QUESTIONS
- The following are atomic and ionic radii of elements in the same group of the periodic table. The letters are not actual symbols of the elements
Elements Atomic radius Ionic radius A 0.133 0.216 B 0.114 0.195 C 0.099 0.181 - Identify the strongest oxidizing agent.
- Give reasons for answer in (a) above?
- Which element has the highest atomic number? Explain?
- P, Q and S are solutions with pH values
Which solution is likely to be:Solutions pH value P 7.0 Q 6.5 S 5.0 - Water obtained from location near greenhouse?
- Water collected near a contact process plant.
- Distilled water (1mk)
- Write a balanced ionic equation to:
- Explain how temporary hardness in water is removed using soda ash.
- Give one disadvantage of using hard water in washing.
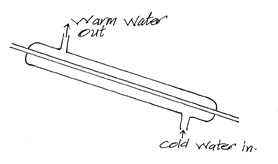
- Draw a simplified diagram of a common Liebig condenser and show direction of water using arrows.(2mks)
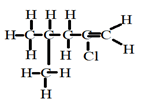
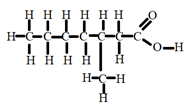
- Draw structures of the following compounds
- 2-chloro-4-methylpent-1-ene. (1mk)
- 3-methylheptanoic acid. (1mk)
- Study the monomer below
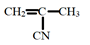
- Draw the structure of its polymer. (1mk)
- A sample of polymer formed from the monomer above has a molecular mass of 4020. Determine the number of monomers making up the polymer. (H=1, C=12, N=14). (2mks)
- Nitric (V) acid is a major product of Ostwald process with 65% purity.
- State how its concentration is increased.
- What gives a yellow colour of the acid? How is it removed?(2mks)
- Name the type of artificial Name the type of artificial radioactivity represented by each of the following nuclear equations.
-
-
- Give two differences between nuclear reactions and chemical reactions. (2mks)
-
- Complete the table below.
Species Number of electrons Number of neutrons 108
Ag +
47 - A given volume of ozone (O3) diffused through a porous hole in 144 seconds. How long would it take equal volume of Sulphur (IV) oxide to pass through same hole? (O = 16, S =32)
- One way to increase the yield of methanol from hydrogen and carbon (II) oxide is to lower the temperature of the system. Why is it not advisable to lower the temperature below the optimum 250ºc. (2mks)
2H2(g) + CO(g) ⇌ CH3OH(g) ΔH = -90vJ/mole - The apparatus below was used to investigate products formed during electrolysis of brine (concentrated sodium chloride).
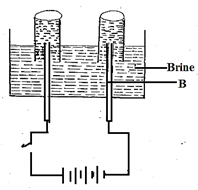
- Write equation at electrode B. (1mk)
- If electrode B was replaced with mercury electrode. Name product formed? Explain.
- A solution contains 7.5g of solute X in 20cm3 of water. When the solution is cooled, crystals of X begin to appear at 10ºc. Determine solubility of solute X at 10ºc.(2mks)
- Explain the difference in melting point of magnesium oxide 3080ºc and phosphorous (V) oxide 563ºc. (2mks)
- How would you confirm presence of lead in an ore? (3mks)
- Why do latent heat of fusion and latent heat of vaporization increase from sodium to aluminum in third period. (2mks)
-
- Write an equation for reaction between chlorine and hot concentrated sodium hydroxide. (1mk)
- Explain how chlorine is used in water treatment. (1mk)
- A fixed mass of a gas occupies 300cm3 at 15ºc and 740mmHg. At what temperature will the gas occupy 450ºc at pressure of 780mmHg? (3mks)
- When a sample of hydrated Iron (II) sulphate (FeSO4.nH2O) was heated until a constant was obtained the following data was recorded.
- Mass of evaporating dish = 50.00
- Mass of evaporating dish + hydrated salt = 55.20
- Mass of evaporating dish + residue = 52.84.
Calculate value of n. (Fe = 56, S = 32, O=16, H=1). (3mks)
-
- Define the term standard molar heat of formation. (1mk)
- Draw an energy cycle diagram to show how the standard heat of formation of ethane (C2H6) can be determined from standard heat of combustion of its element(2mks)
- When a piece of potassium metal is placed in water, it becomes “ball like” and darts on the surface of water as it gets diminished. Explain why the metal become “ball like”.
- The flow chart below shows steps in extraction of Zinc study it and use it to answer questions that follows.
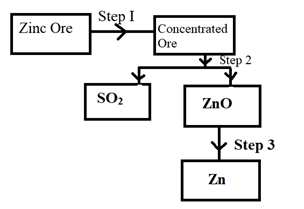
- Name the process in Step I.
- Write a balanced chemical equation in Step 2.
- Name the ore used in extraction of Zinc in above flow chart.
- A mass of 3.2g of XOH reacts completely with 20cm3 of 2.0M H2SO4(aq)
- Write an equation for the reaction.
- Calculate the relative atomic mass of X in the formula XOH. (O=16, H=1). (3mks)
- A Compound whose general formula is M(OH)3 reacts as shown below:
- M(OH)3(s) + OH-(aq) → M(OH)-4(aq)
- M(OH)3(s) + 3H+aq → M3+(aq) + 3H2O(l)
- What name is given to compounds which behave like M (OH) in the two equations above? (1mk)
- Name two elements whose hydroxide behave like that of M. (2mks)
- Diamond and graphite are allotropes of carbon.
- What are allotropes? (1mk)
- Explain why graphite conducts electricity while diamond does not? (2mks)
- A piece of blue and red litmus paper were placed in a beaker containing water into which aluminum chloride had been dissolved.
- Is dissolving aluminum chloride in water physical or chemical process. (1mk)
- State and explain the observation. (1mk)
- Consider electrochemical cell below
Zn(s) / Zn2+(aq) // Pb2+(aq) / Pb(s)- Name the electrode in above cell. (1mk)
- Write half ionic equation involving oxidation in above electrochemical cell. (1mk)
- Name the possible salt bridge.(1mk)
- The diagram below is a part of a set up used in preparation of a particular gas in the laboratory.
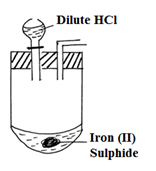
- Complete the diagram to show how dry sample of gas can be collected. (3mks)
- Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction in the diagram. (1mk)
- When SO2 sulphur (IV) oxide gas is bubbled through acidified KMnO4 solution the reaction takes place according to the following equation.
- Calcutate the oxidation number of manganese in:
- MnO-4
- MnO4
- During the reaction was manganese oxidized or reduced? Explain.(1mk)
- Calcutate the oxidation number of manganese in:

MARKING SCHEME
-
- C
- Smallest atomic radius.It has a greater nuclear pull of electrons hence attracts electrons more.
- A½ it has largest atomic radius
-
- Q
- S
- P
-
- Ca2+(aq) + CO2-3(aq) → CaCO3(s)
Or
Mg2+(aq) + CO2-3(aq) → MgCO3(s) - Formation of calcium/magnesium octadecanoate which dirties white linen.
Or – wastage of soap (1mk)
- Ca2+(aq) + CO2-3(aq) → CaCO3(s)
-
-
-
-
-
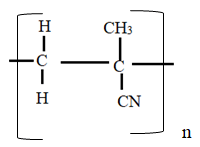
- R.A.M of monomer = (4 x 12) + (5 x 1) + (1 x 14) = 67
No of monomers = 4020
67
= 60 units
-
-
- By distilling it over concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid or phosphorous (V) oxide.
- Dissolved nitrogen (IV) oxide formed due to decomposition of HNO3.
Removed by bubbling air through the acid.
-
-
- Nuclear fusion
- Nuclear fission
Accept any two correct (2mks)Nuclear reactions Chemical Reactions Involves protons and neutrons
Involves large amounts of energy.
Not affected by environmental factorsInvolves valence electrons
Little amount of energy is released
Affected by environmental factors
-
- Number of electrons 47
Number of neutrons 61 - 144 = √48
TSO2 64
(TSO2)2 = 64 x (144)2
48
(TSO2)2 = 27648
(TSO2)2 = √27648
= 166.28sec - The rate of the reaction would be low. Decrease in temperature below optimum reduces the kinetic energy of reacting particles (molecules) hence reducing the number of effective collisions. (less effective collisions per unit time)
-
- 2H+(aq) + 2e → H2(g)
- Sodium metal would be deposited.
Mercury electrode is not inert: sodium ions would be preferentially discharged.
- 7.5g → 20cm3 of H2O
x → 100cm3 of H2O
x = 7.5 x 100
20
= 37.5g/100g of water. - Magnesium oxide has a giant ionic structure with strong ionic bonds that require a lot of energy to break.
Phosphorous (V) oxide has simple molecular structure with weak vanderwaal forces that require less energy. (2mks) - Crush the ore
Add nitric (V) acid to dissolve.
Filter to obtain the filtrate.
To the filtrate add potassium iodide solution
A yellow ppt formed confirms presence.
Or
To the filtrate add sodium chloride solution
A white precipitate is formed.
Warm the mixture
Dissolves to form a colourless solution confirms
(3mks) - Across a period proton increases sodium has less protons that have a weaker metallic bond compared to aluminum that has more number of delocalized electrons hence stronger metallic bonds.
-
- 6NaOH(aq) + 3Cl2(g) → NaClO3(aq) + 5NaCl(aq) + 3H2O
- Lowers the pH of water hence killing the microorganism.
- P1V1 = P2V2
T1 T2
750 x 300 = 780 x 450
288 T2
T2 = 780 x 450 x 288
750 x 300
T2 = 176.28k (3mks) - FeSO4 : H2O
Mass 2.84 2.36
R.F.M 152 18
No of moles 2.84 2.36
152 18
0.01868 0.311
Mole ratio 0.01868 0.1311
0.01868 0.01868
1 : 7
N = 7 (3mks) -
- The enthalpy change that occurs when one mole of a substance is formed from its constituent elements under standard conditions.
-
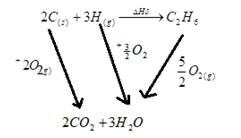
- The reaction is highly exothermic, the heat evolved melts potassium to a silvery ball.
-
- Froth flotation
- 2ZnS(s) + 2O2(g) → 2ZnO(s) + SO2(g)
- Zinc blende (3mks)
-
- 2XOH(aq) + H2O4(aq) → X2SO4(aq) + 2H2O(l)
- Mole of acid = 2.0 x 20
1000
= 0.04moles
Moles of XOH
1mole = 0.04
2moles = x
= 0.08
R.F.M of XOH = 3.2
0.08
= 40
x + 16 + 1 = 40
x = 40 - 17
x = 23 (3mks)
-
- Amphoteric
- Zinc
Lead
-
- Crystalline forms of an element that occurs in the same physical state.
- Graphite uses 3 valence electrons out of the four in covalent bonding one electron remains delocalized.
In diamond all the four valence electrons takes part in covalent bonding.
-
- Chemical process.
- Blue litmus paper turns to red and the red litmus remains red.
AlCl3 is hydrolyzed by water to form an acidic solution. (2mks)
-
- Anode – Zinc/Zn
Cathode – Lead/Pb - Zn(s) → Zn2+aq + 2e
- Filter paper soaked in concentrated solution of KNO3/NaNO3
Or U-tube filled with KNO3/NaNO3 solution.(1mk)
- Anode – Zinc/Zn
-
-
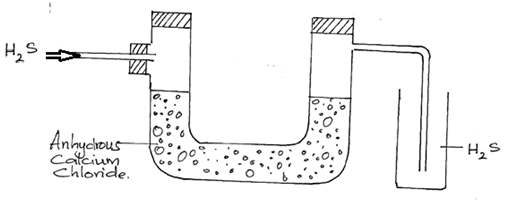
- drying agent
- method of collection
- workability
- FeS(s) + 2HCl(aq) → FeCl2(aq) + H2S(g)
-
-
-
- Mn + 4(-2) + -1
Mn = -1 + 8
Mn + +7 - Mn + 4(-2) = 0
Mn - 8 = 0
M = +9
- Mn + 4(-2) + -1
- Oxidised; manganese has lost an electron to be oxidized to manganese of positive +8. (3mks)
-
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Cekenas Mock Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students