INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Answer all the questions in the spaces provided
- Mathematical tables and silent electronic calculators may be used
- All working must be clearly shown where necessary
- This paper consists of 13 printed pages
FOR EXAMINERS USE ONLY
|
Questions |
Maximum Score |
Candidate's Score |
|
1 |
11 |
|
|
2 |
14 |
|
|
3 |
12 |
|
|
4 |
11 |
|
|
5 |
12 |
|
|
6 |
10 |
|
|
7 |
10 |
|
|
TOTAL |
80 |
|

QUESTIONS
- The diagram below shows an experiment to demonstrate the properties of hydrogen as a reducing agent Study it and answer the questions that follow
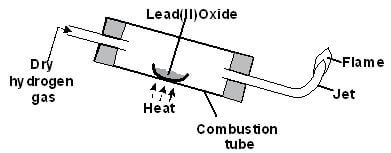
- Before lighting hydrogen gas at the jet, it is important to drive off all the air in the combustion tube Explain (1 mark)
- State what would be observed in the boat containing lead (II) oxide at the end of the experiment (1 mark)
- Write chemical equations for the reaction taking place;
- In the combustion tube (1 mark)
- At the jet as the flame burns (1 mark)
- Why should the supply of hydrogen continue until the apparatus are cool? (1 mark)
- Why is it important to clamp the glass tube or combustion tube in a slanting position? (1 mark)
-
- Cars in Mombasa rust faster than in Kisumu Explain (1 mark)
- Give the factors that are necessary for rusting (1 mark)
- Name two methods used to prevent rusting (1 mark)
- Explain why a nail paced in a sealed tube containing tap water rusts while a nail placed in a sealed tube containing boiled water fails to rust (1 mark)
- State two industrial uses of oxygen gas (1 mark)
- The grid shown below represents part of the periodic table Study it and answer the question that follow The letters do not represent the actual symbol of the elements
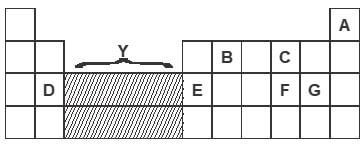
- What type of bonds would be formed between C and G Explain (2 marks)
- Write the formulae of the compounds that would be formed between:
- D and G (1 mark)
- E and G (1 mark)
- State and explain how the compounds formed in (b) above compare in their melting points in terms of structure and bonding (2 marks)
- Give the formulae of the oxides of the elements D and F and state the nature of each oxide
- D oxide (2 marks)
Formulae
Nature - F oxide (2 marks)
Formulae
Nature
- D oxide (2 marks)
- Which of the elements shown does not form an oxide? Explain (1 mark)
- Which two elements shown on the grid are good conductors of electricity? Explain (2 marks)
- What name if given to the group of elements represented by letter Y in the periodic table? (1 mark)
-
- Brine usually contains soluble calcium and magnesium salts Explain how sodium carbonate is used to purify brine (2 marks)
The diagram below represents a diaphragm cell used to electrolysed pure brine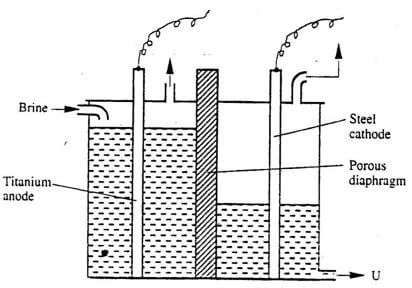
- Write the equations for the reactions that take place at :-
- Cathode (1 mark)
- Anode (1 mark)
- Name:
- Product at U (1 mark)
- Another material that can be used instead of titanium (1 mark)
- The impurity present in the product at U (1 mark)
- State two functions of the diaphragm (2 marks)
- Give one industrial use of the product at U (1 mark)
- State two environmental hazards associated with extraction of sodium metal (2 marks)
- Write the equations for the reactions that take place at :-
- Brine usually contains soluble calcium and magnesium salts Explain how sodium carbonate is used to purify brine (2 marks)
- The diagram below illustrates the contact process for the manufacture of sulphuric (VI) acid
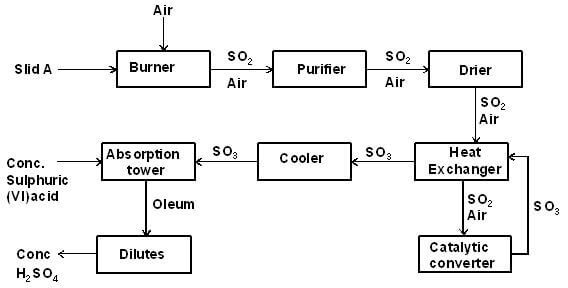
Study it and answer the questions that follow- Name three possible identities of solid A (1½ marks)
-
- Name two impurities removed by the purifier (1 mark)
- Why is it necessary to remove the impurities? (1 mark)
- Write down the equation for the reaction that takes place in the catalytic converter (1 mark)
-
- Name two catalysts that can be used in the converter (2 marks)
- Which of the two catalysts is most commonly used and why? (1 mark)
- Why is sulphur (VI) oxide not absorbed directly into water? (1 mark)
- Give the equation for the reaction that takes place in the absorption chamber (1 mark)
- Name the main pollutant in the contact process (½ mark)
- Name one method by which the pollution is controlled in the contact process (1 mark)
- Study the table below and answer the questions that follow;
Reduction Half-reaction Eq(Volts)
Ag+(aq) + e- ® Ag(s) + 080
Cu2+(aq) + 2e- ® Cu(s) + 034
2H+(aq) + 2e- ® H2(g) 000
Zn2+(aq) + 2e- ® Zn(s) -076
Na+(aq) + e- ® Na(s) -271- Which is the strongest reducing agent in the above half equations? Explain (2 marks)
- Calculate the electromotive force of a cell consisting of Zinc and silver electrodes immersed in solutions of their respective ions (2 marks)
- Give the cell representation of the cell in (b) above (1 mark)
- The diagram below represents an experiment set up used for the electrolysis of aqueous copper (II) sulphate solution Study it and answer the questions that follow;
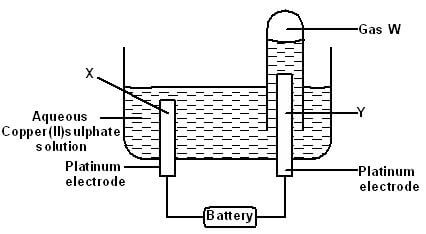
- Name electrodes X and Y (2 marks)
- Name gas W (1 mark)
- Write the overall equation of the reactions taking place at electrodes X and Y (1 mark)
- If a current of 04A was passed through the cell for 15 minutes, calculate the mass of copper that would be liberated (Relative atomic mass of copper = 64, 1F = 96,500C) (3 marks)
- The scheme below shows a series of reactions starting with ethanol Study it and answer the questions that follow
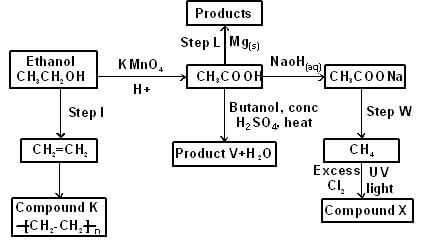
- Give the type of reaction, the reagent(s) and the condition(s) necessary for step 1 to take place (1 mark)
- Write the equation for the reaction that takes place in step L (1 mark)
- Name product V and give the equation responsible for its formation (2 marks)
- Give the reagent(s) and condition(s) necessary for step W to take place (1 mark)
- Give the IUPAC name and structural formula of compound X (1 mark)
- Name compound K and state the type of reaction involved in its formation (2 marks)
- If the relative molecular mass of K is 44800, determine the value of n (C = 12, H = 1) (2 marks)
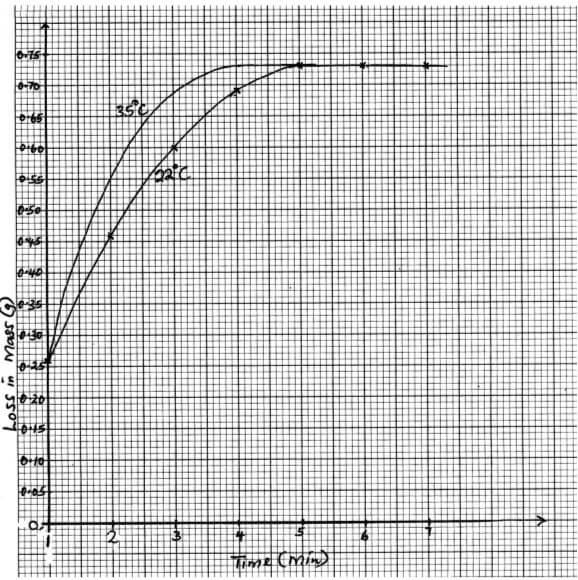
- The set up below is used to measure the change in mass during the course of the reaction between dilute hydrochloric acid (excess) and marble chips at 22°C
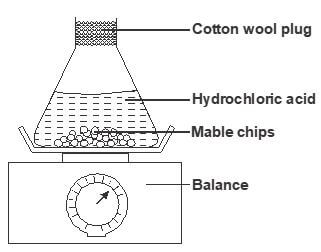
Changes in mass were noted at one minute intervals and were as follows- Give an equation for the reaction taking place in the flask (1 mark)
- Why did the mass of the flask change with time? (1 mark)
- What is the role of cotton wool at the mouth of the flask? (1 mark)
- Plot a graph of loss in mass (Y-axis) against time (X-axis) Label the curve 22°C (3 marks)
Time (min)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Loss in mass(g)
0.26
0.46
0.60
0.69
0.73
0.73
0.73
- On the graph same axis as in (d) above, sketch the graph you would expect to obtain if the experiment was repeated at 35°C Label the curve 35°C (2 marks)
- State what would happen if the marble chips were replaced with the same mass of marble powder Explain (2 marks)
- Why is it not advisable to use sulphuric (VI) acid in place of hydrochloric acid in this experiment? (1 mark)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- This is to avoid an explosion because a mixture of hydrogen and air is highly explosive1
- Grey solid observed 1
-
- PbO(s) + H2(g) → Pb(s) + H2O(l)1
- 2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(l)/(g)1
- To prevent re-oxidation of the hot metallic lead by atmospheric oxygen1
- To prevent water formed in the reaction form running back into the hot part of the glass tube that can cause it to crack1
-
- Mombasa is around the Indian Ocean whose water is salty while Kisumu is around lake Victoria whose water is fresh½
Salt accelerates rusting hence cars in Mombasa will rust faster than in Kisumu½ - Water ½ and oxygen ½
- Oiling, greasing, painting, galvanizing, electroplating, sacrificial protection, use of silica gel.(any two for 1mk)
- Tube of tap water contains dissolved oxygen while tube of boiled water has no oxygen. 1
-
- A mixture of oxygen and acetylene burns with hot flame used in welding and cutting of metals
- Oxygen mixed with hydrogen is used in rocket fuel
- Oxygen is used in steel making where it oxidizes impurities in molten iron.
- Oxygen is used in hospitals for patients with breathing problems
- Oxygen is used by high mountain climbers and deep sea divers. any two for 1mk
- Mombasa is around the Indian Ocean whose water is salty while Kisumu is around lake Victoria whose water is fresh½
-
- Covalent1 Both elements are non-metals1
-
- DG21
- EG31
- DG2 has higher melting point than EG3 1
DG2 has giant ionic structure with strong ionic bonding1
EG3 has a molecular stricture with weak van der waals forces1 -
- DO1 Basic oxide1
- FO21 acidic .oxide1
e) A½ It is a noble gas with the outermost energy level fully occupied by electrons½
f) D and E1 they contain delocalised electrons1
g) Transition elements/Transition metals1
-
- add aqueous sodium carbonate 1 to precipitate ½ calcium carbonate and magnesium carbonate and filter. ½
- Cathode
- 2H+(aq) + 2e → H2(g) (1 mark)
- Anode
- 2Cl-(aq) → Cl2(g) +2e- (1 mark
- Cathode
- Name:
- Product at U
- Sodium Hydroxide/ NaOH 1
- Another material that can be used instead of titanium (mark)
- Graphite/platinum 1 reject carbon
- The impurity present in the product at U (1mark)
- sodium chloride/ Nacl 1
- State two functions of the diagram (2marks)
- To prevent mixing of chlorine gas with sodium hydroxide. To allow free movement of ions. 1
- It prevents the mixing of chlorine gas and hydrogen gas. 1
- Product at U
- Give one industrial use of the product at U. (1 mark)
- Manufacture of soap/detergents 1
- Used to make bleaching agents
- Used to make bleaching agents
- Used in purification of bauxite
- In paper industry
(Accept any one correct)
-
- Chlorine gas produced is very poisonous and it affects the respiratory system of animals
- Causes acid rain that causes corrosion of buildings / yellowing of plants etc.
- add aqueous sodium carbonate 1 to precipitate ½ calcium carbonate and magnesium carbonate and filter. ½
-
- Sulphur, iron (II) sulphide, zinc (II) sulphide, lead (II) sulphide, copper (i) sulphide
any 3 -
- Dust ½, arsenic compounds /arsenic oxide½
- To avoid poisoning of the catalyst 1
- 2SO2(g) + O2(g) → 2SO3(g)1
-
-
- Vanadium (V) oxide 1
- Platinum /platinised asbestos 1
-
- Vanadium (V) oxide½
- It is cheaper and not easily poisoned ½
-
- The reaction is highly exothermic causing the solution to boil forming mist1 of sulphuric (VI) acid spray which is corrosive
- Sulphur (IV) oxide ½
-
- Recycling the unreacted gases 1
- Reacting the unreacted gases with oxides or carbonates of metals or with heated carbon
any one
- Sulphur, iron (II) sulphide, zinc (II) sulphide, lead (II) sulphide, copper (i) sulphide
-
- Na(s)/Sodium metal 1
- It has the highest negative reduction potential 1 /(Eº) - +0.80 - (-0.76)½ = + 0.80 + 0.76 = + 1.56V1
- Zn(s) /Zn2+(aq) //Ag+(aq) /Ag(s)1
-
- X - Cathode1 Y - anode1
- Oxygen1
- 4OH-(aq) + 2Cu2+(aq) → 2Cu(g) + 2H2O(l) + O2(g)1
- Q = It Q = 0.4 x (15 x 60) ½
= 360C½
Cu2+(aq) + 2e- → Cu(s)½
2 x 96500 = 64g
360 = ?
360 x 64½ = 0.1194g1
19300
- Na(s)/Sodium metal 1
-
- Type of reaction: Dehydration½
Reagent : Concentrated Sulphuric (VI) acid ½
Condition: 170ºC - 180ºC (single value in that range) ½ - Mg(s) + 2CH3COOH(aq) → (CH3COOH)2Mg(aq) + H2(g)1
- V - Butylethanoate1
- CH3COOH(aq) + CH3CH2CH2CH2OH(l) → CH3COOCH2CH2CH2CH3(aq) + H2O(l)1
- Reagent: Soda lime½
- Condition: Heat½
- Name: Tetrachloromethane/ carbon tetrachloride ½
- Structure:½
- Name: Polyethene/polythene½
- Type of reaction: Addition reaction/Addition polymerization1
- Molecular mass of -CH2 - CH2 -
- = 14 + 14
= 28½
n = 44800½ = 1600
- = 14 + 14
- Type of reaction: Dehydration½
-
- CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → CaCl2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)1
- The carbon (IV) oxide formed escaped into the atmosphere1
- To prevent acid from spraying out1
- In the graph paper (3mks)
- 1mk for curve 35°C
-
- The reaction rate would increase½
- Marble powder offers a larger surface area than chips, which causes the rate of reaction to increase1
- There would be formation of insoluble calcium sulphate that would coat calcium carbonate (Marble chips) stopping the reaction1
Download Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Bunamfan Post Mock 2021 Exams.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

