Displaying items by tag: Energy
Force and Energy - Grade 5 Science and Technology Revision Notes
Gravity
Demonstrating Gravity
- Hold and suspend erasers in the air. Release them and tell what happens.
- Identify what causes the objects to act as they do. Name and define the cause.
- The fruits and leaves fell to the ground due to a force acting on them. The erasers dropped to the ground due to a force acting on them. This force is known as gravity.
- Gravity is defined as the force acting on objects pulling them down.
Effects of gravity on an object.
- The force that pulls down things is called the force of gravity.
- When you throw a ball into the air, gravity pulls it back down. When you release a stone suspended in the air, gravity pulls it down to the ground.
- When the books are tipped at the edge of the desk, the fall down due to gravity.
- Gravity causes fruits and leaves to fall from trees.
- Gravity is a force that pulls things down. It is also called the normal force.
Application of Gravity.
- The force of gravity enables the following in our lives:
- Gravity causes a ball you throw in the air to come down again
- It cause a glass to drop down and fall onto the floor
- It causes us to move down and slide
- It causes apple to fall down from apple tree
- It keeps us firmly on earth, otherwise we would float away into space.
- It causes a pen that rolls off your desk to fall onto the floor
- It causes water to move down a river and waterfall.
- It causes a rock to roll downhill.
Sound
Energy Producing sounds
- Sounds are produced when we the following
- Clap our hands
- Stamp our feet
- When we whistle.
- When we hot a drum
- Playing guitar
- Sound is the energy that things produce when they vibrate.
Loud and soft sounds
- Volume is the amount of sound something produces.
- It is the measure of the loudness of sound. Loud sounds are produced by big vibrations, while low sounds are produced by small vibrations.
- The energy of a sound determines its loudness. The greater the energy the greater the sound.
- Whispering makes a soft sound while shouting to a friend across a playground makes a loud sound.
- Fire alarms and car’s horn are examples of loud sounds, while whispering to a friend and the sound of blowing wind are examples of soft sounds.
Identifying areas with loud sounds
- Areas that produce loud sound in the environment include:
- Industries
- Music shops
- Markets
- Stadia (plural for stadium)
Sound pollution
- Sound pollution is defined as sounds or noises that are loud, annoying and harmful to the ears.
Effects of sound pollution
- The effect of sound pollution on human health and behaviour include the following:
- Loss of hearing - the immediate effect of noise pollution to a person, over a period of time is reduced hearing ability. Over a time a person may completely lose his or her hearing.
- Poor concentration - loud and continuous noise makes a person lose concentration on any activity that they are carrying out.
- Irritability - loud and continuous noise at home and at school may result in irritability which lead to aggressive behaviour.
- Sleep disturbances - loud noise disturbs your sleep and keeps you awake.
- Interferences with communication - loud noise makes people unable to communicate freely. You may find it difficult to understand or even hear what someone else is saying.
Protecting self from loud sound
- Turning down devices producing loud sound
- Using hearing protection devices when in a place with loud sound.
- Avoid areas with loud sound.
- Staying in houses with soundproof walls.
Heat Transfer
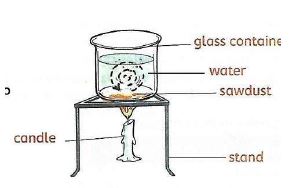
Demonstrating Transfer of heat in liquids
- Materials
- Sawdust
- A glass container
- A stand
- Water
- A matchbox
- A source of heat (a candle)
Procedure
- Fill in the glass container with water
- Place a small amount of sawdust in the water
- Allow the sawdust to settle at the bottom of the container
- Place the glass container on the stand
- Heat the container using candle as the source of heat
- Observe what happens.
- As the water continues to heat, a steady rise of sawdust is observed. This is because the water at the bottom of the glass container gets hotter, expands and rises.
- The cold water at the top then moves downwards and takes the place of the risen hot water.
- The cycle repeats itself. The sawdust particles show a movement in the water called convection currents.
- Therefore, heat is transferred in liquids through convection.
(convection currents in liquids)
(heating water via convection)
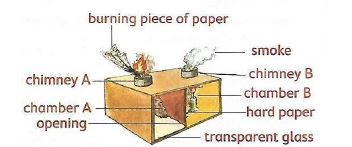
Demonstrating transfer of heat in gases
- Materials
- A small carton box with a top
- Hard paper or piece of carton
- A piece of paper
- A short candle
- A matchbox
Procedure
- Make a chimney on each end of the top of the box
- Divide the box with hard paper or a piece of carton to make two chambers A and B. place the transparent glass on the side of the box for viewing.
- Light up a candle. Put the lit candle below the chimney B on the box. Close the box.
- Place a burning piece of paper over chimney A as shown in figure 6
- Observe chimney B and tell what you see.
- Record your observations.
- The burning paper produces smoke that moves from chamber A to Chamber B through the opening.
- The candle in chamber b heats the smoke coming from chamber A, which becomes lighter and rises.
- As the smoke rises up it moves up through chimney B. Cooler air enters Chamber A through chimney A, creating a circular motion known as convection currents.
- These currents can be viewed through the transparent glass.
- The transfer of heat in gases is known as Convection
(convection in gases)
Application of convection in everyday life
- Convection of heat is used in everyday life by many ways. These ways include:
- Ventilating buildings
- Inflation of hot air balloons
- Heating of food in a microwave
- Formation of land and sea breezes
- Boiling of water in a sufuria or kettle
- Vehicle engines
Transfer of heat by radiation
- When you stand in the sunlight, you can feel the warmth of the sun. The heat energy from the sun is transferred to your skin through radiation.
- When you sit beside a fire, you feel warm. The warmth of the heat from the fire is transferred from the fire to you through radiation.
Application of radiation in everyday life
- Radiation is used in everyday life in many ways. These ways include:
- Warming ourselves using electric heaters
- Using solar heaters in the house
- Drying clothes and grains
- Using greenhouses to aid growth of plants
Energy - Class 6 Science Revision Notes
Light
How light travels
- Light travels in a straight line away from the source.
- Light travels to all directions from the source.
Transparent Materials
They are materials that allow all light to pass through them and one can see through them clearly.
Examples: Clear glass, Clear water, air
Uses of transparent materials
- They are used in making:
- Car windscreens
- Spectacles
- Window panes
- Lamps
- Glass walls
Translucent Materials
They are materials that allow only little light to pass through them.
Examples:
- Frosted glass
- Tracing paper
- Oiled or waxed paper
Uses of translucent materials
They are used in making:
- Skylights
- Toilet and bathroom window panes
- Ambulance windows.
Opaque Materials
They are materials that do not allow any light to pass through them.
When light hits an opaque materials a shadow is formed.
Examples:
- Wood
- Stone
- Metals
Reflection of Light
Reflection is the bouncing back of light when Materials that reflect light are called reflectors.
Reflection happens when light hits a smooth shinny surface.
Types of Reflection
- Regular reflection
- Irregular (diffused)
Characteristics of the image in a plane mirror
- The image is upright
- The image is behind the mirror
- The image is the same size as the object
- The image is laterally inverted.
Refraction of Light
It is the process in which light bends or changes direction when it moves from one medium to another. (air to water)
Effects of Refraction
- Objects appear bent or broken
- Objects appear bigger
- Swimming pool appear shallower
Making a Rainbow
A rainbow is formed by the refraction of light. To be formed raindrops and sunshine is required.
The process of splitting light into seven different colours is known as dispersion.
A group of seven colours in the rainbow is known as spectrum
Energy - class 8 science revision notes
Energy Transformation.
The law of energy conservation statesthat, energy cannot be created or destroyed but can be changed to other forms of energy.
| Forms of energy | Sources |
| Potential energy (stored) | Possessed by objects at rest. Found in fuels, dammed, water, elastic rubber. |
| Kinetic energy (motion) | Possessed by moving objects. Found in running water, wind, moving stone, moving car etc. |
| Chemical energy | Found in chemicals, fuels, food, car battery, dry cells, candlewax and all fuels |
| Heat energy | Main source is sun. Other sources include; friction, burning fuels, electricity and food. |
| Light energy | Main source is sun. Other sources include; stars, electricity, lamps et |
| Magnet energy | Found in magnets, loadstones and electromagnet |
| Sound Energy | Produced when objects vibrates. Sources include; pianos, guitas, drums etc |
| Mechanical energy | Produced as a result of potential energy and kinetic energy. Examples include; rotating turbines, hammer stricking a gong, between a bicycle and road |
| Elastic potential | Found in streched rubber band or compressed spring. |
Energy Conservation.
Energy conservation means protecting, preserving, restoring and managing energy resources.
Ways of Conserving of Energy.
- Using energy sparingly by:
- Switching bulbs off when not needed.
- Using public transport instead of private vehicle.
- Using bicycles or walking for short distance.
- Using vehicles with low fuel consumption.
- Using thermosflask and hot pots to keep food hot.
- Using energy saving bulbs.
- Using energy efficient devices.
- Modern jiko/improvised jiko
- Clay cookers.
- Using renewable forms of energy.
Renewable forms of energy refers to forms that are inexhaustible like wind, water, sunlight, food, biogas and forests.
Non-renewable sources of energy are those that can get exhausted when use like petrol, diesel, kerosene, natural gas
Advantages of Renewable Energy.
- Are cheap.
- Do not pollute the environment.
- Help to conserve non renewable forms of energy.
- Readily available and in abundance.