Displaying items by tag: kenya
Innovative Gardening Notes PDF
Innovative gardening is about being creative and shrewd in gardening.
This page is a full-on guide to everything you need to know about innovative gardening, including;
- What is Innovative gardening?
- What is innovative gardening in agriculture
- Quick facts about innovative gardening
- Importance of innovative gardening
- How to prepare an innovative garden
- Types of innovative gardening methods
- Other innovative gardening ideas
- Transplanting seedlings
- Gardening practices on vegetables in the innovative gardens
- Harvesting vegetables from innovative gardens
- Importance of innovative gardens for Grade 5 learning - Kenya
- Revision exercise on Innovative Gardening with answers
Click on the highlighted topic/subtopic above to quickly go to the innovative gardening topic/subtopic in these notes that you want.
Innovative Gardening
What is innovative gardening - In Agriculture, innovative gardening is about being inventive in how you efficiently utilize what you have around you to grow and cultivate plants that you can use in your home or that you can sell.
Innovative gardening is basically applying new technology and methods in Agriculture. Innovation in terms of how and where your crops are grown.
The plants that you can grow in your innovative garden range from horticultural plants like flowers to indigenous food crops like spider weeds, arrow roots, cassava, sorghum and sweet potatoes and vegetables like kale (Sukuma wiki) and spinach.
Can you name more indigenous food crops ?
Quick facts about innovative gardening
- Innovative gardens can be used to grow crops on small spaces of land.
- They are innovative ways of growing crops in small spaces.
- We can grow our own food using innovative gardens.
- Sacks can be arranged in small flower gardens or along the paths.
- The bottles can be placed on vertical walls to make vertical gardens.
- Plastic tubes can also be placed along vertical walls and held with clips.
- Bottles can also be hanged vertically on the roof of the balcony.
- People with a small piece of land can use innovative gardening to grow crops.
- Innovative gardening is a way of conserving water.
- Innovative gardening contributes to environmental conservation by re-using some materials such as plastic bottles that would pollute the environment.
- Waste plastics, wires, metals and wood can be reused to practise innovative gardens.
- Innovative gardening enables families to obtain food at all times.
- Innovative gardening can be done at home.
- The community can learn innovative gardening practices.
- The environment is kept clean by collecting and reusing plastic bottles, metals and wires from construction sites.
- Water at home is used economically to grow the crops.
From these quick facts can you identify some importances of innovative gardening?
Importances of innovative gardening
-
Produces vegetables and fruit.
-
Saves money.
-
Less rubbish ends up in landfills.
-
Encourages "reduce, reuse, and recycle"
-
Enhances record-keeping abilities.
-
Contributes to the protection of the environment.
-
Livens up of dull places/space, including workplaces or shops or parks.
-
Encourages responsible living
Some examples of innovative gardening methods:
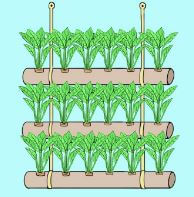
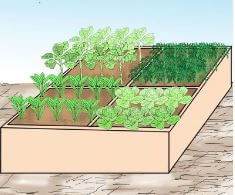
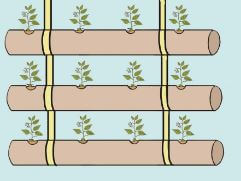
Vertical and Horizontal Gardening
- Vertical gardening is crowing crops above the ground. This is used to minimize the space for practicing crop production. It can be used in places where is enough land to practice gardening on a large piece of land. This practice also save water.
- Vertical innovative gardens occupy smaller ground space than the horizontal gardens.
- Some horizontal gardens do not need containers.
- The importance of vertical gardening is that it is easy to control weeds, pest and diseases. Crops produced from vertical gardens are also clean because they don’t get into contact with soil.
- Leafy vegetables such as kales and spinach are harvested when they large enough to use for cooking. They are carefully plucked using hands to avoid uprooting the whole plant.
- Fruit vegetables are plucked when they are ripe. Tomatoes should be carefully picked when they are ripe.
Activity 1
Finding out differences between vertical and horizontal innovative gardening.
Use digital devices or print resources to find information on innovative gardening.
Let us Find Out
Working in groups
Look at the types of innovative gardening practices in the following pictures:
- From the pictures, identify vertical innovative garden and horizontal innovative garden.
- What differences can you see between the vertical and the horizontal innovative gardens?
- Which of the two types of innovative gardening practices use a lot of ground space?
- Use magazines, newspapers or library books to get information on innovative gardening.
- Photocopy the information from newspapers and magazines, cut them out and paste them in exercise books.
- Label the pictures pasted in the album.
- Name the album “innovative gardening.”
- Share your findings with the other groups.
Let us understand
- Vertical innovative gardens occupy smaller ground space than the horizontal gardens.
- Some horizontal gardens do not need containers.
- The album created from the print resources can be used to store information on innovative gardening.
- The album can be used to present the same information when needed.
Working in groups
- Name type of crops suitable for the vertical innovative gardening.
- Name the crops suitable for the horizontal innovative gardening.
- Describe innovative gardens which need more ground spaces.
- In groups, discuss the innovative gardening practices you would practice at home.
Note:
- Deep rooted crops are suitable for horizontal innovative gardening.
- There are many ways in which innovative gardening can be practiced.
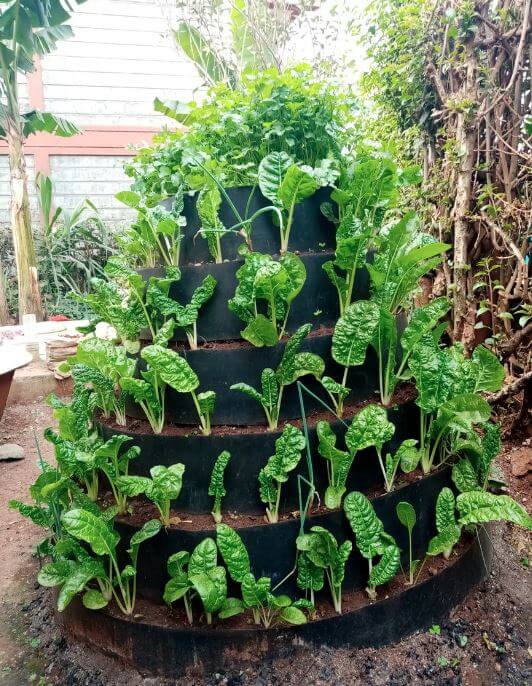
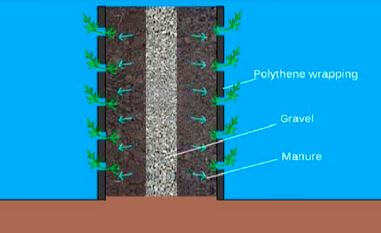
Multi-storey Farming Using Dam liners
- The multi-storey gardens are constructed using dam liner materials with a 0.5-1mm thickness. They are cut into different sizes and fastened using bolts and nuts at the ends to form circular rings with a diameter of 4ft.
- The soil around the terrace is mixed with the less acidic and fine goat manure on a 1:1 ratio. The base of the garden is wider to make the multi-story gardens stable.
- The storeys reduce in size by 2-4 inches upwards, forming a pyramid-shaped structure with terraces that allow for the smooth flow of water downwards. The storeys rise to a maximum of 6 or 8 terraces from the ground. Therefore, the farmer can choose to grow different crops on each terrace.

- The importance of this innovation is that it provides a solution to water scarcity. With less water and using this method, one can ensure food security, effective water utilization, and effective land utilization. Can be used when there is limited land space.
- The dam liners have a longer lifespan of over ten years as they are ultraviolet-heat treated.
- Allows smooth water flow downwards and lasts for ten years compared to sacks or old mosquito nets widely used by Kenyan farmers.
- You can plant vegetables like kales, Sukuma, carrots, onions, indigenous vegetables and other vegetables.

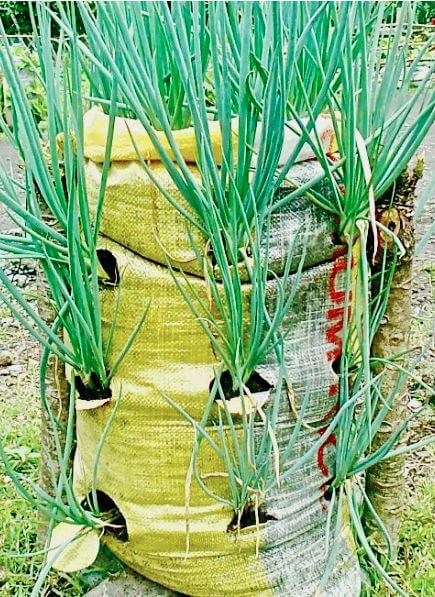
Sack garden
- A sack garden is a type of horizontal and vertical garden
- A sack garden is created by taking a breathable sack like a ‘gunia,’ putting stones horizontally at the bottom, then packing the bag with soil mixed with manure and compost. Put a vertical tube at the center packed with stones to help you build the middle vertical column as you keep packing the bag with the soil mixed in with manure. Water the bag thoroughly, on top of the stone column and the sides of the bag. The soil must be well moist. Make holes that are 15 cm apart around the bag. Do not make holes in the stone layer at the bottom of your bag. Carefully place plants into the hole and on top of the sack. Be careful not to damage the plant roots. Water the plants well, and you are done. Your sack garden is ready.
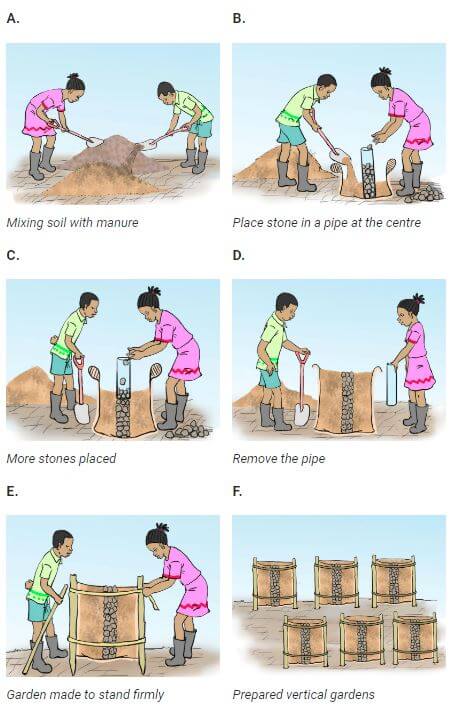
- Mixing compost manure with top soil makes soil fertile for innovative gardens
- Stone columns allow water to flow to the lower level of the sack.
- Holes are made to enable water to drain.
- Sack garden can be arranged to form vertical or horizontal innovative gardens.
- Like multi-storey farming, sack gardening allows you to grow more plants in less space. This is because the sacks prevent the root systems from spreading too far and inhibiting the growth of other plants.
- The primary advantage of growing your plants in a sack or bag seems to be that they grow in an isolated environment. You know exactly what type of soil they are growing in, and you ultimately control what goes in it. Since the plants grow in much more isolated spaces, the risk of animals and pests (such as slugs) is significantly lower.
- By growing your plants in sacks, you can place them very close to each other without having to worry about that. As a result, you can grow more plants in less space.

- Since you use sacks or bags to grow your plants, virtually no cleaning is also involved.
- As the amount of direct sunlight that reaches your garden changes throughout the growing season, quickly moving your plants can come in handy if some are getting too much direct sunlight during the warmest months of summer.

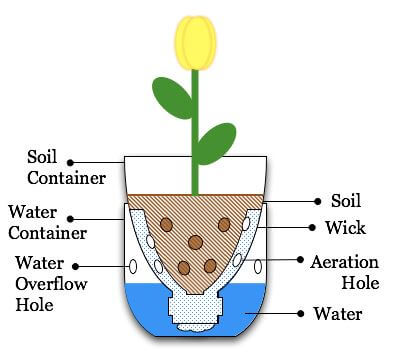
Wick irrigation garden
- This farming helps better utilize water and upcycling plastic water bottles. Numerous plastic bottles are being used in Kenya today; reusing these water bottles as planters is a great way to help the environment.
- You can grow any vegetable or herb in the bottle.
- It is a simple hydroponic system that is relatively easy to make. It utilizes a reservoir of water to feed and water the plants in place of soil.
- It uses an absorbent wick to pull moisture into the growing medium, self-watering the plant(s). This works by capillary action: as moisture in the growing medium is taken up by the plant roots or lost to evaporation, the wick will continually pull water from the reservoir below, replenishing the moisture.
- This method significantly reduces the time you need to water your plants manually.
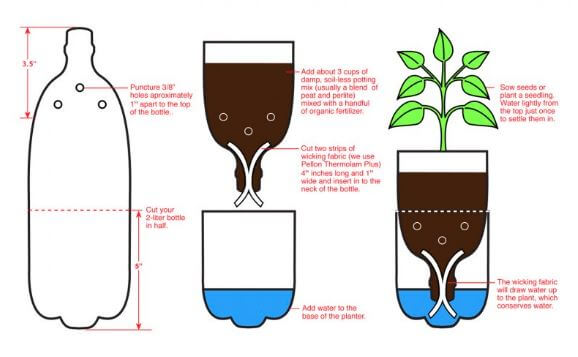
- Plastic bottles are used to make vertical gardens when placed or hanged on wooden frames or walls.
- Plastic bottles can also be painted on the outside to make them colourful.
- Painted plastic bottles can be arranged along pathways to form horizontal innovative gardens.

- Plastic pipes can be used to make vertical and horizontal innovative gardens for planting vegetable seeds.
Other innovative gardening ideas
Expandable step gardens

One Pot Garden

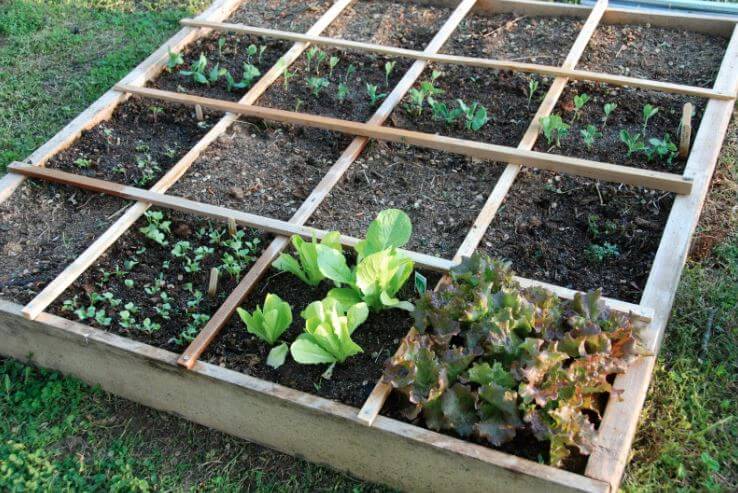
Square Foot Gardening


Gutter Gardens
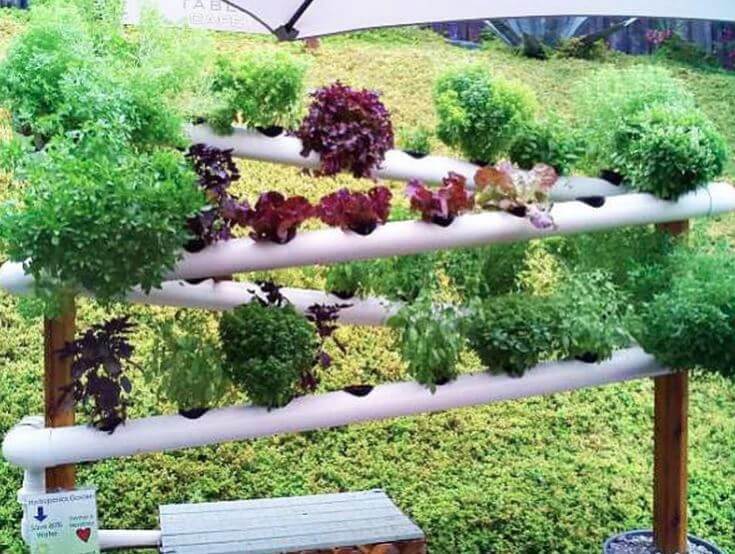

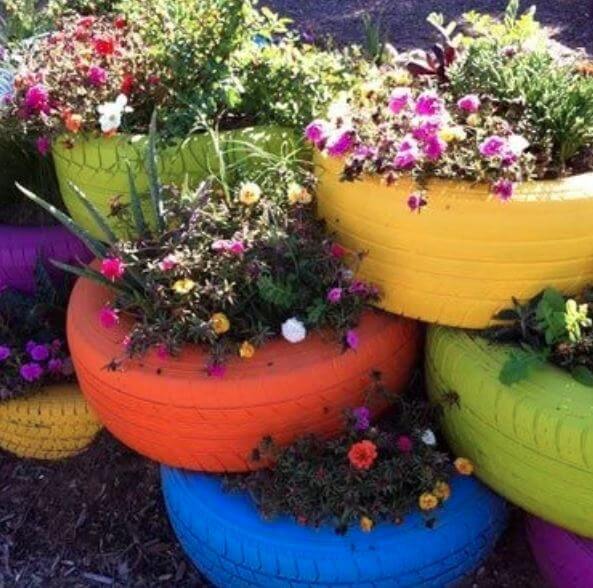
Tyre garden

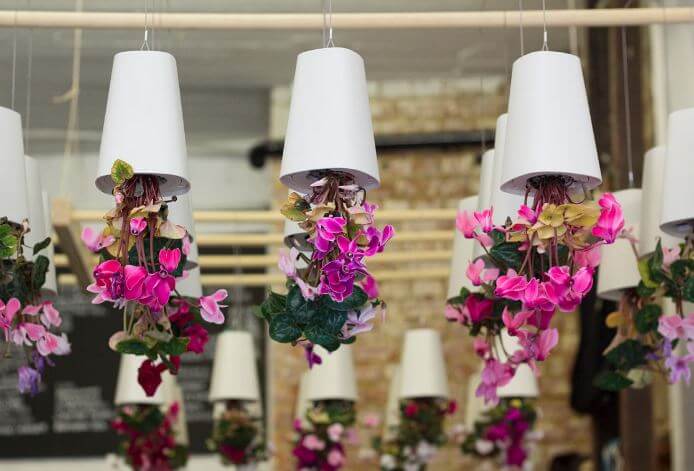
Sky Planters

Transplanting seedlings
- Seedlings to be transplanted should have a ball of soil around the roots.
- Seedlings should be transplanted late in the afternoon or when it is cloudy.
- Seeds sown in the plastic pipes should be given little water to avoid flooding them.
Gardening practices on vegetables in the innovative gardens
- Thinning
- Weeding - uprooting all roots from the innovative garden
- Watering
- Removal of diseased plants by uprooting them from the innovative gardens.
Remember to:
- Avoid damaging the roots of the vegetable crops during weeding and thinning
- Take care not to apply too much water to the plants.
- Weeds should be uprooted as soon as they appear.
- Record keeping is important for the gardening practices.
Harvesting vegetables from innovative gardens
- Only mature vegetables are harvested.
- Onion bulbs become large while leaves bend and dry off.
- Cabbage heads become firm.
- Kales, spinach, coriander, lettuce, pigweed and black nightshade are harvested when the leaves grow large.
- Avoid damage to the vegetables when harvesting.
- The vegetables are weighed after harvesting.
Importance of innovative gardens for Grade 5 learning
Students to understand that:
- Innovative gardening helps us carry out different practices responsibly.
- Some of the materials used at home can be recycled and used on the innovative gardens.
- Record keeping skills are important in a gardening project.
Revision Exercise on Innovative Gardening Questions and Answers
Questions
- Vertical innovative gardens occupy………………………….. space than horizontal innovative gardens. (More, less).
- Identify whether the innovative gardening practices below are horizontal or vertical gardenning
- Re-using plastic bottles for innovative gardening helps us:
- Increase water sources
- Control soil erosion
- Conserve the environment
- Which one of the following materials is not suitable to make a soil container for innovative gardens?
- Metal pipes
- Wooden boxes
- Sacks
- Plastic bottles
- Writing paper
- Identify the type of innovative garden shown in the following pictures.
- Harvesting kales from the innovative gardening is done when:
- Leaves are large
- Leaves turn yellow
- Leaves are small
Answers
- Less
-
- Both horizontal and vertical
- Both horizontal and vertical
- Horizontal
- Horizontal
- Control soil erosion
Conserve the environment - Metal pipes
Writing paper -
- Sack garden
- Vertical and horizontal bottle garden
- Vertical garden
- Horizontal garden
- Sack garden
- Vertical and horizontal bottle garden
- Sack garden
- Horizontal garden
- Vertical and horizontal bottle garden
- Sack garden
- Leaves are large
Kenya Indigenous Musical Instrument - CBC Grade 5 Music Revision Notes
Wind Instrument
- They are also called aero phones. They are played by blowing
These instruments have a permanent tuning which is acquired during construct - This is because upon constructions, wind instruments remain of fixed length, have a fix number of holes and a fixed blowing hole.
- They vary in shape, size and material used to make them. They are grouped in the following sub- classes”
- Horns- made from animal horns or natural hollow or hollowed out wooden tubes. Among some communities horns are joined to a gourd. E.g.
- Oluika- luya
- Lalet-kalenjin
- Oporo/tung’-Luo
- Coro-kikuyu
- Kikundit-kipsigit
- Adet-turkana
- Aluti-Teso
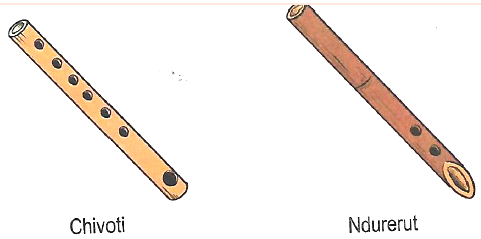
- Flutes-Are made from materials such as bamboo, swamp reeds, twig or wooden tubes. Currently improvised using plastic tubes.
Flutes vary in length and number of finger / pitch holes from one community to another.
Other features that can be used to distinguish or differentiate flutes are:
- closed at both ends
- Open at both ends
- Open at one end and closed at another end
- Notched at the blowing end (part of the end is v-shaped)
- Round at the blowing end
- End blown (also oblique)
Side blown (also traversely blown-this means the blowing hole is at the side of the flute.)
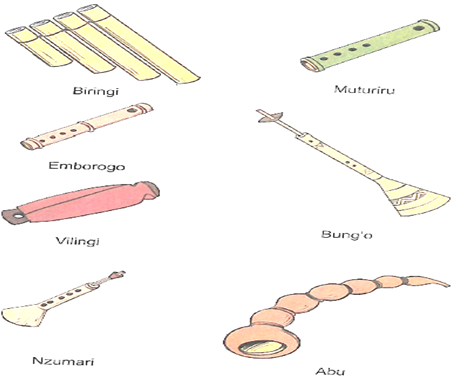
Indigenous flutes from the diverse Kenyan communities include:
End blown flutes (oblique)- Muturiri-Gikuyu
- Auleru-Teso
- Asili/Odundu-Luo
- Ndererut-Kalenjin
- Ebune/Elamaru-Turkana
Traversely held flutes - Chivoti-Digo, Rabai, Duruma
- Ekibiswi-Kuria
- Emborogo-Kuria
- Umwere-Kuria
- Mulele-Luhya
- Whistles – these wind instruments are made from hollow tubes or reeds which are bound together. The different length makes it possible to produce different varied pitches when the instrument is blown e.g. biringi of Agikuyu, vilingi of the Akamba.
- Reed instruments – double reed instruments have two reeds at the mouthpiece which is made from reeds. The two reed instruments have a tip shield made out of a coconut shell of metal coin
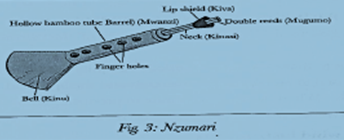
The lip shield- holds the reed in place and prevents air from escaping. The reeds vibrate when air is blown into the instrument thus producing sound. The Nzumari and the Bung’o played among some of the mijikenda community such as Digo and Rabai.
Functions of parts of flutes
- Bamboo reed - this is the main framework of the instrument and it also serves as the resonator
- Blowing hole – it is a hole through which air is blown causing the production of sound
- Pitch hole – are closed and opened with alternating finger movements to produce varied pitch when playing the melody.
- Closed – end = this part direct the sounds towards the open end.
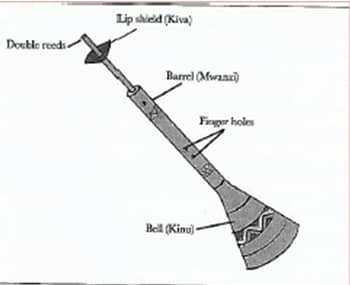
FUNCTIONS OF THE PARTS OF REED INSTRUMENTS
- Hollow bamboo reed – this is the main body of the instrument which act as a resonator
- Bell - it is used to make the sound louder or amplify the sound
- Neck - use to attach the double reeds and the lip shield
- Double reeds - when blown, they vibrate to produce sound
- Lip shield – this is where the lip rest when blowing
SKILLS OF PLAYING WIND INSTRUMENTS
- Some are held traversely while others are end blown
- Positioning of the lips – the lower lip is placed on the lower part of the blowing hole
- Blowing- air should be blown across the blowing hole. The amount of air being blown depends of the wind instrument.
- Tonguing - the tongue is used to put the accent on
- Fingering – closing and opening of finger holes in an alternating manner assist to produce varied pitch.
- Breath control – it’s also referred to as phrasing and should be done at appropriate places when playing the wind instrument.
Western Musical Instrument
Descant Recorder
Recorder fingering chart
Skills of playing the recorder
- Posture – correct poster will help in breathing deeply in order to get good sound out of the recorder.
- Breath control – enables them to achieve the good phrasing when playing the descant recorder.
- Holding – should be held properly with both left handed and right handed learners. The recorder is end blown.
- Embouchure - refers to the position and the use of the lips and teeth in playing wind instrument. It includes shaping the lips to the mouthpiece of the musical wind instrument
Embouchure is important because it affect the production of quality of sound - Articulation – (preparing the tongue) air flow is critical to the production of good tone or sound on the descant recorder. Blowing too much air will leard to production of squeaking sound.
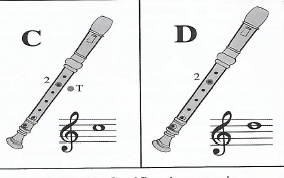
- Fingering – the left hand should be placed in the first three holes, while the right hand should be placed in the rest of the holes. Holes should be covered completely, failure to which will cause air to escape and a squeaking sound will be produced.
When holes on the descant recorder are covered completely, small round marks will be imprinted on the fingersTHE NOTES B, A AND G
They are played using the left hand and are organized logically with fingers moving in a sequential order.
Music Staff Notation
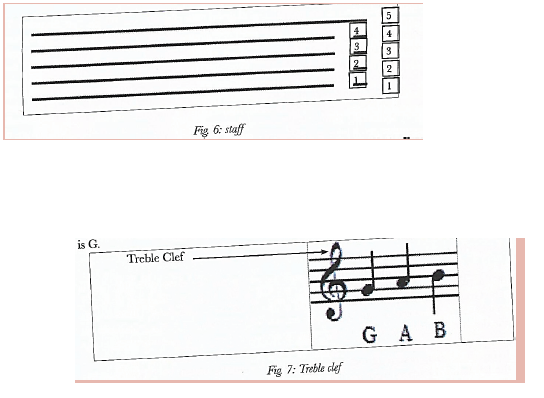
THE STAFF- this is a set of five parallel line and four spaces on which music is written.
The lines and spaces are named using the seven letters of the English alphabets A,B,C,D,E,F, and G.
Naming is made possible using clef. The treble or G clef is used to establish the pitches of the staff
Music for the descant recorder is written on the staff using the treble Or G clef.
Fingering notes is illustrated below
NEW NOTES C AND D
- They are fingered using the left hand as shown below
- The left hand thumb hole is left open when playing the note D
Kenyan Folk Dances
Dance - a form of art involving rhythmic movement’s f the body in response to music
It is an expression of norms, values, belief, attitudes and customs of the community.
In traditional African society dances are for specific groups of the performance e.g. boys, girls, boys and girls, young women and
Categories of participants
- Soloist – introduces dances, it is also known as Solo choral response or call response singing.
Roles of a soloist- Starting the dance
- Ending dance
- Help capture the message and the mood of the dance
- Pitching the dance songs
- Cuing dance on the change of melodies, movements and dance formations.
- Dancers – perform dance movements, create formations
- Dancers – perform dance movement. create formations
- Lead dancers – remind dancers the next dance style and formation. Guide other dancers in creating the varied dance styles/movement and formations to ensure transitions to ensure transitions are smooth.
- Singers - respond to the call of soloist. Make performance lively. Communicate the message and the mood of the dance
- Instrumentalist – make the dance performance lively.
Melodic instrument helps in pitching the performance.
Help in keeping the steady beat of the songs.
Assist to cue singers and dancers on the change of melodies, dance styles and formations to ensure smooth transition.
Provide rhythmic and melodic support to the rhythms and melodies in dance. - Audience and onlookers – make participants feel appreciated
Their participations bring the dance to life
Costumes
This involves styles of dress or clothes worn by the participants in dance performance. Roles of costumes in dance performance include:
- To depict the cultural community it is drawn from.
- To adorn the participant
- To distinguish the different roles played by various participants of the dance
- Influence the participant level of confidence
- Allow dancers or the wearers freedom of movement and formation
- Give information about certain role or characters due to elaborate details of the costumes
- They give the participant of the dance aesthetic appeal
- Are associated with the costumes and habits of a group of people
- Gives the participant dignity
- Help the identify the community the song originates from
- Create uniformity among the participant
- In modern times dance performance use uniform costumes made of sisal and banana leaves
- In each community there are items of value which the participants use during dancing. These items are also known as artifacts which includes shields, swords, skis and traditional tools.
Body Adornment
- It is an art which involved decorating the body, these vary across communities and can be permanent or temporary
- Permanent body adornment is done by piercing, scarification or tattoos, both are used to enhance beauty and also have social and ritual significance
- Some adorn using temporary designs using pain, ochre and henna to decorate the skin. The decoration can symbolize a variety of meaning e.g. social, economic or marital or even political status of the wearer.
- In some communities it is used to enhance the feminity or masculinity of an individual.
- The most common method used nowadays is by water emulsion pain
The type of body adornment used is influenced by the occasion /event or an individual’s stage in life.
Ornaments
Are accessories, articles or items used to add beauty or decorate the appearance of the participants in dance.
In some communities’ beadwork is an integral part of making ornament, beads used in making ornaments can vary in shape, size and colour. The ornaments include.
- Earring
- Armlets/armbands
- Anklets
- Necklaces
- Feathers
Creating /composing
Is a succession of sound with long, short or equal duration. It is the pattern of the music in a given time. It can exist without a rhythm.
The long and short the French rhythm names are used to create different rhythms and represented by different matching symbol. These musical symbol are the musical notes.
| French rythm name | Length of sound |
| Taa | 1 long sound |
| Ta-te | 2 long sounds |
| Taa-aa | 2 long sounds |
| Taa-aa-aa-aa | 4 long sounds |
| French rythm name | Note symbol | Note name | Length of sound | Number of beats |
| Taa | |
Crochet | 1 long sound | 1 beat |
| Ta-te | |
Quavers | 2 long sounds | ½ a beat for each quaver |
| Taa-aa | |
Minim | 2 long sounds | 2 beats |
| Taa-aa-aa-aa | |
Semibreve | 4 long sounds | 4 beats |
Words have their natural speeches style which dictates whether to be given either along or a short beat. Syllables in words can be stressed while others are not.
The stressed syllables occurs as strong beats while the unstressed syllables as week beats.
The beats are divided into groups of two beats, three beats or four beats
Melody
Is a sequence of pleasant sounds that makes up musical phrase
It is a tune that sound nice or pleasant to the ears
An understanding of high and low sounds is essential in identifying melodic variations within a song. Variation to simple melodies can be created by
- Repetition
- Changing doh
- Changing rhythms
- Changing note
- Changing words
Hand Signs
It is a good way of understanding and recognizing pitch. These are gestures used to indicate pitch in sol –fa.
When using hand gestures to guide the pitch of the ‘’doh’ is movable (it is not fixed)
Hand signs showing sol-fa syllables

Hand signs showing sol-fa syllables
Citizenship - Class 6 Social Studies Revision Notes
- Patriotism
- African Socialism
- Democracy And Human Rights
- Law Peace and Conflict Resolution
- The Government of Kenya
Patriotism
- This is love for ones country
- It is an element of a good citizen
- A person who loves his country is called a patriot
Ways of demonstrating patriotism
- Obeying the laws
- Respecting other people and their property
- Participating in elections
- Offering services when called upon
- Payment of taxes
- Keeping the secrets of the countries
- Not engaging in corruption
- Talking good of our country
- Being royal
- Attending national celebrations
- Giving support to other kenyans
African Socialism
- It is a national philosophy
- It was adopted in the year 1965
- Was introduced by Jomo Kenyatta and Tom Mboya
- It was established through the introduction of sessional paper no.10 of 1965
- It emphasizes the spirit of togetherness
- It aims at achieving political and economic development
- It encourages equal treatment
- People are encouraged to live in harmony
Importances of African Socialism
- It promotes political democracy
- It emphasizes equality of all
- It urges people to respect others rights
- Encourages the development of mutual responsibilities
- It units all kenyans
- It encourages equal distribution of wealth
- vii. It encourages development in kenya
Democracy And Human Rights
Democracy
- It means majority rule
- In democracy majority of the people’s will is respected
Main principles of democracy
- Principles of democracy refers to rules that are generally acceptable in governance
- They include;
- Promotion of justice to all
- Promotion of equality before the law
- Promotion of freedom for all people
- Provision of equal opportunities for all citizens
- Recongnizing that power belongs to citizens
- Respect of people’s rights
- In democracy elections are valued
Human Rights
- These are freedoms and privileges entitled to all Kenyans
- They are in chapter four of the constitution
- The section in the constitution with the human rights is called the bill of rights
Rights
- Right to life
- Right to education
- Right to information
- Right to vote
- Right to own property
- Right to equality
- Right to shelter
- Right to food
- Right to marry
Freedoms
- Ability to make choices or do things without being stopped by others
- They include;
- Freedom of worship
- Freedom of movement
- Freedom of assembly
- Freedom of association
- Freedom of expression
- Freedom from discrimination
- Freedom of speech
Rights of People With Special Needs
- Right to access special education
- Right to equal employment
- Right to protected from discrimination
- Right to access special equipments
- Right to be represented in parliament
- Right to equality before the law
- Right to fair trial
Responsibility of Persons With Special Needs
- They should be law abiding
- Respect their leaders
- They should not misuse their privaleges
- They should not misuse their rights
- They should take responsibilities to build the nation
- Participating in elections
- Take part in community projects
- Being elected in leadership positions.
Law Peace and Conflict Resolution
Laws
- Rules guiding people to ensure peace and harmony
Peace
- A state of calmness when there is no war
Conflict resolution
- This is the process or act of solving or settling a disagreement.
Factors that Promote Peace
- Tolerance
- Equal opportunities for all
- Equal distribution of resources
- Dialogue i.e discussing issues to bring understanding
- Games and sports
- Obeying the laws
- Respecting others
- Accountability of all people fairly
- Listenning to the opinion of others
Factors that Undermine Peace
- These are things that result to a conflict
- Religious differences
- Political differences
- Civil wars
Border disputes - Unequal distribution of resources
- Robberies and cattle rustling.
- Uneployment
- Corruption
- Unequal application of the rule of law
- Intolerance
- Violation of people’s rights
- Tribalism and nepotism
Importance of Peace
- Leads to development
- Children are able to learn and go to school freely
- Leads to effective governance
- Tourism is developed
- In a peaceful state people enjoy their rights and freedoms
- Promotes good relations between people and country
- Promotes businesses and investments
- People can move freely to places within
The Government of Kenya
Arms of The Government
- Legislature
- Executive
- Judiciary
Elections
- Held after every five years
- Supervised by the IEBC – independent electoral and boundaries commission
Functions of IEBC
- Register voters
- Keeping and revising voters registers
- Registering and clearing candidates for elections
- Conducting of voters education
- Establishing polling stations
- Supervising of elections
- Counting of votes and announcing results
- Review the contituencies boundaries
- Supervising and conducting a referendum
- Recommends the creation of new constituencies
- Appoints and trains officials to supervise elections
- Determines the number each political party will niominate in the parliament
- Sets the campaign period
- Announces the election dates
- Settles disputes related to nomination
The Civil Electoral Process in Kenya
- Carried out in a ward
- The head of a ward is the county represetative or the member of the county assembly
- County representatives are elected by the citizens
Qualifications of a County Representative
- Must be a kenyan citizen
- Must be 18years and above
- Must be able to read and write in both english and kiswahili
- Must be a registered voter
- Must be a member of a party or an independent candidate
- Must be of sound mind
- Must be staying in the ward
- Must be supported by atleast seven members of a ward
- Must have an ID card
- Must present his nomination papers to the returning officer
- Must pay a nomination fee of 1000 to the IEBC
The Electoral Process
- Dissolution of the county assembly
- The speaker declares all the seats vacant
- IEBC announces the election date
- Political parties nominate their civil candidates
- Candidates present nomination papers to the IEBC
- IEBC announces the campaign period
- IEBC organizes voting equipments and materials
- IEBC appoints and trains election officials
- Election materials are taken to polling stations
- Voting is done from 6.00am to 5.00 pm on the day of election
- Voting is done by the use of secret ballots
- Counting of votes is done and witnessed by the observers and party representatives
- Presiding officers announces results at the polling stations
- All polling stations in the ward submit their counted votes to the returning officer and the winner is officially announced.
How a County Representative May Lose His Civil Seat
- In case of death
- Resignation from the seat
- If declared bankrupt by a court of law
- If civil election is nullified
- If he is jailed for more than six months
- Incase of a nominated county representative the IEBC may nullify the nomination
- Incase one is declared insane
- In case one looses his kenyan citizenship
- Resignation or defecting from his/her party
- If he misses 8 consecutive sittings in the county assembly.