INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Write your name and index no in the spaces provided above.
- Sign and write the date of exam in the spaces provided above.
- Answer all the questions in the spaces provided after each.
- All working must be clearly shown where necessary.
- Candidates should check to ensure that all pages are printed as indicated and that no questions are missing.
- All answers should be written in English.

QUESTIONS
- The table below gives information about some elements. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements. Study the information and answer the questions that follow.
Element Atomic radius(nm) Ionic radius (nm) Formula of oxide Melting point(0c)
M 0.364 0.421 M2 O -119
K 0.830 0.711 KO2 837
P 0.592 0.485 P2 O3 1466
R 0.381 0.446 R2O3 242
Q 0.762 0.676 QO 1054
- Identify two elements that are non-metals. Give a reason. (2mk)
-
- State the valency of elements Q and R. (1mk)
Q
R - Write a formula of a compound formed when Q combines with M. (1mk)
- What type of bond exists between Q and K. (1mk)
- State the valency of elements Q and R. (1mk)
- The melting point of the oxide of R is lower than that of the oxide of P. Explain. (2mks)
- Identify two elements that would react with each other most vigorously. Give a reason(2mks)
- Element P would be suitable for making utensils for boiling water. State two properties that make the element suitable for the use. (2mks)
- In order to find the portion by volume of one of the main constituents of air, a sample of air was passed through two wash bottles; the first containing aqueous sodium hydroxide and the second containing concentrated Sulphuric (VI) acid and was then collected in a gas syringe.
- Suggest a reason for passing air through:
- Aqueous sodium hydroxide. (1mk)
- Concentrated Sulphuric (VI) acid. (1mk)
- The volume of the gas collected in the syringe was 80cm3 . This was passed several times over hot copper powder until no further contraction of volume took place. After cooling to the original temperature, the volume was found to be reduced to 63.2cm3.
- Explain the change in appearance of copper powder as the experiment progressed. (2mks)
- Calculate the percentage of the air used up. (2mks)
- Name the main gas remaining in the syringe. (1mk)
- Explain the purity of the main gas remaining in the syringe. (2mks)
- A piece of sodium metal was exposed to air for some time. Write an equation for any one reaction that occurred. (1mk)
- Suggest a reason for passing air through:
- The set-up below was used to prepare dry sample of hydrogen Sulphide gas
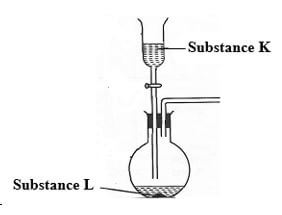
-
- Complete the diagram to show how the gas was collected. (1mk)
- Identify the following: - (2mks)
- Solid K
- Solution L.
- State and explain the observations made in the flask(1mk)
- When hydrogen Sulphide gas was passed through a solution of Iron (III) chloride, the following observations were made: -
- The colour of the solution changed from reddish-brown to green and a yellow solid was deposited. Explain the observations. (2mks)
- In the manufacture of Sulphuric (VI) acid by contact process Sulphur (IV) oxide is made to react with air to form Sulphur (VI) oxide as shown: -
2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2SO3(g)- Name the catalyst currently being used in this reaction. (1mk)
- Give the two reasons why this catalyst is most preferred. (2mks)
- Explain why sulphur (VI) oxide gas is absorbed in concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid before dilution. (1mk)
-
- Study the flow chart below then answer the questions that follow.
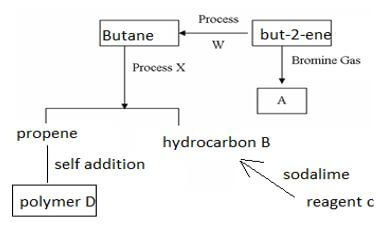
-
- Draw and name two isomers of substance A (2mks)
- Name(3mks)
process W
process X
reagent C
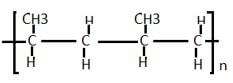
- Draw two repeated units of polymer D(2mks)
- Ethyne is a hydrocarbon belonging to the alkyne homologous family .
- Identify two reagents used to prepare ethyne in the laboratory (1mk)
- Name the third member of this family (1mk)
- DESCRIBE a chemical tests that can be used to distinguish between C2H6 and C2H4 . (2mks)
-
- Study the scheme below and answer the questions that follow.
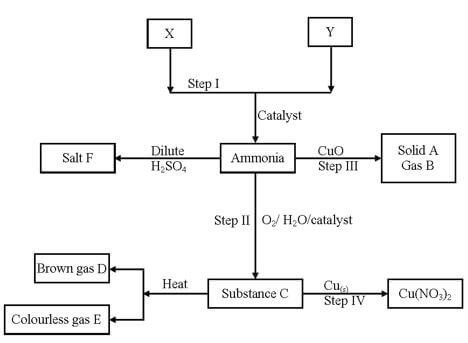
- State the sources of the substance X and Y. (2mk)
X
Y - Identify the catalyst used in step I and how it is made to be effective. (2mk)
Catalyst-
Effecting- - Name the substance A, B, C and E. (2mks)
A
B
C
E - Write the chemical equations that shows
- The formation of substance C. (1mk)
- The reaction between substance C and copper metal. (1mk)
- Describe a chemical test for gas E. (1mk)
-
- State one economic use of substance F. (1mk)
- Name the optimum conditions for the production of ammonia gas. (1mk)
- State the sources of the substance X and Y. (2mk)
- Study the diagram below and use it to answer the questions that follow.
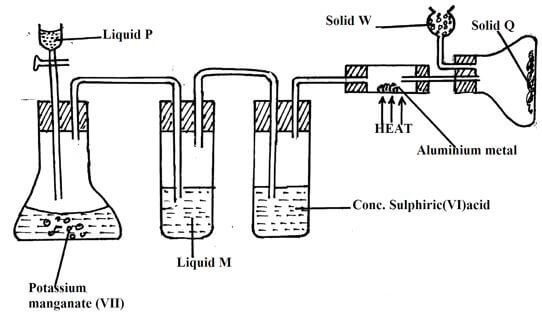
- Name liquid:
P(1mk)
M(1mks) - What is the function of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid in the set-up? (1mk)
- Suggest a suitable reagent that can be used as solid W. (1mk)
- State the role of solid W in the set-up. (1mk)
- Explain why solid Q collect further away from heated aluminium metal. (1mk)
- In the reaction above, 0.645g of aluminium metal reacted completely with 1800cm3 of chlorine gas at room temperature. Determine the molecular formula of solid Q, given that its relative formula mass is 267 (Al = 27.0, Cl = 35.5, molar volume of gas at r.t.p is 24.0 litres)(3mk)
- Name liquid:
-
- Define the term salt?(1mk)
- State the name given to the following behavior of salt;(2mks)
- When hydrated sodium carbonate crystals are exposed for two days ,they form a powder.
- When calcium chloride crystals are left in the open ,a colourless solution is formed .
- Write balanced chemical equation to describe the effect of heat on the following salts.(3mks)
- Potassium nitrate.
- Ammonium chloride.
- Copper carbonate
- Describe how a pure and solid sample of lead sulphate can be prepared given the following reagents; Dilute nitric (iv) ,Solid sodium sulphate , Lead oxide and distilled water.(3mks)
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow.
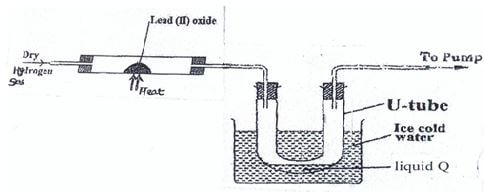
-
- State and explain the observation(s) made in the combustion at the end of the experiment(2mks)
- Identify a metal oxide that can be used in place of lead (II) oxide(½ mark)
- Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction taking place in the combustion tube (1mk)
- Describe one chemical test for liquid Q . (2mk)
-
- Explain what would happen if magnesium oxide was used instead of lead (II) oxide in the experiment (1½ mks)
- State two observations made when a small clean piece of sodium metal is dropped into a trough containing liquid Q(1mks)
- Name any one use of Hydrogen gas. (1 mark)
-

MARKING SCHEME
-
- M 1/ 2mk and R1/ 2mk.
The ionic radius is larger 1mk than the atomic radius implying they gain electrons - I Q=2 1mk R=3 1mk II QM2 1mk III Metallic (1mk)
- The oxide of P is ionic (1mk) with a giant ionic structure that requires a lot of energy to break, the oxide of R is molecular. 1mk
- M and K 1mk M is a non-metal with the smallest (mk) atomic radius hence most electronegative K is a metal with the largest atomic radius (mk) hence most electropositive.
- Has high melting point (1mk) and good conductor (1mk) of heat being a metal
- M 1/ 2mk and R1/ 2mk.
-
-
- To remove carbon(iv) oxide. (1mk)
- To dry the air (1mk)
-
- Turn from red brown to black (1mk) Copper is oxidized to copper (ii) oxide (1mk)
- 80-63.2cm3 = 16 .8 cm3 (1mk) 16.8 80 ? 100 21% (1mk)
- Nitrogen. (1mk)
- Impure (1mk) it contains noble gases like Argon. (1mk)
- Hissing sound/ Melts into a silvery ball/ floats/ darts on the surface
-
-
-
- downward delivery method (1mk)
- L- iron II Sulphide (1mk)
K- dilute HCl (1mk) - black solid dissolves forming a green solution
- Fe3+ is reduced or Fe2+ (1mk)
H2S is oxidized to sulphur. (1mk) -
- Vanadium V oxide (1mk)
- its cheaper, its less susceptible to poisonous
- the reaction is highly exothermic producing fumes of H2SO4 which are dangerous. (1mk)
-
-
- Study the flow chart below then answer the questions that follow.
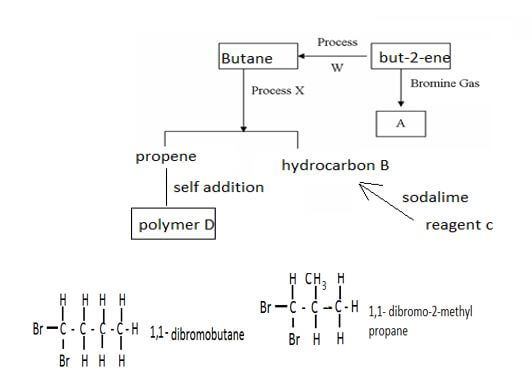
others 1,2- dibromobutane , 1,3- dibromobutane 1,4- dibromobutane, 2,2- dibromobutane, 2,3- dibromobutane, 1,2 dibromo- 2 methyl propane.. (3mks)-
- process W hydrogenation
- process X cracking
- Reagent C sodium ethanoate
-
-
-
- Calcium carbide and water
- butyne
-
test
C2H4
C2H6
BURN
Yellow sooty flame
Blue flame
Acidi. Kmno4
Purple to colourless
Purple colour retained
Bromine water
Yellow to colourless
Yellow colour retained
- Study the flow chart below then answer the questions that follow.
-
- X/Y –Nitrogen obtained from air
Fractional distillation of liquid oil fractional
X/Y – hydrogen conversion of natural gas a by product of cracking crude oil fraction - Finely divided iron
Impregnated with aluminium oxide -
- A copper metal don’t accept symbols
- B nitrogen gas
- C nitric (V) acid
- E oxygen
-
- 4NO2(g) + 2H2O(l) + O2(g) → 4HNO3(l)
- Cu(s) + 4HNO3(aq) → Cu(NO3)(aq) + 2NO2(g) + 2H2O(l)
- It relights/rekindles a glowing splint 1mk
-
- As a nitrogen fertilizer
- Temperature of 400 – 500ºC
Pressure of about 500 atm
- X/Y –Nitrogen obtained from air
-
-
- P- concentrated hydrochloric acid
M - Water - To dry chlorine gas
- Anhydrous calcium oxide
- To absorb unreacted Cl2(g)
- When heated, aluminium chloride sublimes hence it is formed in vapour form and solidifies at cooler parts of apparatus
- Moles of aluminium used = 0.645/27= 0.023889moles
Moles chlorine used 1800 = 0.075moles
2400
Mole ratio 0.023889 : 0.075
0.023889 0.023889
1 : 3.1395
1 : 3
E.f = AlCl3
Mf = (E.f mass) x n
Mass 267 = (27 + 35.5 x 3)n
267 = 133.5n
n = 267
133.5n
n = 2 mf: Al2Cl6
- P- concentrated hydrochloric acid
-
-
- A substance formed when some or all of the replaceable hydrogen atoms of an acid are wholly or partially replaced by a metal or an ammonia radical. 1mks
-
- Efflorescence. 1mks
- Deliquescence. 1mks
-
- 2KNO3(s)→2KNO2(S)+O2(g)
- NH4Cl(aq)→NH3(g)+HCl(l)
- CuCO3(s)→CuO(S)+CO2(g)
- React excess lead oxide with dilute nitric (v) acid to form lead nitrate solution.Add water to potassium sulphate to form a solution.react lead nitrate with the potassium sulphate , Filter, rinse the residue with distilled water and dry between filter papers.(3mks)
-
-
- Yellow/orange lead (ii) oxide turns grey. 1mk
Lead (ii) oxide was reduced by hydrogen to lead. - Copper (ii) oxide/Fe3O4.
- Yellow/orange lead (ii) oxide turns grey. 1mk
- PbO(s)+H2(g)→Pb(s)+H2O(L) .1mks
- Add anhydrous copper (ii) sulphate ,it will turn from white to blue.1mks OR Add anhydrous cobalt (ii) chloride ,it will change from blue to pink.1mks
-
- No reaction, Magnesium is more reactive than hydogen.1mks
- Hissing sound, mks
Darts on the surface,
Floats on the surface,
Melts into a silvery ball
- Manufacture of ammonia/HCl WTTE
-
Download Chemistry Questions and Answers - KCSE 2022 Pavement Form 4 Trial 1 Pre-Mock Examination.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

