SECTION A (48 marks)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided.
-
- Outline the procedure of connecting an ammeter to take a measurement in a circuit. (2 marks)
- Figure 1 shows a resistor with colour bands.
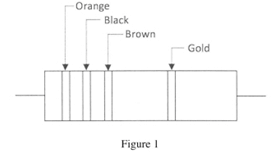
Determine its:- nominal resistance;
- maximum resistance.
-
- State two reasons for using a circuit diagram when troubleshooting an electrical equipment (2 marks)
- State four components of a bill of materials in project fabrication. (2 marks)
-
- Explain the effect of each of the following in a p-n junction: (2 marks)
- forward bias;
- reverse bias.
- State the meaning of each of the following ratings of a light emitting diode: (2 marks)
- I(Fmax)
- V(Ftyp)
- Explain the effect of each of the following in a p-n junction: (2 marks)
- Figure 2 shows a transformer whose primary impedance is 1 kΩ
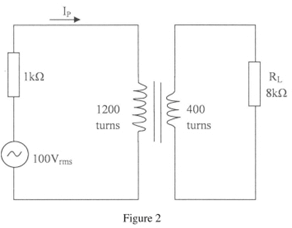
Determine the:- primary current 1
- voltage across R.
- With the aid of labelled diagrams, illustrate the arrangement of magnetic domains in:
- unmagnetised material;
- magnetised material. (3 marks)
-
- Figure 3 shows a voltage divider circuit.
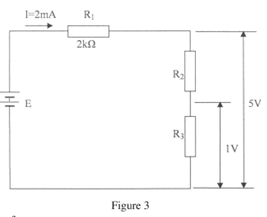
Determine the value of;- E;
- R2;
- R3
(4 marks)
- A consumer has the following loads connected to the supply:
- five 60 W lights for 4 hours;
- one 2 kW kettle for hour.
Calculate the total:- energy consumed;
- cost of energy used if the rate is 80 cents per unit. (3 marks)
- Figure 3 shows a voltage divider circuit.
-
- State three safety precautions to be observed by an operator using a portable electric drill. (3 marks)
- Name four communication service provider companies currently operating in Kenya. (2 marks)
-
- Name four types of insulating materials used in electrical circuits. (2 marks)
- State three advantages of PVC conduit wiring systems. (3 marks)
-
- Calculate the inductance required to cause resonance at 150 kHz when the capacitance is 1.0 pF. (2 marks)
- In a 240V circuit, the load current is 2.5 A. If the power factor is 0-6, calculate:
- apparent power;
- true power (3 marks)
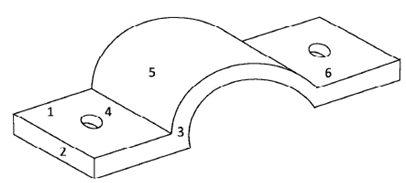
- Make a free hand isometric drawing of a conduit saddle. (5 marks)
SECTION B (52 marks)
Answer any four questions from this section in the spaces provided.
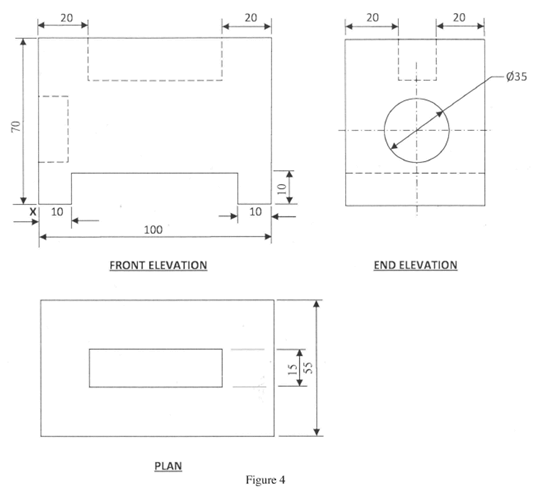
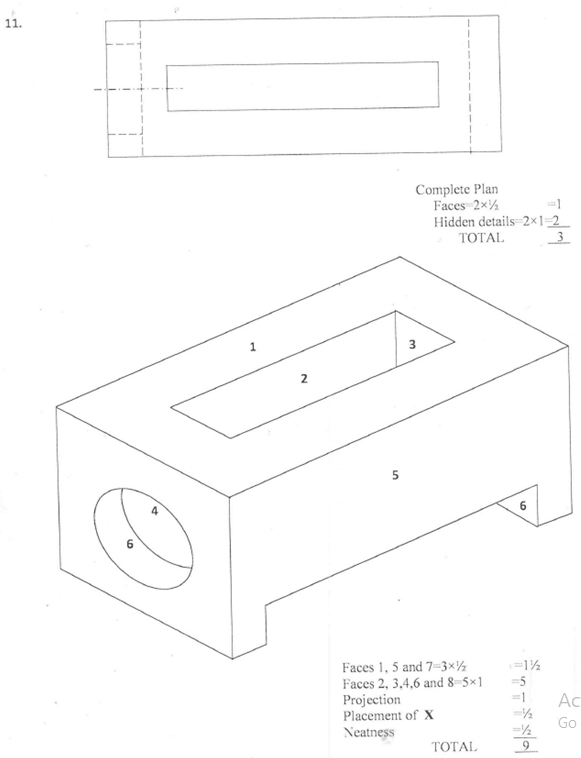
- Figure 4, in the next page, shows the front elevation, end elevation and an incomplete plan of an object.
- Complete the plan;
- On the isometric grid provided, draw the isometric projection of the object making X the lowest point. (13 marks)
- Figure 5 shows waveforms A and B. Their vertical and horizontal scales are given.
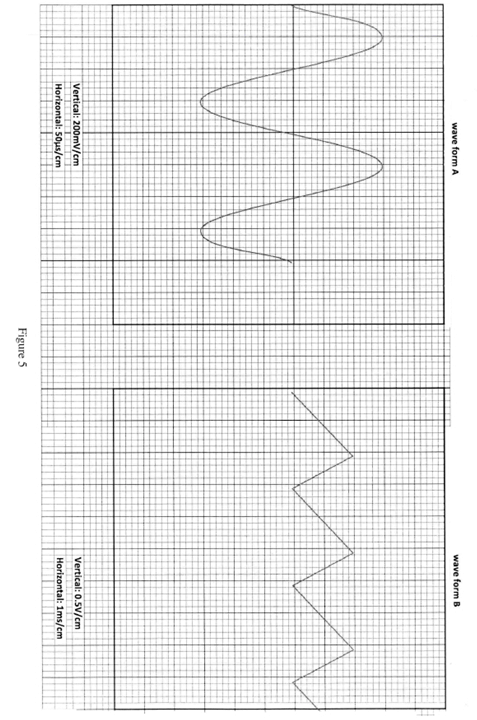
- Name each of the two waveforms. (1 mark) (2 marks)
- State the number of cycles displayed in each waveform.
- Calculate:
- frequency of waveform A;
- amplitude of each waveform;
- RMS voltage of waveform A. (10 marks)
-
- Draw a labelled diagram of a consumer unit with the following final circuits.
- lighting circuit;
- water heater circuit;
- bell circuit;
- cooker circuit;
- ring circuit.(11 marks)
- State the typical fuse ratings for any four of the final circuits in (a).(2 marks)
- Draw a labelled diagram of a consumer unit with the following final circuits.
- Figure 6 shows an amplifier circuit whose current gain is 50.
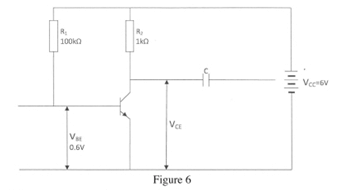
-
- Name the type of transistor;
- State the function of the capacitor C.
- Name the type of biasing. (3 marks)
(10 marks)
- Calculate the values of: (i) voltage across R,; (ii) base current 15;
- collector current I;
- voltage V.CE
-
- Figure 7 shows an R-L-C circuit.
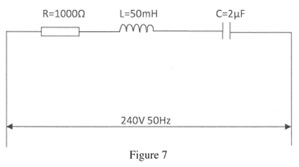
- Calculate the:
- impedence of the circuit; (7 marks)
- Current (3 marks)
- Draw the phasor diagram. (3 marks)
- Calculate the:

MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A
-
- Procedure of connecting an ammeter to take measurements in a circuit
- Turn - off the power
- Ammeter should be connected in series with the load current.
- Observe polarity.
- Select the range starting from the highest.
-
- Nominal resistance
Orange Black Brown
3 0 x 101 = 300 Ω
` Nominal = 300 Ω (1 mark) - Maximum resistance
300 + 5% = 315 Ω (2 marks)
- Nominal resistance
- Procedure of connecting an ammeter to take measurements in a circuit
-
- Circuit diagram
- Shows connection of every component.
- Shows values of components.
- Shows the position of the components.
- Shows functionality of the circuit.
- Bills of materials
(any 2 x 1 = 2 marks)- Materials/parts.
- Quantity.
- Size.
- Estimate costs.
- Circuit diagram
-
-
- Forward bias
reduces the PN-junction (depletion layer) and hence the diode conducts - Reverse bias
increases the PN-junction (depletion layer) hence the diode does not conduct (2 marks)
- Forward bias
-
- IF(max): is the maximum forward current that the diode can pass without burning out. (1 mark)
- VF(typ): is the forward voltage across the diode at the typical operating current. (1 mark)
-
-
- Ip = V
R
= 100 Vrms
1 kX
= 0.1 A - N1I1 = N2I2 (1)
`1200 x 0.1 = 400 x I2
I2 = 120 = 0.3A
400
V2 = I2R2
= 0.3 x 8000
= 2,400
(5 marks)
- Ip = V
-
Drawing
Labelling
Direction
Drawing
Labelling
Direction
-
-
- E = 5 + ^I x R1h
= 5 + ^2 # 10-3 x 2000h
= 5 + 4
=9V - R2 = V2 = 4V = 2kX
I 2mA - R3 = V3 = 4V = 0.5k
I 2mA
- E = 5 + ^I x R1h
-
- Energy consumed
Lights 5 x 60 x 4 = 1.2 kwh
Kettle 1 x 2 x 0.5 = 1.0 kwh(4 marks)
Total energy = 2.2 kwh (1) - Cost of energy
= 2.2 x 80 = 1.76 sh (1)
- Energy consumed
-
-
- Safety precautions to be observed (3 marks)
- Ensure that the equipment is properly earthed.
- Do not use it in damp areas.
- Always remove the plug from the socket when the equipment is not in use.
- When using extensions, ensure the joints are firm and insulated using the electricians insulation tape.
- Hold it firmly.
- Avoid loose clothing like ties.
(any 3 x 1 = 3 marks)
- Communication service providers in Kenya
- Telkom Kenya
- Safaricom
- Airtel
- Yu
- Safety precautions to be observed (3 marks)
-
- Insulating materials used in electrical circuits
(4 x 21 = 2 marks) or any other existing ones- PVC
- Porcelain
- Magnesium oxide
- Paper
- Rubber
- Air
- Formica = 2 marks)
- Advantages of PVC
- Easy of erection.
- It is cheap.
- It is resistant to corrosion.
- It is light.
- There is no risk to earth leaks.
- Insulating materials used in electrical circuits
-
- Inductance required
(any 3 x 1 = 3 marks)
= 1
4π2(1.5 x 105)2(10-12)
= 1.13 x 10-3 H
= 1.13 H -
- Apparent power
= IV
= 2.5 x 240
= 600 VA - True power
(2 marks)
= apparent power x power factor
= 600 x 0.6
= 360 w
- Apparent power
- Inductance required
Faces
Holes
Projection
(5 marks)
SECTION B
-
-
- Name of waveforms
- sine wave
- saw tooth
- Number of cycles
- 2 cycles (1)
- 3 cycles (1)
-
- Frequency of waveform A
1 Where T = period
T
T = 50n x 4
= 200 μs (1)
f = 1 = 1 = 10 6
T 200 x 10-6 200
= 5 kHz (1) - Amplitude
A = Vpk = 200 mV x 3 (1)
= 600 mV (1)
= 0.6 V
B = Vpk = 0.5 V x 2 (1)
= 1 Vpk (1) - RMS value of A
= 0.707 x Vpk (1)
= 0.707 x 0.6
= 0.424 V (1)
(13 marks)
- Frequency of waveform A
- Name of waveforms
-
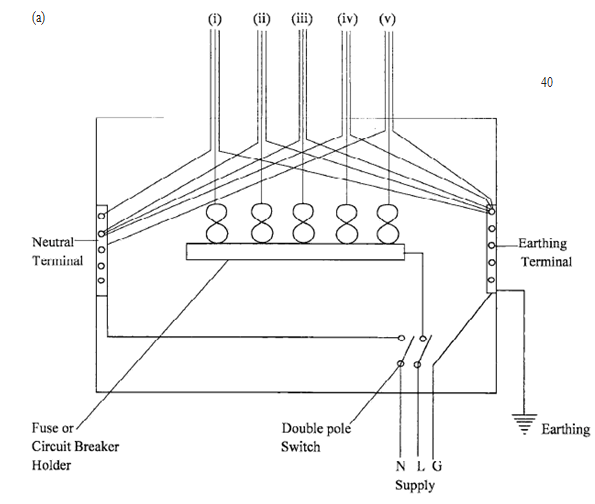
Correct Drawing = 8
Labelling 6 items = 3-
- Lighting circuit = 5A
- Ring circuit = 30 A
- Water heater = 20 A
- Door bells = 5 A
- Cooker unit = 45 A (11 marks)
(Total = 11 + 2 = 13 marks)
-
-
- Type of transistor
NPN (1) - Function of capacitor C
To block D.C (1) - Type of biasing
Fixed bias (1)
- Type of transistor
-
- VR1 = VCC - Vbe (1)
= 6.0 - 0.6
= 5.4 V (1)
(3 marks) - IB = VR1 = 5.4
100 x 103
5.4 x 105
= 5.4 x 105
= 54 μA - IC = βIB (1)
= 54 x 10-6 x 50 (1)
= 2.7 mA - Voltage VCE
VR2 = IC x R2 (1)
= 2.7 mA x 1 x 103
= 2.7 V (1)
VCE = VCC - VR2 (1)
= 6 - 2.7 V
= 3.3 V (1)
- VR1 = VCC - Vbe (1)
-
-
-
- XL = 2rfL
= 2r x 50 x 0.05
= 15.70 Ω (1)
XC = 1
2rfc (1)
= 2r x 50 x 2 x 10-6
= 1592 Ω
Z = √R2 + ^XC - XLh2
10002 + ^1592 - 15.7h2
= 1866 Ω (1) (7 marks) - Current = V
Z
= 240
1866
= 0.12 A
- XL = 2rfL
-
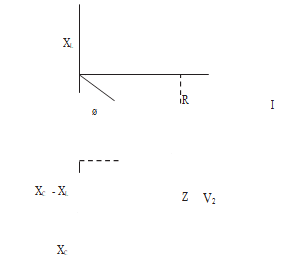
Axes
Labelling
(3 marks)
Download Kenya Certificate Of Secondary Education(KCSE 2013) Electricity Paper 1 with Marking Scheme.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

