Change of state
Effects of heating matter.
- Matter - everything around us. All materials and substances that exist and occupy space.
- States of matter - different forms of substances, that is solids, liquids and gases.
- Change of state - to turn from one form to another, for example from solid to liquid. It occurs when matter absorbs or loses energy.
- When solids are heated, they change their states of matter. Some solids such as candle wax and cookin fat, melt into liquid, while ice cubes melt into water (liquid)
- The process in which a solid changes to a liquid is called melting.
- There are some solids that change to gases when heated, for example mothballs. The process in which a solid changes directly to a gas is called sublimation.
Heating Liquids.
- Some liquids change their state of matter through heating.
- Water (liquid) changes to water vapour (gas) when heated.
- The process in which a liquid boils and changes to a gas is called evaporation.
Effects of cooling matter.
Cooling water vapour
- When vapour is cooled it changes to liquids. This means that it has changed its state from gaseous state to liquid state.
- The process in which a gas changes to a liquid is called condensation. Cooling Liquids
- When liquids such as water, melted fat and melted candle wax are cooled, they harden and become solids.
- They change from liquid state to solid state.
- The process in which a liquid changes to a solid is called freezing.
- When gases such as mothball vapour are cooled, they become solids without forming liquids first. A mothball is made up of a substance known as naphthalene whose vapour changes from gaseous state to solid state on cooling.
- The process in which a gas changes directly to a solid without going through the liquid state is known as deposition.
Application of change of state of matter.
- Heating is used to dry grains, fish and other foods to preserve them. It also dries clothes and salt through evaporation.
- Heating of water bodies causes evaporation and cooling of air forms rain through condensation.
- Cooling preserves food and also makes ice through freezing. Solid metal melts into liquid on heating.
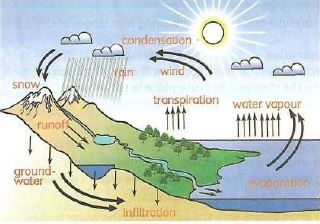
Water cycle
- A cycle is something that happens over and over again. It has no beginning and no end. The following are the water cycle stages:
Stage 1: Evaporation and Transpiration.
- The water cycle begins with the sun heating the water bodies. As the water heats up, it evaporates.
- In addition, green plants also release water vapour into the air in a process called transpiration. The vapour rises up into the sky.
Stage 2: condensation
- High up in the sky, the temperatures are cool. Water vapour in the clouds cool down and becomes liquid water. This liquid water is stored in clouds. The process of water vapour turning back into liquid is called condensation.
Precipitation
- The water falls from the sky in the form of rain, snow or hail through precipitation.
Runoff and infiltration
- As the water fall on the ground, the water forms streams and rivers and collects in lakes and oceans. This is known as run-off. Besides runoff, water is also absorbed into the soil.
- This is called infiltration. The water get stored as groundwater. The cycle then continues.

Acids and Bases
Identifying acids and bases
- Most substances are both acids and bases in nature.
- However, we cannot taste each and every substance to tell whether it is an acid or a base.
- In order to taste whether it’s an acid or base we use a litmus paper to find out whether a substance is acidic or basic in nature.
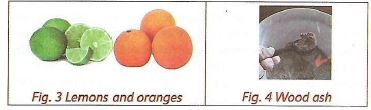
- The litmus paper is known as an indicator. Indicators change their colour when they are dipped in a solution containing an acidic or a basic substance. Lemon juice turns the blue litmus paper red. This means that lemon juice is an acidic
- Wood ash solution turns red litmus paper blue. This means that the wood as solution is a base.
- Common substances used as acids and bases
- Blue litmus paper turns red when dipped into:
- Lemon juice
- Grape juice
- Orange juice
- Sour milk
- Therefore, soap, antacid tablets, baking soda and wood ash are bases.
Physical properties of acids and bases
Acids
- They have sour taste
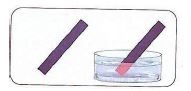
- They turn blue litmus paper red.
(testing acid using blue litmus paper)
Bases
- Have bitter taste
- They are slippery when touched
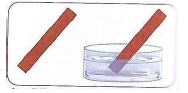
- Turn red litmus paper blue
(testing base using
Uses of acids and bases
Acids
- Acids in fruits such as lemon and orange is used to enhance taste in drinks and to flavor
- Lemon acid is used in some cultures to make milk sour
- Vinegar contains acid that is used for cooking purposes and it is also used to give salads a delicious taste.
- Vehicles have batteries that have an acid which is used to produce electricity.
Bases
- There are various items used on a daily basis that contain bases. They include:
- Baking powder is used to bake bread, burns and doughnuts
- Antacid tablets are used to relieve heartburn.
- Soap is used for bathing. We use detergents to wash our clothes
- We clean our teeth using toothpaste.
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 30/-
Get on WhatsApp for 30/-
Download Matter - Grade 5 Science and Technology Revision Notes.
Tap Here to Download for 30/-
Get on WhatsApp for 30/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students