- The paper consists of three sections A, B and C.
- Answer all questions in section A and B
- Candidates must answer the questions in English
SECTION A: (30 marks)
- State four advantages of mixed farming to the farmer (2 marks)
- State two reasons for forage conservation (1 mark)
- Give four reasons for using certified seeds for planting (2 marks)
- State four activities carried out by young farmer’s club in Kenya (2 marks)
- Give two benefits of possessing title deed to a farmer (1 mark)
- State four ways of classifying crop pest (2 marks)
- State four observable indicators of economic development of a Nation. (2 marks)
- State two effects of HIV /AIDS on agricultural production. (1 mark)
- State four factors which may affect the quality of Hay. (2 marks)
- State four reasons why burning is discouraged as a method of land clearance. (2 marks)
- Give two forms in which nitrogen is absorbed by crops from the soil. (1 mark)
- State four factors that determine the stage at which crop is harvested (2mks)
- Name two types of non-competitive markets (1 mark)
- State four agricultural activities that may pollute water (2 marks)
- Name four appropriate sites for Agroforestry trees. (2 marks)
- State four characteristics of good seedling for transplanting (2 marks)
- State four financial documents kept by a poultry farmer. (2 marks)
- Name any two types of labour records. (1 mark)
SECTION B: (20 marks)
Answer all question in this section in the space provided
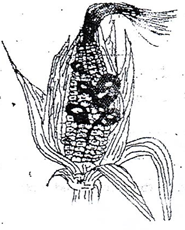
- Below is a diagram showing a crop disease
- Identify the crop disease (1 mark)
- State three control measures for the crop disease (3 marks)
- Name the category in which the disease is classified (1 mark)
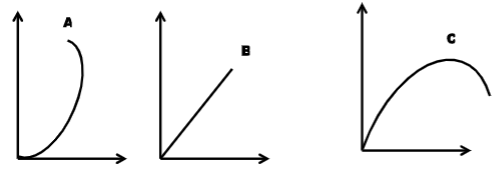
- The following illustration show different production function curves in agricultural economics. Study them and answer the questions that follows.
- Identify the production function curves labeled A and B (2 marks)
- What does the law derived from the production labeled C state (1 mark)
-
- Which one of the three production function curves is rare in agriculture. (1 mark)
- Give reason for your answer in (i) above (1 mark)
- The following is a farm record Mrs. Sanda had kept as at 30th June 2006. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow
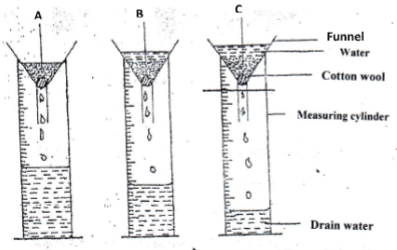
Prepare the balance sheet from the above information for Mrs Sanda’s farm (5mks)Cash in hand 20,000 Cash in bank 66,000 Buildings 50,000 Disc plough 16,000 Debtors 16,000 Working tools 12,000 Bank overdraft 24,000 Creditors 20,000 Loan 50,000 Cattle 40,000 Land 80,000 - The diagram below illustrates an experiment on soil. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow
- State the aim of the experiment (1 mark)
- If the volume of water illustrated in the measuring cylinder was observed after one hour, identify the soil samples labeled
A: …………………………………………………………………...….. (1 mark)
B: ……………………………………………………………………… (1 mark) - State two ways in which the soil structure of the sample labeled C above can be improved (2 marks)
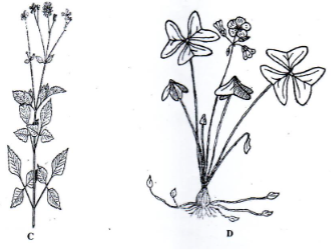
- The diagram below illustrates common weeds in arable land, study them carefully and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the weed labeled
C…………………………………………………………………….….. (1 mark)
D………………………………………………………………………... (1 mark) - Classify the weed labeled C according to plant morphology. (1 mark)
- Explain the reason why it is difficult to control the weed labeled D. (2 marks)
- Identify the weed labeled
SECTION C (40 marks)
Answer any TWO questions from this section
-
- Describe seven problems of marketing of agricultural produce (7 marks)
- State five importance of crop rotation (5 marks)
- Describe cultural pest control (8 marks)
-
- Describe eight factors that contribute to competitive ability of weeds. (8 marks)
- Describe the harvesting of coffee (5 marks)
- Describe production of onion under the following sub-heading
- Seedbed preparation (3 marks)
- Field management practices (4 marks)
-
- Give five reasons why land consolidation should be encouraged in Kenya (5 marks)
- Discuss seven ways by which the government of Kenya can improve on maize production to ensure food security in the country (7 marks)
- Discuss four farming practices that may destroy soil structure. (8 marks)
MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A (30MKS)
-
- Mutual benefit between crops and livestock
- High output for unit area
- Diversification (failure by one enterprise can be compensated by the other)
- Maximum use of land
(½ ×4 =2mks)
-
- To be used during dry period
- Can be sold to generate income
- To distribute available forage throughout the year
- To ensure better and full use of available land
(½ ×2=1mk)
-
- Prevent spread of pest and disease
- For high germination percentage
- To increase yield per unit area (production)
(½ ×4=2mks)
-
- Participate in national ploughing contest
- Participate in free planting
- Participate in national show and exhibitions
(½ ×4=2mks)
-
- Can be used to secure credit facilities (loan)
- Act as security of tenure (minimize land disputes)
- Enables the farmer to lease/sell the land or part of the land
- The farmer can do long term and permanent investment
(½ ×2=1mk)
-
- Mode of feeding
- Crops attacked
- Stage of development of pests
- Stage of growth of the attacked
- Level of damage
- Place where they are found
(½ ×4=2mks)
-
- Infrastructural development
- Gross domestic products
- Per capital income
(½ ×4=2mks)
-
- Lack of motivation to i9nvest in farming
- Diversification of agricultural funds to medication
- Lack of strength to work in the farm hence low labor
- High independency hence low living standards
(½ ×2=1mk)
-
- Forage species used
- Stage of harvesting (leaf: stem ration)
- Length period\
- Weather condition during drying period
- Condition of the storage structure
- (½ ×4=2mk)
-
- Destroy soil structure
- Kills living organisms
- Destroys soil organic matters/mineral
- Lead to poor soil aeration
- Alters soil PH
( ½ ×4=2mks)
-
- Nitrate ion ( NO3-)
- Ammonium ion (NH+4)
(½ ×2=1mk)
-
- Chemical concentration
- Weather condition
- Market demand (price)
- Level of maturity
(½ ×4=2mks)
-
- Monopolistic market
- Oligopolistic market
- Monopsonistic market
(½ ×2=1mk)
-
- Cultivating along the river banks
- Excess use of fertilizers
- Excess use of pesticides
- Overgrazing (stocking)
(½ ×4=2mks)
-
- Homesteads
- Riverbanks
- Slopes
- Swampy areas
(½ ×4=2mks)
-
- Should be healthy (free from pest and diseases)
- Should be vigorously growing
- Should be pencil thick
- Should be 8-10cm tall
- Should be 4-6 follage leaves
(½ × 4=2mks)
-
- Invoice
- Statement
- Delivery note
- Receipts
- Purchase order
(½ × 2mks)
-
- Labour utilization records
- Mast roll labour records
( ½ ×2mks)
SECTION B (20MKS)
-
- maize smart (1x1 -1mk)
-
- Use of certified seed
- Use of clean planting material
- Crop rotation
- Proper field hygiene (1x3 -3mk)
- Fungal disease (1x1 -1mk)
-
-
- A - Increasing production formation curve
- B - Constant production formation curve (1x2 -2mks)
- Increase in input increases output up to a point in which any additional input leads to a decrease in output (1x1 -1mk)
- Because there are other factors that influence agricultural production apart from the factors of production e.g. environmental factors (1x1 -1mk)
-
- Mrs. Sand farm balance sheet as at 30th June 2006
Liabilities Assets Long Term Loan 50,000Bank Overdraft 24,00074,000Short TermCreditor 20,00094,000Capital 206,000
300,000Fixed Assets Building 50,000cattle 40,000Land 80,000 170,000Current AssetsCash 20,000Bank 66,000DSC Plough 16,000Debtors 16,000Tools 12,000130,000300,000 -
- to compare drainage of different soil types (1x1 -1mk)
-
- A - sandy soil
- B - loamy soil (1x2 -2mks)
-
- construction of cumbered beds
- panting of trees
- underground pipes
- French drains (1x2 -2mks)
-
- C-Black jack (1×1=1mk)
D- Oxalis (1×1=1mk) - Broad leaf (1×1=1mk)
- Has the underground structure (bulbs) which goes deep/spread hence difficult to control 2×1=mk)
- C-Black jack (1×1=1mk)
SECTION C
-
-
- Statutory interference by the Government in agricultural marketing causing artificial shortages.
- Poor training for people involved in marketing Leading to heavy losses to farmers.
- Bulkiness of most agricultural produce making transportation difficult and expensive.
- High perishability of most agricultural produce leading to low quality.
- Seasonality of agricultural produce leading to price fluctuations.
- Inadequate storage facilities leading to heavy losses of produce.
- Poor infrastructure leading to high transport costs and spoilage of agricultural produce.
- Change in market demand due to time lag between production and marketing.
- Change of supply of agricultural produce leading to fluctuation of market prices.
- Inadequate market information to farmers leading to selling of farm produce when the prices are low,
- Lack of capital to finance various marketing functions, for example: advertising and transportation.
- Competition with synthetic products leading to loss of market.
-
- Increase Soil Fertility
- Get Better Nitrogen Use
- Improve Soil Structure
- Prevent Soil Erosion
- Increase Crop Yields
-
- Use of healthy planting materials - Prevent infection.
- Proper pruning - discourage disease causing organism.
- Planting resistant varieties - withstand the effect of certain diseases.
- Use of field hygiene - kill disease causing organism.
- Rogueing - destroying pathogens which could cause the disease.
- Proper drying of cereals or pulse - done before storage to make seed coat difficult to be attacked.
- Proper spacing - control some diseases.
- Quarantine - prevent spread of the disease.
- Timely harvesting - reduce disease build up.
- Close season - avoid build up of disease causing organism.
- Crop rotation - reduces disease build up.
-
-
-
- Ability to produce large quantities of seeds..
- Weed seeds remain viable in the soil for a long time.
- Easy and successful dispersal mechanism of most weed seeds.
- Ability of sonic weeds to propagate vegetatively.
- Ability to survive even under adverse environmental conditions.
- Ability to complete their life cycles in a short time.
- Elaborate or extensive root system.
-
- Pick red ripe berries/cherries;
- Spread the berries on sisal mats and sort them out into Grades 1, 2 and 3 (Mbuni)
- Deliver grades 1 and 2 to the factory for pulping same day;
- Dry grade 3:
- Deliver grade 3 to factory at the end of harvesting season;
- Picking interval of 7 - 14 days.
-
-
- Clear the land;
- Prepare the land early;
- Plough/dig deeply and eradicate all weeds:
- Harrow to a moderate tilthffine tilth/appropriate tilth.
-
- Thinning in directly planted crops to reduce competition;
- Weeding should be done carefully so as not to damage shallow roots.
- Remove excess soil from root region.
- Do not compact the soil around the bulb:
- Top dress with nitrogenous fertilizer/CAN at a rate of 250 Kg per ha three months after planting;
- Spray with appropriate pesticide/chemical to control pests especially thrips;
- Spray with fungicides or practice crop rotation to control fungal diseases:
- Watering during dry spell/season.
-
-
-
-
- Proper supervision
- Saves time and travel costs between plots:
- Easy to offer extension services on the actual and on-spot inspection of land:
- Encourages sound farm planning and adoption of crop rotation programmes;
- Encourages soil conservation and land improvement;
- Encourages mechanization due to enlarged holdings:.
- Encourages construction of permanent structures/undertake long term project investments;
- Enhances weed, pest and disease control.
-
- Farmers training cg. in FTCs on improved methods of maize production.
- Provision of extension services to advise farmers on modern maize production techniques cg. irrigation. use of certified, irrigation, pest and disease control to reduce cost of production.
- Provision of subsidies on farm inputs eg. fertilizers.
- Provision of credit facilities cg. through AFC. to finance maize farming operations.
- Imposing high taxation on imported wheat and maize products to discourage importation and protect local fanners.
- Quality control to ensure production of high quality maize that can attract foreign markets.
- Supporting research into new and improved varieties of maize for high yields.
- Farm input supplies
- Provision of marketing services
- Provision of drying and storage facilities
- Provision of tractor - hire service.
- Ensuring effective control of pests/diseases/weeds.
- Ensuring effective soil and water conservation measures.
-
- Use of heavy machinery creates hardpans;
- Over cultivation which over pulverizes soil;
- Cultivating very wet soil using heavy
- Machinery creates hardpans;
- Deforestation destroys soil cover;
- Overstocking destroys soil cover;
- Burning cracks the soil and destroys soil cover;
- Continuous cropping over pulverizes soil;
-
Download Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Bondo Mocks 2021 Exams.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students