- This paper consists of three sections A, B and C.
- Answer all questions in section A and B.
- Answer any two questions in section C.
- All answer must be in English.
SECTION A (30MARKS)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided
- Name a breed of camel with two humps (½mks)
- State two types of roughages as used in livestock nutrition (1mk)
- Give two reasons why it is advisable to dehorn cattle (1mk)
- Give three properties of clean milk (1½mks)
- Name the tool or equipment used to carry out the following routine livestock practices
- Castration (½mks)
- Vaccination (½mks)
- What is the role of iron in livestock nutrition? (1mk)
- List two importance of fish farming in Kenya (1mk)
- Name two hormones that in fluence milk let-down in dairy cattle (1mk)
- Name two exotic breeds of dairy goats reared in Kenya (1mk)
- What is the role of a crop in the digestion system of poultry? (2mks)
- Name two zoonotic diseases of livestock (1mk)
- Give four routine practices carried out during calf rearing (2mks)
- State two factors that determine the amount of water required by an animal (1mk)
- List three methods of outbreeding as used in livestock nutrition (11/2mks)
- Outline four conditions necessary for artificial incubation (2mks)
- List three sources of lipids in livestock diet (11/2mks)
- Name two parasites of bees (1mk)
- State four qualities of an ideal calf pen (2mks)
- Give four reasons why stones are good as construction materials (2mks)
- Name a disease transmitted by the following vectors (1mk)
- Tsetse fly
- Brown ear tick
- List four requirements in a deep litter house (2mks)
- Give two causes of soft shells in eggs (2mks)
SECTION B (20MKS)
Answer all questions in this section in the spaces provided - Study the diagram and answer questions that follow.
- Identify the condition or deficiency disease as illustrated in J and K above
J (1mk)
K (1mk) - Name cause of the deficiency condition in
J (1mk)
K (1mk) - Give one remedy to control condition K in lactating cows (1mk)
- Identify the condition or deficiency disease as illustrated in J and K above
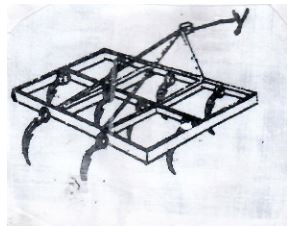
- Below is a diagram illustrating a farm implement. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the implement (1mk)
- State:
- The role of the part labelled Y (1mk)
- Three uses of the implement on the farm (3mks)
- List two maintenance practices carried out on the implement (2mks)
- The diagram below represents methods of identifications in livestock. Use them to answer questions that follow.
- Name the three methods shown above (11/2mks)
- State three importance of identification method shown above (11/2mks)
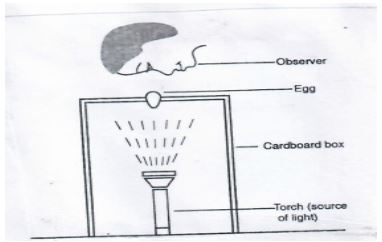
- The diagram below illustrates a common practice in poultry production
- Identify the practice (1mk)
- Give abnormalities of eggs that can be observed using the above illustrated practice (4mks)
SECTION C (40MKS)
(Answer any two questions from this section)
-
- Discuss causes and control of cannibalism in poultry. (10mks)
- Highlight various measures that famers undertake to control tapeworms (5mks)
- Explain the importance of streaming up in dairy cattle (5mks)
-
- Describe the precautions undertaken while handling farm tools and equipment(10mks)
- Discuss contagious abortion disease under the following sub headings:
- Animals attacked (2mks)
- Casual organism (2mks)
- Symptoms (2mks)
- Control measures (4mks)
-
- Discuss the structural and functional differences between petrol and diesel engines (10mks)
- Describe general characteristics of indigenous cattle breeds (5mks)
- Outline five general methods of disease control in livestock (5mks)
MAKING SCHEME
- Bactrian (½ mk)
-
- Succulent roughages 2x ½ = (1mks)
- Dry roughages
-
- Dehorned animals use less space
- For easy handling of animals(make animal docile)
- To prevent injury to the farmer and other animals
- Prevent destruction of farm structures 2x ½ =(1mks)
-
- Free from pathogens
- No hair, dirt or dust
- Has good flavour
- Its chemical composition is within the expected standards
- It is of high keeping quality 3x ½ = (1½mks)
- Should be pure white in colour
-
-
- Burdizzo
- Rubber ring
- Elastrator
- Scalpel (1 x ½ = ½ mks)
-
- Hypodermic needle and syringe
- Drenching gun (1 x ½ = ½ mk)
-
- Formation of haemoglobin in blood (1mk)
-
- Source of income to the farmer
- Source of food/ source of protein
- Source of employment
- Source of raw materials to industries 2 x ½ = (1mk)
-
- Oxytocin
- Adrenaline
- Alpine / prolactin 2 x ½ = (1mk)
-
- Saanen
- Toggenburg
- British alpine 2 x ½ = (1mk)
-
- Moisten the food
- Temporary storage of food (2 x 1 =(2mks)
-
- Brucellosis
- Rabies
- Tuberculosis
- Anthrax
- Mastitis 2 x ½ = (1mk)
-
- Feeding
- Parasite control
- Disease control
- Castration
- Removal of extra teat
- Identification 4x ½ = (2mks)
-
- Ambient temperatures
- Type of food eaten by animal
- Level of production
- Amount of work done by an animal
- Weight/body size of an animal
- Species of an animal 2 x ½ = (1mk)
-
- Outcrossing
- Upgrading
- Cross breeding 3 x ½ = (1 ½ mks)
-
- Temperature must be maintained at 37.50c – 39.40c
- There should be enough air circulation
- Relative humility must be maintained at 60%
- Egg turning 4 x ½ = (2mks)
-
- Oil seed by products e.g cotton seed cake
- Animal’s products and by-products e.g milk, bone meal
- Pasture foliage 3 x ½ = (1 ½ mks)
-
- Wax moth
- Ants
- Honey badger
- Bee louse 2 x ½ = (1mk)
-
- Well ventilated
- The roof should be leak proof
- Draught free
- Proper lightning
- Single housing 4 x ½ = (2mks)
-
- Fire resistant
- Durable
- Resistance to insect damage
- Resistance to weathering 4 x ½ = (2mks)
-
- Trypanosomiasis/ nagana rej: sleeping sickness
- East coast fever ( ½ mk)
-
- Litter
- Feed troughs
- Water troughs
- Roosts or perches
- Nests
- Laying nests 4 x ½ = (2mks)
-
- Deficiency of calcium
- Deficiency of vitamin D
- Marek’s disease (2mks)
SECTION B
-
- J – Curled toe paralysis (1 x 1 =1mk)
K – Milk fever (1 x 1 = 1mk) - J – Deficiency of vitamin B2 (1 x 1 = 1mk)
K− Deficiency of calcium (1 x 1 = 1mk) -
- Treatment using calcium borogluconate solution intravenously
- Providing feeds rich in calcium (1 x 1 = 1mk)
- J – Curled toe paralysis (1 x 1 =1mk)
-
- Spring tine harrow (1 x 1 = 1mk)
-
- For attachment of the implement to the tractor. (1 x 1 = 1mk)
-
- Break up soil clods
- Level seedbed
- Improve soil aeration
- Collects trash
- Removal of rhinomatous weeds from the soil
- ACC. Couch grass (first 2 x 1 = 2mks)
-
- Clean after use
- Tighten loose nuts and bolts
- Lubricate moving parts
- Replace worn out tires
- Paint metallic surface when storing
- Implement for long (first 2 x 1 = 2mks)
-
-
- Ear tagging
- Ear notching
- Neck strap (first 3 x ½ = 1 ½ mks)
-
- For selection and breeding
- Disease control and treatment
- Feeding
- Record keeping
- Culling (first 3 x ½ = 1 ½ mks)
-
-
- Egg candling
-
- Double yoked egg
- Blood spot in egg
- Cracks in shell
- Broken egg shell
- Whether the egg is very porous (4 x 1 = 4mks)
SECTION C
-
- Causes
- Imbalanced diet: A diet deficiency in nutrients leads to the birds practicing cannibalism
- Overcrowding makes birds easily detect moving organisms on each other
- Too bright light in the poultry house
- Introduction of new birds in the flock
- Prolapse of the cloaca in laying birds
- Presence of external parasites on the birds e.g poultry lice (5 x 1 = 5mks)
Control- Provide adequate floor space for the birds
- Feed birds on a balanced ration
- Keep birds according to age groups
- Cull perpetual cannibals
- Isolate and treat injured bird
- Debeaking aggressive cannibals
- Hanging green edible vegetables to keep birds busy (5 x 1 = 5mks)
-
- Routine deworming using suitable drugs
- Proper disposal of human waste
- Practicing rotational grazing
- Proper meat inspection
- Ploughing pasture land to kill cysts (5 x 1 = 5mks)
-
- Promote production of high quality colostrum in the next lactation
- Ensure rapid growth and development of foetus to ensure healthy and strong calf at birth
- Build up enough body reserves for the cow before the next parturition
- Build up energy for nutrition
- Increases and maintains high milk yield after birth
- Promote good health of the mother (5 x 1 = 5mks)
- Causes
-
-
- Tools should be left in a safe place after use
- Use the correct tool for the correct purpose
- Maintain tools and service them to remain in good working condition and last longer
- Tools should be handled correctly when in use to avoid damage to the tool and injury to the user.
- Use safety devices i.e fire extinguishers and first aid kits in the workshop to reduce accidents.
- All tools should be stored properly in tool cabinets or in tool racks to prevent injury
-
-
- Cattle
- Sheep
- Goat
- Pigs (any 2 x 1 = 2mks)
-
- Brucella abortus (in cattle)
- Brucella suis (in pigs)
- Brucella malitensis (in goats and sheep) (any 2 x 1 = 2mks)
-
- Spontaneous abortion/ premature birth
- Retained after birth/ placenta
- Bareness in cows and low libido in bulls.
- Yellowish, brown, slimy, odourless discharge from the vulva after abortion (Any 2 x 1 = 2mks)
-
- Use of AI
- Cull and slaughter all affected animals
- Vaccinate all young animals.
- Avoid contact with the aborted foetus
- Carry out blood test/ screening for animals selected for breeding.
- Maintain high hygiene in the farm. ( any 4 x 1 = 4mks)
-
-
-
-
(rej: any answer that does not give a comparative response) (5 x 2 = 10mks)Petrol engine Diesel engine Has carburetor Has an injection pump Fuel and air are mixed into the carburetor before getting into the engine cylinder Fuel and air are mixed within the cylinder Fuel is ignited by an electric spark Fuel is ignited by compression of air and fuel mixture in the cylinder It produces less smoke because petrol is fully burnt. Produces a lot of smoke because diesel is partially burnt. Petrol engine is light in weight and suited for light duties. Diesel engine is relatively heavy and suited for heavy duty. -
- They have hump that store fat
- Highly tolerant to high temperature
- High resistance to tropical diseases
- They can walk for long distances in search of food and water
- They have long calving intervals of more than one year
- They have low production of both meat and milk
- They have slow growth rate leading late maturity (5 x 1 = mks)
-
- Vaccination
- Disinfection and use of antiseptics
- Proper nutrition
- Proper hygiene
- Quarantine
- Proper housing
- Isolation and treatment of sick animals
- Prophylaxis
- Proper breeding and selection (5 x 1 = 5mks)
-
Download Agriculture Paper 2 Questions and Answers - BSJE Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students