INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES:
- You are supposed to spend the first 15 minutes of the 2 ½ hours allowed for this paper reading the whole paper carefully before commencing your work.
- Marks are given for a clear record of the observation actually made, their suitability, accuracy and the use made of them.
- Candidates are advised to record their observations as soon as they are made
- Non-programmable silent electronic calculators may be used.
QUESTION 1
You are provided with the following: -
- 2 dry cells
- A cell holder
- A switch
- An ammeter
- Five connecting wires
- Wire mounted on the metre rule labelled x
- A micrometer screw gauge [ to be shared
- A Voltmeter
Proceed as follows
- Measure the diameter of the wire three times and determine the average diameter,
- D ………………. m (2 marks)
- Determine the cross-section area of the wire, A………………. m2 (1 marks)
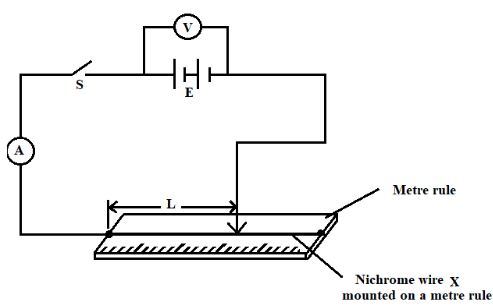
- Connect the circuit as shown in the figure below.
- Measure the voltage E from the Voltmeter, before closing the switch.
E = ................................ (1 mark) - Adjust the length, of the wire to 0.2m, close the switch, S and read the value of current and record in the table below.
Length, (m) 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 Current, I (A) 1/I (A−1) - Repeat the procedure in (c) above for the values of lengths given. (5 marks)
- Calculate the value of 1/I and record in the table above. (1 mark)
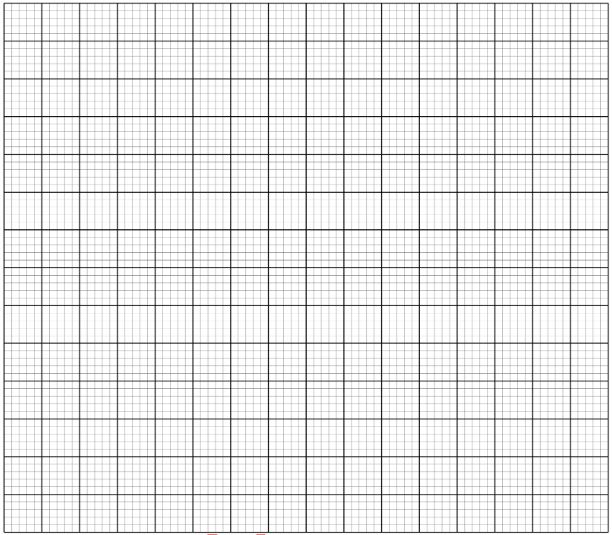
- On the grid provided plot a graph of 1/I (y- axis) against l (5 marks)
- Determine the gradient of the graph. (2 marks)
- Given that, 1/I = δ/EAl + r/E , determine the value of δ and r. (3 marks)
QUESTION 2
You are provided with the following:
- a metre rule
- knife edge raised 20 cm above bench
- one 50 g mass and one 100 g mass
- a beaker or any container
- some thread
- some water in a beaker
- Liquid L in a beaker
- tissue paper
- A triangular glass prism
- A piece of soft board
- Four optical pins
- Four office pins
A sheet of plain paper
PART A
Proceed as follows:
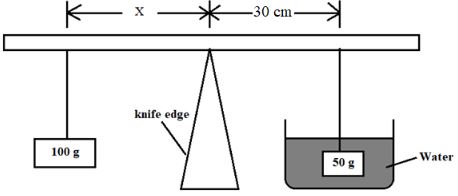
- Balance the metre rule edge and record the reading at this point
Balance point = cm (1 mark)
For the rest of this experiment the knife edge must be placed at this position - Set up the apparatus as shown in the figure below.
- Use the thread provided to hang the masses such that the positions of support can be adjusted. The balance is attained by adjusting the position of the 100g mass.
Note that the distances X is measured form the knife edge and the 50g mass is fully submerged in the water. - Record the value of X .
X = cm (1 mark) - Apply the principle of moments to determine the weight Ww of the 50 g mass in water and hence determine the up thrust Uw in water
Ww N (2 marks)
Uw N (1 mark) - Remove the 50 g mass from the water and dry it using tissue paper.
- Maintaining the distance of 30cm in step (d), now balance the metre rule when the 50 g mass is fully submerged in the liquid L Record the value of the distance X.
X= cm (1 mark) - Apply the principle of moments to determine the weight WL of the 50 g mass in the liquid L and hence determine the upthrust UL in the liquid
- WL = (2 mark)
- UL = (1 mark)
- RD of liquid L (2 marks)
PART B
Proceed as follows:
- Place the plain sheet of paper on the soft board and pin it using the office pins at the comers. Trace the triangular prism outline of the prism on the sheet of paper (use the upper part to leave space for two other outlines on the same page). Label the vertices of the outline at A, B and C. Remove the prism from the paper.
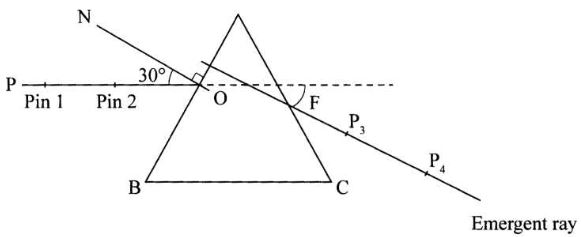
- On the outline at a point O near the centre of side AB draw a normal ON.
- Draw a line PO at an angle of 30° to the normal ON as shown in the figure below.
- Replace the prism accurately on the outline. Fix two optical pins vertically on line PO at different points (see the figure below).
- View the images of the two pins through side AC of the outline. Fix a third and fourth pin vertically such that they are in line with the images of the first and second pin. Remove the prism and the pins. Draw a line joining the marks made by the third and fourth pins and extend it to join line PO (also extended) as shown below.
Measure F, the angle of deviation of the emergent ray. (2 marks) - Repeat part (e) for other angles of incidence shown in the table below. (Draw a fresh outline of the prism for each angle of incidence)
Complete table 1 (3 marks)
Angle of incidence 30° 50° 70° Angle of deviation - Determine:
- E the angle of emergence (between the emergent ray and the normal at the point of emergence) at the least angle of deviation. (2 marks)
- K given that K = 2sin sin (30 + Fo/2) (where F0 is the least angle of deviation) (2 marks)
CONFIDENTIAL
INSTRUCTIONS TO SCHOOLS
- The information in this paper is to enable the head of the school and the teacher in charge of Physics to make adequate preparations for the Physics practical examination. NO ONE ELSE should have access to this paper or acquire knowledge of its contents.
- The teacher in charge of physics should NOT perform any of the experiments
- Utmost care must be taken when handling the confidential.
Each candidate should be provided with the following:
Question One
- A metre rule
- 3 optical pins
- 2 small wooden blocks (atleast 4 cm x 4cm by 1cm )
- A stop watch
- A stand, a boss and clamp
- A piece of sellotape
- Question Two
- A triangular glass prism
- A piece of soft board
- 4 optical pins
- Two sheets of plain paper
- Thumb pins/Thumb stacks
- Ammeter (0-1A)
- A voltmeter (0 – 3V) or (0 – 5V).
- A switch.
- A micrometer screw gauge (may be shared).
- 6 connecting wires (two with crocodile clips at the end.)
- One new dry cell (size D 1.5V)
- Cell holder.
- A nichrome with marks AB along its length with length 20cm labeled A B mounted on a cardboard or piece of wood (Nichrome wire SWG 32 and diameter =0.27 ±0.01mm)
MARKING SCHEME
(b) 0.37 + 0.38 + 0.36
3 (Average concept a must for one to score)
= 0.37mm
D = 0.00037 m (1 mrk)
(c) Area = 22/7 x (3.7/2 x 10−4)2 = 1.076 x 10−7 m2 (1 mrk)
(e) E = 3,0 ± 0.2V (1 mrk) 1d.p a must
(f)
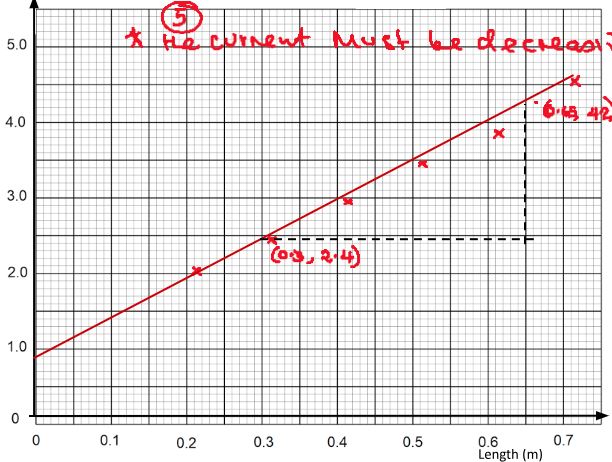
| Length, (m) | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 |
| Current, I (A) | 0.50 | 0.42 | 0.34 | 0.29 | 0.26 | 0.22 |
| 1/I (A−1) | 2.000 | 2.381 | 2.9412 | 3.448 | 3.846 | 4.545 |
< I < 0.20
(h) Any correct 5 within the range (5 mrks)
A1 - award for correctly labelled axis and unit of the quantity given
S1 - award if the scale is uniform, simple and accommodative
P2 - Award 2 marks if all the points in the table are correctly plotted. Deny one mark for between 3 and 5 points plotted correctly. Otherwise give a zero
L1 - Award one mark for line of best fit. (MUST pass through atleast three points)
(j) Slope = Δ1/l(A−1) = 4.2 − 2.4 (2 mrks)
Δ/(m) 0.65 − 0.30
= 5.143A−1m−1
(k) Slope = δ/EA (2 mrks)
δ = 5.143 x 3.0 x 1.076 x 10−7
= 1.6602 x 10−6 Ωm
1/l intercept = r/E
r = 3.0 x 0.8 = 2.4Ω (2 mrks)
Question 2
Part A
(a) Balance point = 50.0 cm ± 1 cm (1 mrk) 1dp a must
(d) x = 14.0 cm ± 1 (1 mrk) 1dp a must
(e) F1d1 = F2d2
1 x 14 = F2 x 30
F2 = 0.4667 N (2 mrks) Use student's value
Uw = 0.5 − 0.4667
= 0.0333N (1 mrk) Use student's value
(g) x = 14.2cm
(h) (i) 1 x 14.2 = WL x 30 (1 mrk) 1dp a must
WL = 0.4733N (2 mrks) Use student's value
(ii) UL = 0.5 − 0.4733
= 0.02667N (1 mrk)
(iii) RD of L = 0.02667 = 0.8001
0.03333
Part B
(f)
| Angle of incidence | 30° | 50° | 70° |
| Angle of deviation | 45° | 40° | 46° |
( 3mrks)
±, deny if no units.
Each value within the range a mark
(g) (i) θ − = 27° (1 mrk)
E = 90 − 27 = 53° (1 mrk) mark student's value
(ii) K = 2 sin sin ( 30 + F0/2)
= 2 sin sin ( 30 + 38/2) (1 mrk)
= 2 sin sin 49
= 1.509 (1 mrk)
Mark student's value
Download Physics Paper 3 Questions and Answers with Confidential - BSJE Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students