Instructions to candidates:
- Write your name, Admission Number and school in the spaces provided above
- Sign and write the date of examination in the spaces above
- Answer ALL the questions in the spaces provided below each question
- Mathematical tables and silent electronic calculators may be used
- All working MUST be clearly shown where necessary
- This paper consists of 14 printed pages
FOR EXAMINER’S USE ONLY
|
QUESTIONS |
MAXIMUM SCORE |
CANDIDATE’S SCORE |
|
1 -30 |
80 |
|
|
TOTAL SCORE |
80 |
|

QUESTIONS
- Molten sodium chloride and graphite both conduct electricity State their difference in electrical conductivity (2mks)
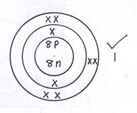
- Element R has atomic number 8 and a mass number 16
- Draw the atomic structure of element R (1mk)
- Explain why R forms a hydride with a low boiling point (1mk)
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow
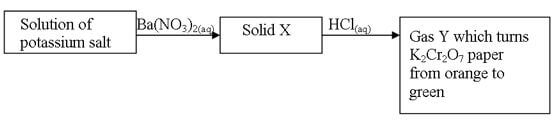
- Name
- Solid X (1mk)
- Gas Y (1mk)
- Name
- Compare the second ionization energy of magnesium with its first ionization energy Explain your answer (2mks)
- The set-up represented below can be used to separate ethanol from its mixture with water
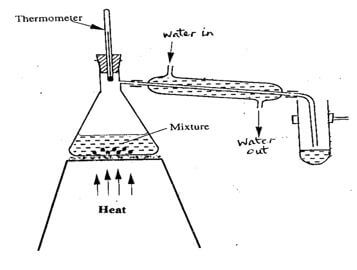
- Identify an error in the set-up (1 mk)
- Name this method of separation (1 mk)
- What properties make it possible to separate ethanol from water by this method? (1 mk)
- Element K has two isotopes 20K and 22K with relative abundance of 90% and 10% respectively
- What are isotopes? (1 mk)
- Determine the relative atomic mass of element K (2 mks)
- Xg of Potassium hydroxide were dissolved in water to make 100cm3 of solution50cm3 of solution required 50cm3 of 2M Nitric acid for complete neutralization Calculate the mass X of Potassium hydroxide (3mks)
- Sulphur burns in air to form a gaseous product
- What is the colour of the flame of burning sulphur? (1 mk)
- Give an equation for the reaction that takes place when the gaseous product is bubbled through water (1 mk)
- State one importance of the product formed in (ii) above (1 mk)
- The figure below shows a paper that was placed horizontally across the middle of a non-luminous flame and quickly withdrawn
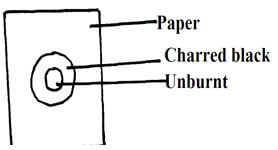
- Explain the observations (1mk)
- Why is luminous flame not used for heating in the laboratory? (1mk)
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow
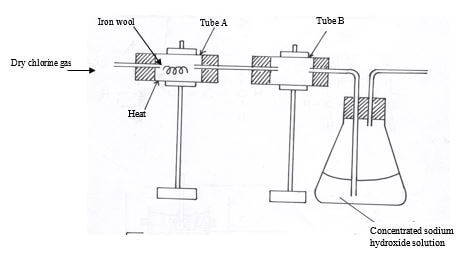
- What is observed when the hot iron wool reacts with chlorine gas? (1mk)
- What is the purpose of:
- Tube B (1mk)
- Concentrated Sodium hydroxide solution (1mk)
- The table below shows results obtained from experiment carried out on a suspect salt solution M
Experiment
Results
I. A few drops of Barium nitrate added to solution M
No ppt/ colourless solution
II. A few drops of lead (II) nitrate added to solution M.
White ppt
III.Ammonia solution added dropwise until in excess
White precipitate
Colourless solution- Identify the cation and anion present in solution M (1mk)
Cation (½ mk)
Anion (½ mk) - Write an ionic equation for the formation of white precipitate in experiment II (1mk)
- Write the formula of the Ion responsible for formation of colourless solution in experiment III (1mrk)
- Identify the cation and anion present in solution M (1mk)
- The diagram below shows a set-up of apparatus used to prepare oxygen gas and pass it over burning candle The experiment was allowed to run for several minutes
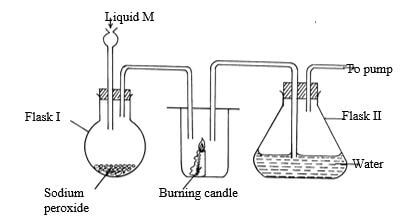
- Identify liquid M (1mk)
- The pH of the solution in flask II was found to be less than 7 Explain (2mks)
- Write an equation for the reaction that forms oxygen gas in the set up (1mk)
- Briefly explain the following
- Alkaline earth metals are generally less reactive than alkali metals (1mk)
- Melting point of alkali metals decrease down the group while melting point of halogens increases down the group (2mks)
- Group VIII elements are gases at room temperature (1mk)
- How would you obtain a sample of pure iodine from a mixture of iodine and lead (II) sulphate (2mks)
- The table below indicates the PH values of solutions labelled A, B, C, D and E
Identify the solution:Solution
A
B
C
D
E
pH value
5
13
2
10
7
- Containing highest concentration of hydrogen ions ( ½ mk)
- That is likely to be ethanoic acid Give a reason (1mk)
- That is likely to be common salt solution ( ½ mk)
- The table below shows physical properties of some substances Use the information to answer the questions that follow
Electrical conductivity Substance
Density (gm-3)
M-P (Oc)
B.P (Oc)
Solid
Liquid M
O
P
Q
R
3.5
0.8
3.8
21.4
1.53
801
-114
3550
-39
660
1413
-84.9
4827
357
2470
POOR
POOR
POOR
GOOD
GOOD
GOOD
POOR
POOR
GOOD
GOOD
- Which of the elements is a liquid at room temperature Explain (1mk)
- Identify the type of structure in
P
R (1mk) - Which element would be the most suitable for use in over-head electric wire transmission? (2 mks)
- An element Y has relative atomic mass 6939 and atomic number 3 it has two isotopes with atomic mass 6015 and 7016 Calculate the relative abudance of the isotopes (3mks)
-
- Give the name of the organic compound formed when methanol and ethanoic acid reacts in the presence of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid (1mk)
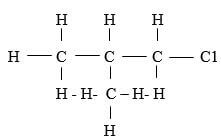
- Write the structural formula of 2 – methylpropane (1mk)
- The diagram below shows how magnesium reacts with steam
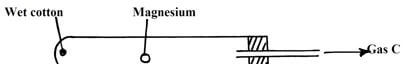
- Gas C would not be produced as in the set-up but when certain condition is introduced gas C is produced On the diagram indicate the condition that was omitted (1mk)
- Describe how gas C is produced after the mistake was corrected in the set-up (1mk)
- Study the information in the table below and answer the questions that follow The letter do not represent the actual symbols of the elements
Element Atomic number Electronic arrangement
X 16
Y 19- Complete the table by writing the electronic arrangement of the elements (1mk)
- Which type of bond is formed between X and Y Explain (2mks)
- Hydrogen chloride gas was passed into water as shown below
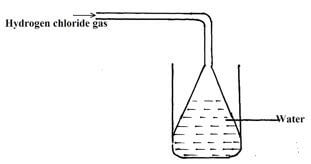
- When a blue litimus paper was dropped into the resulting solution, it turned red Give a reason for the observation (1mk)
- What is the function of the funnel? (1mk)
- The paper chromatogram below shows the identification of unknown metal ions in mixture M The reference ions X, Y and Z are also shown The experiment was done in an ascending method
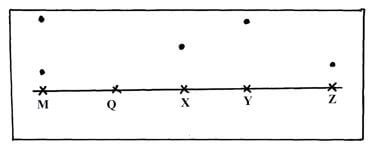
X – Vanadium (IV) ion (V4+)
Y – Chromium (III) ion (Cr3+)
Z – Copper(II) ion (Cu2+)- Name the ions present in the mixture M (1mk)
- Indicate the solvent front on the diagram (1mk)
- Mixture Q contains all the three ions Show the chromatography of Q (1 ½ mks)
- The set-up below shows the preparation of carbon (II) oxide
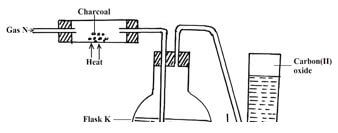
- Name gas N (1mk)
- What is the purpose of sodium hydroxide in flask K? (1mk)
- Why is it necessary to carry out this experiment in a fume cupboard? (1mk)
- Determine the oxidation states of the underlined elements (2mks)
- Fe (CN)63-
Oxidation state of Fe - K [Cr (CN)6]4+
Oxidation state of Cr
- Fe (CN)63-
- The diagram below shows a structure (i) of water molecules
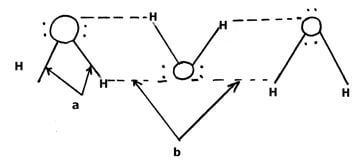
- Name the bonds labelled ( 1 mk)
a
b - Using dots () and cross(x) diagram show the bonding in the compound phosphonium ion
PH4+ (H = 1, P = 15) (1mks)
- Name the bonds labelled ( 1 mk)
- When dry hydrogen gas was passed over a heated lead (II) oxide sample in a combustion tube and the gaseous product cooled, a colourless liquid was obtained
-
- Name the colourless liquid ( ½ mk)
- Describe a chemical test you would use to confirm the colourless liquid in a (i) above (2mks)
- What observation can be made in the combustion tube at the end of the experiment? ( ½ mk)
- Write a chemical equation for the reaction between hydrogen and heated lead (II) oxide (1mk)
-
- State one use of:
- Calcium nitrate (1 mrk)
- Magnesium hydroxide (1 mrk)
- Coloured flower placed in a gas jar containing gas X immediately turned colourless A solution of gas X in water formed a white precipitate with silver nitrate solution The precipitate was insoluble in nitric (V) acid but dissolved in excess aqueous ammonia
- What is the identity of gas X? (1mk)
- Write down the balanced chemical equation of the reaction that took place when:
- Solution of gas X in water reacted with silver Nitrate solution (1mk)
- Aqueous ammonia was added to the resulting mixture in b(i) above (1mk)
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow
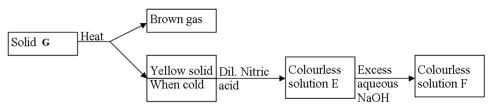
- Identify solid G (1mk)
- Write the formula of the complex ion in solution F (1 mk)
- Describe how you would obtain solid sample of sodium carbonate from a mixture of lead carbonate and sodium carbonate powders (2mks)

MARKING SCHEME
- NaCl – by mobile ions
Graphite – by mobile electrons /delocalized electrons -
 (1mk)
(1mk)
(ii) The hydroxide of R has a molecular½ structure with van-derwaals½ forces in between the molecules. (1mk)
-
-
- Barium sulphite 1mk
- Gas Y – Sulphur (IV) oxide1mk
-
- 2nd ionization energy is greater than first ionization energy of magnesium. ½ second electron is attracted more because protons are more than electrons1
-
- Direction of flow of cold water into and out of the Liebig condenser is wrong 1
- Distillation 1
- Ethanol and water are miscible ½
Their boiling points are different ½
-
- Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same atomic number but different mass numbers 1
- 90 x 20 + 10 x 22 1
100
= 20.2 1
- KOH(aq) + HNO3(aq) → KNO3(aq) + H2O(l)
R.F.M of KOH = 56½
Moles of HNO3 = 50 x 2 = 0.1½
1000
Mole ratio is 1:1 ½
Hence moles of KOH in 50cm3 = 0.1
In 100cm3 is 0.2 moles ½
Mass of X = 0.2 x 56 = 11.2g ½ -
- Blue 1
- SO2(g) + H2O(l) → H2SO3(aq) 1
- Bleaching agent 1
-
- Outer part of non-luminous flame is hotter as there is complete combustion of gas ½
Inner part contains unburnt gases since there is no supply of enough air, paper is unburnt ½ - Produces soot ½ not hot ½ due to incomplete combustion of gas 1mk
- Outer part of non-luminous flame is hotter as there is complete combustion of gas ½
-
- chlorine reacts vigorously½ with hot iron forming dark-brown crystals of iron (III) chloride.½ (1mk)
-
- To collect the iron (III) chloride½ which is a sublimate½ (1mk)
- It reacts½ with excess chlorine gas to avoid emission of poisonous½ chlorine gas into the air (1mk)
-
- – Zn2+ ½
- Cl - ½ - Pb2+ (aq) + 2CL-(aq) → PbCl2(s)
- [Zn ( NH4)] 2+
- – Zn2+ ½
-
- Liquid m = water
- CO2 ½ formed by burning candle, slightly soluble ½ forming an acidic ½ solution
- H2O(l) + Na2O2(s) → 2 NaoH(aq) + O2(g)
-
- Alkali metals lose one electron hence require less energy than alkaline earth meals which lose 2 electrons 1mk
- Alkali metals down group increase in atomic radius hence decrease in strength1 of metallic bond
Halogens increase in size down the 1 group increase strength of van der waals forces - Exist as mono atomic molecules with weak van der waals forces
- Heat the mixture iodine sublimes and is collected in the cooler part of the vessel leaving lead(II) sulphate behind 1
-
- C ½
- A – weak acid ½ ionizes partially
- E ½
-
- Q½- The melting point is below 25ºc while melting point is above 25ºc½ (1mk)
-
- P Giant atomic structure½
- .R Metallic structure½ (1mk)
- R½. -Has low density½ with high melting ½and boiling points.
Is good conductor of electricity½
- Ram = RamY1 x Abudance + Ram Y2 x abundance
100
6.939 = 6.015y + 7.016Y21
100
6.939 = 6.015y1 + 7.016(100-Y1)1
100
693.9 = 6.015Y1 + 701.5 – 7.016Y1
Y1 = 7.7%
Y2 = 100 – 7.7 = 92.3%1
-
- Methylethanoate 1
-
-
- Wet cotton when heated produce steam ½ which react with hot magnesium to form magnesium oxide and hydrogen gas ½
-
- X – 2.8.6 ½
Y – 2.8.8.1 ½ - Ionic / electrovalent 1 because X is a non metal element while Y is a metal 1
- X – 2.8.6 ½
-
- Hydrogen chloride gas is acidic, therefore dissolved in water to give an acidic solution of hydrochloric acid which turned blue litmus paper red.
- To prevent sucking back1mk
-
- – Chromium (III) ion ½
- Copper (II) ions ½ 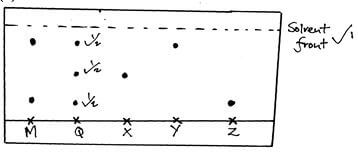
- Check on the diagram
- – Chromium (III) ion ½
-
- Carbon(IV) oxide 1
- To absorb excess /unreacted carbon(IV) oxide gas 1
- Carbon (II) oxide is poisonous 1
-
- -1 R
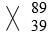
-
- a- Covalent bond ½
B – Hydrogen bond ½ 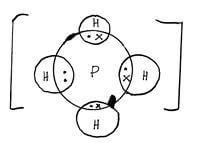
Diagram
Correct electron distribution
Change and brackets
- a- Covalent bond ½
-
-
- Water ½
- – Use anhydrous copper(II)sulphate white if it changes to blue crystals then its water 1
- Anhydrous cobalt (II) chloride blue1 changes to pink 1
- Grey solid ½
- PbO(s) + H2(g) → Pb(s) + H2O(l) bal ½ mk s.s ½ mk
-
-
- nitrogenous fertilizer 1
- in anti-acid medicine 1
-
- Chlorine gas /Cl2
-
- HCl(aq) + AgNO3(aq) → AgCl(s) + HNO3(aq) B.E ½ ss ½
- AgCl(s) + 2NH3(aq) → [Ag(NH3)2]+-(aq) + Cl-(aq)
AgCl(s) + 2NH3(aq) → Ag(NH3)2Cl(aq)
-
- Lead (II) nitrate /Pb(NO3)2 1mk
- [Pb(OH)4] 2-
-
- Add distilled water to the mixture and stir ½
- Filtre to obtain a filtrate of sodium carbonate and insoluble lead carbonate ½
- Heat the filtrate to dryness to obtain dry sodium carbonate solid 1
Download Chemistry Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Mathioya Mock 2021 Exams.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

