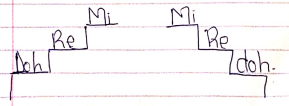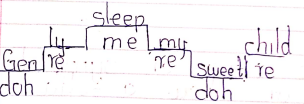Stella
Creation - CRE CBC Grade 7 Notes
- Accounts of Creation
- Christian responsibility over animals, fish and birds
- Christian responsibility over plants
- African teachings on responsibility over plants and animals
Accounts of Creation
The Biblical Accounts Of Creation
- First account
- Second account
The first biblical account of creation
Genesis 1:131, 2:1-4
- It gives record on what was created within the first 6 days.
- Humans’ beings were created last
Day God's Creation First Day and light and darkness Second Sky/dome/firmament Third Earth(land, plants and water bodies Fourth Heavenly bodies( sun, moon and stars) Fifth Sea creatures and birds Sixth Land creatures and man Seventh God rested and called the day Sabbath - From the first account of creation, we learn God is all powerful because He created the universe with one command.
- He is a God or order. He created the universe and everything in it in an orderly manner.
- God is the provider. He provides for human beings to meet their needs.
- Leisure time was instituted.
The second Biblical account of creation
Genesis 2;4-25
- In the second account of creation, there was no one to cultivate the land when God created the universe.
- God took soil from the ground and formed man. God breathed life into him
- Human beings were created first.
- Man was created out of dust
- God breathed life into mans nostrils
- Man was put into the Garden of Eden.
- The tree of knowledge and life giving stood in the middle of the garden.
- Men was commanded to use everything in the garden except tree of knowledge of good and evil
- The forbidden fruit from the tree was not supposed to be eaten.
- Eating from the tree would result to death.
- God gave man the responsibility to take care of the environment
- God created all birds and all animals
- Man was given the responsibility of naming all the creatures
- He named all the birds and animals, but none was suitable helper for him
- Adam became lonely.
- A woman was created out of Adam’s rib for companionship and a helper.
Attributes/nature of God from the Genesis stories of creation
- God is omnipotent/ all powerful
- God is orderly and perfect
- God is omnipresent/ everywhere
- God is transcendent
- God is the sustainer/ provider
- God is the sole creator
- He is a moral God
- He is a loving God
- He is a spirit
- He is everlasting/ self existence
- God is source of goodness
- God is Holy
- God is a worker
- There is only one God.
Similarities and Differences between The Two Biblical Accounts of Creation
Similarities in the two biblical accounts of creation
- In both accounts, God is the sole creator
- In both God created male and female
- In both, human beings are special
- In both God provides for human beings
- In both, human beings are given domination over the rest of the creation
- The uniqueness of human beings is brought forth in the second accounts
- Man shares in the life of God since he is made in the likeness of God
- Creation involves both the living and non-living things.
Differences in the two biblical accounts of creation
| First Account | Second Account |
| 1.Days on the order of creation are given | There is no mention of the days on order of creation |
| 2.Marriage is made for procreation | Marriage is made for companionship |
| 3.Man was created last | Man was created first |
NB
- There is a chronological order of events in the first account of creation as opposed to the second
- In the first account, male and female are created at the same time whereas in the second account man is created first then woman is out of his ribs
- In the first account, creation is out of the command “let there be”, yet, in the second, man is made out of dust
- In the first account, man names what he creates as opposed to the second where man is given the opportunity to name the animals
- A Sabbath day allocated for rest appears on the first while in the second account it wasn’t mentioned
- The Garden of Eden mentioned in the second account wasn’t in the first
- In the second creation account are four rivers (Tigris, Euphrates, Gihon and Pishon), which were not mentioned in the first
- Man was given a responsibility to till the land in the second but not in the first
- In the second account, the forbidden tree appears but this misses in the first account
- In the first account, God created human beings for procreation while in the second account they were created for companionship
- The second account of creation is human centred while the first does not shore this. It is man centred
- In the first account God created in union with the spirit (Holy Trinity) while in the second account God is alone
- In the first account human beings were created last while in the second they came first
- The first account takes six days to be complete unlike the second where days were not mentioned
- In the first account, God appreciates everything he creates. We are not told this in the second.
Importance of learning about creation
- Helps us to know and understand God’s creation work.
- Helps to appreciate God’s great work
- Helps us to know how the first account differs from the second on
Similarities and differences between the biblical account and African creation stories
Africans view creation
- Africans believe that creation originated from God the creator.
- Each community has a myth that explains its origin
- Africans see God as mysterious in his deeds, for they fail to explain how he created the earth.
- Africans see human beings as special and that God creates everything for them.
- God provided the first human beings with all the necessities of life.
- The first people lived happily with God and lacked nothing.
- Marriage was mainly for procreation.
Similarities - biblical account and African creation stories
- In both, God is the sole creator.
- Man is the climax of creation.
- God is supreme.
- In both, man was given a wife for company.
- God is portrayed as a potter.
- God is the provider
- Creation of human took place at the end of the creation of things
Differences Between the biblical account and African creation stories
- In biblical view, the order of creation is given, while the order of creation in the traditional view is not mentioned
- In biblical view , everything was created to benefit human beings, some communities believe that god gave specific things to specific communities
Christian responsibility over animals, fish and birds
Biblical teaching on responsibility given to human beings over animals birds and fish
- Christians have stewardship over Gods creation and they should care for everything in it
- Our responsibility is to take care of these creations and use them for our benefits but in a responsibly way
Pupil’s activity
Page 19-20
Ways in which Christians apply biblical teachings to protect animals , fish and birds
- According to Genesis 2:15-20 and James 3;7 human beings are give authority to name and tame animals , birds and fish.
- The responsibility to name the animals and birds means man was given authority to control all the creatures
- Taming animals is a show of authority over them.
Pupil’s activity
Page 20-21
Ways in which Christians promote and protect animals, fish and birds
- There are different strategies for taking care of God’s creatures like
- Constructing good houses for domestic animals
- Fencing our farms well to keep away wild animals
- Animals need food, shelter and security to be healthy.
Pupil’s activity
Page 21-22
Reducing conflicts between human beings and wild animals
The Kenya constitution protects animals from violence, overworking them when they are unwell, starvation, denial of water, abandonment, poisoning, careless surgery procedures, hunting and killing them.
We should learn to co exist with wild animals to reduce conflicts with them.
Pupil’s activity
Page 22-23
Importance of protecting animals, fish and birds
- Animals, fish and birds are important to human beings
- They provide food, clothing and income.
- Some animals provide manure for farming.
- Animals are companions and help us to work
- Their products support dairy industries, wool industries, leather and fishing industries.
- These sectors employ many people
- Birds help in the pollination of plants. As a result human beings, animals and birds also get food.
Pupil’s activity
Page 22-25
Christian responsibility over plants
Different plants found in the environment
Pupil’s activity
Page 27-28
Responsibilities given to human beings over plants
Genesis 1:29, Genesis 2:15, Psalms 104:14
They were to be in charge of the Garden of Eden
To eat from the fruits of the garden
To take care of God’s creation.
- God has provide us with plants. Human being have been given the responsibility to take care of the plants to benefit themselves and animals.
- We care for plants by applying manure, weeding, watering and spraying pesticides.
- We also take care protecting them from animals that feed them
Pupil’s activity
Page 28
How Christians apply biblical teachings on the care for plants and conserve the environment
Human beings have a responsibility to conserve the environment. We can conserver the environment by
- Through afforestation and reafforestation
- Evading/eradicating environmental pollution.
- Use of proper farming methods e.g. contours farming.
- Conserving water towers.
- Through provision of education, geared towards teaching people how to cope with the environment.
- Carrying out irrigation
Ways in which prudent use of plants contributes to economic growth
- Prudent use of plants contributes to economic growth.
- Prudent is the careful use of what you have to benefit you now and in the future.
- Prudent use of plants means taking care of plants, using what they produce carefully so that they can benefit us now and in the future
- Economic growth is an increase of plants in the production of goods and services from one period of time to another.
- It is good to take care of plants and harvest them properly. These practices will ensures that there is food for consumption. The surplus can be sold to avoid wastage and earn revenue.
- Storing farm produce well after harvest is important.
- One can use the harvest for a period and save the farmer from buying the same foodstuff in the future.
- The money which would have been used to purchase similar produce is used for other purpose.
- Well stores seeds can be planted in the future, saving one from buying the same farm input.
- Reforestation and replanting crops ensure that one has enough to use and at the same time, ensure a regular supply of the produce to the farmer. This contributes to steady source of income.
African teachings on responsibility over plants and animals
There are different types of plants and animals that Africans keep.
Some crops initially grown by specific African communities in specific geographical locations
The Africans took care of plants and animals as a responsibility from God
Types of indigenous plants
- Cassava
- Sweet potatoes
- Millet
- Sorghum
- Yams
- Pumpkins
- Arrowroots
Types of indigenous animals
- Cattle
- Chicken
- Bees
- Goats
- Camels
- Donkey
The importance of taking care of plants and animals in African context
- They were sources of food.
2. The plants provided medicinal herbs
3. Other plants provided wood for construction of houses and making utensils
4. Wood was used as a source of energy
5. Plants and animals provided materials for making musical instruments like kayamba
6. Some plants and animals were also used as totems.
7. Animals provided skins and hides for making clothes
8. Some animals like dogs provide security to man
9. Other were used as pack animals and others were used for transport. Example donkey
10. Animal horns were used for horn blowing which was means of communication.
Ways in which Africans promoted care and conservation of all types of plants
- The Africans protected plants by weeding, pruning, mulching, shading, trapping and scaring away animals that fed on the plants.
- They also preserved seeds of the plants to last longer during dry periods and to protect them from small such as rats and weevils.
This conservation ensured that Africans had seeds to plants during the rainy seasons. - Preserved seeds and plants served as source of food during drought.
- Africans used fire to make plants sprout out more serving as food for the animals.
How Africans ensured protection of all types of animals and birds
African ensured protection of all animals, fish and birds in different ways
Pupil’s activity
Page 42
How Africans ensured protection of fish
- Avoid overfishing
- Use of proper nets
Pupil’s activity
Page 43
How Africans promoted health of animals
- Africans cared for and protected domestic animals against wild animals by fencing their compounds and sleeping in the same place with the animals.
- They scared away wild animals that predated on their domestic animals by using different methods. Eg use of scarecrows, fire, noise
- In the events of disease. Africans treated their animals using selected plants such as Aloe vera while making them healthier by providing lick stones with mineral salts. They knew how to take care of animals during birth which ensured the growth in population.
- Animal products such as meat were preserved to last long for use during drought. Preservation was a way of ensuring food was not wasted
- Young animals were left to suckle up to a time when they could eat grass and other types of vegetation.
Introduction To CRE - CRE CBC Grade 7 Notes
Importance of studying CRE
The meaning of studying CRE
- CRE involves the study of religious beliefs and practices of Christians.
- It is the study of how human beings depend on God and how God intervenes to save human beings.
- CRE is a subject studied in Kenyan schools to develop the mind, behaviour and character of the learners.
- It is also a subject that shows God’s relationship with man.
Importance of studying CRE
Studying CRE is important because
- It makes one understand that God the Father, the Son and the Holy Spirit operate as one.
- It helps one dispute knowledge and attitude s to make the right decisions in life.
- Enables one think critically and make moral decisions on challenges affecting one’s life and the society
- One becomes exposed to cultural heritage, enhancing national unity through respect for each community.
- One develops as a whole person, body, soul and spirit
- One becomes courageous in the study of creation one is empowered to utilise the ability to control God’s creation
- It helps you relate with each other well through care and hospitality
- The moral values you acquire helps you to take care of the environment
- One acquires respect for oneself and hence living a productive life
- One acquires the principle of sharing and social justice, enabling them to coexist with others
- One acquires the skills that enable him or her promote economic development
- It enables one to acquire ICT skills as they search for more knowledge
- One develops communication skills through discussion and debate with other learners.
NB
- It provides answers to life mysteries e.g. the question of life after death, the origin of mankind, etc.
- It enables students to develop vivid awareness of God and how God reveals himself.
- It is a career subject, whose learners major in Law and theological training.
- It instils respect, protection and conservation of God’s creation.
- It highly promotes human dignity.
- It helps students to appreciate their culture as well.
- It equips the youth with life skills such as critical thinking, which enables them to face challenges wisely.
- With regard to national goals of education, it promotes national development by instilling a positive attitude towards work. It equips learners with values that promote economic development.
- It helps learners to understand themselves better.
- It enables students to see the power of God controlling their own lives. It enables students to respond adequately to God’s teachings and to relate well to others.
- It is a service of natural guidance.
- It promotes cultural integration.
- It promotes social equality and justice.
How Cre Helps Us To Relate Well With Others
- It has helped developed skills as ability to listen
- It helps acquire values such as respect for self and others
- It helps someone to make moral decisions. This helps people to associate with the right people
- Obedience to God’s command of loving our neighbour teaches us to care about others
Moral And Religious Values Acquired From Studying Of Cre
- Humility
- Respect
- Hard work
- Discipline
- Honesty
- Integrity
- Responsibility
- Unity
- Love
- Hospitality
Elements of a Music - Grade 4 Music Revision Notes
Elements of Music
- Music has a purpose.
- It is composed of elements that makes it recognizable
- These are components or composition of music. They include:
- Message
- Type of Song
- Rythm
- Melody
- Pitch
- Tempo
- Dynamics
- Type of songs
- Its a song gospel, patriotic, folk topical
- Message
- Depends with what the song is saying. Education, Corona, Sickness, Aids
- Rythm
- pattern of the music
- Pitch
- Tones might be high or low.
When singing, we use solfa notes
D R M F S L T D
Composing/ Creating Music - Grade 4 Music Revision Notes
Composing/ Creating Music
- Before creating music we need to know how to create rythm and beat
- You can use claps, sounds and taps
- These rythms are cretaed using our mouths, hands and our legs
Composing Music
Sol-fas ladder
- Music is combined of tunes. The tunes can be ascending or descending
- The rising and falling of tunes are organized in sol-fas Notation
- They are from low to high
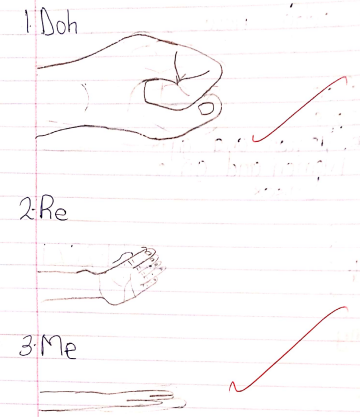
d, r, m, f, s, l, t, d
doh, rey, me, fah, soh, lah, te, doh
Ascending
- When the pitch goes from low to high
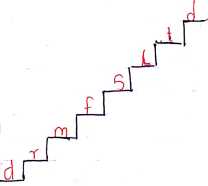
Descending
- When the pitch goes from high to low
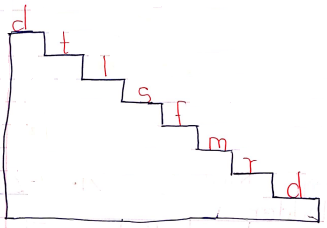
Notes
- From the solfa notes we get the category of sounds.
- Bass - Men
- Tenor - Boys
- Alto - Women and girls
- Soprano - Women and girls
- Barrytone - Unisex
Solfa Signs
- They are signs or symbols used to denote or show a solfa note.
Doh Re Me
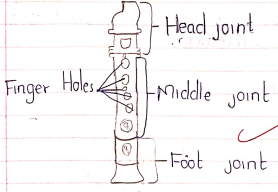
Descant Recorder
- It is a wind instrument played by blowing
- Its a type of flute
Care and Maintenance
- Keep away from heat or sun.
- Avoid sharing
- Clean after use
- If you want to share, clean it first.
Singing - Grade 4 Music Revision Notes
Singing With Expressions
- Expressions is someone's feelings. Someone can be sad, serious, happy, laughing, Angry, wondering, wow
Dynamics
- When we sing loudly or softly. We are always singing with dynamics. Song can be sang loudly or smoothly
Articulation
- Singing smoothly or in a detached manner which is called articulation
- Is the speed of the song or beat. it can be low or fast.
The Main Voices in a Choir
- Bass - Men
- Tenor - Boys
- Alto - Women
- Soprano - Girls
- Barrytone - All
English National Anthem
Stanza 1
O God of all creation
Bless this our land and nation
Justice be our shield and defender
May we dwell in unity
Peace and liberty
Plenty be found within our borders.
Stanza 2
Let one and all arise
With hearts both strong and true
Service be our earnest endeavour
And our homeland of Kenya
Heritage and splendour
Firm may we stand to defend.
Stanza 3
Let all with one accord
In common bond united
Build this our nation together
And the glory of Kenya
The fruit of our labour
Fill every heart with thanksgiving.
Music Costumes
Costumes are dresses and clothes we wear in a certain function. During music, costumes are put on to match tthe song, season, dance or message
Examples of Costumes
- Sisal skirts
- Lesos or Kitenges
- Hide and skin clothes
- Animal's skin(hat)
- Jingles
- Colours
- Beads and necklaces
- Leafs clothes
Resources and Economic Activities - Grade 4 Social Studies Revision Notes
Resources
- Resources are things that we use to create wealth.
- Resources can be man-made things or natural.
Main resources in our county
Examples
- Land
- Minerals
- Animals
- Forests
- Water
- Soil
- Manpower
PUPIL’S ACTIVITY
PAGE 69-71
Ways in which resources are conserved in the county
- We should make good use of our resources.
- The protection of resources is known as conservation.
- This can be done through
- Building gabions
- Conserving wild animals
- Fencing
- Planting trees
- Protecting animals
- Conserving water
- Avoid overgrazing
- Avoid poaching
Economic Activities
Economic activities in the county
- Economic activities helps to earn a living
- We use resources to carry economic activities.
- Economic activities are things that people do in order to create wealth
- Refers to the use of resources available in order to create wealth or earn a living
Main economic activities in the county
Examples
- Mining
- Fishing
- Saw milling
- Agriculture
- Transport
- Communication
- Pottery
- Basketry
- Trading
Importance of economic activities
- People in the county earn money from various economic activities.
- This improves their standard of living
- Economic activities like farming have led to development of other industries.
- These industries have led to development of roads, hospitals and schools.
PUPIL’S ACTIVITY
PAGE 77-80
Trade
Trade in the county
- Trade is the buying and selling of goods and services.
- It Is also the exchange of goods and services for money
- People sell goods that they have and buy what they do not have.
Methods of trade in the county
- Barter trade – it is a method of trade where communities exchanged goods for other goods.
For example: exchanging a bag of potatoes for two goats. - Currency trade – is the use of money to pay for goods and services For example: people use money to buy food or clothes
PUPIL’S ACTIVITY
PAGE 81-83
Benefits of trade in the county
- Creation of employment
- Improvement of transport and transport
- Earns foreign exchange
- Promotes cooperation and understanding
- Promotes growth of town (urbanization)
- Promotes agricultural sector
- Source of revenue for the government
- Promotes interaction and exchange of ideas
PUPIL’S ACTIVITY
PAGE 83-85
Lawful trading activities in the county
- Lawful trading activities are business that are accepted in the county.
- These activities involve selling goods and services that have been approved by the county government.
- One needs a license from the county government before engaging in trading activities
- This makes the trading activity lawful.
- Engaging in a trading activity without a license is unlawful.
- If you do not pay tax, your trading activities will be considered unlawful.
- Traders pay taxes to county government
- We should encourage all people to engage in lawful trading activities.
PUPIL’S ACTIVITY
PAGE85-87
Industries
Industries In Our County
- An industry is a place where raw materials are made into useful products.
- Industries are the processes and activities to produce final goods from raw materials
- A factory is a place where raw materials are turned into new and useful products
Types of industries
- Processing
- Also called primary industries
- The produce goods used in other industries
- Mostly deals with agricultural products
- Examples of processing industries
- Coffee and tea processing industries
- Manufacturing
- Manufacturing industries
- Also called secondary industries
- Relies on some goods from primary industries
- Some uses raw materials directly
- Examples of manufacturing industries
- Cement making
- Oil refineries
- Glass making industries
- Paper making industries
- Medicine making industries
- Assembly
- To assemble is to put together
- It involves putting together items to get a complete item
- Examples of assembling industries
- Motor vehicle assembly
- Bicycle assembly
- Radio assembly
- Television assembly
- Service
- They provide services
- Examples of service industries
- Banking
- Hotels
- Printing and publishing
- Transport and communication
- Insurance
- Tourism
- Jua kali
- Uses the locally available materials
- Operates in open air
- Requires little capital to start
PRODUCTS FROM INDUSTIRES IN THE COUNTY
| Industry | Raw materials | Products |
| 1) Creameries | Milk | Cheese, butter, milk, powder |
| 2) Cement making | Limestone | Cement for building houses |
| 3) Car Assembly | ||
| 4) Jua Kali | Scrap metals | Jikos, |
| 5) Bakeries | Wheat | Cakes, Flour |
| 6) Weaving | Sisal | Ropes |
| 7) Pottery | Clay | Pots and ceramic made materials |
| 8) Shoe making | Leather, hides | Shoes |
| 9) Wood Carving | Tree, woods | Sculpture of animals like a lion |
| 10) Brick Making | Stiones, Bricks | Bricks for building |
PUPIL’S ACTIVITY
PAGE 90-92
Benefits of industries in the county
- Creates employment
- Promotes trade
- Source of revenue to the government through taxes
- Leads to development of infrastructure
- Leads to urbanization
- It is a form of income to Farmers when they sell their produce to the industries and get money
- Promotes agriculture
- Improves the peoples living standards
- Industries provide goods that we need in our lives
Culture And Social Organizations - Grade 4 Social Studies Revision Notes
Culture
- Culture is people’s way of life.
- Each community has its own way of doing things.
- Communities have different types of foods, dressing, songs, dances, ceremonies and festivals.
- Culture is passed from one generation to another.
Aspects Of Traditional Culture In The County
| Aspect of culture | What is common in my community |
| 1. Food | Kalenjins Drink such as mursik(sour milk) Animal's blood mixed with fermented milk Cereals such as millet (bek/kilipsiongik) and sorghum (mosongik) Meat (pendo) Mushroom (popek) Vegetables such as isoik Maasai Drink milk and blood and soup Meat from goats, sheep and cattle Agikuyu Cereals such as lablab beans (njahi), peas (njugu) and beans (mboco) Crops like sweet potatoes (ngwaci), cassava (mwanga), yams (ikwa), and arrowroots (nduma) Fruits such as terere (aramantha) stinging nettle kahurura and manage Irio ( mashed beans, maize, potatoes and green vegetables) |
| 2. Dressing |
|
| 3. Housing | |
| 4. Ceremonies |
|
| 5. Songs and dances |
|
| 6. Games and sports | |
| 7. Festivals |
Examples: music festivals, harvesting festivals, drama festivals |
| 8. Traditional medicine practises |
|
Importance of aspects of traditional culture
- Culture promotes unity among the members of the society through sports and games, festivals and ceremonies.
- Through culture, young people are able to learn good morals and values.
- Culture makes us unique through language, types of food we eat and the dressing styles.
- Tourists pay some money to see our culture. This money helps the government to develop our country.
- Promote love and kindness
- Promote responsible people in the society
- Promote honesty
- They develop good habits
The school
- A school is a place where pupils go to be taught or to learn
- Is an educational institution designed to provide learning to learners with the support of teachers
- A school mainly equips learners with knowledge and skills
- A school trains individuals to be responsible or useful members of the society
- We have government and private schools
History of the school
- Every school has a history.
- The history tells us when and how the school started.
- It also tells us about the achievement of the school.
- This history gives the school an opportunity to focus on future plans.
PUPIL’S ACTIVITY
PAGE 59-61
School motto and core values
- A school motto is a short statement of what a school believes in.
- School core values are important believes that guide the members of the school.
PUPIL’S ACTIVITY
PAGE 62-64
Practising School Motto And Core Values In School
PUPIL’S ACTIVITY
PAGE 62-65
School routine
- A daily school routine is a list of activities that the school does every day.
- Is the programme of activities that have been planned to take place every day in the school
- Day schools and boarding schools have different routines
- A school routine is prepared by the school administration
- School routine should be as per the guidelines of the ministry of education.
- A school routine is clearly indicated on the school timetable
Importance of a school routine
- It helps the school to run smoothly
- It ensures order and harmony in the school
- Helps in bringing up all round pupils
- Helps to train pupils to be responsible
- Helps in proper time management
- Helps to strengthen discipline among pupils
- Ensures that all activities in the school are allocated times
People and Population - Grade 4 Social Studies Revision Notes
Interdependence Of People
- Interdependence means depending on each other.
- In our county people depend on each other
- For example we go to the market to buy what we do not have. Other people go to the market to sell what they have in excess.
- We all need each other.
- Life becomes easier and enjoyable when we depend on each other.
PUPIL’S ACTIVITY
PAGE 33-34
Ways in which people depend on each other
- People also depend on each other through various means. They include:
- Food
- Treatment
- Education
- Market
PUPIL’S ACTIVITY
PAGE 35-37
Benefits of Interdependence
- It promotes love and unity among people
- It brings development e.g. the development of roads which connect different communities.
- It discourages tribalism, racism and corruption
- It leads to the exchange of culture, goods and services.
- Through interdependence people are able to
- Live in unity
- Get assistance or support
- Appreciate each other’s culture
- Do what they cannot do on their own
- Get what they do not have
- Get new ideas and knowledge
Population Distribution
- Population refers to the number of people living in a given/particular place
- Population distribution refers to how people are spread over in an area
PUPIL’S ACTIVITY
PAGE 41-43
Population Distribution In The County
- Population of our county is not evenly distributed
- Some areas are;
- Sparsely populated
- Medium/moderately populated
- Densely populated
- Areas with many houses are densely populated.
- Areas with few houses are sparsely populated.
- Areas with few houses far away from each other are unevenly distributed.
PUPIL’S ACTIVITY
PAGE 43-46
Common patterns of population distribution
- Linear pattern – this is where the houses are arranged in a line.
- Clustered pattern – this is where houses are close to each other.
- Scattered pattern – this is where the houses are spread out.
PUPIL’S ACTIVITY
PAGE 47-49
Patterns of population distribution in our county
PUPIL’S ACTIVITY
PAGE 49-51
Natural And Built Environments - Grade 4 Social Studies Revision Notes
Natural environment
- Natural environment refers to all living and non-living things that occur naturally
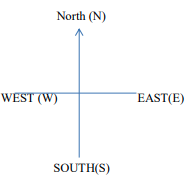
Compass Direction
- A compass is used to tell direction of one place from another
- The compass has four points namely:
- North
- South
- East
- West
- The points of a compass are called cardinal points.
- A compass is used to show direction on a map
- The arrow of the compass always points to the north
- East shows the direction from which the sun rises.
- West shows the direction to which the sun sets.
Using cardinal points to give direction
PUPILS ACTIVITY
PAGE 4-9
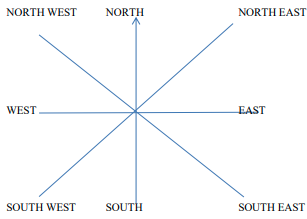
Eight compass points
- There are four other points of a compass that are found between four cardinal points.
PUPILS ACTIVITY
PAGE 8-11
Location and size of the county
- Our country is made up of several counties
- There are 47 counties in Kenya
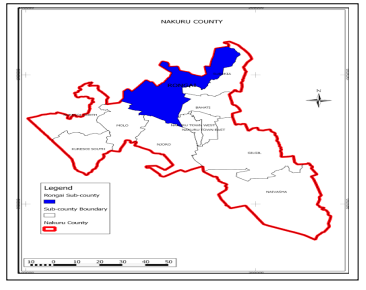
- Our school is located in Nakuru County
Sub counties that make up our county Nakuru are
- Naivasha
- Gilgil
- Nakuru central
- Rongai
- Kuresoi
- Molo
- Njoro
- Nakuru north
- Subukia
- Bahati
Location and size of the county in relation to the neighboring counties
- Our country is made up of several counties
- There are 47 counties in Kenya
- Our school is located in Nakuru County
Counties that neighbor our county Nakuru
- Baringo county to the north
- Laikipia county to the north east
- Nyandarua county to the east
- Kiambu county to the south east
- Kajiado county to the south
- Narok county to the south west
- Bomet county to the west
- Kericho county to the west
Physical Features In The County
- Physical features are natural things we see on the surface of the earth
- They show how the land looks like
- Examples of physical features
- Rivers
- Lakes
- Mountains
- Plains
- Valleys
- Swamps
- Plateaus
- Springs
- Hills
- Oceans
RIVERS
- A river is a natural flow of water in a valley
- Rivers flow throughout the year are called permanent rivers
- Rivers flowing only during wet season are called seasonal rivers
- An area where the river starts is called a source
- Small streams that join the main river are called Tributaries
- A point where two or more rivers meet is called a confluence
- Where the river drains forms its mouth
Examples of rivers in our county
- River Subukia
- River Amalo in Olenguruone
- River Molo
- River Chawai in Mau forest
- River Chinga in Subukia
- River Kabazi
- River Chania in Bahati
- Shrine stream
Some seasonal rivers
- River Nyarugu in Njoro
- River Bagaria
- River Lolderi
- River Kirimu
WATER FALLS
- It is the flow of a river over a very high place to the ground
Some examples of water falls in our county
- Bagaria water falls along R.Bagaria
- Songongo water falls along R.Chewai
- Glory and along the Subukia escarpment
LAKES
- It is a large depression on the surface of the earth that is filled with water
- Examples
- Lake Nakuru
- Lake Elementaita
- Lake Naivasha
- Lake Oloidien
HILLS
- It is an area that is higher than the surrounding land
- Hills are smaller than mountains
- Examples
- Hyrax hills
- Lions hills
- Man hills
- Eburu hills
- Kerugue hills
- Gilgil hills
- Jogoo hills
- Lesirwa hills
- Jumatatu hills
- Kasambara hills
- Kianjoya hills at miti mingi
- Elge wood hills
- Arashi hills
- Kerima Ndege hills in mbogoini
- Gitunga hills
- Mwiteithia hills in Mbogoini lower subukia
- Honeymoon hill in Nakuru National park
MOUNTAINS
- It is a large part of the earth surface that is much higher than its surrounding
- Examples
- MT. Menengai
- MT, Longonot
- MT. Suswa
The highest mountain in Nakuru County is MT. Longonot near Maai – Mahiu, Naivasha Sub County
PLAINS
- It is a large low land that is generally flat
- Elementaita plains
- Kigio plains
- Rongai- boror – ngata plains
VALLEYS
- It is a depression between two areas that are high or raised
- Valleys that rivers flow through them are called Valley Rivers
- Examples
- Great rift valley
- Nyatoru valley in Kiambogo
- Subukia valley
SWAMPS
- Are lowlands filled with water and covered by swamps Examples
- Kiptungar swampsnear Mau forest
- Sasumua swamp near Muchorwe moto
- Wila swamp in kuresoi
- Silbwet swamp in keringet in kuresoi
SPRINGS
- It forms where water flows out of the ground from an underground source
- Examples
- Lake Elementaita springs
- Lake Nakuru springs
- Labere springs
- Oljorai springs
- Kariandusi springs
- Chamuka springs
PLATEAUS
- It is a raised piece of land that is flat at the top
- Examples
- Metha plateau
- Kiambogo – Ndabibi area near Nyatoru valley
OCEANS
- Are very large areas of water where water from different rivers collect.
Examples
Indian Ocean
Importance of physical features
- Water for domestic and industrial use
- Home for wildlife
- Used for irrigation
- Tourist attraction
- Used for transport
- Clay collected at the river banks is used for modeling
- Rivers act as boundaries
- Plains are good grazing grounds
- Valleys are good for farming
Conserving physical features
- Physical features can be conserved by
- Plating more trees
- Not cutting down trees
- Prevent overuse and deforestation of forest.
- Avoid pollution of water bodies.
- Educate people on importance of physical features.
Seasons in the county
- There are 4 seasons in a year
- These are:
- Hot
- Cold
- Dry
- Rainy
PUPIL’S ACTIVITY
PAGE21-23
Activities in different seasons
- People carry out different activities each season.
- People wear different types of clothes during different seasons.
Season Activity Hot 1. Harvesting crops
2.Dry 1. Preparing land
2.Cold 1. Weeding crops
2.Rainy 1. Planting crops
2.
PUPIL’S ACTIVITY
PAGE 24-26
Built Environment
- Built environments refer to the human made environment.
- For example schools
- Some of the buildings we see today were built long time ago. They are part of built environment.
Historic built environment in the county
- These are structures/environments that remind us of our history or where we have come from
- Historic built environment refers to features made by people
- These features have a historic value
- They include
- Museums
- Monuments
- Historical buildings
- Cultural centers
- Historical sites
Historic built environments
| Name of the built environment | County | Type-museum, monuments, building, cultural centres | |
| 1. | Fort Jesus | Mombasa | |
| 2. | Bomas of Kenya | Nairobi | Cultural Centre |
| 3. | Hyrax museum | Nairobi | Museum |
| 4. | Lord Egerton Castle | Nakuru | |
| 5. | Jomo Kenyatta Monument | Nairobi | Monument |
| 6. | Nairobi Museum | Nairobi |
Importance of the historic built environment
- They create a sense of belonging
- They serve as resources learning centres
- Attracts tourist and earn as foreign exchange in our county
- They enable social interactions with friends, family and community when we visit them
- Many people are employed to work in historical buildings, museums, and take care of monuments
- They remind us and teach us about our culture
- They are sources of information for learning
- They are used as recreational areas for relaxation
Ways of caring for historic built environments.
- Repair the destroyed parts of historic built environments
- Handle items in the historic environments with care
- Develop conservation messages and place them at historic built environments
- Educate other people on the importance of historic built environments
- We can also repair broken parts, guard and dust them.
- We can clean, clear bushes, paint or fence the area.
- We should take care of our historic built environments.
Participating in caring for historic environments
PUPIL’S ACTIVITY
PAGE 31-32
Indigenous Kenyan Craft - Grade 4 Art and Craft Revision Notes
Basketry
Basketry: traditional twine technique
- Basketry is the making of baskets by weaving or braiding long slender pieces of material (as reed or sisals).
- Basketry is a traditional craft practised by many communities.
- It involves
- Weaving
- Twining
- Plaiting or sewing flexible fibres
Identifying basketry traditional items
- There are many items made using basketry technique
- They include
- Containers for storing grains and food
- Items for decorative purpose
- Household goods such as baskets, trays, furniture and baby cots.
- In some communities, basketry technique is used to make houses, barns, granaries, chicken coops, fish traps and winnowing trays.
Materials needed for basketry
- Materials can be natural or synthetic
- Natural materials include
- Thin flexible sticks
- Plant roots
- Vines
- Variety of grass such as elephant grass
- Banana fibres
- Cane
- Bamboo
- Stem
- Raffia
- Sisal
- Palm leaves
- Osier
- Reeds
- Rattan
- Wattle sticks
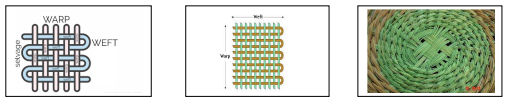
Weaving a circular mat using the twinning technique
- In twinning technique the wrap and two sets of wefts are used
- Warp are the threads that form the framework of a woven item
- The wefts are the threads which go over and under the wrap.
- The wefts are twinned around the warp.
How to weave a circular mat using the twining technique
- Collect the necessary materials need from your local environment e.g. banana fibres, knives, reeds, sisal fibre, palm leaves
- Prepare the fibres for weaving
- Set up the warp in order to start weaving.
Done by arranging several fibres into a star shape - Tie the fibres at the centre
Pupil’s activity
Page49-50
Weaving a circular mat
- Cut the warp to the required size.
- Set the warp in a tar shapes
- Pick the weft and start twinning around the warp
- Continue weaving until you achieve the size you required.
Finishing and neatening the edges of a woven circular mat
- To make the mat neat and prevent the weft and warp from coming off, you need to finish the edges neatly.
- This is done either by stitching or binding.
- First cut off the lose fibres and tuck in the warp then stitch or bind.
- Stitching is done by using a thread and needle to stitch along the edges.
- Binding is done by stitching a cloth around the edges of the circular mat.
- You can also tuck in the warp in place and use other fibres to warp the edges
Displaying circular woven items
Pupil’s activity
Page 50
Leatherwork
Leatherwork: thronging technique
- Leather is obtained from hides and skins of animals.
- Large animals like cattle and others with hair give hides.
- Smaller animals like young one of calves, goats give us skins.
- Leather is used to make traditional items like musical instruments (drum), bags, hats, furniture, jewellery, sheaths.
Sources of leather
- Skins e.g from goat
- Hides e.g from cow
Leather items
- Drums
- Shields
- Hats
- Bags
- Masks
Collecting traditional leather items
You can collect hides or skin from the local environment.
Thronging technique
- Before making an article from leather, a design should be laid out and the different pieces cut out carefully.
- The various pieces are then joined together either by gluing or sewing.
- Articles can also be stitched together using strips of leather called thongs.
- The technique of joining two or more pieces of leather using thongs for lacing when making an article is referred to as thonging
Making drums using thronging technique
Pupil’s activity
Page 53-57
Materials need to make a simple drum
- Leather material
- Cutting tools such as a pair of scissors, knives or blades
- Old containers such as buckets, tins or hollow wood
- Marking tools
- Mallets
- Hammer
- Rulers.
Identifying thongs on drums
- Every community has their own unique way of constructing the drum.
- Some drums are covered with a membrane on the top side and others on both top and bottom.
- The membrane on top or bottom of the drum can be attached by lacing using thongs.
- The internal shape of every drum is what gives it the quality of sound produced.
- Drum produce sound by beating.
How to cut thongs
- Thongs should be stretchable as possible
- The best way to cut thongs is either diagonally or in a circular way if the piece of lather available can allow.
- By cutting this way the thong will not be cut easily when stretched during lacing.
- Look for old leather item
- Cut out a big piece from the item
- Lay your piece of leather on a flat surface
- Measure the size of the thong needed and mark using a pen
- Using a pair of scissors, cut the strips as accurate as possible.
Process of making a drum
- Cut out leather pieces so that they are slightly wider than the container for making the resonator of the drum.
- Make similar number of holes on the cut out leather for the top and bottom pieces
- Cut out the thongs for joining the top and bottom pieces of leather.
- Place the cut out leather at the top and bottom
- Use the thongs to lace the pieces of leather firmly in place.
Pupil’s activity
Page 57
Pottery
- Pottery is the art of making containers or articles such as cups, plates, flower vases and pots out of clay.
- Pinch method is one of the technique of modelling pots and containers.
Modelling – Pinch technique
- The pinch method involves shaping containers of various sizes and shapes by pressing on the walls using thumb and forefingers.
- The process can be used to model simple containers such as cups and sugar dishes.
- Containers made using pinch technique are referred to as pinch pots.
- Another name for pinch pots is thumb pots
Identifying pinch pots
- Cups
- Pots
- Sugar dishes
- Plates
- Flower vases
Materials need to model a pinch pot
- Clay
- Sticks or incising tool
- A container with water
- Papers or leaves for placing the clay and modelled articles
How to model a container using the pinch technique
Clay preparation
- Collect clay from the local environment.
- Remove impurities such as stones, roots
Preparing clay
- After collecting the clay and removing impurities, mix the clay thoroughly by pressing it over and over again until the moisture is evenly distributed.
- This processing is known as kneading
- The process is important because it removes air bubbles from the clay, making it uniform and easier to work with.
Modelling a pinch pot
- Take a lump of clay and roll it into a ball then hold it on the palm of one hand.
- Make a hole in the ball by pushing the thumb of the other hand into the lump of clay
- Rotate the clay while pinching against the wall of the container using thumb and fingers to widen the hole and shape the pinch pot. Ensure the wall of the container is of even thickness.
- Place your thumbs inside the pinch pot then press it gently on a flat surface to give it a stable base. Shape the lid as well. This can be done using fingers or by pressing it gently on a flat surface.
- Use a stick, a scraper or your hand to smoothen the pitch pot. you may wet your hands with water as you smoothen the article. Do not pour water on the container as you smoothen as this may cause it to become soggy and crumble or crack.
- Leave the container to dry slowly under a shade. Cover the pinch pot si that it dries slowly.
Modelling pinch pots of varying sizes and shapes
- Pinch pots are used for different purposes.
- That is why they can be modelled in different sizes and shapes depending on their purpose.
- They can be small, wide or thin
Pinch of different sizes and shapes
Pupil’s activity
Page 61-62
Methods of decorating clay items
- Modelled clay are decorated to make them more attractive.
- Methods of decorating include
- Stamping
- Scratching
- Incising
- Stamping involves pressing an object on wet clay articles before they are completely dry.
- Scratching technique, shallow marks are made on the walls of wet clay using sharp tools such as nails, sharp stick or wire
- Incising technique is done by cutting out patterns on the walls of the wet clay article.
- A sharp object such as wire can be used to decorate the articles using incising technique.
Materials need to decorate a pinch pot
- Clay for modelling
- A textured item such as maize cob, aloe vera leaves or comb
- Incising tools such as sticks, wire, thorn or blade
- A container with water
- Hollow objects such as a hollow stick, straw, biro pen or biro lid
- Papers or leaves for placing the clay and modelled articles.
Making and decorating a pinch pot by stamping
Pupil’s activity
Page 63-64
Making and decorating a pinch pot by incising
Pupil’s activity
Page 63-64