commands the heating element to turn on and off.
It calculates time, display time and rotates the plate - Mp3 and DVD players are able to store, read data and play music and videos
- Drones have computers that enable user to control them.
The computers in drones enable them to capture images and videos and transmit them to the users - Digital watches have computers to display time in numbers and set an alarm clock
Using different types of computers in performing tasks
Pupil’s activity
Page 35-6
Computer User Environment
Computer user environment is an area equipped with devices, facilities and other components that provide suitable conditions for the use of computers
Examples are cyber cafe and computer laboratories
Factors to consider when setting up a computer user environment
- Accessibility
Computer user environment should be set up in a place where the intended user can easily reach - Good lighting
The room should be well it - Ventilation
The environment should be well ventilated, have free circulation of air and be free from heat, dust and moisture which can damage a computer system - Power source
A computer user environment should have a reliable source of power to prevent loss of data and damage of computers - Space
The floor space should allow free movement of people using the computer user environment - Security
A computer user environment should be secure with strong doors and windows.
It should also have system in place to prevent unauthorised access - Fire fighting equipment
Should be available at all times in case of a fire - User friendly
The computer user environment should be made user friendly by ensuring there is comfortable furniture - Proper cabling
Should be done from the power sources to the devices
The cable must be insulated and laid away from busy areas of the room to prevent people from getting electrocuted or tripping
Resources for setting up a computer user environment
When setting up a computer user environment, you need
- Desks and chairs
- Computer system
- Extension cards and electrical cables
- Good lighting
- Printers
- Scanner
- Projector
- UPS
Safety precautions and practise in the computer user environment
- Do not eat or drink in a computer user environment
- Do not touch naked wires
- Only allow authorised people. Avoid welcoming strangers
- Organise your desks before leaving
- Enter and exit quietly from the computer user environment
- Do not rush or push each other
- Avoid carrying pointed objects near computers
- Remove shoes entry to minimise dust
- Always follow the proper procedure for starring and shutting down the computer to avoid loss of data
Emerging trends in computer user environment
- Introduction of smartphones and small portable computers has made it easier for people to access computer services
- This means that the computer user environment is no longer confined within walls. It goes where a person has access to a computing device goes
- Mobile phone companies have made connectivity easy by availing network services to the people. This made it easy to access computer services anywhere at any time
Physical Parts Of A Computer
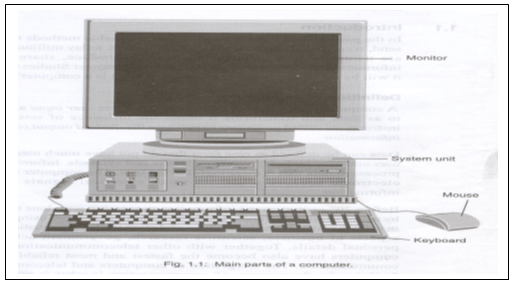
What are the physical parts of a computer?
Functions of the physical part of a computer
- Monitor
- Used to displaying information for example pictures and text
- Keyboard
- Used for typing and giving instructions to the computer
- The system unit
- Contains the devices oof a computer that Process data and gives information such as CPU
- Speakers and headphones
- Are used for listening to music and audio files
- Printer
- Is used for printing text on paper
- Mouse
- Is used for selecting items and giving instructions to the computer by clicking
- Flash disks
- Is used for storing and transferring information
- Scanner
- Is used to take images of paper documents and displaying them on a computer
- Cables
- Are used to connect different parts of a computer
Connecting the physical parts of the computer
Pupil’s activity
Page 45-46
How to minimise wastage in computer usage
- We can reuse or recycle the physical parts of a computer
For example
- If a device is in good working condition but longer in use it can be sold for some money to someone who will reuse it
Such devices can also be donated to people who need them - A computer monitor can also be used as a television screen with little modification
- We can transform a system unit to a lockable cabinet by removing the inside components and installing a lock.
- Physical parts of a computer can be used to make art for example the keys of the keyboard
- The physical parts of a computer can be sent to the manufacturer or sent to a recycling centre where they are taken apart, their components sorted and recycled.
Interacting with physical parts of a computer
Pupil’s activity
Page 48-49
Hands On Skills Concepts
Starting a computer
- Switch on the power source
- Press the power button of the monitor then press the power button of the system unit to start your computer
Wait for the computer to finish the booting process - Click on your user account. Type your username, enter your password and press enter to sign in to the computer
Shutting down a computer
- Close all the programs that may still be running
- Click on the start button and select the power button
- Click the power button. A window showing power option will appear
- Click shut down for the computer to undergo the shut down process
Function of the keys on a computer keyboard
- Delete (Del) key. It is used to erase characters to the right of the cursor, (i.e., from left to right).
- Esc
- Home
- Pg up
- Pg dn
- End
- Backspace key - It has a backward arrow ( ) marked on it.√ Used to erase characters to the left of the cursor (i.e., from right to left on the same line). When pressed, it makes the cursor move one space backwards and the immediate letter or number to the left is erased.
- Crtl
- Tab
- Caps lock
- Enter
- Shift
A Cursor is a blinking underscore ( __ ) or a vertical beam (I ) that shows where the next character to be typed will appear.
Categories Of Keys Of A Computer Keyboard
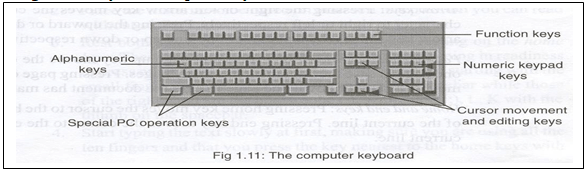
Alphanumeric keys
Keys are labeled with alphabetic letters A-Z, numbers arranged in a line 1,2, ……..0 respectively and symbols like:?,], % etc. This group also includes the following keys: cap lock, enter tab. space bar and backspace.
Caps lock key: Pressing this key let's the user type in upper case-letters,(capitals) To switch back to lower case letters simply press the same key again.
Enter key (return key): Pressing this key forces the text cursor to move to the beginning of the next line. A cursor is a blinking underscore (-) or a vertical beam (I) that shows where, the next character to be typed will appear. The enter key is also used to instruct .the computer to execute a command that has been selected on the screen.
Tab key: This key is used to move the text cursor at set intervals on the same line e.g. 10 mm, 20 mm etc.
The space bar: This bar creates a space between words during typing.
The backspace key: This key deletes characters from right to left on the same line.
Function keys
Function keys are usually located along the top of the keyboard. They are labeled FI, F2 up to FI2. They are used for tasks that occur frequently in various programs. For example pressing FI key in J most programs starts the HELP MENU.
Navigation and and editing keys - Cursor movement
Cursor movement keys are used to move the cursor on the screen. These keys are:
Arrow keys: Pressing the right or left arrow key moves the cursor one character to right or left respectively. Pressing the upward or downward arrow key moves the text cursor one line up or down respectively.
Page up and page down keys: Pressing page up key moves the cursor up one page in case the document has many pages. Pressing page down key moves the cursor down one page in case the document has many pages.
Home and end keys: Pressing home key moves the cursor to the beginning of the current line. Pressing end key moves the cursor to the end of the current line.
Editing keys are used to delete or insert characters in a document. These are:
Insert key: This key helps the user to insert or replace a character at the cursor position.
Delete (Del) key: This key deletes characters at the cursor position from left to right.
Special PC operation keys.
These keys are rarely used singly but in combination with other keys to give special instructions to the computer. They include SHIFT, CTRL, ALT and ESC keys.
Numeric keypad keys
The numeric keypad consists of a set of numbers 0 to 9 and the arithmetic signs like + (addition), ¬ (minus), * (multiplication) and / (division). They are located on the right hand side of the keyboard. The keypad is meant to help the user to rapidly enter numeric data. The numbers on the numeric keypad can only be used when the, situated on the numeric keypad, is turned on.
Use of pointing devices in a computer
- Most computers use a mouse as the main pointing devices.
- Laptops use a trackpad
- Other pointing devices that can be used with a computer are
- Trackball
- Pointing stick
- Joystick
- stylus
There are 5 common pointing devices operations
Clicking: This means pressing and releasing the left mouse button once. A click often selects an object.
Double clicking: This means pressing the left button twice in quick succession. Double clicking usually opens a file or starts a program
Right clicking: Pressing the right hand side mouse button once displays a list of commands from which the user can make a selection. This list of commands is called a shortcut menu or context sensitive menu. It is called a context sensitive menu because the commands on it apply to the right clicked item.
Drag and drop: This is whereby the user drags an item from one location on the screen to another. The procedure to accomplish this operation is as follows:
- Point to the item you want to drag.
- Press the left hand side mouse button and hold it down
- Slide the mouse until the pointer reaches the desired position on the screen.
- Finally release the mouse button and the item will be dropped in the new location.
Scrolling – the sliding movement of images, videos or text across a display screen either vertically or horizontally
Interacting with the keyboard and pointing devices of a computer
Pupil’s activity
Page 58-60
Computer System Overview
A system – is a set of things working together to achieve a common goal or objective
A computer system – is a collection of parts that work together to receive, process, manage and present data and information
Identification of computer system components
The computer system consist of 3 components
- hardware
These are physical components of a computer system that you can touch
Examples: keyboard, mouse, monitor, CPU - software
These are a set of instructions that direct a computer on what to do during processing.
They include operating system and programs like MS WORD, MS EXCEL - liveware of peopleware
These are the users who command or direct computers to perform given task
This term also refers to the people that develop the software and hardware components of a computer
Functions Of A Computer Components
- computer hardware
- accepts data and instructions
- process data
- stores data
- produces information
- communicates with devices and users
- computer software
- manages computer resources
- provides computer interface
- stores and retrieves data and instructions
- does mathematical calculation
- liveware
- designs and develops software and hardware
- operates a computer system
- enters data
- controls computer environment
Using computer system components
PUPIL’S ACTIVITY
PAGE 63
Linkage among components of a computer system
- The liverware uses hardware components to input data and give instructions to software
- The software in turn process the data and executes the instructions then gives the information through hardware.
- The information is then used by the liveware for decision making or fed back into the computer as data
Importance Of Computer Systems In The Society
- Business
Computer systems have enabled efficiency in record keeping, allowing long process to take a shorter time through automation.
They have also brought about online advertisement and sales using the internet - Communication
Computers are connected through networks allowing for faster cheaper and safer communication across the globe - Shopping
People today can shop online for goods and services and pay for them using online channels enabled by computer systems - Socialising
Computer systems have made it possible for people to socialise and conduct viral meetings through various social media platforms - Employment
Computer systems have provided employment opportunities
Eg software development and design - Entertainment
People can access a variety of music, films and computer games on their computers - Education
The internet is a huge information resources that is easily accessible compared to textbooks.
Learners are also able to learn online without the need to attend classes physically
Computer Hardware Concepts
Categories of hardware in a computer system
Computer hardware components are classified as
- Input devices
- Output devices
- CPU
- Storage devices
Functions Of Computer Hardware Categories
- Input devices
Enables user to enter data that needs processing and the instructions on how to process it
Examples: mouse, keyboard, touchpad, light pen, joystick, scanner, microphone - CPU
Process the data entered into a computer according to the instructions - Output devices
Present information that has been processed in different forms for example text, sound and pictures
Examples of output devices: monitor, printer, speakers, projector, plotter, headphones - Storage devices
Saves data, information, computer software and running operations
Examples: hard disk, memory card, flash disk
Selecting appropriate hardware for different situations
Consider
- Reliability
- Cost
Using different elements of computer hardware
Pupil’s activity
Page 71-73
Input Devices
Enables user to enter data that needs processing and the instructions on how to process it
Input devices in a computer system
Examples: mouse, keyboard, touchpad, light pen, joystick, scanner, microphone, barcode scanner, digital camera, capacitive and infra-red touch screens, 2D and 3D scanners
Categories of input devices
| Keying devices | Pointing devices | Digitiser | Scannning devices | Gaming controllers | Visual and Imaging Devices | Voice Input Devices |
| Keyboard | Mouse | Scanner | Barcode scanner | Joystick | Digital Camera | Microphone |
| Touchpad | Digital Camera | 2D scanner | Steering wheel | Image scanner | ||
| Joystick | Microphone | 3D scanner | Video recorder | |||
| Touchscreen | ||||||
| Trackball |
Selecting appropriate input devices for different situations
When selecting input devices you can consider the following factors
- User needs
The device should meet the need of the user - Cost
The device should be affordable according to user’s budget - Functionality
Devices should serve the purpose it was intended - User friendliness
The device should be easy to use - Compatibility with hardware
Devices selected should be able to connect and work together with other available devices in the computer - Level of expertise
Devices selected should meet the technical skills of the user.
Using input devices to perform tasks
Pupil’s activity
Page 77
Reusing input devices to minimise wastage
Input devices which are still functional can be used in the following ways
- Old and functional keyboards can be sold or donated to be reused with other compatible computer system
- Input devices which are in good condition and not in use can be donated to people who need them in the community
- Functional computer inputs can be used to set up other computers
- Obsolete and dysfunctional input devices can be sent to recycling facility where they will be recycled to make new products.
Central Processing Unit
The CPU is the part of a computer that process data
Locating the CPU in a computer system
Pupil’s activity
Page 80-81
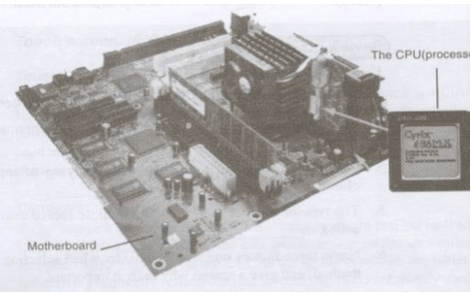
NB
Motherboard is a frame which holds and allows communication between the components of the computer system
The CPU is located on the motherboard
Functional elements of the CPU in a computer system
The CPU performs all types of data processing operations in a computer system
CPU has 3 components
- Control unit
- Arithmetic logic unit
- Special memory
Arithmetic and logic unit – ALU
Performs calculations like addition and subtraction
It also performs logical operations which mainly involve comparison of data
Control unit
Coordinates movement of data between the processor and the memory
Special memory
Stores data and information required during processing.
Most of the CPU operations are performed by the ALU
The control unit moves data between the ALU and the special memory and also tell the ALU what to do.
The ALU then process data and store the result in a special memory
Types of processors in computing devices
There are 6 types of CPU
CPUs are classified according to the number of cores they have
The core of a CPU receives instructions and perform calculations, or operations to satisfy the received instructions
| Type of processor | .Number of cores | Examples |
| Single core | 1 | Intel 4004 |
| Dual core | 2 | Intel core duo, AMD X2 |
| Quad core | 4 | ATHLON II X4, INTEL CORE I3-10100 |
| Hexa core | 6 | INTEL CORE I5-11400, INTEL CORE I5-11600K |
| Octa core | 8 | INTEL CORE I7-11700K, INTEL CORE I7-11700 |
| Deca core | 10 | XEON SILVER 4114T |
Performing tasks using computers with different processors
Pupil’s activity
Page 84-85
- Processors receive input data, process it and generates results.
- It computes data and receives instructions in almost all actins carried out in a computer.
- Processors determines the speed with which a computing device processes information
- Computers with fast processors have high processing power and often give information faster
Output Devices
Present information that has been processed in different forms for example graphics, tactile or text, sound (audio), video and pictures
Output devices of a computer system
Monitor, printer, speakers, projector, plotter, headphones, Braille embosser
Functions of output devices in a computer system
- Monitor
Display data in text and graphics - Speakers
Gives information in form of sound - Headphones
Produce audio information - Printers
Produce text or picture information on a paper - Projectors
Gives visual information by projecting it on a flat smooth surface like a wall or white board - Plotters
Produces digital created graphics and drawings
Plotters use a pen to draw lines on paper - Actuator
A part of a device or machine that helps to create physical movement using signals from a computer - Braille embosser
A device that presses dots onto paper for people with visual impairment to read using their fingers
Categories of computer output devices
| Output devices | ||
| Visual output | Audio output | Physical output |
| Produces text or graphics | Produces sound | Produce movement |
| 1. Monitor | 1. Speakers | Printer |
| 2. Screen | 2. Headphones | Plotter |
| 3. Projector | 3. Earphones | Actuator |
| Braille embosser | ||
NB
- Hardcopy refers to data printed out on paper
It could be text, photographs, illustrations or any data that can be printed
| Advantage of hard copy | Disadvantage of hard copy |
| It is considered permanent data as editing and changing is not easy | It is expensive to produce as t requires paper, ink and printer |
| It does not need electricity, special devices or software to display | It is not easy to move from one place to another |
| When properly stored it is not easily lot | It requires a lot of physical storage space |
| It is not subjected to data stealing and cyber attacks | It can be stolen or destroyed through wear and tear or by environment factors such as fire, water |
- Soft copy is information stored and displayed in a computer
| Advantage of soft copy | Disadvantage of soft copy |
| It is easy to move from one place to another | It is vulnerable to cyber attacks and data theft |
| It is cheap to produce as it does not require paper or ink | It requires electricity, a device and software to display |
| Large amount of data and information can be stored without the need for a lot of physical space | It is considered temporary data which can be easily altered or manipulated |
| It is beneficial to the environment as it reduces the number of trees cut too make paper |
Selecting appropriate out devices
Factors that you consider when selecting output devices are
- Output quality
- User friendliness
- User needs
- Suitability to the function it is supposed to carry out
- Compatibility with the available devices
- The cost of purchasing and maintaining the output devices
Uses of output devices
We care and use output devices safely by
- Keeping the devices away from water and dust
- Avoiding exposure to foods and fluids
- Always powering off the devices after use
- Connecting only with compatible devices
- Cleaning and servicing the devices regularly
- Ensuring secure connection of the devices before use
Technological trends in development of output devices
Output devices have constantly been replace with new devices due to improved technology from innovators
Technological trends enables fast evolution of output devices which suit user needs better, are cost effective, friendly to the environment, secure and able to multitask
- Computer displays which are used to create clear, high quality, digital displays
- Wireless speakers and headphones which are more portable, have noise cancelling capability and produce better sound quality
- Better Braille embossers that give better quality Braille while producing very little noise. They also recognise speech and give speech feedback, making them user friendly
- Printers which produce better quality hardcopies, can be secured using passwords, are compact, cost effective and easy to use
Ports And Cables
Port
A physical slot of a computer through which peripheral devices are connected.
All input and output devices of a computer are connected on the ports
Cable
A chord that connects and enables transfer of data or power from one device to another
A computing system has ports and cables that enable communication between the differebt components of a computer
Identifying cables and ports
Pupil’s activity
Page 97
Types of cables and ports used in a computer
There are 2 types of cables
- Power cables
These allow for power transmission and distribution from the source to all computer hardware components - Data cables
These carry data and allows for communication between devices in a computing system
| Data cable | Description |
| 1. USB cable and port | The universal serial bus is used to connect all devices to PCs like printers, keyboards, external hard disk, mice, scanners, cameras, and many more |
| 2. PS/2 cable and ports | This is used to connect the keyboard and mouse to the computer. |
| 3. Serial cable and port | This is used to connect hardware components such as mouse, doem and printer. It can also connect old models of computers together to allow the transfer of large files |
| 4. Parallel cable and port | Parallel ports and cables connect computers and peripheral devices |
| 5. Ethernet | This cable and ports connects the computer to a network and the internet |
| 6. VGA cable and port | The VGA port and cable connects most computer models to their monitors |
| 7. Audio cables and ports | This cable connects computers to audio devices such as speakers, headphones and microphones |
| 8. RCA connectors | Digital output devices produce better quality audio. This is achieved using the RCA connectors |
| 9. Digital video interface DVI cables and ports | DVI connects video source, such as a video display controller to a display device such as a computer monitor |
| 10. HDMI port and cable | High definition media interface connects a computer to high definition and ultra high definition devices like computer monitors, HDTVs, BLU-RAY players, gaming consoles and high definition cameras |
Relate cables to their corresponding ports in a computer
Pupil’s activity
Page 100
Connecting cables to their corresponding ports
Pupil’s activity
Page 101-102
NB
- Ports enable the connection of output and input devices to a
- Ports allow computers to connect to networks
Computer Setup
Setting up a computer is connecting all the hardware devices and preparing software programmes for a computer to function properly.
Problems experienced when setting up computers
- lack of skills in setting up computers
- difficulty matching cables to their respective ports
- inability to identify and correct failed connections
- lack of skills in installing operating systems
- lack of reliable power source to power devices
- damaged or broken cable pins due to improper fixing
eg forcing a cable to a wrong port - damaged hardware devices that do not work
- computer and monitor not turning on due to faulty power cables or improper fixing of cables to the power supply
How to set up a computer
- setting up a new computer
- setting up a laptop
Pupil’s activity
Page 104-106
Setting up computers
The following are tools and equipments need for computer set up
- system unit
- Monitor
- Screwdriver
- Speakers
- Cables
- UPS
- Keyboard
- Power tester
- Surge protector
- Mouse
- Power extension cables
Some ways of ensuring safety when setting up computers include
- Ensure there is a stable power supply that can power on a computer before the connection
- Use a UPS or surge protector for power connection to the CPU and monitor
- Make sure your hands are completely dry to avoid electric shock and damaging any computer parts with moisture
- Handle all the parts of a computer with care. Place each component carefully on a hard flat surface. Be careful not to drop any parts
- Ensure your computer has enough room to allow for proper ventilation. If there is no free flow of air the computer can be damaged or cause fire.
- Be sure to connect all cables to the appropriate ports
- If a cable does not connect easily to a port, don’t forcefully push it in to avoid damaging it. Check that you are connecting it to the right port and that the pins and holes align
- Manage cables properly when setting up a computer. Ensure nothing is pressing on them and that they are not located in a place where they can be stepped on or tripped over
- Do not spill foods or liquids on the computer
- Always switch on the monitor before the CPU to display any errors or messages while booting
Setting up computers for use
Pupil’s activity
Page 109
Overcoming challenges experienced when setting up a computer
- Researching and learning how to set up a computer properly
- Researching and learning how to match cables to their respective parts checking that all connections are properly made
- Replacing or repairing damaged parts
- Ensuring that there is a reliable source of power
- Observing safety precautions when setting up a computer
Practising booting computers
- To tell that a computer is properly setup, we must switch it on and see if all the components are working well. This process is called booting up a computer
- The steps of booting a computer are as follows
- Switch on the main power supply on the socket
- If the computer is connected to the UPS, switch its power button on.
- Switch on the monitor by pressing the power button
- Switch on the system unit by pressing the power button
- Upon switching the system unit on , the computer performs a power on self test where the computer checks hat al components are connected and functioning well
- The computer then displays the name of the operating system followed by a display of icons on the computer monitor
Agriculture and Technology - Grade 7 Agriculture Revision Notes
Off Season Cropping Techniques
Off season cultivation refers to the production outside of their typical cropping cycle.
The main objective of off season cultivation is to produce and supply to the market during their lean period.
Importance/Advantages of off season cropping
- It helps in the more effective and efficient use of land and farm resources.
- The per-unit result of off-season planting is excellent.
- Consumers nowadays prefer fresh veggies even when they are not in season, and off-season vegetable cultivation can meet this need.
- It is sometimes feasible to gain foreign exchange by exporting fresh veggies.
- It is a great source of preventive food that also contributes to nutritional security.
- It's a good choice for seed production.
Technologies For Off Season Cropping
- Drip irrigation
Crop yields can increase through improved water and fertility management and reduced disease and weed pressure. When drip irrigation is used with polyethylene mulch, yields can increase even further.
These benefits are only possible when a drip irrigation system is properly designed, managed, and maintained.
Advantages of drip irrigation
- Lower-volume water sources can be used because trickle irrigation may require less than half of the water needed for sprinkler irrigation.
- Lower operating pressures mean reduced energy costs for pumping.
- High levels of water-use efficiency are achieved because plants can be supplied with more precise amounts of water.
- Disease pressure may be less because plant foliage remains dry.
- Labor and operating costs are generally less, and extensive automation is possible.
- Water applications are made directly to the plant root zone. No applications are made between rows or other nonproductive areas, resulting in better weed control and significant water savings.
- Field operations, such as harvesting, can continue during irrigation because the areas between rows remain dry.
- Fertilizers can be applied efficiently through the drip system.
- Irrigation can be done under a wide range of field conditions.
- Compared to sprinkler irrigation, soil erosion and nutrient leaching can be reduced.
- Container gardening
The following crops best suited for container/pot gardening;- Beans
- Beets
- Tomatoes
- Cucumber
- Onions
- Peas
- Radish
- Carrots
- Potatoes
- Squach
- Brinjal(Eggplant)
- Ladies Finger (okra)
- Capsicum/Pepper/ Green Chilies
- Leafy vegetables such as lettuce, Kale, Methi(Fenugreek), Coriander (cilantro)

Factors to consider when establishing framed suspended gardening for off season crops
- Can it be established along pathways
- Can it enhance beauty
- Can it grow within a short period of time (not a perennial crop)?
- Is there space for the containers
- Mechanisms put in place to manage pests and diseases.
Off Season Production Techniques
- Taking use of and utilizing various agro-climatic conditions.
- Improved varieties are chosen.
- Adjustment of planting time.
- Making plastic tunnels, polythene houses, and permanent glass houses to provide controlled environmental conditions.
- Staggered planting
- Succession planting – planting two different at different times in one farm- one with a faster maturity.
Construction of suspended garden design
Refer to learner’s book
Value Addition Techniques
Value-added agriculture generally focuses on production or manufacturing processes, marketing or services that increase the value of primary agricultural commodities, perhaps by increasing appeal to the consumer and the consumer's willingness to pay a premium over similar but undifferentiated products.
Benefits include:
- increased income,
- employment creation,
- improved food safety,
- food security,
- nutritional benefits and
- greater consumer confidence.
There are four major ways that value is added to crops along the value chain:
- product transformation, e.g. frying, drying
- distribution,
- storage, and
- added service.
The value of farm products can be increased by cleaning, cooling, cooking, combining, churning, culturing, grinding, extracting, drying, handcrafting, packaging and distributing, as well as by adding information, education or entertainment,
Adding value to groundnuts
Apart from just eating them raw or cooked, groundnuts can be used to produce oil, paste, flour or sauce used in cakes and cookies obtained by grinding nuts, and peanut butter.
Adding value to Potatoes
This can be done through boiling, frying, smashing.
Learners to check on how to add value on other products
Importance Of Addition On Crop Produce (explained)
- Increased revenue. Any addition adds a percentage of increased financial value to the produce and has the effect of improving the incomes of the local farmers.
- Value addition allows the farmer to focus on the consumer while producing and through meeting expectations, he can create a loyal market around the product.
- Increased shelf life is a benefit any farmer would want. The longer the product can stay without getting spoilt, the more the guarantee one has of a product selling at their preferred price and time. Milk for instance, hardly lasts over 24 hours but with boiling, it can last more days while with further processing into ghee, the same milk can last months.
- With value addition comes increased bargaining power. Brand Creation is one of the de facto results of value addition and a fact that your product can be directly identified with you or your farm which is important in an industry where customers exercise a lot of brand loyalty. It allows them to always and readily identify with you as well as win you more referral customers.
- value addition creates employment opportunities for people who work there like; industrial chemists, food processors, factory laborers
- Wastage and disposal of unwanted refuse is curtailed since they can be made into different quality products. This helps to ensure zero waste and protect the environment.
Animal Production - Grade 7 Agriculture Revision Notes
Animal Handling
Forms Of Animal Handling (humane Methods)
The objective of humane animal handling is to move animals with minimum stress to both the animals and handler. Considerate handling reduces the risk to the animal of pain, injury and suffering.
Planning the restraint procedure
When preparing to restrain a patient, always make sure the area has enough room, is clean, dry, and well lit
- A plan should be discussed:
- Move any costly equipment
- Nonslip area
- Temperature should be considered
- What should be done if animal happens to get away from restrainer
- Back up plan (Plan B!)
Rabbit Restraint & Handling
Picking Up
Grab scruff of the neck with one hand and lifting up while placing the other hand under the rump for support or wrap patient securely in a towel.
Holding
Use the same technique but the hand under the rump is moved to support the abdomen.
Rabbits seldom bite but many cause injury with their hind legs or may be injured if placed on a smooth surface
Rabbit’s foot pads are covered with fur which causes a lack of traction
Can lead to dislocation of their hip or spinal fracture, when they try to move or hop
Rodents Restraint & Handling
Mice
Grasp the tail close to the body with one hand
Use the other hand to grasp loose skin in the neck and shoulder area.
Larger Rodents and Ferrets
Make sure the animal is awake to avoid bites
Hold in one hand, cup other over its head
Wrap thumb and index
finger around neck and under chin
Do not over tighten fingers around chest as this can impair breathing
Avian Restraint
Birds
Highly trained personnel
Can stress easily
Do not squeeze thorax
Sensitive to overheating
Small to medium sized
Grasp from behind, finger and thumb on sides of head, others around body
Large birds require 2 hands
Towel can also be used

Cats Restraint & Handling
Cats tend to be one of the most difficult during restraint when they become upset and aggressive from stress
Safely restrain and have control over head
Cat bags: control the limbs and head
Squeeze cages: wire boxes with small slots that allow injections to be given

Inhuman handling of animals in the community

Solutions to animal’s mistreatment
- Be an example of kindness to other pets. ...
- Intervene if you witness animal cruelty, abuse or neglect. ...
- Report animal cruelty, abuse or neglect. ...
- Teach your children to have respect for animals. ...
- Demand stricter laws for the protection of animals. ...
- Shelter an animal in need.
Importance Of Human Treatment Of Animals
- Improved levels of animal health and care will deliver better animal welfare, more efficient livestock production, safer animal-sourced foods and healthier, improved livelihoods.
- Animals that are well fed and watered, kept in clean and comfortable conditions, and that are handled well with opportunities to express important behaviours are less likely to die prematurely or show poor growth than less well cared for animals.
- They are more productive with more efficient use of resources such as time, labour and feed for livestock production bringing benefits including improved food security and greater income.
- Furthermore, avoiding stress before slaughter reduces contamination of meat with harmful bacteria and affects the quality, and value of the meat.
- Animal welfare is therefore also environmental protection. However, it is not only animals in stables or private households that need to be protected, but also animals in the wild. There they need above all plenty of space, clean water, fresh air, and sufficient food and shelter.
General Management of Pets
Characteristics Of Pets
- Dependent on Humans to Live – A pet needs to be given food, water, and shelter by its owner. Being domesticated means the animal depends on its owner for all of its care.
- Lives in a Home – A pet lives in a home. Some pets such as parakeets and hamsters live in cages. Alternatively, dogs and cats wander freely around a home and may have their own bed to sleep in.
- Needs a Veterinarian’s Care – Pets need care from a veterinarian. The type of healthcare a pet needs depends on what type of pet it is. An iguana and a beagle need completely different types of vet care!
- Some Pets Can Be Trained – A dog can learn how to sit, stay, and heel in a course of obedience training. Parrots can be taught to talk, and some cats can be taught by humans to do tricks.
- Devoted to Its Owner – Pets are often devoted to their owners. They can establish a trust with their owner over time. In fact, some pets want to be with their owners 24/7!
- Provides Companionship – A pet is meant to be a companion to its owner.
- Pets are Different from a Therapy Animal – A therapy animal receives specific training in order to provide support and care to its owner. As an example, some therapy dogs are trained to recognize the signs of a seizure in their owner. The dog responds by trying to get the person to a safe place. Alternatively, a pet is there strictly as a companion.
- Different from a Farm Animal – A cow or a chicken living on a farm serves a specific purpose. A cow provides milk while a chicken lays eggs to be eaten or sold. This makes farm animals a little different than traditional pets.
- Can Be Common or Uncommon – When you think of a pet you probably picture a dog, a cat, a bird, a fish, or a gerbil. Those are common choices for pets. Some people prefer less common or exotic pets such as snakes, iguanas, spiders, and ferrets. As long as an owner can offer appropriate care, many animals can live happily as pets.
- Cannot Survive in the Wild – One of the main characteristics separating pets from other animals is a pet can’t survive in the wild. It has been domesticated or raised under a person’s care. So, releasing a pet snake into the wild doesn’t mean it will know how to find food or shelter. In fact, it will likely die.
Different types of pets reared in the community
A pet is a domesticated animal that lives with an individual or family. There are popular, well-known pets like dogs and cats
- Dogs
- Cat
- Rodents
- Fish
- Birds
- Turtles
- Snake
Factors To Consider When Selecting A Pet For Rearing
Choose a pet that will suit your lifestyle and surroundings. For instance:
- How often are you home? If you work long hours, a dog may not be a good choice of pet, as all dogs require lots of companionship. In this case, pets such as fish might be more suitable.
- How large is your backyard, and do you have good fencing? If you have a small backyard or poor fencing, then a dog may not be a good choice. You could consider a pet such as a cat that lives indoors with you.
- Are you prepared to have more than one pet? Some types of animals, such as birds and rabbits, need the company of each other to stay happy and healthy.
- How much money can you afford to spend on your pet? All pets are expensive — even animals that are cheap to purchase, like fish, birds and guinea pigs, can cost a lot of money when it comes to buying and setting up tanks, cages and hutches. Some dog breeds will cost more to keep than others. Large dogs need more food, some breeds of dogs need regular clipping of their coats.
- Are you renting? Your landlord may not let you to own a cat or a dog. You may want to consider other pets such as fish.
- Do you live in an apartment? Some birds, such as parrots, can be very noisy, and may attract complaints from neighbours. You may want to consider a quiet pet such as a cat, or fish.
- Do you have young children? Some types of pets tolerate children better than others.
- Are you prepared to have your pet inside with you? Dogs should not be left in the backyard all day — they need to spend time inside the house with you, in order to remain happy and healthy.
- Does your council require cats to be confined to your property? If so, you must be prepared to have your cat live inside with you, or to buy or build cat proof fencing or a cat enclosure.
- How much time do you have to exercise your pet? Dogs need daily walks. Some breeds of dog are more energetic than others and may need longer or more frequent walks.
- How much time do you have to train your pet? Dogs, particularly puppies or young dogs, need time spent on toilet training and basic obedience training. Puppies and kittens also require lots of socialization, and regular small meals throughout the day, during the first 6 months of life. You may be better off adopting an adult dog or cat, who is already house trained and socialized.
Acquiring a pet for rearing
- Adoption is the best choice
Adoption of a pet from a shelter is the best way to find a new companion. There are many animals in shelters waiting for a new home to call their own, including a large variety of breeds, sizes, and ages of animals. Some shelters also rehome small mammals such as rabbits, guinea pigs and hamsters who are often sadly taken to shelters when the children they have been bought for have lost interest in caring for them. The benefit of rehoming from a reputable animal shelter is that the animals will have been assessed both in terms of their health and behaviorally - Brokers,
- pet stores,
- neighbors,
- professional breeders,
- commercial kennels,
- puppy mills, and animal shelters
Management Practices In Rearing Of Pets
- Colostrum feeding
- Weaning
- Disbudding - Arresting the horn growth at an early age, when the horn root is in the bud stage is called disbudding.
- Ear tagging
- Castration
- Vaccination schedule for adult animals
- Disinfection
- Quarantine
- Isolation of sick animals
- Insuring the animals
- Disposal of carcass
- Record maintenance
Preparation Of Animal Products
Different animal products include:
meat and meat products, poultry products (meat and eggs), fish, shellfish, dairy products (milk and cheese), and non-food products such as fiber (wool, mohair, cashmere, and leather)
Factors To Consider When Grading Eggs
The grade is determined by the
- interior quality of the egg
- the appearance and condition of the egg shell.
- Eggs of any quality grade may differ in weight (size).
- Weight or Volume
- cleanliness
- Size,
- Colour
Factors considered in detecting defects when grading eggs
- blood spot,
- meat spot,
- mold,
- stuck yolk,
- addled egg and
- embryonic growth
Processing Raw Honey
The process of honey harvesting and extraction most likely happens on separate days. These are the tools required:
Honey Harvest
- beekeepers suite - mesh helmet and folding veil would do it, with some layers of clothes
- smoker with fuel (dry branches, leaves, etc.) and a lighter
- frame super - where frames with honey combs will be put for transportation
- sting resistant gloves
- hive tool - to move the frames, scrape wax, etc.
Honey Extraction
- heated knife - to unseal honey cells
- uncapping fork - to unseal honey cells missed by the heated knife
- tub for wax/honey
- extractor! - fancy cylindrical piece of equipment, used to extract honey
- food-grade bucket - to catch honey out of the extractor
- double sieve - catches wax and impurities as honey is poured from extractor
- containers - final destination of honey before consumption
The process of honey harvesting and extraction most likely happens on separate days. These are the tools required:
- Harvesting
Light the smoker. Use dry branches, hay or newspaper. The smoke dulls the bees' receptors, and prevents them from releasing the alarm odor, a volatile pheromone. The smoke also makes bees gorge on honey, which further pacifies them
- Prepare Supers
The frames with honey comb are transported in supers. Have them handy. You may also want to have a cloth to cover the super with frames full of honey to prevent bees or other insects from getting to them.
- Open Sesame

Using the hive tool, lift the hive lid and blow some smoke in the hive. Open lid slowly. Our bees were pretty calm, but that is not always the case! - Honey Frame Inspection
Pull the frames out of the super and inspect the honey combs. Depending on how busy the bees were, how warm it was and if the hive didn't swarm you will know how much honey you have.
- Extraction

Now the best part! Take the frame of capped honey. Mount the frame above the tub for wax and honey. Use the heated knife to unseal the cells. Lean the heated knife on the edges of the frame and under 30 degree angle and move "fast" - don't linger too long, it burns the honey! Repeat for both sides of the frame.
The heated knife takes off most of the caps. For the leftover ones, use the uncapping fork and gently shave off the caps. - Pour Out Slowly!

Place your food-grade bucket under the extractor spigot. Use a double sieve to catch the wax and impurities as the honey starts pouring out of the extractor. - Prepare Containers

Wash your jugs, jars or whatever containers you will put the honey in. Air dry.
Extracting Honey Without A Honey Extractor
For small apiaries, harvesting honey without an extractor can be a fun and inexpensive option. We’ll cover two methods that do not require an extractor: the crush and strain method, and the cut comb method. Both of these extraction methods sacrifice comb, meaning your bees will need to draw out new comb before they can produce more honey — which can mean a smaller harvest the next year. This may factor into your decision about which method you use.
The crush and strain method is a low-cost honey processing technique. You simply scrape the honeycomb off of the frame into a bucket, then crush the comb. Place a sieve in another bucket or container, pour the crushed comb into the sieve, and strain it overnight. This process may be best suited for hobby beekeepers who only have one or two hives. The honey will move more quickly in a warm room, and you may be able to get more honey if you stir the crushed combs a few times and scrape large wax flakes off of the inside of the strainer.
Cut comb honey is an elegant way to package and use your harvest. There are tools available for cutting and packaging comb, but a good-quality kitchen knife does the job nicely, as well. This method works only for frames that contain wireless wax foundation or no foundation — you cannot use this method with frames that use plastic foundations, and wired wax foundation will limit the sizes and shapes of combs you can cut. Choose frames that are fully capped and sealed — this indicates that the honey will have the right amount of moisture to prevent spoiling.
Importance of sorting and grading eggs
- Sorted eggs bring more money to the investor than unsorted.
- It reduces wastage.
- separates eggs into grades of quality.
- A bad egg can be dangerous to consume and negatively affect someone's health.
Importance of processing raw honey
- improves the honey's appearance,
- increases its shelf-life, and
- kills yeast cells that can affect the taste of the honey.
- It can prevent fermentation.
- It delays crystallization.
- removes impurities.
Crop Production - Grade 7 Agriculture Revision Notes
Preparation Of Planting Site
Preparing land for planting is one of the most important parts of cultivating abundance. Whether you're planting fruit trees, wildlife corridors, or an annual garden, prepping the soil in the first place is the best way to set yourself up for success over the long haul.
There are numerous methods that you can use for preparing land for planting that will help me make the living world around me come alive.
- One-Time Tilling

- Mulch Alone
- Sheet Mulching
- Double Digging
- Solarizing

- Animals (focus on chickens and pigs)
Crop Establishment
Categories of planting materials
Types of Planting Materials
- Seeds (seasoning herbs, legumes, corn)
- Seedlings (most vegetable crops)
- Cuttings (cassava, potato, yam, ginger, dasheen, tannia, eddoes)
- Suckers (banana, plantain)
- Budded/ grafted plants (fruit trees)
Certain Factors need to be considered when you are choosing planting matter or seedlings from nurseries or plant shop.
Environmental Factors
- The surroundings should be free from overgrown bushes, generally clean, no waterlogged conditions
- Seedlings should be in conditions that are free from excess shade. If seedlings have too much shade they do not “harden off” and they have difficulties when they are transplanted.
Seedling Characteristics
The seedlings should:
- Be of the appropriate age (seedlings with 4-6 healthy green leaves)
- Be free from pests and diseases
- Have healthy white roots (good root development, with no balling of roots)
- Show vigorous, healthy growth
- Be of uniform appearance
- Have the proper Shoot to Root ratio (2:1)
Methods Of Planting Various Crops
- Broadcasting: Generally, the seeds are broadcast-sown and later planked. This method of sowing is easier and area coverage is quick. However, uniform population cannot be maintained since the seeds are not placed in uniform depth and germination may not be uniform. The skill of the labour is important to sow the seeds evenly covering the entire field. Broadcast-sowing is normally practiced under dryland condition. Seed requirement is generally high for broadcast sowing.
- Sowing behind the country plough: In this method, sowing is taken up behind the country plough operation. Seeds are dropped in the furrow opened during ploughing and subsequently covered while the next adjoining furrow is formed. Bold seeded crops like groundnut are sown by this method in drylands. It is important to take up sowing at the appropriate soil moisture so that the depth of sowing is uniformly maintained.
- Drill sowing or drilling: Drill sowing is one of the best methods that provides uniform plant population since seeds are uniformly dropped in the furrows. Animal drawn or power operated seed drills are used for this purposes; seed cum fertilizer drill can also be used. By this way, depth of sowing can be maintained; fertilizer can also be applied simultaneously. Pelleting of small sized seeds may reduce the risk of irregular dropping. Since sowing is taken up in lines, intercultural operations can be easily practiced. It is possible to take up sowing of intercrops also.
- Dibbling: In the method, a seed or few seeds are put in a hole and covered. Under irrigated condition, seeds are dibbled in lines or on the sides of the ridges maintaining optimum intra- row spacing, e.g. maize and cotton. Though this method is laborious and time consuming, it gives rapid and uniform germination and the requirement of seed is less than in broadcasting.
Methods of Plant Propagation
- Cutting
This is cutting the vegetative part of the plant (leaf, stem, and root) and then planting it again to regenerate the whole plant. The three types of cutting are named after the plant part being detached/cut:
- Stem cutting
- Leaf cutting
- Root cutting
- Division
This is a suitable technique for perennials (plants that live for more than two years). It involves dividing the plant by digging and moving it to an already prepared site. This helps the plant to rejuvenate and reduce water and nutrient competition.
- Layering
In this technique, the attached and bent branch of the plant is covered with soil and allowed to root. After the emergence and development of roots that specific part of the plant is cut and allowed to grow as a new plant. This is called ‘layering’.
- Grafting
This involves cutting a twig of one plant and joining it with the stem of another plant in such a manner that they form a unit and function as one plant. It is a bit of a complex process but allows you to bring the desired character to your plant. However, be sure to sterilize your hands and tools to make sure you don’t transfer any infections during the process.
- Budding
In this method, a cut is made in the rootstock and a single bud with little or no wood is inserted into it in such a way that they unite and grow as a new plant.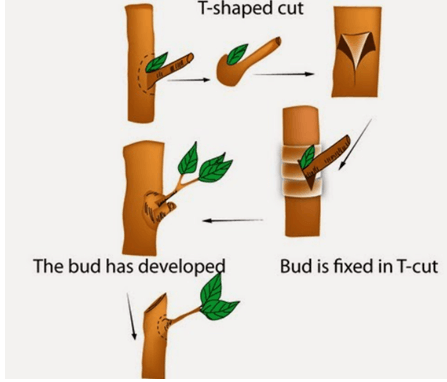
Time of planting depends on the following factors
- Soil and weather conditions
- The kind of crop to be planted.
- The time the produce is desired.
Crop Management
- Adoption of best crop management practices improves crop productivity and can contribute to greater yields with improved quality.
- Crop management is the set of agricultural practices performed to improve the growth, development and yield of crops.
- It begins with a seedbed preparation, sowing of seeds and crop maintenance; and ends with crop harvest, storage and marketing.
- The timing and sequence of agricultural practices depend upon several factors, such as winter or spring crops; harvested products such as grain, hay and silage; sowing methods-broadcast and row-crops; and, plants age, soil, climate and weather conditions.
Physical Methods Of Weeding
Manual control
Manual control is the use of the hands or handheld tools to deal with. An advantage of manual control is that it minimizes soil disturbance, and decreases the likelihood of erosion and seed germination.
Hand pulling
Hand pulling aims to remove the entire plant, including its roots, from the soil. This method is useful for small-scale infestations. It is best to hand-pull weeds after rain, when soil is moist. Sturdy gloves should be worn to avoid prickles, blisters or sap burns to the skin. It is not appropriate for all weed species, such as those with underground bulbs.
Hand tools such as broad knives and trowels can be used to remove underground parts of weeds (such as bulbs) that may reshoot. In some cases it is necessary to dig out the crown of the plant. This requires the growing part of the plant to be cut beneath the ground using a knife.
Grubbing or chipping
This method requires weeds to be dug out using a mattock or chip hoe. Depending on the plant, it may be important to expose the root system, and remove the crown.
In some cases, the mattock or chip hoe is used to cut the stem of the plant below the ground. This method is useful when the ground is hard. Gloves should be worn to avoid blisters.
Mechanical control
Mechanical control is the use of powered tools and machinery to manage weeds and is best suited to larger infestations. Care should be taken to minimise soil disturbance.
Slashing, mowing, dozing, pushing and felling
At times, controlling weeds using mechanical methods is preferred. However, care should be taken when machinery is used in the process.
Disturbing the soil with mechanical control can:
- increase the likelihood of seed germination
- damage native vegetation.
Bulldozers and chainsaws can be used on woody and tree weeds where they are pushed or felled and finally snigged (dragged away). These methods are only suitable in certain situations, as they create high levels of soil and vegetation disturbance. Also, shoots and seedlings require follow-up attention.
Grading or scalping the top layer of soil is an effective method of removing a seedbank. As this method greatly disturbs the soil, it is best suited for areas that are to undergo complete rehabilitation.
Earth Up
Earthing up refers to the act of heaping soil around the root zone of the potato plant. It is one of the primary production practices that must be done to increase the potato yield.
Advantages of earthing up
- improves tuber formation/expansion/roots/pods formation
- Improves drainage around the crop
- Conserves water/soil
- Facilitates harvesting of tuber crops
- Root protection

Managing Plant Spaces
Thinning
When the young seedlings are too close to each other, they do not grow well. They do not find enough nourishment in the soil and their leaves do not have enough room to develop.
Leave only the strongest plants and remove the others. This is called thinning.
When you take out the seedlings that are small, diseased or misshapen, be very careful not to damage the seedlings which remain in the beds.
At the end, pack down the earth around the base of the plants and water them.
Staking
Vegetables with long and weak stems, for example beans and tomatoes, need stakes.
A stake is a stick firmly embedded in the earth. It is best to use hard wood, which does not rot.
Pruning
Certain vegetables, like tomatoes, beans, eggplant, need pruning.
Nip off surplus buds. Then there will be more fruits and they will be bigger.
Gapping
When the seeds fail to germinate, empty spaces are seen within the rows. This if left unfilled can make the farmer incur losses as a result of low yields. The filling up of these spaces or the replacement of ungerminated seeds is called gapping.
Advantages of thinning and gapping
Both thinning and gap filling ensures ideal plant population and optimum utilization of sunlight, space, nutrients, moisture and other inputs which ultimately increases yield.
Crop Hardening
- Hardening, or "hardening off," is the process of allowing a plant to transition from a protected indoor or greenhouse environment to the harsh outdoor conditions of fluctuating spring temperatures, wind, and full sun exposure.
- A gradual introduction of these outdoor stresses will cause the plant to accumulate carbohydrates, to trigger more root development, to reduce the amount of freeze-prone water in the plant, and to actually thicken its cell walls. Plant growth will change from soft and supple to much firmer and harder.
Hardening Timetable
- Start the process of moving plants outdoors about two weeks before the weather will be favorable enough for the particular plant to live outdoors.
- Check seed package instructions or inquire where you purchase seedlings as to when the plant can tolerate outdoor conditions. (Keep in mind that air temperature is often warmer than soil temperature.)
- This Vegetable Planting and Transplanting Guide provides guidance for when some popular crops can be planted outdoors.
Hardening Process
- When temperatures are at least 45-50ᵒ, move plants outdoors to a shady, protected spot.
- Initially place in the shaded, sheltered location for two to three hours.
- Gradually increase the amount of sunlight the plants receive over the two-week period. The last day or two, the plants can spend 24 hours outside.
- Reduce the amount of water plants receive, but do not allow them to wilt.
- Avoid placing seedlings outdoors on windy days.
- Cold frames are excellent places to harden plants, but another spot that provides protection, such as a porch, will work.
- Pay attention to the weather forecast; if temperatures will fall below 45ᵒ, be prepared to bring the plants inside.
Keep in mind that the overall goal of hardening is to slow the growth of the plants to allow them to adjust to a change in conditions. After proper hardening, even warmth-loving vegetables, such as tomatoes, can withstand an unexpected dip in spring temperatures.
Importance of crop management practices
Learners to work on them.
Conserving Agricultural Environment - Grade 7 Agriculture Revision Notes
Soil Pollution Control
Def: Soil pollution - refers to anything that causes contamination of soil and reduces the soil quality.
- It occurs when the substances causing the pollution reduce the quality of the soil and convert the soil inhabitable for microorganisms and macro organisms living in the soil.
- Soil contamination or soil pollution can occur either because of human activities or because of natural processes.
- However, mostly it is due to human activities. The soil contamination can occur due to the presence of chemicals such as pesticides, herbicides, ammonia, petroleum hydrocarbons, lead, nitrate, mercury, naphthalene, etc. in an excess amount.

Causes of Soil Pollution
- Soil pollution is a complex occurrence, and it can be triggered by a variety of things and activities, from the littering of cigarette butts to excess use of chemical fertilizers.
- Every cause is linked with another. It is quite difficult to pinpoint one particular cause. However, the leading causes are listed below.
- Industrial Activity - Industrial activity has been the biggest contributor to the problem of soil pollution, especially since the amount of mining and manufacturing has increased. Most industries are dependent on extracting minerals from the earth. As a result, the industrial waste lingers on the soil surface for a long time and makes it unsuitable for use.
- Agricultural Activities - The utilization of chemicals has gone up tremendously since technology has provided us with modern pesticides and fertilizers. They are full of chemicals that are not produced in nature and cannot be broken down by it. As a result, they seep into the ground after they mix with water and slowly reduce the fertility of the soil.
- Waste Disposal - While industrial waste is sure to cause contamination, there is another way in which we are adding to the pollution. Every person excretes a certain amount of personal waste in the form of urine and feces. While much of it moves into the sewer system, there is also a large amount that is dumped directly into landfills in the form of diapers. Even the sewer system ends at the landfill, where the biological waste pollutes the soil and water.
- Accidental Oil Spills - Oil leaks can happen during the storage and transport of chemicals. This can be seen at most of the fuel stations. The chemicals present in the fuel reduces the quality of soil and make it unsuitable for cultivation. These chemicals can enter into the groundwater through the soil and make the water undrinkable.
- Acid Rain - Acid rain is caused when pollutants present in the air mix up with the rain and fall back on the ground. The polluted water could dissolve away some of the essential nutrients found in the soil and change the structure of the soil.
Effects Of Soil Pollution
Soil influences almost all aspects of our daily lives. Sometimes we fail to understand it. As a result of this, we sometimes fail to understand the effect that soil pollution has on our daily lives. Polluted soil means stunted crops or even a toxic underground water table. Some major effects of soil pollution are:
- Effect on Health of Humans - Considering how soil is the reason we are able to sustain ourselves, the contamination of it has major consequences for our health. Crops and plants that are grown on polluted soil absorb much of the pollution and then pass it on to us. This could explain the sudden increase in small and terminal illnesses. The soil pollution can even lead to widespread famines if the plants are unable to grow in it.
- Effect on Growth of Plants - The ecological balance of any system is affected due to the widespread contamination of the soil. Most plants are unable to adapt when the chemistry of the soil changes so radically in a short period of time. Fungi and bacteria found in the soil that bind it together begin to decline, which creates an additional problem of soil erosion.
The fertility of the soil slowly diminishes, making land unsuitable for agriculture and any local vegetation to survive. The soil pollution causes large tracts of land to become hazardous to health. Unlike deserts, which are suitable for their native vegetation, such land cannot support most forms of life. - Decreased Soil Fertility - The toxic chemicals present in the soil can decrease soil fertility and therefore decrease the soil yield. The contaminated soil is then used to produce fruits and vegetables, which lack quality nutrients and may contain some poisonous substances to cause serious health problems in people consuming them.
- Poisoning of the Underground Water Table - Soil pollution also leads to the poisoning of the underground water table. Since this water is stored beneath the layers of the soil, the toxins in the soil could easily percolate slowly and steadily into the water table.

Possible Solutions to Soil Pollution
Soil pollution is a complex problem that ought to be solved. It is essential that we all realize how important soil is to us.
The earlier we realize this, the better we will be able to solve the problem of soil pollution. It is a complex problem, and thus, it requires everyone, from an individual to the government, to work in complete unison. Listed below are a few things that could help in reducing soil pollution.
- Reduced Use of Chemical Fertilizers - Chemical fertilizers do more harm than good. While proper amounts could enhance the fertility of the soil, an excess of it actually poisons the soil. The excess of chemical fertilizers could pollute the soil in several ways. It could mess with the pH levels of the soil. It could also destroy the good microorganisms in the soil. Not only that, but the runoff from such soils also causes water pollution as well. Thus, using chemical fertilizers is like a double-edged sword.
- Reforestation and Afforestation Should Be Promoted - One of the major causes of soil pollution is soil erosion, which is caused due to deforestation.
It is natural that, with an ever-growing population, humankind needs more and more space to expand their civilization. Often, it is achieved at the cost of the health of the soil.
To prevent this from happening, reforestation of a deforested area should be promoted. Also, afforestation should be promoted and encouraged in the barren lands.
The roots of the plants bind the soil particles together and even capture good microorganisms in the soil. It also ensures the maintenance of the underground water table. - Recycle and Reuse Products - These steps not only reduce waste generation but also ensure that soil pollution is reduced. At present, plastic forms a significant portion of the generated waste. More often than not, this wastes are buried in landfills.
In these landfills, these plastics and other materials decompose slowly and release toxic materials into the soil. These toxic substances are very harmful to the health of the soil and are a major source of soil pollution.
By reusing and recycling things, we would ensure that lesser wastes are dumped in these landfills, and this, in turn, would reduce soil pollution. - Promote Use of Natural Manure - Natural manure is one of the best sources of nutrients for the soil. It is harmless and completely organic. It adds essential nutrients to the soil and restores the health of the soil. It has no harmful by-products that could harm the soil or the environment in any way.
- Create awareness - In order to ensure that a problem like soil pollution is solved, it is essential that every individual must get involved. It is with their involvement that things can work out better. Awareness programs could be designed so that people understand soil pollution better. If people are aware, they will help, even subconsciously.
Safe Farming Practices That Prevent Soil Pollution
Different types of soil conservation methods ensure long-term usage of land and keep it productive for future generations. Let’s consider their benefits in regard to soil conservation.
- Conservation Tillage - The conservation tillage aims at addressing wind and water erosion by covering the earth with vegetation (either crops or their residues) and limiting the number of tilling operations. Another significant aspect is to choose the proper time for field operations, depending on the soil types. For example, clay ones are better to till after harvesting while other types are better to plow before seeding.
- Contour Farming - The soil conservation method proves efficient in slope territories and suggests planting species along the contour. Rows up and down the slope provoke soil erosion due to water currents while rows along the contour restrain it. An impact of terracing is similar: it also helps to conserve soil and reduce its degradation processes.

- Strip Cropping - In this case, farmers combine high-growing crops with low-growing ones for the sake of wind protection, like when corn grows in strips with forage crops. The strip cropping practice works even better when high-growing crops are intensified in the sides where winds blow most frequently. An extra benefit is the organic matter material from the low crops.

- Windbreaks - As the name suggests, this soil conservation practice is used to reduce the power of winds and its disruptive effect on soil. These are trees or bushes to shelter crops from snow and winds planted in several rows. Depending on the number of rows, we can distinguish windbreaks properly (up to five rows) and shelterbelts (six and more).

- Crop Rotation - Crop rotation vs. mono-cropping farming suggests changing agro species instead of planting one and the same for many subsequent seasons.
Farmers applying this soil conservation method reap numerous benefits. Crop rotation helps them improve the earth structure with diverse root systems, to mitigate pest establishments, and to add nitrogen to the land with legumes known as nitrogen-fixing plants. - Cover Crops - This soil conservation technique is another way to avoid bare soils and additionally benefit from planting cover crops – secondary species – in-between growing cash crops for different reasons like to:
- produce forage and grazing material for cattle;
- provide green manure;
- assist in weed control;
- retain moisture;
- ensure a natural environment for microorganisms and minor animals;
- balance nitrogen concentration (either releasing or accumulating it with certain plants).
- Buffer Strips - These are trees and bushes on the banks of water bodies to prevent sediment, water wash offs. Their roots fix the soil to avoid slumping and erosion, canopies protect from excessive sunlight to water inhabitants and falling leaves are a source of organic matter and food of minor aquatic animals

- Integrated Pest Management - Pests are a great nuisance to agriculturalists and have been a major issue to tackle while chemicals poison nature leaking to water and the atmosphere. It is important to eliminate synthetic herbicides replacing them with organic ones or establishing biological enemies of pests whenever possible, rotating crop species to minimize increasing pest populations in the same field for years, and using alternative techniques in complex.
Benefits of Soil Conservation
Humankind in general and farmers in particular benefit from numerous advantages of soil conservation. This agricultural practice contributes to sustainability in a number of ways:
- Boosts earth quality and productivity. Maintaining the natural environment for earth-dwelling organism’s increases fertility and reduces the necessity of chemical fertilizing, thus boosting yields and saving costs at the same time.
- Mitigates erosion. Soil conservation methods to reduce erosion and depletion help agriculturalists to avoid the expansion of new lands when territories become infertile.
- Promotes water infiltration and increases its storage. The soil conservation technique of minimum tillage vs. conventional plowing affects soil moisture by reducing cracking and evaporation as well as rising the infiltration rate.
- Aids air and water purification. The importance of soil conservation relates to water supplies, and the earth functions as a natural filter to purify water. Soil conservation mitigates the concentration of pollutants and sediments. In its turn, water is the basic condition to dissolve nutrients for plants. Soil carbon sequestration and reduced chemical applications contribute to air purity, too.
- Gives food and shelter for wildlife. Land with growing vegetation is a living environment for animals; it is not only the source for nourishment but their home as well.
“When the well is dry, we know the worth of water.”
– Benjamin Franklin, Poor Richard’s Almanack for 1733
Water Conservation Methods In Farming
- Mulch - We cannot overemphasize the importance of mulching. Mulch is something laid on the surface of the soil to protect the soil from the air, water and the sun.
To mulch, first weed the soil then spread a thick layer of organic mulch on the soil. Examples of organic mulches are:- Chopped leaves
- Straw
- Grass clippings
- Wood chips
- Shredded bark
- Pine needles
Mulching helps save time and labour as it discourages weeds and pests and conserve water through reduced evaporation.
- Irrigate early morning or dusk - At the hottest and driest time of the year it is most efficient to water your crops in the morning or in the evening. This avoids water loss from evapotranspiration (water evaporating from the land and leaves of plants). Evaporation happens most in the midday sun.

- Don’t over-water - It’s a common misconception that plants would be happy with lots of water all of the time. But often farmers are over-watering crops unnecessarily. Save water! Plants will only take what they need and then all that extra water goes to waste through evaporation, run-off or infiltration.

- Check for leaks and damage - If you’ve already invested in an irrigation system, make sure you’re not losing any water before it reaches the crops. Irrigation pipes and equipment can become damaged or blocked which causes leaks. Thoroughly check your equipment for leaks and repair them so that all the water you have gets to the crops.

- Drip Irrigation - Drip irrigation systems deliver water directly to a plant’s roots, reducing the evaporation that happens with spray watering systems. Timers can be used to schedule watering for the cooler parts of the day, further reducing water loss.
Importance Of Water Conservation In Farming
- It minimizes the effects of drought and water shortages. By reducing the amount of water we use, we can better protect against future drought years.
- It helps to preserve our environment. Reducing our water usages reduces the energy required to process and deliver it to homes, businesses, farms, and communities, which, in turn, helps to reduce pollution and conserve fuel resources.
- It helps to preserve our environment. Reducing our water usages reduces the energy required to process and deliver it to homes, businesses, farms, and communities, which, in turn, helps to reduce pollution and conserve fuel resources.
Water Retention Structures To Conserve Surface Runoff
Water Retention Structures means a structure designed to retain a large volume of water
There are various methods of water retention to conserve surface runoff, this include:
- Water retention Ditches - Ditches are man-made waterbodies that are used mainly to drain the land.

- Earth Basins - is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point

- Water retention pits – is an artificial pond with vegetation around the perimeter and a permanent pool of water in its design.

Minimum Tillage Practices That Conserve Water In Farming
Tillage practices refer to the tillage operations carried out between the harvest and following sowing/cultivation operation. Tillage, crop rotation and soil cover are practices related to pesticide and nutrient runoff, soil erosion, soil compaction etc. Some of the minimum tillage practices include:
- Use of herbicides;
- Uprooting/slashing;
- Use of cash crops;
- Limiting cultivation to the point planting;
- Proper timing of cultivation;
- Mulching
There are other different tillage practices distinguished are:
- Conservation tillage
- Conventional tillage
- Zero tillage
Conservation tillage can include the following systems:
- Strip tillage or zonal tillage refers to a system where strips 5 to 20 cm in width are prepared to receive the seed whilst the soil along the intervening bands is not disturbed and remains covered with residues. The system causes more soil disturbance and provides less cover along the rows than zero tillage.
- Tined tillage or vertical tillage refers to a system where the arable land is prepared with equipment which does not invert the soil and which cause little compaction. For this reason, the surface normally remains with a good cover of residues on the surface.
- Ridge tillage is a system of ridges and furrows. The ridges may be narrow or wide and the furrows can be parallel to the contour lines or constructed with a slight slope, depending on whether the objective is to conserve moisture or to drain excess moisture. The ridges can be semi-permanent or be constructed each year which will govern the amount of residue material that remains on the surface.
Conventional tillage
Refers to the arable land treated by conventional tillage which involves inversion of the soil, normally with a moldboard or a disc plough as the primary tillage operation, followed by secondary tillage with a disc harrow.
Zero tillage
Refers to the arable land on which no tillage is applied between harvest and sowing. Zero tillage is a minimum tillage practice in which the crop is sown directly into soil not tilled since the harvest of the previous crop. Weed control is achieved by the use of herbicides and/or appropriate mulching and stubble is retained for erosion control.
Agroforestry
It’s the cultivation and use of trees and shrubs with crops and livestock in agricultural systems.
Characteristics of Agroforestry
While selecting tree species for agroforestry systems, the following desirable characteristics should be taken into consideration. Though all desirable characters are not found in a single species, but their multiple uses are taken care of.
- Tree species selected should not interfere with soil moisture
- Tree species selected for agroforestry should have very less water requirement
- Should not compete with main agricultural crops for water.
- Tree species should be deep tap rooted so that they can draw water from deep strata of the soil.
- Tree species should not compete for plant nutrients
- Tree species should not utilize more plant nutrients
- They should help in building soil fertility,
- Leguminous tree species which fix atmospheric nitrogen in their roots should be prefered.
- The root system and root growth characteristics should ideally result in to exploration of soil layers that are different to those being trapped by agricultural crops.
- Tree species should not compete for sunlight
- Tree species should not interrupt sunlight falling on the crops.
- Tree species should be light branching in their habit.
- Trees permit the penetration of light into the ground and promote better crop, pasture growth and yield.
- Tree species can withstand pruning operation if it possess dense canopy.
- Tree species should have high survival rate and easy establishment
- Trees species should have high survival percentage,
- Leave little or no gaps after transplanting.
- Hardy tree species are easy to establish.
- They have less mortality percentage because they can tolerate transplanting shocks easily.
- Trees should have the ability to regenerate lateral roots within a short period of time after transplanting.
- Tree species should have fast growing habit and easy management
- Tree species for agroforestry system should be essentially fast growing,
- Rapid growth, especially in the early years,
- Tree should have short rotation (the period between planting and final harvesting)
- Fast growing species
- Tree species should have wider adaptability
- A tree species selected for agroforestry combinations must have a wider adaptability.
- Tree species should have high palatability as a fodder
- Most of the Indian farmer’s rear livestock separately and cut and carry method of fodder production is quite prevalent.
- Therefore, in agroforestry, farmer must select those tree species which are palatable to livestock and had a high digestibility.
- Tree species should have shelter conferring and soil stabilization attributes
- Some tree species, because of their inherent growth habit and adaptability, are especially helpful in providing protection for soils, crops and livestock.
- Tree species should have capability to withstand management practices
- Many agroforestry systems demand extensive pruning and lopping of the trees in order to maximize production. In such cases, the trees must be able to withstand such treatment without drastically restricting growth rate.
- Tree species should have nutrient cycling and nitrogen fixation attributes
- Within an agroforestry system, trees can play an important role in recycling nutrients, leached down through the soil profile and minerals released from weathering parent material such as rocks and sediments.
- These nutrients are used in the growth and development of the tree, many returning to the top-soil in form of dead leaves, twigs, flowers and seeds which slowly decompose on the surface, or are eaten by animals.
- Although all trees play some role in maintaining the nutrient status of the soil through recycling.
- Deciduous trees drop most of their leaves in autumn leaving a thick mat of leaves on the ground, whereas most evergreen species maintain some level of litter fall throughout the year.
- Another important factor is the ability of many tree species to convert atmospheric nitrogen into organic nitrogen for their own use through complex symbiotic relationship between Rhizobium bacteria and their fine roots.
- The bacteria form nodules on the roots which can convert nitrogen gas, as it is in the atmosphere, into usable nitrogen for the plant.
- The litter of these nitrogen fixing trees is generally high in nitrogen, thus increasing the nitrogen status of the soil.
- Tree species should have thin bark
- Species selected for agroforestry combinations should not shed its bark regularly but it should retain for longer period as bark shedding creates unhygienic conditions for under-ground crop.
- Tree species should be free from chemical exudations
- The species selected for agroforestry combination must be free from chemicals as these chemicals affect the growth of under-ground crops.
- Tree species should have easily decomposable leaves
- The suitable tree species for agroforestry will be that one in which fallen leaves decompose with fast rate.
- The leaves of most of the legume tree species are small in size, decompose quickly and easily, and add a large quantity of organic matter and nutrients to the soil.
- Tree species having broad leaves such as teak, mango and banyan should not be preferred for agroforestry system.
- They contain more fibre matter and also require longer time for decomposition. Further, broad leaves when fall on the tender crop plants, block their photosynthetic activities.
- Tree species should have their multiple uses
- The selected tree species should have multiple uses.
- The tree should yield more than one of the main produce like fuelwood, leaf fodder, edible fruit, edible flower and fibre.
- Tree species should have high yield potential
- High yield potential is the most important criterion of selection of tree species for agroforestry systems as the main aim is to obtain overall more output per unit area. Care should be taken before collection of seeds and seedlings that they are being procured from reliable source.
Suitable tree species for agroforestry
- Leucaena leucocephala
- Gravillea robusta
- Calliandra catothrysus
- Mangifera indica
- Sesbania sesban
- Lantana camara
- Cajanus cajan
Characteristics Of Agricultural Crops For Agroforestry
- Agricultural crops should be short duration and quick growing.
- They should be at least partially tolerant to shade.
- Most of them should belong to Leguminous family.
- They should respond well to high density tree planting.
- They should bear some adverse conditions, like water stress and/or excess of watering;
- Crops should return adequate organic matter to soil through their fallen leaves, root system, stumps, etc.
- Crops should appropriately be fitted in intensive or multiple cropping system.
Advantages/importance Of Agroforestry
- Saves labour since some operations can be done at once for both plants and trees
- Gives higher combined yield
- Provide wide variety of agricultural produce
- Reduces the risks of total failure
- Crops benefit from nitrogen fixing trees.
- Trees help in holding the soil firmly
- Some trees act as livestock fodder.
- Provides a wider variety of agricultural produce.
Disadvantages of Agroforestry
- Mechanization is difficult.
- Use of pesticides and fertilizer may be difficult.
- Productivity may suffer because the skills for managing the different trees
Financial records in Business - Grade 7 Business Studies Revision Notes
- Business Transactions
- Methods Of Payments For Goods And Services
- Importance Of Financial Documents In Record Keeping In Business
Business Transactions
- A business transaction is a deal between two or more people involving exchange of goods and services in terms of money.
- Business transaction may take place on cash basis; in which case goods are paid for before or on delivery or a short while after delivery
- Business transaction may also take place on credit basis; which means payment is made after a specified period from the date of delivery of the goods or the provision of the services
Documents Used At The Inquiry Stage
This is the first stage in transaction. An inquiry is a request by a prospective buyer for information on available goods and services. It is aimed at establishing the following;
- Whether the goods or services required are available for sale
- The quality or nature of the products available
- The prices at which the goods or services are being sold
- The terms of sale in respect to payment and delivery of goods or services Some of the documents used at this stage include;
Letter of inquiry;
This is a letter written by a potential buyer to the seller to find out the goods and services offered by the seller.
A letter of inquiry can be general or specific. A specific letter of inquiry seeks for information about a particular product.
Reply to an inquiry
The seller may reply to the letter of inquiry by sending any of the following documents;
- Price list
- A catalogue
- Quotation
- A tender
- A price list
This is a list of items sold by the trader together with their prices. The information contained in a price list is usually brief and not illustrated and may include;- Name and address of the Seller-List of the goods and services
- The recommended unit prices of the products -Any discounts offered
Price list show the prices of the commodities at that time.
- A catalogue;
A catalogue is a basket which briefly describes the goods a seller stocks.
It is normally sent by the seller to the buyer when the buyer sends a general letter of inquiry. It usually carries illustrations on the goods stocked, and could be in the form of attractive and colorful pictures
The content of a catalogue includes the following;- Name and address of the seller
- Details of the products to be sold; inform of pictures and illustrations
- The prices of the products
- After-sales services offered by the seller
- Packaging and posting expenses to be incurred
- Delivery services to be used
- Terms of sale
Catalogues carry more information than the price list and they are more expensive to print.
- Quotation;
This is a document sent by a seller to a buyer in response to a specific letter of inquiry. It specifies the conditions and terms under which the seller is willing to supply the specified goods and services to the buyer.
The content of a quotation includes the following;- Name and address of Seller-Name and address of the buyer
- Description of goods to be supplied -Prices of the commodities
- Terms of sale i.e. discounts, time of supply, delivery -Total of the goods to be supplied
Quotations are normally in form of letters, but many large-scale businesses have pre-printed quotations forms which they readily send to the potential customers.
- A Tender
This is a document of offer to sell sent by a seller to a buyer in response to an advertised request
Tenders contain the following;- Date when the tender advertisement was made -Mode of payment
- Date of making document -Discounts given
- Name and address of prospective seller called the tenderer
- The prices at which the goods can be provided
- Period of delivery -Mode of delivery
- Tenders are delivered in sealed envelopes which are opened by the buyer on a specified date
The winning tender is usually awarded on the of the lowest quoted price although the buyer is not obliged to accept this especially if quality is likely to be low
Tenders are not binding unless accepted by the buyer.
- A price list
Documents Used At The Order Stage
After receiving replies to inquiry in form of price list, catalogue or Quotation, a prospective buyer will study the terms and conditions stated in them, and then may decide to buy products or not.
- An Order
If a prospective buyer decides to purchase an item(s), he or she then places an order
An order is a document sent by a potential buyer to a seller requesting to be provided with specified products under specified terms and conditions
-An order issued for goods is called a local purchase order (LPO) An order issued for services is called a local service order (LSO)
Ways of making an order- Filling an order form. This is a pre-printed document that is used for making orders
- Writing an order letter
- Sending an e-mail, faxing or sending a short text message
- Giving a verbal order. Verbal orders have the disadvantage in that they can be misunderstood and there would be no record of items ordered
Where written orders are made, the potential buyer keeps a copy of the order for use in verifying the goods ordered when they are delivered.
A written order may contain the following;- Name and address of the buyer
- Name and address of the seller
- The number of the order
- Quantities ordered and total amount to be paid
- Description of the goods ordered
- Price per item
- Special instructions on such matters as packaging and delivery
- Acknowledgement note
On receiving the order, the seller sends the buyer an acknowledgement note An acknowledgement note is a document sent by the seller to the prospective buyer to inform him/her that the order has been received and it is being acted upon.
After sending the acknowledgement note, the seller has to decide whether to extend credit to the buyer or not. At this stage, the seller has the following options;- If the seller is convinced that the buyer is credit worthy, arrangements are made to deliver the ordered goods or services to the buyer.
- If the seller is not sure of credit worthiness of the buyer, a credit status inquiry can be issued to the buyer’s bankers or to other suppliers who deal with the buyer to ascertain the credit worthiness.
- If the buyer is not credit worthy then a polite note or a pro forma invoice can be sent to him/her
A proforma invoice
This is a document sent by the seller to the buyer requesting the buyer to make payment for goods or services before they are delivered. It indicates that the seller is not willing to grant the buyer credit.
Functions of a proforma invoice
- A polite way of asking for payment before the goods are delivered
- Sent when the seller does not want to give credit
- Used by importers to get customers clearance before goods are delivered
- Issued to an agent who sells goods on behalf of the seller
- Show what the buyer would have to pay if the order is approved
- Can be used to serve as a quotation
Circumstances under which a pro-forma invoice may be used
- If the seller does not want to give credit
- If the seller wants to sell goods through an agent
- If the seller wants to get clearance for imported goods
- If the seller wants it to function as a quotation
- If the seller wants to inform the buyer what he/she pay if the order is approved e.t.c
Documents Used At The Delivery Stage
After the seller has accepted the order sent an acknowledgement note and where necessary the pro-forma invoice, the seller then prepares the goods for delivery to the buyer. This can be done in the following ways;
- The seller can ask the buyer to collect the goods
- The seller can deliver the goods to the buyer using his/her own means of transport
- The goods can be delivered to the buyer through public transport
- The services(s) can be rendered to the buyer at the sellers or the buyer’s premises or at any convenient place.
The main documents that are used at this stage are;
- Packing note; Before delivery goods are packed for dispatch. This is a document prepared by the seller showing the goods contained/packed in every container, box or carton being delivered to the buyer
- A copy of the packing note is packed with the goods to make/help the buyer have a spot check.
The contents of a packing note include; - Description of goods packed
- Quantities of goods packed
- The means of delivery
NOTE: A packing not does not contain prices of goods. This ensures that those people involved in checking and transporting goods do not know the value of goods. This is done as a precaution against theft.
- A copy of the packing note is packed with the goods to make/help the buyer have a spot check.
- Advice note; This is a document sent by the seller to the buyer to inform the buyer that the ordered goods have been dispatched. It is usually sent through the fastest means possible.
- It contains the following;
- The means of delivery
- A description of the goods
- The quantity dispatched -Date
- Name and address of buyer and seller
Functions of an advice note- Informing the buyer that the goods are on the way so that in case of any delay in delivery, the buyer can make inquiries
- Alerting the buyer so that necessary arrangements can be made for payments when the goods arrive
- Can serve as an acknowledgement note, where one is not sent/
- Delivery note; This is a document sent by the seller to the buyer to accompany the goods being delivered.
-A delivery note is always made in triplicate (3), one copy remains with the seller and two sent to the buyer.
-When the goods reach the buyer, he/she confirms that the goods are the ones ordered for and that they are in the right condition by comparing the delivery note, the order and the goods. If the buyer is satisfied with the goods, he/she signs the two copies, retains the original and send the copy back to the seller. This serves as evidence that the goods have been received in the right condition and in the right quantities.
-Some businesses keep delivery books in which the buyer signs to indicate that goods have been received in good condition. A delivery book is used by the seller if he/she delivers goods by himself/herself as an alternative to a delivery note
The content of a delivery note includes the following;- Name and address of the seller
- Name and address of the buyer
- Date of delivery
- Delivery note number
- Description of the goods delivered
- Quantities of the goods delivered
- Space for the buyer to sign and comment on the condition of the goods received.
- Consignment note
This is a document prepared by a transporter to show that he/she has been hired to deliver specified goods to a particular buyer. This document is used when goods are delivered to the buyer by public means of transport e.g. by trains.
-The seller is the consignor, the buyer is the consignee and the goods the consignment
-The transporting company prepares the consignment note and gives the seller to complete and sign. The seller then returns the note to the transporter (carrier) who takes it together with the goods to the buyer.
-On receiving the goods, the buyer signs the consignment note as evidence that the goods were actually transported.
The content of a consignment note includes the following;
- Details of the goods to the transported
- Name address of seller (consignor)
- Name and address of buyer (consignee)
- Terms of carriage and conditions of transporting the goods
- The transportation cost
- Handling information
- Destination of goods
- Goods Received note; This is a document sent by the buyer to the seller to inform him/her that goods sent have been received. It usually prepared in duplicate, the original is sent to the seller and the copy retained by the buyer.
The contents of the goods received note include;
- Date of the document
- Name and address of the buyer
- Name and address of the seller
- Corresponding purchase order
- Details of goods received
- Date the goods were received.
- Returned goods note/Damaged goods note; If goods are damaged on the way, the buyer may return them to the seller. The buyer may also return goods for other reasons e.g.
- Wrong type of goods
- Excess goods
- Wrong quality goods
-When the goods are returned, the buyer informs the seller of the return by sending a goods returned note.
-A goods returned note is a document sent by a buyer to a seller to inform him/her that certain goods are being returned to the seller.
-Where the goods are returned because of damage, the note may be referred to as the damaged goods note.
The contents of the goods returned note include; - Details of goods that have been returned to the seller
- Date goods are returned
- The number of (GRN)
- Order number
- Delivery number
- Name and address of both buyer and seller
-When the seller receives the note together with the goods, he issues a credit note
Documents Used At The Invoicing Stage
This stage involves the seller requesting or demanding for payment from the buyer for the goods or services delivered.
Some of the documents used at this stage include:
- Invoice
This is a document sent to the buyer by the seller to demand for payment for goods delivered or services rendered.
There are two types of invoices namely:- Cash invoice-This is sent when payment is expected immediately after delivery thus acting as a cash sale receipt
- A credit invoice-This is sent when a buyer is allowed to pay at a later date.
Functions of an invoice- It shows the details of goods sold i.e. quantity delivered, unit price, total value of the goods and terms and conditions of sale.
- It is a request to the buyer to make payment
- It serves as an evidence that the buyer owes the seller a certain amount of money
- It is used as a source document in recording the transaction in the book of accounts.
The contents of an invoice include the following:- Invoice number
- Name and address of the seller
- Name and address of the buyer
- Date document is prepared
- Details of goods repaired
- Unit prices of goods delivered
- Total value of goods
- Discounts offered
- E and O.E printed at the bottom
The letters E and O.E (Errors and Omissions Excepted) means the seller reserves the right to correct any errors and omissions made in the invoice. -On receiving the invoice, the buyer verifies the contents using the local purchase order and the delivery note. If the invoice is in order, the buyer makes arrangements to pay the amount stated.
Businesses which offer services issue a document called a bill, which serves the purpose of an invoice.
- Credit note
This is a document sent by the seller to the buyer (credit buyer) to correct an overcharge. It is used to inform the buyer that the amount payable by him/her has been reduced
An overcharge is an excess amount charged beyond the right price. Causes of overcharge may include;- Arithmetical errors like wrong addition
- Price overcharges
- Inclusion of wrong or unordered items in the invoice
- Failure to deduct the allowable discounts
- Return of goods (damaged goods)
- Failure to note the return by the buyer of packing cases or containers used to deliver goods to him/her
- Use of wrong price list.
-The purpose of the credit note is to reduce the total invoice amount by the amount of the overcharge.
-A credit note is usually printed in red to distinguish it from other documents.
-Contents of a credit note include;- Name and address of the seller and the buyer
- Credit note number
- Date document is prepared
- Description and value of goods returned by buyer (in case that was done)
- Total overcharge
Reasons why a seller would send a credit note to a buyer/circumstances under which a credit note is sent to a buyer.- When there is an overcharge in an invoice
- When the original invoice had indicated items that were not supplied -When the buyer returns empty cases/crates that had been charged in the invoice.
- When the buyer returns some goods to the seller
- If the buyer was entitled to a discount which was not given or taken care of in the invoice.
- Debit note
This is a document sent by the seller to the buyer to correct an undercharge on the original invoice. It is used to inform the buyer that the amount payable by him has been increased.
-A debit note acts as an additional invoice.
-An undercharge arises when amount charged on products is less than their right price.
Causes of undercharge include:- Price undercharges on items
- Arithmetic errors/mistaken in calculation
- Omission of items in the invoice
- Retention of crates and containers that were not involved by the buyer
- Deductions of more discount than what was give/intended
Circumstances under which a debit note will be sent to the buyer- When there is an undercharge in the invoice
- If the buyer had been given a discount that was not due to him
- If some items had been omitted in the original invoice
- If the buyer decides to retain some empty containers or crates
Differences Between a debit note and a credit note
| DEBIT NOTE | CREDIT NOTE |
| 1) Issued to correct an underchargeon the invoice. | 1) Issued to correct an overchargeon the invoive. |
| 2) Written on blue or black. | 2)Usually written in red |
| 3) Issued when containers have notbeen returned | 3) Issued when containers have been returned. |
Documents Used At The Payment Stage
This is the final stage of a credit business transaction. It takes place after the invoice has been received and ascertained to be correct or where necessary, corrections made.
The documents used at the payment stage include;
- Receipt
This is a document issued to the buyer by the seller as proof that payment has been made.
-Payment can be done in cash, cheque, other forms of money or in kind -The receipt also serves as a source document for making entries in books of accounts.
Contents of the receipt include;
- Date of payment
- Name of the person making payment
- Name of person/institution receiving payment
- Amount paid in words and figures
- Means of payment
- Receipt number
- Signature of person issuing the receipt.
-The issuance of a receipt by the seller to the buyer after receiving payment marks the end of the credit transaction between the seller and the buyer (where payment has been done in full)
-A receipt serves the same purpose as the cash sale slip
- Statement of Account
This is a document prepared by the seller and sent to the buyer, giving a summary of all the dealings/transactions between them during a particular period of time, usually a month. It has the following details;
- Date when it was prepared
- Name and address of the seller
- Name and address of the buyer
- Account number
- Date column-where the date of each transaction is recorded
- Particulars (Details)column-where the explanation of each transaction is shown
- Money column
- Debit column-increases in the amounts payable due to credit sales or under charge correction.
- Credit column-Decrease in the amounts payable due to overcharges corrected or payments recorded.
- Balance column-Amount owing after each transaction (Balance outstanding)
- Any discounts allowed to the buyer
- Date when the buyer is expected to clear the balance
- Terms of credit e.t.c.
-The statement of account enables the buyer to ascertain the correctness of the transactions which have taken place with the seller over the stated period.
- IOU
An IOU (I owe you) is a document written by the buyer and sent to the seller to acknowledge a debt.
-It does not specify date when settlement will be made. -It acts as evidence that a debt exists.
Methods Of Payments For Goods And Services
These are the methods or ways the buyer may use to settle debts arising from a business transaction. These are various means of payments that can be used. These means of payments can be put into the following groups;
- Cash
- Means of payment provided by the post office
- Means of payments provided by the commercial banks
- Means of payments which arise from private arrangements between sellers and buyers
- Other means of payment. E.g. Mobile transaction, Online payments like paypal
Cash
- This refers to the use of notes and coins to make payments. Currency notes and coins are issued by the central Bank of Kenya and are therefore legal tender
- Legal tender means everyone is obliged by law to accept them as a means of payment i.e. no one can refuse to accept them as they are backed by the law.Notes and coins are available in different denominations as follows; Coins; 5cents, 50cents, sh.1, sh.5, sh.10 and sh.40
Notes; sh.10.sh.20, sh.50, sh.100, sh.200, sh.500 and sh.1000. - Coins are suitable for settling small debts and are acceptable as legal tender up to a certain maximum e.g. 50cents coins the maximum is sh20 and sh.1 the maximum is ksh.100.
Advantages of cash as a means of payment:
- It is the only means of payment which is a legal tender
- Convenient for settlement of small debts
- Convenient to people with or without bank accounts
- Cash is readily usable
Disadvantages of cash as a means of payment
- Not convenient to carry around
- Cash can be lost or stolen easily as it is readily usable
- Payment is difficult to prove unless a receipt is issued
Circumstances under which cash payment is appropriate
- Where the amounts involved are small
- Where the payee (receiver) does not accept other means of payment
- Where cash is the only means available
- Where the payee requires cash(money) urgently
- Where there is need to avoid expenses associated with other means of payments
Means Of Payments Provided By The Banks
Commercial banks are financial institutions that accept deposits to and withdrawals from them.
They also lend money to customers. Examples of commercial banks include: Commercial bank of Kenya, National bank of Kenya, Barclays bank, and Co-operative bank e.t.c
-There are various means of payments provided by the commercial banks. They are:
- Cheques
- Bank drafts/bankers cheques
- Credit transfers
- Standing orders
- Travellers cheques
- Telegraphic transfers
- Debit cards
- Electronic fund Transfer(E.F.T)
Cheques
This is a written order by an account holder with the bank (drawer) to the bank (drawee) to pay on demand a specified amount of money to the named person (payee) or the bearer
Parties to a cheque
- Drawer-This is the person or institution who writes and issues the cheque.He is usually a current account holder with the bank
- Payee-The person or institution to be paid
- Drawee-The bank (where the drawer has an account) Details on a cheque; they include:
- Date when it is issued
- Name of the drawer
- The name of the payee, except in bearer cheques
- The name of the drawee(bank)and branch from where it is issued
- Amount to be paid in figures and in words
- The account number of the drawer
- The signature of the drawer
- The cheque number and bank code
- The appropriate revenue stamps
Types of cheques
- Open cheques
- Crossed cheques
- Bearer cheques
- Order cheques
- Open cheques
This is acheque that can be presented for payment over the counter. You present it and cash is paid to you. - Crossed cheques
This is acheque that bears two parallel lines on the face. This means the cheque cannot be cashed over the counter. The cheque is deposited in an account (payee’s account)
The payee then withdraws the money from his/her account
A crossed cheque can be opened by the drawer signing twice on its face. -A crossing can be general or special- General crossing-general crossings only contains the two parallel lines. This implies that the cheque will be paid through any bank in which it is deposited.
- Special crossings-Has other instructions included in the crossing i.e;
- Not negotiable-Means the cheque can be transferred by the payee to a third party, but he third cannot transfer the cheque (only the original payee can transfer the cheque)
- Account payee only-Means the cheque should be deposited in the account of the payee.
- Not transferable-Means there is no negotiation or transfer of the cheque
- Bearer cheques-This cheque does not have the name of the payee written on it. The person presenting it to the bank is the one who is paid.
- Order cheque-The cheque bears the name of the payee. The bank pays this particular payee the amount stated in the cheque after proper identification
Dishonouring a cheque
A cheque is dishonored if the bank refuses to pay and returns the cheque to the drawer.
-A cheque can be dishonored due to the following reasons:
- Insufficient funds in the account
- If the signature on the cheque differs from the drawers specimen signature in the bank.
- If the cheque is stalc i.e. presented for payment after six months from the date of issue.
- If the cheque is post dated-meaning the cheque is presented for payment earlier than the date on the cheque
- If the amount in figures is different from the amount in words
- If there are alterations on the cheque which are not countersigned by the drawer
- If the cheque is torn, dirty or defauld making it illegible
- If the account holder(drawer) is dead and the bank is aware of the fact
- If the drawer instructs the bank not to pay the particular cheque
- If the cheque contains errors which need to be corrected
- If the drawer becomes bankrupt or insane
- If the drawer has closed his/her account.
Advantages of using cheques
- They are more secure than notes and coins because if they are lost or stolen, they can be traced to the person who cashed them.
- They are convenient to carry and can be used to pay large sum of money which would be otherwise inconvenient to pay using cash
- They can be transferred to a third party to make payment/cheques are negotiable
- Payment can be made by cheque without the need to travel to make payment
- They provide a record of payment because of the counterfaits.The counterfaits acts as proof that payment has been made.
- Under special circumstances, they can be cashed or discounted before maturity.
Disadvantages of using cheques
- Cheques can be dishonored
- Requires the payee to go to the bank and in some cases to have an account
- The drawer pays some charges e.g. charges for the cheque book
- Can only be issued by an account holder/the drawer must have an account
- They are not readily acceptable by everybody
- They do not provide immediate cash
Circumstances under which a cheque is appropriate as a means of payment
- Where the amount of money involved is large
- Where the policy of the business demands so
- Where a cheque is the only means available
- Where there is need to avoid other risks associated with other means of payments
Bank drafts/Banker’s cheques
-This is a cheque drawn on a bank i.e. a cheque drawn by one bank to another requesting the latter bank to pay a named person or institution a specified sum of money and charge it to the drawing bank
-It can also be drawn by a bank on the request of a customer. The customer fills in an application form obtained from a bank and hands it over to the bank together with the money she wants to transfer and a commission for the service.
-The bank then prepares the cheque and gives it to the applicant who can then send it to the payee
-A bank draft has the drawing bank’s guarantee for payment. It is therefore more readily acceptable than personal cheques.
-It is suitable when urgency is desired in the payment as it is more readily acceptable.
Credit Transfer
This is a means of payment provided by commercial banks to their current accounts holders who want to pay many people using one cheque/at the same time
-One cheque is drawn and is usually accompanied by a list of the people to be paid, the amount to be paid to each person and the addresses of the bank branches where the payment is to be made.
-The bank then ensures that a credit transfer is affected to the various bank branches and each payee is paid
-A credit transfer is usually used by employers to pay salaries to their staff members.
Standing Order
This is an instruction to a bank by an account holder to pay a named person or an organization a fixed amount of money at regular intervals over a specified period of time or until stopped
-It is a very useful means of payment for business people as it enables them to regularly pay their recurrent bills e.g. water, insurance, electricity, loan payment, hire purchase payment e.t.c
Traveler’s Cheques
This is a cheque drawn by one bank to another requesting the latter to pay a specified sum of money to a named bearer, who usually would have bought that cheque from issuing bank. The cheque holder pays the value of the cheque plus the charges for the services to the issuing bank.
-Travellers cheques are usually issued in fixed denominations and are very convenient for travel purposes, hence their name. They enable a person to travel without having to carry a lot of cash. The cheques are also readily acceptable as a means of payment.
Telegraphic Transfers
This is a method /means of transferring money offered by commercial banks to anybody who wants to send money to another. The sender is required to fill an application form and provide the following information among others:
-His/her name -The amount of money to be remitted
-Name of the payee -The bank where the money would be paid. The applicant is charged a commission and telegraph fee. The paying bank sends a telegram to the payee who has to identify himself/herself before the payment is made The method is fast and safe.
Debit Cards
These are plastic cards issued by financial institutions e.g. banks that enables a person to purchase goods and services from any business that accepts them. Debit cards are used to make payments from money held in ones accounts and are therefore an alternative to cash payments. Examples are ATM cards.
Electronic Fund Transfer (E.F.T)
EFT is a method of transferring money from one account to another where computers are used. The sender is required to fill an electronic fund transfer form provided by the bank which instructs the bank to transfer money from his/her account to a named account.
Information is then sent to the payee’s bank electronically and the amount in the account is increased accordingly. The method is very fast.
Means Of Payments Provided By The Post Office
The post office provides means of payments that can be used to transfer money from one person to another.
The means of payments provided by the post office to facilitate payments includes,
- Money orders
- Posta pay
- Postal orders
- Postage stamps
- Premium bonds
- Money orders
A money order facilitates the transfer of money from one person to another through the post office (and/or bank)
A money order is usually for a specified sum of money usually purchased with cash from the post office
A person wishing to send money using this method visits a post office and completes an application form. Some of the details contained/given in the form include:
- The amount of money to be remitted
- Name of the payee
- The name of the post office where the money order will be cashed
- Name and address of the sender
- Whether the money order is to be ordinary or sent by telegraph
- Whether the sender wishes to be informed if the money has been paid
- Whether the money is to be paid through a bank account or at the post office counter.
The application form, money to be remitted and commission for the service is handed to the post office cleark who prepares the money order and gives it to the sender who may post it or send it to the payee.
-Telegraphic money orders, the post office sends a telegram to the payee informing him/her to go to the post office and claim the money. -Before payment is made, the payee must; - Identify himself/herself by producing an ID card
- Identify the person who sent the money.
-The sender of the money is left with a counterfoil which serves as evidence that money was sent and it can be used to reclaim the money if it did not reach the payee
-Money order may be open or crossed. A crossed money order bears two parallel lines drawn diagonally on its face and must be deposited in the bank account of the payee. It cannot be cashed over the counter at the post office.
-An open money order can be presented for payment at the post office counter.
Circumstances under which money order is appropriate- Where it is the only means available
- Where other means are not acceptable
- Where there is need to avoid inconveniences or risks associated with other means
- Posta pay
This is an Electronic Fund Transfer (EFT) service offered by the postal corporation of Kenya, for sending and receiving money instantly from various destinations both locally and internationally.
-The person sending money fills in a form called ‘send form’ giving the following details;
- Name, address and telephone number of sender
- Name, address and telephone number of receiver
- Pay city, town and location of the receiver
- Signature of the sender
- Amount to be sent
-The sender hands over the form, the amount of money to be sent and the commission to the post office clerk for processing
-The transfer is done via the internet through a machine that gives a twelvedigit number for the transaction called the ‘Transaction control number’(TCN).The sender then conveys this number, amount sent and pay location to the recipient and instructions to the recipient to visit the named post office for payment. This message is usually conveyed through the quickest means possible such as a telephone call
-The sender is given a copy of the processed ‘send form’ as proof that money has been sent. The post office retains the original for record purposes. -When the receiver visits the post office, he/she will fill a ‘receiver form’ giving the following details;- The transaction number(i.e. the twelve-digit number)
- The expected amount
- The name, address and telephone number of the sender
- The city town or location of the sender
- Signature of the receiver
The receiver then identifies himself or herself by producing an ID card or passport before receiving the money.
Advantages of using Posta pay as a means of payment- Accessibility-Posta pay outlets (post offices) are located countrywide to eliminate movement over long distances to get money
- Ease of use-Sending or receiving money is easy as one only needs to fill a form which is processed immediately
- Speed-the transfer of money is instant (fast)
- Security-Confidentiality in the transmission of money is provided and money is only paid to the person intended
- Convenience-Posta pay services are offered for long hours during the day and pay locations are conveniently located
- Affordability-Posta pay services are relatively affordable as large amounts can be sent at reasonable costs.
- Postal orders
-Postal orders are sold by the post office for the purpose of remitting money -They are available in fixed denominations of sh.5, 10.20,40,60,80,100 and 200
-On buying a postal order, the sender pays for both the face value of the postal order and a commission charged for the service
-Postal orders just like money orders are issued with counterfoils that the sender will keep as evidence of remittance in case the person to whom he/she remits the money does not receive it.
The sender writes the name of the payee on the postal order as a safety measure.
Payment to the bearer can be made in any post office with postal order facilities
Postal orders may also be crossed or open (see crossed and ordinary money orders)
Other Means Of Payment
- Credit cards
- Mobile money transfer services e.g. M-pesa.
- Credit cards(plastic money)
- These are plastic cards that enable a person to purchase goods or services on credit from any business willing to accept the card
- They are both a means of payment and a term of payment
- Mobile money transfer services e.g. M-pesa
- This is a means of money transfer services provided by mobile phone service providers to their customers (subscribers)
- It can only be used to transfer money between people subscribed to the same mobile phone network e.g. from one safaricom subscriber to another safaricom subscriber, Airtel to Airtel e.t.c
- The sender must register for the money transfer service and is issued with a PIN (personal identification number)
- When money is sent, both the sender and the receiver will receive a message confirming the transfer.
- A person can send money anytime anywhere so long as he/she has value in his/her m-pesa, pesa pap account.
- Each mobile service provider has a range of value that can be transferred using this method.
- A small transaction fee is charges for the transfer i.e. for sending and withdrawing
Benefits of mobile money transfer services- Confidentiality-The secret PIN protects the value in the customer’s account
- Ease of use-The service is easy to use as the agents assists to carry out transaction
- Speed-Money transfer is an instant service conveyed to the receiver via the short message service(SMS)
- Convenience-The service is convenient to both the sender and the receiver, as they only need to go to the nearest agent (money can be sent/deposited or received anywhere)
- Accessibility-The agents e.g. m-pesa agents are located in most parts of towns and also in rural areas. Money can hence be sent and received anywhere and anytime.
- Affordability-The service charges are very low for registered users and very affordable for non-registered users
- Security-Relatively secure when the sender uses the correct phone number of the receiver
Importance Of Financial Documents In Record Keeping In Business
- Knowing Your Financial Situation - You need to know where your company stands daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly, and annually. Are you making money, is your client base increasing or decreasing, do you have enough money in the bank to meet your obligations, are you meeting the goals you set for your business? Without this knowledge, you have little or no control over your business. You need to know how much inventory you have on hand, how much you need to order when you need to order, the credit terms your suppliers offer, the balance in your bank account to cover your payments for running your business such as rent, utilities, office supplies, inventory, employees’ wages, and payroll taxes. Also, you are likely to be in non-compliance with local, state, and federal regulations without proper controls on your finances.
- Meeting Your Tax Obligations
- helps to maximize all the expenses you claim and reduce your tax obligations
- makes it quicker to prepare your accounts at year-end
- gives you the information you need to run your business and help it grow
- helps you plan for tax payments
- helps identify the strengths and weaknesses in your business
- helps manage changes and improvements in your business
- will help you plan to meet financial commitments such paying creditors or employees
- makes it easier to get a loan or sell your business
- avoids over/under tax payments
- helps identify if your business is liable for paying VAT to KRA
- makes it easier to distribute profits to shareholders as dividends or for partnerships where both profits and losses have to be shared.
Government and Global Influence in Business - Grade 7 Business Studies Revision Notes
Government And Business
- Government involvement in business activities is one of the commercial duties it owes its citizens. It is the one that provides the necessary environment for investments to be undertaken by itself, or by the local and foreign investors. This, the government may do in various ways, these include;
- Producing goods and services
- Distributing goods and services
- Advising producers and traders
- Promoting trade and economic development
- Protecting consumers against exploitation by producers and traders
- As a consumer of goods and services
Reasons For Government Involvement In Business
The following are the major reasons for the government’s involvement and participation in business activities;
- To prevent exploitation of the public by private businesspersons especially in the provision of essential goods and services such as sugar, transport, communication etc. the Kenya Bureau of standards (KEBS) regulates the quality of goods consumed in Kenya.
- To provide essential goods and services in areas where private individuals and organizations are unwilling to venture because of low profits/ high risks involved.
- To provide essential goods and services which private organizations and individuals are unable to provide due to the large amount of initial capital required b e.g. generation of electricity, establishment of airlines etc.
- To attract foreign investment by initiating major business projects
- To stimulate economic development in the country e.g. by providing social services
- To provide goods and services which are too sensitive to be left in the hands of the private sector e.g. provision of firearms.
- To create employment opportunities by initiating projects such as generation of electricity.
- To prevent foreign dominance of the economy by investing in areas where the locals are not able to
- To redistribute wealth where returns are very high
- To prevent establishment of monopolies.
Roles/methods Of Government Involvement In Business
The government gets involved in business activities through the following methods:
- Regulation
This refers to Rules and restrictions the government requires business units to follow in their business activities. Through this method, the government ensures high quality goods and services and puts in control measures to protect consumers from exploitation. The government regulation measures include;- Licensing
A license is a document that shows that a business has been permitted by the government to operate. It is usually issued upon payment of a small fee. Licensing is the process of issuing licenses to businesses. Some of the reasons why the government issues licenses include;
- Regulating the number of businesses in a given place at any given time to avoid unhealthy competition.
- To control the type of goods entering and leaving the country.
- To ensure there are no illegal businesses.
- To ensure that traders engage only in trade activities that they have been licensed for.
- To ensure that those who engage in professional activities meet the requirements of the profession.
- To raise revenue for the government.
- Ensuring standards/ enforcing standards; The government regulates business activities by setting standards that businesses should and ensuring that the standards are adhered to. To achieve this purpose, the government has established bodies such as;
- Kenya bureau of standards (KEBS) whose main responsibility is to set standards especially for the manufactured goods and see to it that the set standards are adhered to/ met. Goods that meet such standards are given a diamond mark of quality, to show that they are of good quality.
- The ministry of public health to ensure that businesses meet certain standards as concerning facilities before such businesses can be allowed to operate. Such standards may include clean toilets, clean water and well aerated buildings.
- Legislation; The Government may come up with rules and regulations (laws) that regulate business activities e.g. banning hawking in certain areas, matatus required to carry certain number of passengers e.t.c.
- Licensing
- Training
The government takes keen interest in training and advising people in business about business management strategies and better ways of producing goods and services. The government offers these services through seminars and courses. This is mainly done by the Kenya Business Training Institute (K.B.T.I). - Trade promotion
This is a government initiated and supported policy to encourage local business people to enter into business. This is aimed at increasing the volume and variety of goods and services traded in. Trade promotion is classified as either external trade promotion or internal trade promotion.
Legal Requirements for Starting and operating a simple business in Kenya
- Business Permit
A business permit indicates that you are licensed to operate by the local county government. - KRA PIN
A Kenya Revenue Authority PIN is among the legal requirements that you need to start a business in Kenya. It is used to facilitate tax compliance with all Kenyans and businesses required to file their tax returns yearly.
Taxation In Kenya
Tax: is a compulsory payment by either individuals or organizations to the government without any direct benefit to the payer.
Taxation-refers to the process through which the government raises revenue by collecting taxes.
Purposes/reasons For Taxation
- Raising revenue for government expenditure. This is the main reason for taxation.
- Discouraging /controlling consumption of certain commodities e.g. alcohol and cigarattes which are considered to be harmful.
- Discouraging importation of certain commodities in order to protect local industries. This is done by imposing heavy taxes on such commodities.
- Controlling inflation. Taxation reduces money supply by reducing peoples ‘disposable’ income thereby controlling inflation.
- Reducing inequality in income distribution; this is done by taxing the rich heavily and using the finances raised in provision of goods and services that benefit the poor.
- Influencing locations of businesses. This is done by taxing businesses located in urban areas heavily and those in rural areas lightly hence businesses moving to rural areas.
- Correcting unfavorable balance of payments. High taxes are imposed on imported commodities thereby discouraging their importation leading to an improvement in the balance of payments.
- To protect the key selectors of the economy such as the agricultural sector, by stimulating their growth.
Factors that determine the amount of money raised through taxation
- Distribution of incomes
- Social and political factors
- Honesty and efficiency of tax authorities
- Citizens level of real income
- Economic structure of the country i.e. relative size of the country’s commercial and subsistence sectors.
Principles Of Taxation
These are the characteristics that a good tax system should have. They are also referred to as the cannons of taxation.
A good tax system should be;
- Equitable/principle of equity-Every subject of the state should pay tax in proportion to their income.
- Certain/principle of certainty-The tax that an individual should pay should be clear in terms of the amount, time and manner in which it should be paid. The government should also be fairly certain of the amount of tax expected so that planning can be easier.
- Convenient/principle of convenience-Tax levied ought to be convenient to both the contributor and collector, it should be levied at a time when the payer has money and mode of payment should be convenient to both the payer and the payee
- Economical/principle of economy-The cost of collecting and administering the tax should be lower than the tax so collected.
- Flexible/principle of flexibility-It should be readily adaptable to changing economic times i.e. when the economic conditions of the people improve it should give raised revenue e.g. VAT
- Ability to pay/non-oppressive-A tax system should be designed in a way that the amount charged is not too high to the extent that the contributors are unable to pay or is discouraged from working hard.
- Diversified/principle of diversity-There should be different types of taxes so that the tax burden is on different groups in the society. This also ensures that the government has money at all times.
- Simplicity-A good tax system should be simple enough to be understood by each tax payer. This will motivate them to pay tax.
- Elastic/principle of elasticity-The tax system should be able to generate more revenue for the government by targeting items of mass consumption.