Instructions to candidates
- This paper has two sections, A and B
- Answer all the questions in Section A
- In Section B, answer question 6 and any other TWO questions.
-
- Name two forces responsible for the shape of the earth (2mks)
- State three reasons why the interior of the earth is hot (3mks)
- The table below represents rainfall and temperature figures for a system in Africa.
Month
J
F
M
A
M
J
J
A
S
O
N
D
Temperature
24
24
23
22
19
17
17
18
19
20
23
23
Rainfall (mm)
109
122
130
76
52
34
28
38
70
108
121
120
- Calculate the average monthly temperature for the station (2mks)
- Describe the rainfall pattern for the station (3mks)
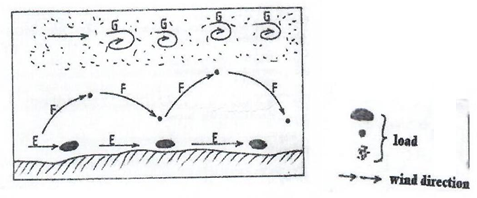
- The diagram below shows way through which wind transport its load.
- Name the ways marked E, F and G (3mks)
- Identify two features formed by wind deposition in desert. (2mks)
-
- What is natural vegetation (2mks)
- State three reasons why Tundra region has scanty vegetation (3mks)
-
- Differentiate between an ocean and a sea (2mks)
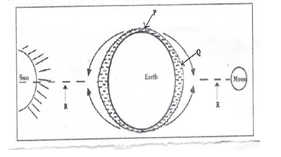
- The diagram below represents occurrence of tides. Name the parts marked P, Q and R. (3mks)
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other two questions from this section
- Study the map of Taita hills and answer the questions that follow.
-
- Measure the distance of river Ruhia from its confluence with river Voi Goshi to grid reference 345270 (2mks)
- Give the location of St Marys’ High School by latitude and longitude (2mks)
-
- Describe the distribution of vegetation in the area covered by the map (4mks)
- Identify methods which have been used to represent relief in the area covered by the map. (2mks)
-
- Draw a cross section from grid reference 310140 to grid reference 370140. Use vertical scale of 1 cm represents 20 meters. (3mks)
- Along the cross-section mark and label the following.
- Hill (1mk)
- All weather road (bound surface) (1mk)
- Teita sisal Estate (1mk)
-
- A bore hole is supposed to be dug in the area covered by grid square 2615.State three factors which may make construction expensive (3mks)
- Citing evidence from the map explain three factors which may favour cattle rearing in the area covered by the map. (6mks)
-
-
- Differentiate between a normal fault and a reverse fault (2mks)
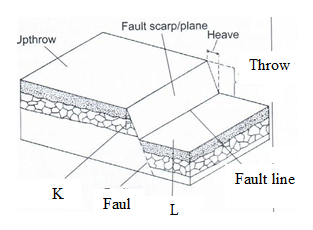
- Study the diagram below and use it to answer question b(i)
- Name the parts labelled H, J, K and L (4mks)
- Give three examples of fault blocks (3mks)
- Using well labelled diagrams, describe the formation of the rift valley by tensional forces (8mks)
- Explain four economic significance of faulting. (8mks)
-
-
- Name two areas in Africa associated with karst scenery (2mks)
- State three characteristic of karst scenery (3mks)
-
- State three ways through springs are formed (3mks)
- Explain three conditions necessary for the formation of an artesan well. (6mks)
- Describe how the following features are formed: -
- Grikes and clints (5mks)
- Stalactite (6mks)
-
-
-
- What is an ice sheet? (2mks)
- Name two mountains in East Africa which are ice capped.(2mks)
- Identify three ways in which ice moves. (3mks)
- Explain three factors that influence the movement of ice from the place it has accumulated. (6mks)
- Describe how an arete is formed (5mks)
- You are required to carry out a field study on erosional features in glaciated lowland areas.
- Give two reasons why you would require a working schedule. (2mks)
- Apart from an arete, name two other erosional features you are likely to observe during the field study. (2mks)
- Give three follow up activities you would undertake after the field study. (3mks)
-
-
-
- What is soil (2mks)
- State three main components of soil (3mks)
- Explain how the following weathering processes contributes to the formation of soil
- Hydration (3mks)
- Oxidation (4mks)
-
- Name the type of soil structures which fits the following descriptions
- Soil particles are arranged in thin sheets on top of each other. (2mk)
- Soil particles are arranged vertically in cylindrical manner (2mk)
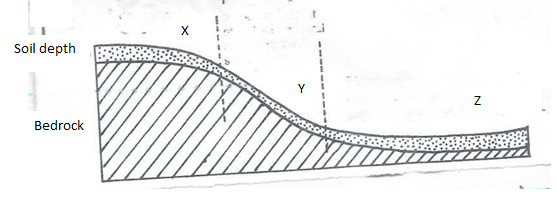
- The diagram below represents soil catena. Identify the nature of soils in the stages marked X, Y and Z. (3mks)
- Explain how the following factors cause soil degradation
- Leaching (2mks)
- Mono cropping (2mks)
- Burring of land (2mks)
- Name the type of soil structures which fits the following descriptions
-

MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A (25 MARKS)
Answer all the questions in this section
-
- Name two forces responsible for the shape of the earth (2mks)
- Forces of gravity
- Centripetal force
- Centrifugal force
- State three reasons why the interior of the earth is hot (3mks)
- Pressure by overlying materials
- The interior cooled at a slower rate
- Heat from radio activity
- Name two forces responsible for the shape of the earth (2mks)
- The table below represents rainfall and temperature figures for a system in Africa.
Month
J
F
M
A
M
J
J
A
S
O
N
D
Temperature
24
24
23
22
19
17
17
18
19
20
23
23
Rainfall (mm)
109
122
130
76
52
34
28
38
70
108
121
120
- Calculate the average monthly temperature for the station (2mks)
248 0c - Describe the rainfall pattern for the station (3mks)
- There is rainfall throughout the year / no dry month
- The highest amount of rainfall is received during hottest month
- Lowest rainfall is received in the coolest month
- The wettest month is march (130mm)
- The driest month is July (28mm)
- The total annual rainfall is 1008 mm/ rainfall amount is moderate
- Calculate the average monthly temperature for the station (2mks)
- The diagram below shows way through which wind transport its load.
- Name the ways marked E, F and G (3mks)
- E – Surface creep
- F – Saltation
- G - Suspension
- Identify two features formed by wind deposition in desert. (2mks)
- Sand dunnes / Barchans / Seif dune / Transverse dunes
- Draas
- Loess
- Name the ways marked E, F and G (3mks)
-
- What is natural vegetation (2mks)
This is plant cover that grows wildly - State three reasons why Tundra region has scanty vegetation (3mks)
- The soil is frozen
- The temperatures are very low
- Short growing period
- What is natural vegetation (2mks)
-
- Differentiate between an ocean and a sea (2mks)
An ocean is a large body of saline water occupying a basin between continents while a sea is a large body of saline water on the margins of continents - The diagram below represents occurrence of tides. Name the parts marked P, Q and R. (3mks)
P – Low tide
Q – High tide
R – Gravity of the sum/ moon
- Differentiate between an ocean and a sea (2mks)
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other two questions from this section
- Study the map of Taita hills and answer the questions that follow.
-
- Measure the distance of river Ruhia from its confluence with river Voi Goshi to grid reference 345270 (2mks)
6 km - Give the location of St Marys’ High School by latitude and longitude (2mks)
- Latitude – 30 25 ‘S
- Longitude – 380 20| E
- Measure the distance of river Ruhia from its confluence with river Voi Goshi to grid reference 345270 (2mks)
-
- Describe the distribution of vegetation in the area covered by the map (4mks)
- Thickets are found to the western part of the map.
- Patches of forest are distributed to the east of Taita.
- Scrubs is evenly distributed through the map
- There are scattered trees evenly distributed.
- Identify methods which have been used to represent relief in the area covered by the map. (2mks)
- Contours
- Trigonometrical stations
- Spot heights
- Cliff and Rock drawing
- Describe the distribution of vegetation in the area covered by the map (4mks)
-
- Draw a cross section from grid reference 310140 to grid reference 370140. Use vertical scale of 1 cm represents 20 meters. (3mks)
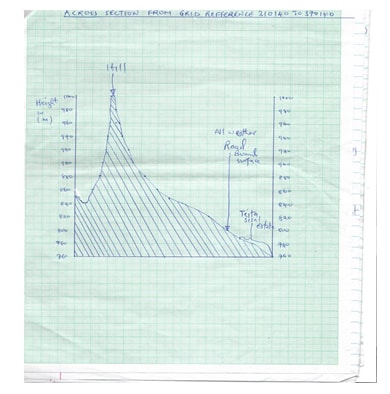
- Along the cross-section mark and label the following.
- Hill (1mk)
- All weather road (bound surface) (1mk)
- Teita sisal Estate (1mk)
- Draw a cross section from grid reference 310140 to grid reference 370140. Use vertical scale of 1 cm represents 20 meters. (3mks)
-
- A bore hole is supposed to be dug in the area covered by grid square 2615.State three factors which may make construction expensive (3mks)
- Deep water table due to high altitude of 1200metres
- Outcrop rocks may be hard to drill
- Difficulty in accessibility due to lack of roads
- Citing evidence from the map explain three factors which may favour cattle rearing in the area covered by the map. (6mks)
- Availability of pasture as evidenced by presence of scrubs vegetation for grazing of the livestock
- Availability of water as evidenced by permanent rivers and dams for watering animals.
- Gently sloping land to the East as evidenced by widely spaced contours for easy movement of livestock as they graze.
- A bore hole is supposed to be dug in the area covered by grid square 2615.State three factors which may make construction expensive (3mks)
-
-
- Differentiate between a normal fault and a reverse fault (2mks)
- Normal fault is caused by tensional forces while reverse fault is caused by compressional forces
- In the normal fault, a block of land slides downwards in relation to another while in reverse fault, a block of land will slide / ride upwards in relation to another
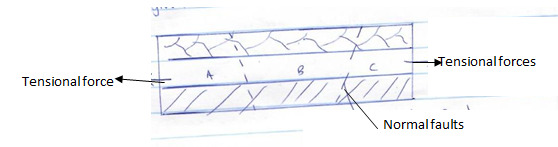
- Study the diagram below and use it to answer question b(i)
- Name the parts labelled H, J, K and L (4mks)
H – Fault scarp
J - Upthrow
K- Hade
L – Downthrow - Give three examples of fault blocks (3mks)
- Usambara
- Pare
- Ruwenzori mountain
- Mathew ranges
- Nyiro Ndoto Mountains
- Name the parts labelled H, J, K and L (4mks)
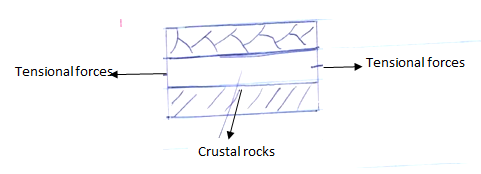
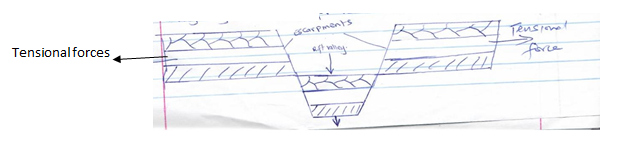
- Using well labelled diagrams, describe the formation of the rift valley by tensional forces (8mks)
- A block of the land / crustal rock is subjected to tensional forces
- As tension forces intensify the block of land cracks up / develops normal faults which divide the given crustal rock block into three blocks
- Eventually the block in the middle is subsided as the side blocks are left standing. The middle block forms the floor of the rift valley as the side of the standing blocks form the walls of the rift valley hence formation of the rift valley by tensional forces
- Explain four economic significance of faulting. (8mks)
- Features resulting from faulting such as the rift valley fault steps are beautiful hence attract tourists
- Faulting leads to formation of depressions which are filled with water to form lakes some of which provide water for irrigation or domestic and industrial uses
- Faulting a cross a river sources may lead to formation of waterfall which is hamessed to provide hydroelectric power
- Faulting process can expose mineral near the earth’s surface hence easen the mining activity
- Features resulting from faulting such as the rift valley fault steps are beautiful hence attract tourists
- Differentiate between a normal fault and a reverse fault (2mks)
-
-
- Name two areas in Africa associated with karst scenery (2mks)
Tanga
Shimoni - State three characteristic of karst scenery (3mks)
- Little surface water
- Rugged / rocky landscape
- Thin soils
- Scanty vegetation
- Underground stream
- Name two areas in Africa associated with karst scenery (2mks)
-
- State three ways through springs are formed (3mks)
- Where permeable rock lies on top of an aquefer
- Where well jointed rocks form a hilly region absorb water through the joints.
- Where a dyke cuts across a layer of permeable rock
- Where a gently sloping layer of permeable rock alternates with layers of impermeable rocks
- Explain three conditions necessary for the formation of an artesan well. (6mks)
- The aquifer must be sandwiched between impermeable rocks to retain water.
- Aquifer must outcrop in a region which is a source of water eg rainy area.
- Aquifer must deep from a region of water intake and the rock layers must form a broad syncline.
- The mouth of the well must be lower than the intake area, this allows water to be forced to the surface by pressure.
- State three ways through springs are formed (3mks)
- Describe how the following features are formed: -
- Grikes and clints (5mks)
- Rain water dissolves carbon(iv) oxide in the atmosphere forming a weak carbonic acid
- The weak carbonic acid reacts with limestone forming calcium hydrogen carbonate which is soluble
- Water enters vertical joints fo limestone which are widened by solution process
- These form gullies called grikes
- The grikes are separated by ridges called clints.
- Stalactite (6mks)
- Rain water mixes with Co2 in the atmosphere forming a weak carbonic acid
- On reaching the surface, the weak carbonic acid reacts with limestone forming calcium hydrogen carbonate.
- Rainwater infiltrates through the joints of limestone forming a solution of calcium hydrogen carbonate.
- The solution drips from the roof of the cave.
- Water and carbon(iv) oxide are released
- Calcium carbonate is deposited on the roof of the cave
- With time the calcium carbonate grows downwards forming fingerlike projections called stalectiles
- Grikes and clints (5mks)
-
-
-
- What is an ice sheet? (2mks)
Ice sheet is a continuous mass of ice covering vast areas of lowland - Name two mountains in East Africa which are ice capped. (2mks)
- Kenya
- Kilimanjaro
- Rwenzori
- Identify three ways in which ice moves. (3mks)
- Plastic flowage
- Basal slip
- Extrusion flow
- Internal shearing
- Explain three factors that influence the movement of ice from the place it has accumulated. (6mks)
- Gradient of the land; ice moves faster when the slope is steep
- Temperatures or seasonal changes; higher temperature result in thawing, leading to faster movement of ice
- Nature of the surface; when the surface on which ice is moving is rough, it causes friction lowering the speed of the movement of ice.
- Size of gracier; Large masses of ice exert pressure which lead to melting of ice underneath. This increases the speed of ice movement.
- What is an ice sheet? (2mks)
- Describe how an arete is formed (5mks)
- Two adjacent cracks (hollows exist on a mountain side
- The two hollows are filled with ice
- The ice erodes the sides through plucking, and deepens the hollow through abrasion.
- Through erosion, the back walls of the hollows slowly recede and eventually the hollows or cirques are separated by a knife edged ridge.
- This ridge is known as an arete
- You are required to carry out a field study on erosional features in glaciated lowland areas. (2mks)
- Give two reasons why you would require a working schedule.
- To ensure all areas are adequately covered
- It is a pointer to show how much time will be required for the study
- In order to remain within the scope of the study topic
- To ensure proper time management / reduce time wastage
- To ensure all relevant areas are allocated adequate time
- In order to ensure there is organization while carrying out the study
- Apart from an arete, name two other erosional features you are likely to observe during the field study.(2mks)
- Crag and tail
- Roche montane
- Depressions
- Ice eroded plains
- Give three follow up activities you would undertake after the field study. (3mks)
- Displaying photographs
- Waiting reports
- Presenting reports
- Discussing findings in class
- Analyzing information collected against the hypothesis
- Give two reasons why you would require a working schedule.
-
-
-
- What is soil (2mks)
Surface layer of the earth composed of broken rock particles and organic matters on which plants grow. - State three main components of soil (3mks)
- Mineral particles
- Soil organic matter
- Soil air
- Soil water
- What is soil (2mks)
- Explain how the following weathering processes contributes to the formation of soil
- Hydration (3mks)
- Mineral in the rock absorb water during rainy period
- The mineral expands causing stress in the rock
- The rock eventually break into smaller pieces thereby forming soil
- Oxidation(4mks)
- Oxygen in air / water reacts with iron compounds in the rock
- Oxides are formed
- Brownish / Yellowish crust is formed on the surface of the rock.
- The crust disintergrates grades making the rock to break into smaller pieces forming soil
- Hydration (3mks)
- Name the type of soil structures which fits the following descriptions
- Soil particles are arranged in thin sheets on top of each other. (2mk)
Plate structure - Soil particles are arranged vertically in cylindrical manner (2mk)
Prismatic / columner - The diagram below represents soil catena. Identify the nature of soils in the stages marked X, Y and Z. (3mks)
- X – Well developed soil
- Y – Thin soil
- Z – Deep / water logged soil
- Soil particles are arranged in thin sheets on top of each other. (2mk)
- Explain how the following factors cause soil degradation
- Leaching (2mks)
- Soil nutrients / minerals are dissolved by rainwater and washed to the lower horizons
- The top layer loses its fertility
- Mono cropping (2mks)
- The crop exhausts a particular mineral in the soil / a particular pest or diseases may accumulate in the soil
- This lowers the soil fertility
- Burring of land (2mks)
- Fire burns humus in the soil / makes the soil dry / kills soil micro organisms
- The soil therefore loses its fertility
- Leaching (2mks)
-
Download GEOGRAPHY PAPER 1 - KCSE 2019 MASENO MOCK EXAMINATION (WITH MARKING SCHEME).
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students