- Indigenous Food Crops
- Vegetable Gardening Practices
- Innovative Gardening
Indigenous Food Crops
- Indigenous food crops are the crops that grow naturally in the garden.
- Some of these indigenous food crops have been adopted by human beings and they are now grown artificially to provide food for Kenyans
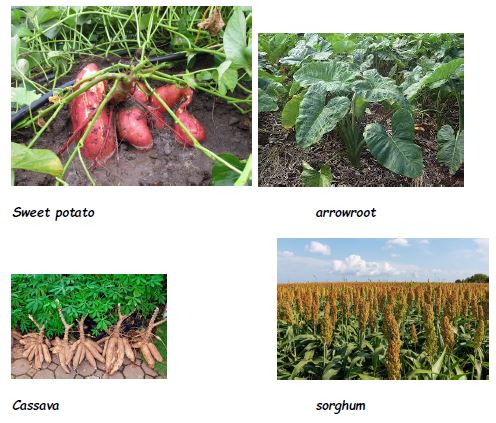
- Examples of these crops include; spider weeds, arrow roots, cassava, sorghum, sweet potatoes and black night shade.
- Indigenous foods crops are much important to our nutrition because they provide required nutrients and minerals to our body.
- They provide carbohydrates from root tubers, vitamins from leafy crops and minerals such as zinc and iron from plant like the black night shade and the spider weeds.
- Indigenous foods are foods that our great grandparents used to eat
- These foods benefit us in a number of ways like providing us with carbohydrates, minerals, vitamins that protect us from diseases, they also help in healing of wounds.
- Also when surplus are sold they generate income
- Some these plants need to be handled with care like stinging nettle can cause an itching sensation on the skin and should be handled with care. Ensure you put on gloves when handling such leaves.
- Therefore they are important in reducing food shortage and hunger in the country. Most of these crops can be grown using organic manure, hence no need of buying expensive artificial fertilizer.
Vegetable gardening practices
- Vegetable gardening is the process of growing vegetable crops. Vegetable group are important to our bodies because the provide carbohydrates to the body.
- Vitamins are best nutrients for the body because they protect our bodies against diseases. Vegetable crop include; tomatoes, cabbage, kales, spinach, cucumber and carrots. A vegetation is a part of a plant that is used as food.
Preparing a seedbed
- A part from providing food, vegetables can also be sold to earn income for farmers.
- Some vegetable are first raised in a nursery before being transplanted. A nursery bed is a small area of land for raising young seedling before they are transplanted to a permanent place called a seedbed.
- A nursery bed is prepared to comprise of fine soil particles. Fallow are made using a stick or an index finger, after leveling the nursery bed and mixing the soil with organic manure.
Sowing seeds on a nursery bed
- The seeds are then spread along the fallows in the process called drilling. Cover the seeds with a thin layer of fine soil.
- Apply dry plant materials to mulch the nursery bed and water it on top of the mulch.
Care for the vegetable seedlings in the nursery
- Vegetable seedlings are taken care of by constructing a shade on top of them to prevent being weakened by direct sunlight and to preserve water, by preventing water lose from the nursery bed through evaporation.
- The seedlings should be watered regularly and weed removed from their midst. When the seedlings are ready, you should transplant them into a seedbed.
Preparing a seedbed for planting vegetable seedlings.
- Transplanting seedlings in the seedbed should be taken care of. This is through weeding, watering and application of fertilizer or manure. Dried up seedlings after transplanting should be replaced in the process called gapping.
- Other practices such as mulching, shading application of pesticides to control pests and diseases are important. Pruning of some vegetables such as tomatoes is needed. This is cutting of excess branches.
- Tall tomatoes varieties need to be trained, so that they grow upright. Once the crops are ready, they need to be harvested in time.
- It is important to keep records of various gardening activities such as the date of planting. This can help us to estimate the expected date of harvesting.
- Some vegetables such as cabbages take between two to three months before they are harvested. Other vegetables may take longer than this.
- Some vegetable fruits are harvested when they are big in size and when they start changing colour. E.g. tomatoes and hot pepper turn red while some pumpkins turn orange.
- However, other vegetable fruits such as sweet pepper may still be harvested when they are green in colour.
- The ripe fruits are picked by the hand. Care is taken so as not to damage the skin of the fruit. Harvesting of the fruit should be done at the right time to avoid over ripening which lowers their quality.
- For leafy vegetables such as kale and spinach, it is good to harvest when the leaves are tender and green. The lower outer leaves are broken from the stem to allow the plant to produce more.
- The cabbage head is removed by cutting the base of the stalk with a sharp panga.
- Bulb onions are harvested when the top leaves start bending and turning yellow. Soil is loosened around the bulbs and then the bulbs are pulled out.
Innovative Gardening
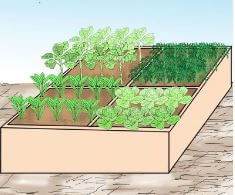
- Innovative gardens can be used to grow crops on small spaces of land.
- They are innovative ways of growing crops in small spaces.
- We can grow our own food using innovative gardens.
- Sacks can be arranged in small flower gardens or along the paths.
- The bottles can be placed on vertical walls to make vertical gardens.
- Plastic tubes can also be placed along vertical walls and held with clips.
- Bottles can also be hanged vertically on the roof of the balcony.
- People with a small piece of land can use innovative gardening to grow crops.
- Innovative gardening is a way of conserving water.
- Innovative gardening contributes to environmental conservation by re-using some materials such as plastic bottles that would pollute the environment.
- Waste plastics, wires, metals and wood can be reused to practise innovative gardens.
- Innovative gardening enables families to obtain food at all times.
- Innovative gardening can be done at home.
- The community can learn innovative gardening practices.
- The environment is kept clean by collecting and reusing plastic bottles, metals and wires from construction sites.
- Water at home is used economically to grow the crops.
Some examples of innovative gardening methods:
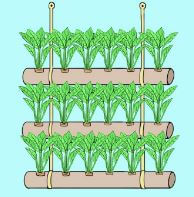
Vertical and Horizontal Gardening
- Vertical gardening is crowing crops above the ground. This is used to minimize the space for practicing crop production. It can be used in places where is enough land to practice gardening on a large piece of land. This practice also save water.
- Vertical innovative gardens occupy smaller ground space than the horizontal gardens.
- Some horizontal gardens do not need containers.
- The importance of vertical gardening is that it is easy to control weeds, pest and diseases. Crops produced from vertical gardens are also clean because they don’t get into contact with soil.
- Leafy vegetables such as kales and spinach are harvested when they large enough to use for cooking. They are carefully plucked using hands to avoid uprooting the whole plant.
- Fruit vegetables are plucked when they are ripe. Tomatoes should be carefully picked when they are ripe.
Activity 1
Finding out differences between vertical and horizontal innovative gardening.
Use digital devices or print resources to find information on innovative gardening.
Let us Find Out
Working in groups
Look at the types of innovative gardening practices in the following pictures:
- From the pictures, identify vertical innovative garden and horizontal innovative garden.
- What differences can you see between the vertical and the horizontal innovative gardens?
- Which of the two types of innovative gardening practices use a lot of ground space?
- Use magazines, newspapers or library books to get information on innovative gardening.
- Photocopy the information from newspapers and magazines, cut them out and paste them in exercise books.
- Label the pictures pasted in the album.
- Name the album “innovative gardening.”
- Share your findings with the other groups.
Let us understand
- Vertical innovative gardens occupy smaller ground space than the horizontal gardens.
- Some horizontal gardens do not need containers.
- The album created from the print resources can be used to store information on innovative gardening.
- The album can be used to present the same information when needed.
Working in groups
- Name type of crops suitable for the vertical innovative gardening.
- Name the crops suitable for the horizontal innovative gardening.
- Describe innovative gardens which need more ground spaces.
- In groups, discuss the innovative gardening practices you would practice at home.
Note:
- Deep rooted crops are suitable for horizontal innovative gardening.
- There are many ways in which innovative gardening can be practiced.
Multi-storey Farming Using Dam liners
- The multi-storey gardens are constructed using dam liner materials with a 0.5-1mm thickness. They are cut into different sizes and fastened using bolts and nuts at the ends to form circular rings with a diameter of 4ft.
- The soil around the terrace is mixed with the less acidic and fine goat manure on a 1:1 ratio. The base of the garden is wider to make the multi-story gardens stable.
- The storeys reduce in size by 2-4 inches upwards, forming a pyramid-shaped structure with terraces that allow for the smooth flow of water downwards. The storeys rise to a maximum of 6 or 8 terraces from the ground. Therefore, the farmer can choose to grow different crops on each terrace.

- The importance of this innovation is that it provides a solution to water scarcity. With less water and using this method, one can ensure food security, effective water utilization, and effective land utilization. Can be used when there is limited land space.
- The dam liners have a longer lifespan of over ten years as they are ultraviolet-heat treated.
- Allows smooth water flow downwards and lasts for ten years compared to sacks or old mosquito nets widely used by Kenyan farmers.
- You can plant vegetables like kales, Sukuma, carrots, onions, indigenous vegetables and other vegetables.
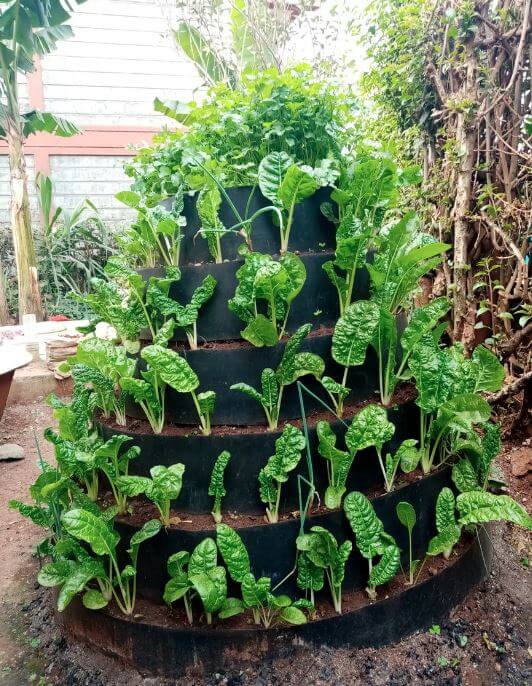

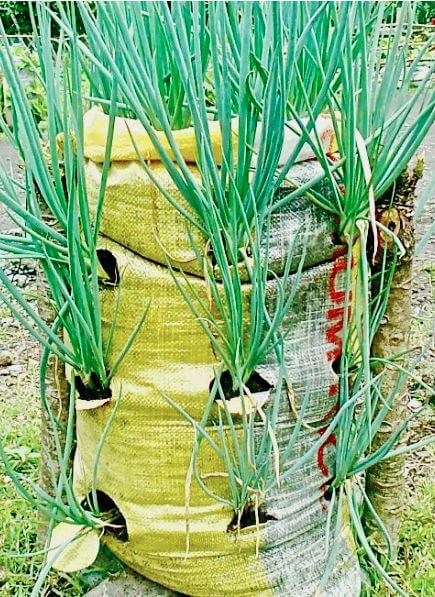
Sack garden
- A sack garden is a type of horizontal and vertical garden
- A sack garden is created by taking a breathable sack like a ‘gunia,’ putting stones horizontally at the bottom, then packing the bag with soil mixed with manure and compost. Put a vertical tube at the center packed with stones to help you build the middle vertical column as you keep packing the bag with the soil mixed in with manure. Water the bag thoroughly, on top of the stone column and the sides of the bag. The soil must be well moist. Make holes that are 15 cm apart around the bag. Do not make holes in the stone layer at the bottom of your bag. Carefully place plants into the hole and on top of the sack. Be careful not to damage the plant roots. Water the plants well, and you are done. Your sack garden is ready.
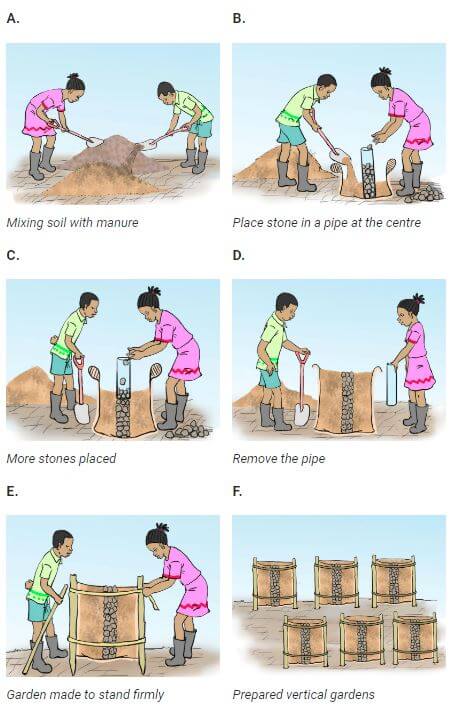
- Mixing compost manure with top soil makes soil fertile for innovative gardens
- Stone columns allow water to flow to the lower level of the sack.
- Holes are made to enable water to drain.
- Sack garden can be arranged to form vertical or horizontal innovative gardens.
- Like multi-storey farming, sack gardening allows you to grow more plants in less space. This is because the sacks prevent the root systems from spreading too far and inhibiting the growth of other plants.
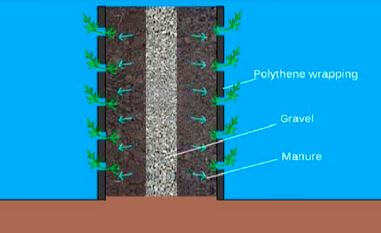
- The primary advantage of growing your plants in a sack or bag seems to be that they grow in an isolated environment. You know exactly what type of soil they are growing in, and you ultimately control what goes in it. Since the plants grow in much more isolated spaces, the risk of animals and pests (such as slugs) is significantly lower.
- By growing your plants in sacks, you can place them very close to each other without having to worry about that. As a result, you can grow more plants in less space.

- Since you use sacks or bags to grow your plants, virtually no cleaning is also involved.
- As the amount of direct sunlight that reaches your garden changes throughout the growing season, quickly moving your plants can come in handy if some are getting too much direct sunlight during the warmest months of summer.

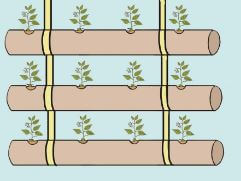
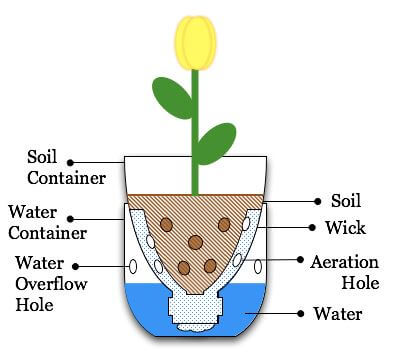
Wick irrigation garden
- This farming helps better utilize water and upcycling plastic water bottles. Numerous plastic bottles are being used in Kenya today; reusing these water bottles as planters is a great way to help the environment.
- You can grow any vegetable or herb in the bottle.
- It is a simple hydroponic system that is relatively easy to make. It utilizes a reservoir of water to feed and water the plants in place of soil.
- It uses an absorbent wick to pull moisture into the growing medium, self-watering the plant(s). This works by capillary action: as moisture in the growing medium is taken up by the plant roots or lost to evaporation, the wick will continually pull water from the reservoir below, replenishing the moisture.
- This method significantly reduces the time you need to water your plants manually.
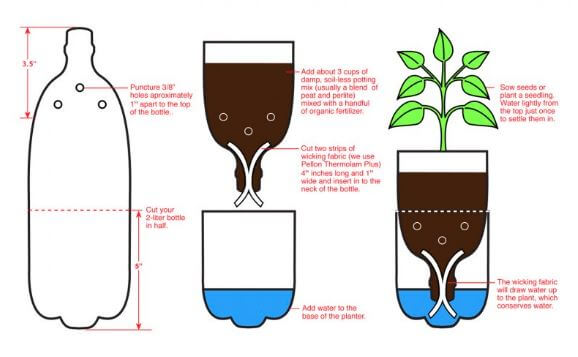
- Plastic bottles are used to make vertical gardens when placed or hanged on wooden frames or walls.
- Plastic bottles can also be painted on the outside to make them colourful.
- Painted plastic bottles can be arranged along pathways to form horizontal innovative gardens.

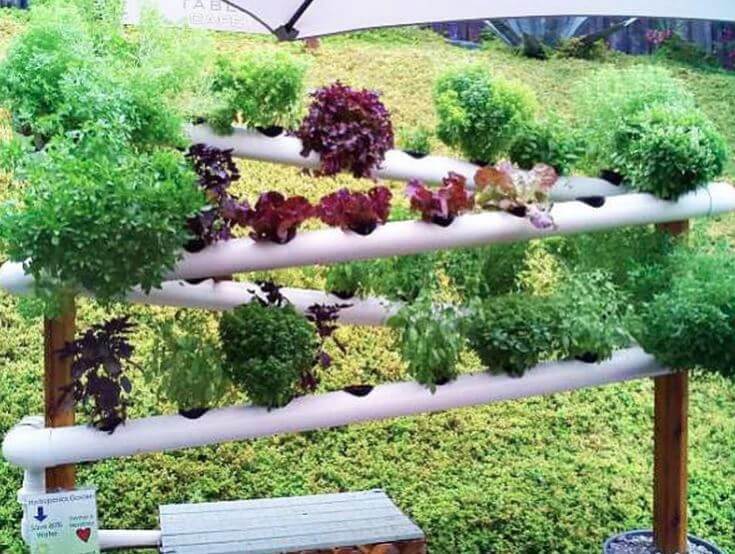
- Plastic pipes can be used to make vertical and horizontal innovative gardens for planting vegetable seeds.
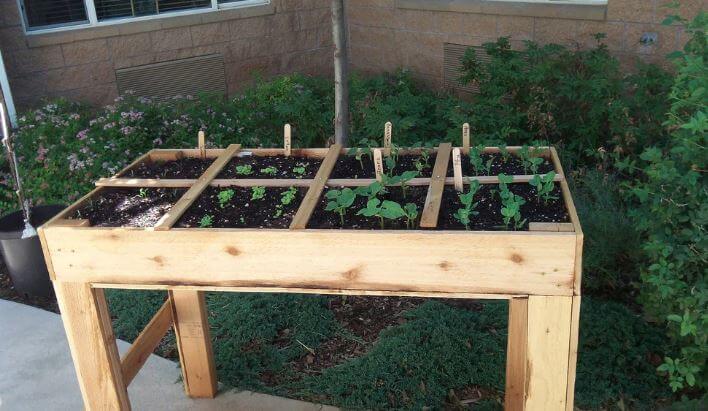
Other innovative gardening ideas
Expandable step gardens

One Pot Garden

Square Foot Gardening
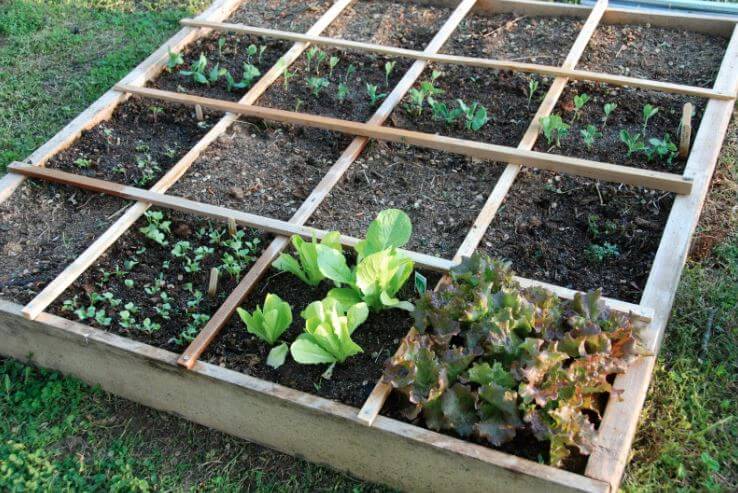


Gutter Gardens

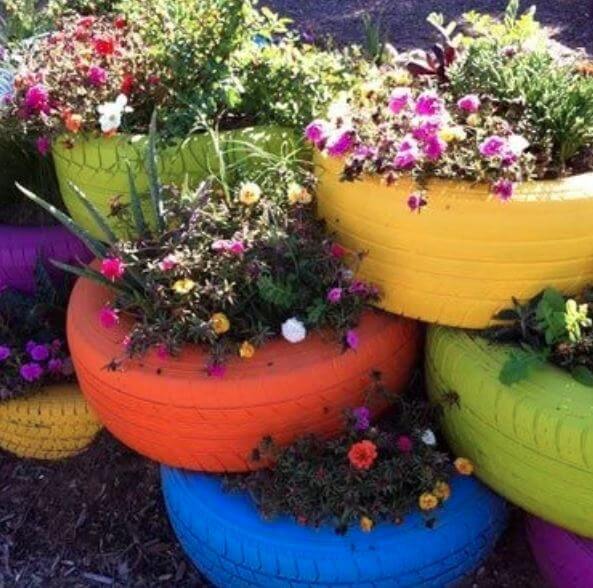
Tyre garden

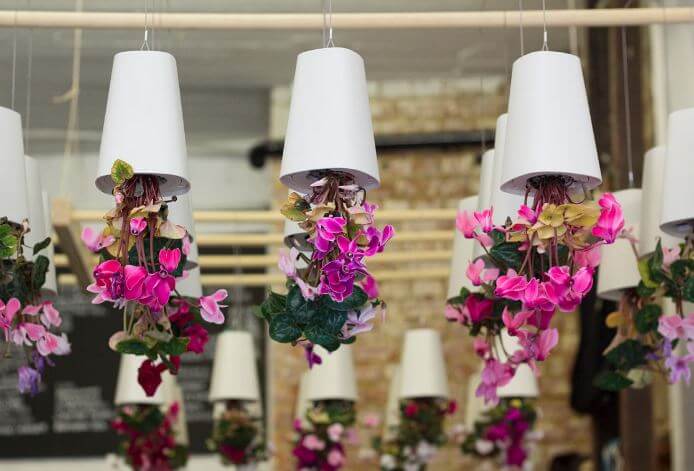
Sky Planters

Transplanting seedlings
- Seedlings to be transplanted should have a ball of soil around the roots.
- Seedlings should be transplanted late in the afternoon or when it is cloudy.
- Seeds sown in the plastic pipes should be given little water to avoid flooding them.
Gardening practices on vegetables in the innovative gardens
- Thinning
- Weeding - uprooting all roots from the innovative garden
- Watering
- Removal of diseased plants by uprooting them from the innovative gardens.
Remember to:
- Avoid damaging the roots of the vegetable crops during weeding and thinning
- Take care not to apply too much water to the plants.
- Weeds should be uprooted as soon as they appear.
- Record keeping is important for the gardening practices.
Harvesting vegetables from innovative gardens
- Only mature vegetables are harvested.
- Onion bulbs become large while leaves bend and dry off.
- Cabbage heads become firm.
- Kales, spinach, coriander, lettuce, pigweed and black nightshade are harvested when the leaves grow large.
- Avoid damage to the vegetables when harvesting.
- The vegetables are weighed after harvesting.
Importance of innovative gardens for Grade 5 learning
Students to understand that:
- Innovative gardening helps us carry out different practices responsibly.
- Some of the materials used at home can be recycled and used on the innovative gardens.
- Record keeping skills are important in a gardening project.
Revision Exercise
Questions
- Vertical innovative gardens occupy………………………….. space than horizontal innovative gardens. (More, less).
- Identify whether the innovative gardening practices below are horizontal or vertical gardenning
- Re-using plastic bottles for innovative gardening helps us:
- Increase water sources
- Control soil erosion
- Conserve the environment
- Which one of the following materials is not suitable to make a soil container for innovative gardens?
- Metal pipes
- Wooden boxes
- Sacks
- Plastic bottles
- Writing paper
- Identify the type of innovative garden shown in the following pictures.
- Harvesting kales from the innovative gardening is done when:
- Leaves are large
- Leaves turn yellow
- Leaves are small
Answers
- Less
-
- Both horizontal and vertical
- Both horizontal and vertical
- Horizontal
- Horizontal
- Control soil erosion
Conserve the environment - Metal pipes
Writing paper -
- Sack garden
- Vertical and horizontal bottle garden
- Vertical garden
- Horizontal garden
- Sack garden
- Vertical and horizontal bottle garden
- Sack garden
- Horizontal garden
- Vertical and horizontal bottle garden
- Sack garden
- Leaves are large
Download Gardening Practices - CBC Grade 5 Agriculture Revision Notes.
Tap Here to Download for 30/-
Get on WhatsApp for 30/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students