GEOGRAPHY
PAPER 1
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- This paper has two sections: A and B.
- Answer all the questions in section A.
- Answer question 6 and any other two questions from section B.
SECTION A:
Answer all questions in this section (25marks)
-
- What is the relationship between Geography and Mathematics (2mks)
- State three reasons why it is important to study Geography. (3mks)
-
- Give three components of the solar system. (3mks)
- State two characteristics of the outer core in the internal structure of the earth. (2mks)
-
- Give two reasons why it is necessary to study the plate tectonic theory. (2mks)
- Name three types of boundaries associated with the plate tectonic theory. (3mks)
-
- State three ways in which plants adapt to hot desert conditions. (3mks)
- State two climatic conditions experienced in Sahara Desert. (2mks)
-
- What is an ocean tide? (2mks)
- Name three types of ocean tides. (3mks)
SECTION B:
Answer question six and any other two from this section (75marks)
- Study the map of Kijabe 1:50,000 provided and answer the following questions.
-
- What is the sheet title of the map provided. (1mk)
- What is the latitudinal extent of Kijabe. (2mk)
-
- Measure the distance of all weather road bound surface from Limuru to the saw mill at grid square 3497. (2mks)
- Calculate the area of thicket vegetation found at the southern part of Kijabe. (2mks)
- Citing evidence from the map, give three social services offered in Kijabe area. (3mks)
-
- Describe the drainage of the area covered by Kijabe area. (5mks)
- Explain two ways how relief has influenced the distribution of settlement in the area covered by the map. (4mks)
-
- Draw a rectangle measuring 6cm by 3cm to represent the area enclosed by easting 27 to 33 and northing 94 to 97. (1mk)
On the rectangle mark the following features
. Thicket vegetation (1mk)
. A Railway (1mk)
. Post office (1mk) - Calculate the new scale of the rectangle (2mks)
- Draw a rectangle measuring 6cm by 3cm to represent the area enclosed by easting 27 to 33 and northing 94 to 97. (1mk)
-
-
-
- Differentiate between weather and climate (4mks)
- State two conditions necessary for the formation of fog. (2mks)
-
- Briefly describe the working of Aneroid barometer. (4mks)
- State three effects of sea breeze on the adjacent land mass. (3mks)
-
- xplain how the following factors influence climate
Ocean currents (2mks)
Altitude (2mks) - State three characteristics of equatorial climate. (3mks)
- xplain how the following factors influence climate
- With the aid of well labelled diagram, describe the formation of land breeze. (5mks)
-
-
-
- What is faulting? (2mks)
- Name three types of faults. (3mks)
-
- State three effects of faulting on drainage. (3mks)
- Briefly describe the formation of a crater by subsidence method. (5mks)
-
- List three causes of earthquakes. (3mks)
- Name three major earthquake zones of the world. (3mks)
- You intend to carry out a field study in the Rift Valley.
- Name three methods of data collection you used. (3mks)
- State three problems you are likely to face during the field study. (3mks)
-
-
-
- List three types of desert according to the nature of the surfaces. (3mks)
- State two factors that contribute to development of deserts. (2mks)
- Highlight three reasons why wind is a dominant agent of erosion in arid areas. (3mks)
-
- Explain two processes of wind erosion (4mks)
- Name three features of wind deposition in arid areas. (3mks)
-
- With the aid of well labelled diagrams describe how a rock pedestal is formed. (8mks)
- Give two ways in which wind transports its load. (2mks)
-
-
-
- Name two types of glaciers. (2mks)
- State two reasons why there are no ice sheets in Kenya. (2mks)
- Explain two processes of glacial erosion (4mks)
- The diagram below shows types of moraine in a valley glacier. Use it to answer the following questions
- Name the type of moraines marked A, B and C. (3mks)
- Explain how the movement of a valley glacier is influenced by the following factors:
Temperature changes (2mks)
Width of a glacier channel (2mks)
- With the aid of well labelled diagrams, describe how a cirque is formed (6mks)
- Students from Mumbai girls intended to carry out a field study on a glaciated lowland area.
- State two objectives intended for the study. (2mks)
- Name two features they are likely to have observed during the field study (2mks)
-
MARKING SCHEME
-
- What is the relationship between Geography and Mathematics (2mks)
- Mathematics principles or formulae are used in Geography to calculate distances or area or population density.
- Geographical information can be analyzed or presented through the application of mathematical techniques.
- State three reasons why it is important to study Geography. (3mks)
- Geography is a career subject e.g. engineering
- Geography creates awareness in the people on the significance of management and conservation of the environment
- In Learning Geography one is able to acquire basic skills and knowledge which contribute to local, regional and national development.
- Through the study of field work, Geo teaches one on how to manage time
- Geo helps learners to develop the skills of observing, reading, analyzing and interpreting maps, photographs, charts.
- Geography focuses on physical study of the earth. One is therefore able to learn and explain the origin of the earth and the solar system.
- What is the relationship between Geography and Mathematics (2mks)
-
- Give three components of the solar system. (3mks)
- Sun
- Comets
- Natural satellites
- Meteorites
- State two characteristics of the outer core in the internal structure of the earth. (2mks)
- Composed of molten rock material
- Is made up of iron and nickel
- Estimated to be about 2100km to 2900km thick
- Temperatures ranging from 3700ºc-5000ºc
- Rocks have a high density averaging 10.5g/cm3
- Give three components of the solar system. (3mks)
-
- Give two reasons why it is necessary to study the plate tectonic theory. (2mks)
- Explains the destruction of structural landforms
- Helps one understand how the earth maintains balance
- Explains the cause of the earthquakes or volcanicity
- Name three types of boundaries associated with the plate tectonic theory. (3mks)
- Divergence/Extension/constructive
- Converging/compressed/destruction
- Transform/conservative
- Give two reasons why it is necessary to study the plate tectonic theory. (2mks)
-
- State three ways in which plants adapt to hot desert conditions. (3mks)
- Some plants have long roots to tap underground water
- Some have small waxy leaves to reduce transpiration
- Some trees shed their leaves during the dry seasons
- Some plants have thick bark stems to store water.
- Some plants produce seed that lie dormant awaiting rains
- Some trees are umbrella-shaped to provide shade to the stem roots
- State two climatic conditions experienced in Sahara Desert. (2mks)
- Rainfall is low/below 250mm per annum
- Rainfall is erratic/flash floods and sporadic rain
- Temperatures are high throughout the year over 300c/hot climate
- Intense solar radiation
- The diurnal range of temperature is very large/very hot days and cool nights
- High rates of evaporation
- Skies are always cloudless
- State three ways in which plants adapt to hot desert conditions. (3mks)
-
- What is an ocean tide.? (2mks)
- Ocean tide is the periodic rise and fall of the ocean water
- Ocean tide is the periodic rise and fall of the ocean water
- Name three types of ocean tides. (3mks)
- Perigean
- Apogean
- Spring
- Neap
- What is an ocean tide.? (2mks)
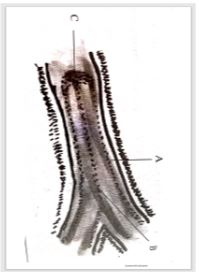
- 6 Study the map of Kijabe 1:50,000 provided and answer the following questions.
-
- What is the sheet title of the map provided. (1mk)
- EAST AFRICA 1:50000 (KENYA)
- EAST AFRICA 1:50000 (KENYA)
- What is the latitudinal extent of Kijabe. (2mk)
- 18.1cm---5’ 6.8cmx5’/18.1cm
6.8cm---? =1’9”
Latitudinal extent =1º00’s to 0º 54’51” s
- 18.1cm---5’ 6.8cmx5’/18.1cm
- What is the sheet title of the map provided. (1mk)
-
- Measure the distance of all-weather road bound surface from Limuru to the saw mill at grid square 3497. (2mks)
- 9.0km+- 0.1
- 9.0km+- 0.1
- Calculate the area of thicket vegetation found at the southern part of Kijabe. (2mks)
- complete squares=3
incomplete squares=15
Area=3+15/2
=3+7.5
=10.5km2+-0.1
- complete squares=3
- Citing evidence from the map, give three social services offered in Kijabe area. (3mks)
- Education service-evidenced by school
- Health services –evidenced by dispensary
- Religious services-evidences by a church
- Measure the distance of all-weather road bound surface from Limuru to the saw mill at grid square 3497. (2mks)
-
- Describe the drainage of the area covered by Kijabe area. (5mks)
- The main drainage feature are rivers e.g. R. Bathi
- Most of the rivers are permanent e.g R.upper Ewaso kedong
- Rivers on Kijabe hill form parallel and radial drainage pattern
- Most rivers form dendritic drainage pattern
- The main rivers are upper Ewaso Kedong and Bathi which flows southwards
- Most rivers are in their youthful stage
- Explain two ways how relief has influenced the distribution of settlement in the area covered by the map. (4mks)
- Most of the setttlements are found at the foot of the escarpment because the land is gently sloping hence can support agriculture
- The escarpment has no settlement because the land is steep.
- Kijabe hill has afew settlement on the eastern side because the land is gentle
- The western side of the hill has no settlement as the land is steep
- The land immediate to the East of the escarpment has many settlements because it is gently sloping
- Describe the drainage of the area covered by Kijabe area. (5mks)
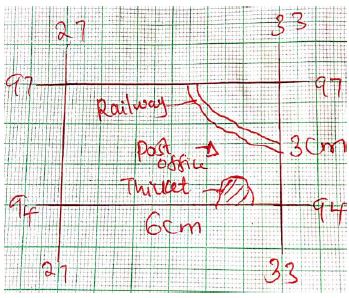
- Draw a rectangle measuring 6cm by 3cm to represent the area enclosed by easting 27 to 33 and northing 94 to 97. (1mk)
- On the rectangle mark the following features
. Thicket vegetation (1mk)
. A Railway (1mk)
. Post office (1mk)
A RECTANGLE FROM EASTNG 27 TO 33 ALONG NORTHING 94 TO 97
Drawn rectangle with title 1mk
Feature each 1mk
(1mk) - Calculate the new scale of the rectangle (2mks)
- 1:50000x2
=1:100000
- 1:50000x2
- On the rectangle mark the following features
-
-
-
- Differentiate between weather and climate (4mks)
- Weather is the atmospheric conditions of a given place over a short period of time while climate is the average weather conditions of a given place over a long period of time.
- Weather is the atmospheric conditions of a given place over a short period of time while climate is the average weather conditions of a given place over a long period of time.
- State two conditions necessary for the formation of fog. (2mks)
- The air must have sufficient moisture
- Clear sky
- Air must be cooled to below the dew point
- Calm conditions to help hold the water droplets in suspension
- Differentiate between weather and climate (4mks)
-
- Briefly describe the working of Aneroid barometer. (4mks)
- This instrument consists of a small metal box containing very little air
- Its top is very sensitive to change in pressure
- It therefore expands when pressure is low and collapses when pressure is high
- These movements are conveyed by a system of levers to a pointer which moves across a graduated scale.
- State three effects of sea breeze on the adjacent land mass. (3mks)
- Lowers temperature of adjacent areas
- May increase rainfall
- May increase humidity
- May lead to convectional rainfall
- May lead to diurnal range of temperature
- Briefly describe the working of Aneroid barometer. (4mks)
-
- Explain how the following factors influence climate
- Ocean currents (2mks)
- Onshore winds blow over cold ocean currents the winds acquire cold temperatures and transfer them to the adjacent coastal land
- Onshore winds blow over warm ocean currents, the winds acquire a warming effect which raises temperatures of the adjacent coast
- Altitude (2mks)
- High altitude areas have lower temperature while low altitude areas have higher temperatures because the atmosphere is heated from below by terrestrial radiation.
- High altitude areas have lower temperature while low altitude areas have higher temperatures because the atmosphere is heated from below by terrestrial radiation.
- Ocean currents (2mks)
- State three characteristics of equatorial climate. (3mks)
- High annual rainfall of 1500-2250mm throughout the year
- Double rainfall maxima
- Experiences heavy convectional rainfall
- High humidity
- Relatively low atmospheric pressure
- High temperature 24-28ºc
- Low annual temperature range 3-5ºc
- Explain how the following factors influence climate
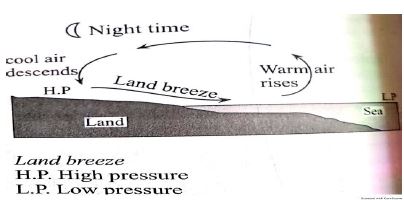
- With the aid of well labelled diagram, describe the formation of land breeze. (5mks)
- At night land loses heat faster than sea water
- Cool dense air over the land creates a high pressure zone.
- The air over the sea is warm and light at night
- The air rises and creates a low pressure zone over the sea
- Cool dense air over the land flows towards the sea to replace the warm rising air
- This cool air blowing from the land to the sea is called a land breeze.
Text -3mks
Diagram -2mks
-
-
-
- What is faulting? (2mks)
- Faulting is cracking or fractioning of crustal rocks due to tectonic forces leading to displacement of rocks on either side.
- Faulting is cracking or fractioning of crustal rocks due to tectonic forces leading to displacement of rocks on either side.
- Name three types of faults. (3mks)
- Normal faults
- Reversed faults
- Shear/tear faults
- Thrust/over
- What is faulting? (2mks)
-
- State three effects of faulting on drainage. (3mks)
- When faulting occurs across a river valley, it may cause the river to disappear into the ground
- Vertical faulting across a river may form a waterfall on the escarpment
- Rift valley forms a depression which may be filled by water to form lakes
- Briefly describe the formation of a crater by subsidence method. (5mks)
- Earth movement forms a vent in the rock of the crust
- Magma reaches the surface through the vent
- The lava piles up around the vent to form a volcanic cone after series of eruptions.
- Pressure underground reduces and the magma stops coming out
- Lava in the vent cools and contracts
- The lava the subsides into the vent
- This forms a funnel shaped shallow depression at the top of the volcanic cone called the crater.
- State three effects of faulting on drainage. (3mks)
-
- List three causes of earthquakes. (3mks)
- Movement of the tectonic plates
- Movement of magma
- Gravitational pressureIsostatic adjustment
- Energy release from the mantle
- Human activities
- Name two major earthquake zones of the world. (2mks)
- Circum-pacific belt
- Mid-Atlantic Ocean belt
- Mediterranean –East indies belt
- List three causes of earthquakes. (3mks)
- You intend to carry out field study in the Rift Valley.
- Name three methods of data collection you used. (3mks)
- direct observation
- taking photographs
- collection of samples
- interviewing
- administering questionnaires
- State three problems you are likely to face during the feld study.-
- harsh weather conditions like sudden rainfall
- accidents may occur during climbing of the steep mountains
- attack by wild animals like snakes and insects
- Name three methods of data collection you used. (3mks)
-
-
-
- List three types of desert according to the nature of the surfaces. (3mks)
- Sandy desert/koum
- Stony desert/reg/serrir
- Rocky desert /Hamada
- Badlands
- State two factors that contribute to development of deserts. (2mks)
- High temperatures leading to high evaporatio
- Prolonged drought/insufficient rainfall
- Cold ocean currents on the path of rain bearing onshore winds.
- Rain shadow effect
- Long distance from the sea
- Highlight three reasons why wind is a dominant agent of erosion in arid areas. (3mks)
- Scarcity or no vegetation cover which exposes land to wind erosion
- Strong tropical winds or storms that occur in deserts
- Presence of dry and loose unconsolidated rock material.
- List three types of desert according to the nature of the surfaces. (3mks)
-
- Explain two processes of wind erosion. (4mks)
- Deflation
- Dry loose materials like dust and fine sand are scooped and then lifted to the air by wind current
- Wind abrasion
- Rock materials carried by wind scour,grind and polish desert rock surfaces
- Name three features of wind deposition in arid areas. (3mks)
- Sand Dunes
- Loess
- Draas
- Explain two processes of wind erosion. (4mks)
-
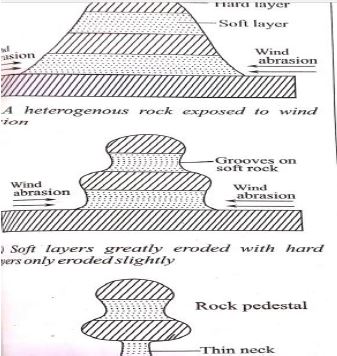
- With the aid of well labelled diagrams describe how a rock pedestal is formed (8mks)
- A large rock mass with alternating horizontal hard and soft layers stand on the wind path
- Weathering and wind abrasion erodes faster on the soft layers than on the hard layers
- Soft layers are eroded inwards forming hollows or grooves while hard layers are left protruding outwards
- Wind abrasion undercuts more near the ground level forming a thin neck
- The result is an irregularly shaped rock pillar called a rock pedestal.
Text -5mks
Diagram -3mks
- Give two ways in which wind transports its load. (2mks)
- Suspension
- Saltation
- Surface creep or rolling
- With the aid of well labelled diagrams describe how a rock pedestal is formed (8mks)
-
-
-
- Name three types of glaciers. (3mks)
- Cirque/corrie glacier
- Valley glacier
- Piedmont glacier
- Continental glacier
- State two reasons why there are no ice sheets in Kenya. (2mks)
- Kenya experiences high temperatures under which ice-sheets cannot form
- Most parts of Kenya are lowlands
- Kenya is found at low latitude region or equatorial area
- Explain two processes of glacial erosion (4mks)
- Plucking/gouging
- Pressure of overlying mass of ice cause freeze-thaw action at the bottom
- Melt water enters cracks and joints on the bedrock
- As water freezes it exerts pressure in the cracking enlarging them
- Enlargement of the cracking leads to disintegration of the rocks
- The broken rocks are then frozen with the ice
- As ice moves it tears out the frozen rocks from the parent rocks a process called plucking
- Abrasion
- Rock materials frozen in the moving ice are dragged over the rocky floor and on the rocky sides of the glacial valley
- The rocks grind and scratch the rocks on the floor and sides of the valley
- This wears and polishes the rocks on the valley bottom and valley sides
- Nivation/freeze-thaw action
- Melt water enters cracks where it freezes and expands due to low temperatures
- Temperature rises and ice in cracks melt
- Repeated freezing and thawing cause pressure in cracks
- The Rocks rot and break.
- Plucking/gouging
- Name three types of glaciers. (3mks)
- The diagram below shows types of moraine in a valley glacier. Use it to answer the following questions
- Name the type of moraines marked A, B and C. (3mks)
- A-Lateral moraine
- B-Medial moraine
- C-Terminal moraine
- Explain how the movement of a valley glacier is influenced by the following factors:
- Temperature changes (2mks)
- In summer temperatures are higher and ice melts and move faster
- In winter temperatures are low hence ice movements is slow due to less melting
- Width of a glacier channel (2mks)
- A wide channel results in slow movement of glacier as the ice spreads out to make a thin layer which exerts less
- pressure hence less melting at the bottom
- A narrow channel causes faster movement as ice is compressed to form a thick layer with more pressure and more melting at the bottom
- Temperature changes (2mks)
- Name the type of moraines marked A, B and C. (3mks)
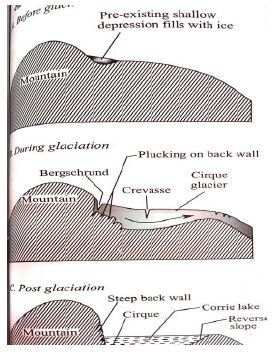
- With the aid of well labelled diagrams, describe how a cirque is formed (6mks)
- Snow accumulates in a pre-existing shallow depression on the mountain side
- Snow gets compacted into ice forming a cirque glacier
- Alternating freeze-thaw cause rotting and disintegration of rocks aprocess called nivation which deepens the hollow
- Abrasion deepens the hollow
- Plucking makes back walls of the depression deeper
- The result is the formation of a deep steep-sided and arm-chair shaped depression called a cirque
4mks –text
2mks -diagram
- Students from Mumbi girls carried out a field study in a glaciated lowland area .
- State two objectives for the study .(2mks)
- to find out the effects of glaciation in the area
- to find out the processes through which the features were formed
- Name two features they are likely to have observed .(2mks)
- till
- drumlins
- eskers
- outwash plain
- State two objectives for the study .(2mks)
-
Download Geography Paper 1 Questions and Answers - MECS Cluster Joint Mock Exams 2021/2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students