Questions
- Light of frequency 5.5x 1014 Hz is made to strike a surface whose work function is 2.5ev. Show that photoelectric effect will not take place. H= 6.6 X 1034Js
- Photoelectrons emitted by illuminating a given metallic surface constitute a “photocurrent”. What is the effect of increasing the intensity of the illumination of the magnitude of the photocurrent?
- The diagram below shows a photocell in action
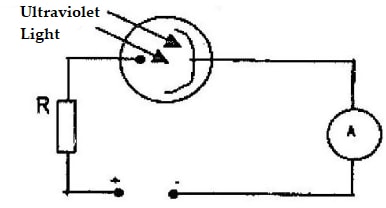
- The photocell is either evacuated or filled with an inert gas at low pressure. Give one reason for this
- What is the function of the resistor R in the circuit?
- State one reason for using a particular radiation such as ultraviolet for a given photocell.
- Explain how the set-up shown in the diagram may be used as an automatic switching device for a burglar alarm.
- A monochromatic beam of radiation is directed on a clean metal surface so as to produce photoelectrons. Give a reason why some of the ejected photoelectrons have more kinetic energy than others.
-
- Describe with the aid of a labelled diagram an experimental set-up for observing the photoelectric effect.
- The table shows the relationship between the wavelength of a radiation falling on a surface and the energy, k of the emitted electrons.
λ (m) × 10-7 1.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 K(J) × 10-19 10 13 20 40 - Plot a graph of energy k(Y-axis) against the frequency, f, of the incident light.
- Determine the work function of the surface used (h=6.663 x 10-34Js)
- Name a device used to convert light energy directly into electric energy.
- Electrons emitted from a metal when light of a certain frequency is shone on the metal are found to have a maximum energy of 8.0 x 10-19 J. If the work function of the metal is 3.2 x 10-19 J, determine the wavelength of the light used.
- The figure below shows ultra violet light striking a polished zinc plate placed on a negatively charged gold leaf electroscope.
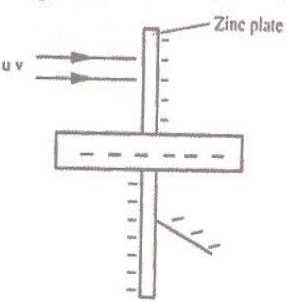
Explain the following observation- The leaf of the electroscope falls.
- When the same experiment was repeated with a positively charged electroscope, the leaf did not fall.
- The work function of a certain material is 3.2 ev. Determine the threshold frequency for the material. (1 electron volt (eV) = 1.6 x 10-19 and planks constant H= 6.62 x 10-34Js)
- State what is meant by the term accommodation as applied to the human eye. (1 mk)
- The graph in the figure below shows the variation of photoelectric current with applied voltage when a surface was illuminated with light of a certain frequency.
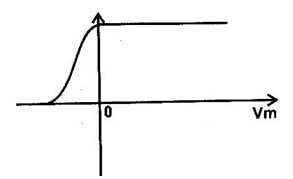
Use this information in the figure to answer questions a and b.- On the same axes, sketch the graph of when light of higher intensity but same frequency is used to illuminate the surface. (1 mk)
- Explain your answer in a above . (1 mk)
- Calculate the energy of a photon of red light and ultra-violet light
(λR = 7.0 x 10-7m: λv = 4.0 x 10-7m) - The wavelength of light from a sodium lamp is 5.9 x 10-7m. A 200W sodium vapour has an efficiency of 40%. Calculate:
- The energy of one quantum of sodium light.
- The number of quanta emitted in one second
- The threshold frequency for potassium is 5.37 x 1014 Hz. When the surface of potassium is illuminated by another radiation, photoelectrons are emitted with a speed of 7.9 x 105 m/s
Calculate:- The work function for potassium
- The k.e of the photoelectrons
- The frequency of the second source
- Explain the term “work function”
- A metal has a work function of 2eV. Calculate the threshold wavelength of the metal given that e= 1.6 x 10-19C and h= 6.63 x 10-19C and Me = 9x 10-31kg.
Answers
- Energy (incoming) = hf = 6.6 x 10-34 x 5.5 x 1014
= 3.63 x 10-19 J
= 3.63 x 10-19 = 2.27 eV
1.6 x 10-19
This energy is less than work function hence no photoelectric emission. - Higher photocurrents or more photoelectrons produced.
- Reduce/ prevent collisions of electrons with air molecules and hence increase current
- Control/ limit current, lowers current
- The energy of the radiation must be greater than the work function of the emitting surface.
- Current flows when uv falls on the cathode; interruption of the uv beam cuts off the circuit: use with relay to switch on a second circuit with alarm.
- Electrons ejected from inside the metal lose more energy on the way out while those on the surface require very little work function to be removed.
-
-
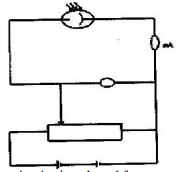
- Work function is given by = hfo
fo is the x- intercept in the graph fo (from graph)
= 1.2 x 1015
Φ= 6. 63 x 10-34 js x 1.2 x 1015
= 7.95 x 10-19
-
- Solar cell (photovoltaic); Photocell/ photo electric cell
- hf = hfo + ½ mv2
Energy of photon (hf) = w.f + k.e
= 3.2 × 10-19 + 8.0 × 10-19
= 11.2 × 10-19
f = c
λ
hc/λ = 11.2 × 10-19
λ = 3.0 x 108 x 6.64 x 10-34
11.2 x 10-19
= 1.76 x 10-7m -
- Photo – electric effect takes place releasing the extra electrons.
- The electrons released are attracted back by the positive charge.
- hf0 = 3.2 x 1.6 x 10-19 J
6. 62 x 10-34
f0 = 7.76 x 1014Hz - The process of the eye lens being adjusted to focus objects at various distances
-
-
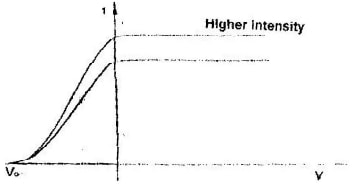
- - The higher the intensity
- Implies greater number of electrons and hence
- Higher saturation current
-
- ER = 2.83 x 10-19J; 4.95 x 10-19J
-
- 3.37 x 10-19J
- 2.37 x 10-20J
-
- 3.56 x 10-19J
- 2.84 x 10 -19J
- 9.7 x 1014Hz
- This is the minimum amount of work required to free an electron from a metal surface
- No = hf0
f0 = w0
h
= 2.0 x 1.6 x 10-19 Hz
6.63 x 10-34
= 4.85 x 1014 Hz
λo = V/f
= 3.0 x 108 ms-1 Hz
4.85 x 1014s-1
= 6.2 x 10-7m - eV = ½ meV2
V2 = 2ev
Me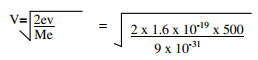
= 1.3 x 107 ms-1
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Photoelectric Effect Questions and Answers - Physics Form 4 Topical Revision.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

