Instructions to the candidates:
- This paper consist of two Section A and B
- Answer all questions in section A and B in the spaces provided
- All working must be clearly shown, and use the CONSTANTS given,
- Ensure that the paper has all the questions
- Take g = 10N/kg, Atmospheric pressure = 760mmHg, density of mercury = 13600Kg/m3
For Examiners’ Use Only
|
SECTION |
QUESTION |
MAXIMUM SCORE |
CANDIDATE’S SCORE |
|
A |
1-11 |
25 |
|
|
B |
12 |
15 |
|
|
13 |
11 |
||
|
14 |
10 |
||
|
15 |
10 |
||
|
16 |
09 |
||
|
TOTAL |
80 |

QUESTIONS
SECTION A (25 MARKS)
Answer All Questions in This Section in the Spaces Provided
- The figure below shows the change in volume of water in a measuring cylinder when an irregular solid is immersed in it.
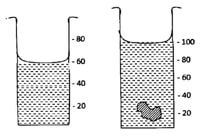
Given that the mass of the solid is 567g determine the density of the solid in Kg/m3. (3 marks) - In a ball and ring experiment, the ball goes through the rings at room temperatures. When it is heated it does not go through the ring, but when left on the ring for some time, it goes through.
Explain this observation. (2marks) - The diagram below shows a uniform wooden beam of length 6m and mass 30kg pivoted as shown below.
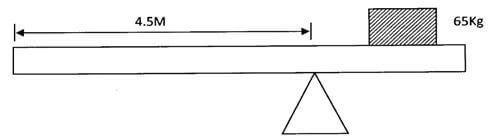
How far from the pivot will the 65kg mass be placed for the beam to be in equilibrium? (3 marks) - The figure 3 below shows an arrangement to demonstrate diffusion through solids:-
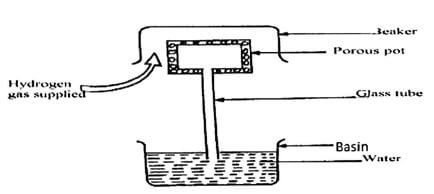
The hydrogen gas is supplied for sometimes then stopped and the beaker removed. State and explain what is likely to be observed when the hydrogen gas supply is stopped. (3 marks) - State how the pressure in a moving fluid varies with speed of the fluid. (1 mark)
- A piece of metal weighs 3N in air and 2N when totally immersed in water. Calculate the volume of the metal. (density of water = 1000kg/m3) (3 marks)
- Explain how a person is able to drink a soda using a drinking straw. (2 marks)
- A needle may float on clean water but sinks when a detergent is added. Explain. (1 mark)
- The identical springs of spring constant 3N/cm are used to support a load of 30N as shown.
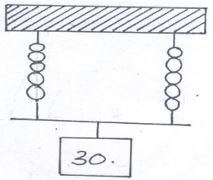
Determine the extension on each spring. (3 marks) - In a vacuum flask, the walls enclosing there vacuum are silvered on the inside. State the reason for this. (1 mark)
- A student set up the apparatus as shown below. The boiling tube was heated in the middle as shown
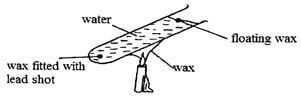
- State the role of the lead shot in the experiment (1 mark)
- With reason, state the wax that will melt firs. (2 marks)
SECTION B (55 MARKS)
Answer all questions in this section in the spaces provided
-
- The figure below shows displacement-time graphs of two objects A and B of equal masses drawn on same axes.
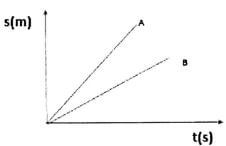
- What does the slope of the graph represent? ( 1mark)
- The same size of force is applied against each object. State with a reason which of the two objects stops in a shorter distance. (2 marks)
- An object moving at 30m/s starts to accelerate at 5m/s2 so that its velocity becomes 50/ms
- Find the distance moved during this acceleration (3marks)
- The object is now braked so that it comes to rest in a time of 5 seconds. Find the braking force if its mass was 2000g. (3 marks)
- State the law of conservation of linear of linear momentum. (1 mark)
- Anobject of the mass 100kg moving at 20 m/s collides with a stationary object of mass 20kg.
They stick together after collision. Determine the:- Total momentum below collision (2marks)
- Total momentum after collision (1mark)
- Their common velocity after collision (2 marks)
- The figure below shows displacement-time graphs of two objects A and B of equal masses drawn on same axes.
-
- Explain why an air bubble increasing volume as it rise from the bottom of a lake to the surface. (2 marks)
- The diagram below shows a set-up used to investigate a particular gas law. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow.
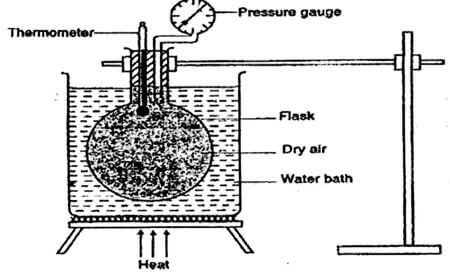
- State with a reason which gas law is being experimented by the set-up. (2 marks)
- Name the two factors that are held constant in the experiment (2marks)
- Give the reason why heating is done through a water bath. (1 mark)
- A balloon of volume 1.5m3 containing helium gas at a pressure of 3.0 x 106 pa is released from the ground when the temperature is 20ºC. What will be the pressure when it reaches an altitude where the volume becomes 3.0m3 and the temperature 5ºC. (3 marks)
- State the kinetic theory of gases. (1 mark)
-
- An immersion heater rated 2.5W is immersed into a plastic jug containing 2kg of water and switched on for one minute. Determine
- The quantity of heat gained by water. (2marks)
- The temperature change for water. (Specific heat capacity of water = 4.2x103Jkg-1K-1(3 marks)
- Explain why a drop of methylated spirit on the back of the hand feels cold. (2marks)
- What makes Freon suitable for use as a refrigerant? (1 mark)
- State two differences between boiling and melting. (2 marks)
- An immersion heater rated 2.5W is immersed into a plastic jug containing 2kg of water and switched on for one minute. Determine
- The figure below shows an inclined plane used to load heavy luggage’s onto a lorry. The length of the place is L metres and the height is h metres, the plane makes angle a with the horizontal
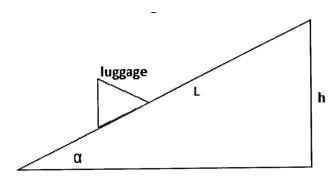
- Show that the velocity ratio is given by 1/sin a (3 marks)
- A man uses the inclined plane above to lift a 50kg load through a vertical height of 4m. The inclined plane makes an angle of 30o with the horizontal. If the efficiency of the inclined plane is 72%. Calculate
- The effort needed to move the load up the inclined plane at a constant velocity. (4 marks)
- The work done against friction in raising the load trough the 4.0 m height. (3 marks)
[Take g = 10N/kg]
-
- State what provides centripetal force for the moon moving round the earth. (1 mark)
- The figure (6) below shows a turnable on which a mass of 50g isplaced 10cm from the center.
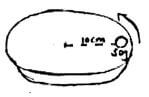
The Frictional force between the 50g mass and the turnable is 0.2N. When the turnable is made to rotate with angular velocity of ω rad/sec, the mass tarts to slide off.- Determine the
- Angular velocity (3marks)
- Time taken to make a complete revolution when moving with the above angular velocity. (2 marks)
- On the figure, draw a path that would be taken by the 50g mass at above position if the turnable suddenly came to stop. (1 mark)
- Determine the
- State two changes can be made to keep the 50g mass from sliding off. (2marks)

MARKING SCHEME
- Volume of water displaced = 100 – 60 = 40cm3√
Volume of water displaced = Vol.of stone = 40cm3
P = M/V (do not award a mark for the formula)
P = 567g/40cm3 = 14.175g/cm3 (correct substitution)√
P = 14.18g/cm3 - The ball expands when heated and cannot go through the ring√, but when left on the ring for some time is heats the ring causing the ring to expand hence it passed through√.
- Clockwise moments = Anticlockwise moments
300 x 1.5 = X x 650√ (correct substitution 1mk)
450/650 = 650x/650
X = 450/650√
X = 0.6923M (at least 2dp)√ - Water rises up the glass tube√
Hydrogen diffuses out the porous pot faster than air diffusing into the pot creating√ partial vacuum (low pressure) hence atmospheric pressure pushes water upwards - Pressure decreases with increase in speed/pressure increases with decreases in speed
- Upthrust = weight of water displaced by the metal
Wt of water displaced = wt in air – wt in water - (3-2) = 1N
Mass of water displaced = 1/10 = 0.1kg
Density of water = 1000kgm-3
Vol.of the water displace 0.1/1000 = 0.001m3
Therefore vol. of metal = 0.001m3 - He sucks the air in the straw reducing the pressure inside the straw√ 1. The greater atmospheric pressure outside pushes the liquid into the mouth√
- Clean water has a high surface tension addition of detergent reduces/breaks/lowers the surface tension√1
- Each spring experiences a force of 30/2 = 15N
F = ke√ e = F/k = 15/3 = 5cm
Each spring extends to 5cm√ - To reflect the outwards or inwards hence reduce heat loss by radiation
-
- Hold wax to prevent it from floating
- Floating wax heat reaches it by convection current (hot water rises)
-
-
- Velocity√
- B√ it moves with a lower velocity√ has less momentum.
-
- V2 = u2+ 2as√
502 = 302+ 2 x 5s√
2500 = 900 + 105
.105/10 = 1600/10
S = 160m√ - F= m ((v-u)/t)√
F = 2000/1000 ((0-50)/5)√
F = -20N√
- V2 = u2+ 2as√
- For a system of colliding bodies the linear momentum is conserved provided no external force acts.
-
- P = mu√
= 100 x 20
= 2000 kg m/s√ - 2000 kg m/s√
- (m1 + m2)v = p√
(100 + 20) v = 2000
120v = 2000
V = 16.67ms√
- P = mu√
-
-
- Pressure√ decreases with decrease in √depth
-
- pressure law, pressure and temperature√ varies
- Volume√
Mass√ - Even distribution of heat√
- 3x106x1.5= p2x3
20+273 273+5
P2 = 1.423 x 106pa - gases are made up of molecules which are in a constant random motion.
-
-
- H = pt
= 2.5 x 1000 x 1 x 60
=150 000 J - mCθ=H
2 x 4200 x θ = 150000
θ = 17.86k
- H = pt
- It evaporates by absorbing latent heat of vaporization
- It evaporates easily
-
Boiling
Melting
1. Pressure increases the boiling point
2. Boiling is change of state from liquid to gas
1. Pressure reduces the melting point
2. Its change of state from solid to liquid
-
-
- V.R = (distance moved by effort)/(distance moved by load )√
= L/h√
But sin a= h/L∴1/sina = L/h √
V.R = 1/sina -
- η = MA/VR x 100%√
72% = MA/(1/sin30 ) x 100%√
72 = (MA )/2x 100
MA = 1.44
MA L/E√
1.44 = (50 x 10)/E
E = 347.22N √ - Work done against function = (100 – 72) % of work input
= 28% of E x dE√
= 28/100 x 347.22 x 4 sin 30√
= 194.44J√
- η = MA/VR x 100%√
- V.R = (distance moved by effort)/(distance moved by load )√
-
- gravitational force
-
-
- FR = mω^2r√
0.2 = 50/1000 ω2 x 10/1000√
.w2 = 40
. ω=6.325 rad/s√ - ω = 2π/T
6.325 = 2 x 22/(7/T)√
T = 2 x 22/7 x 1/6.325
T = 0.9938s√
- FR = mω^2r√
-
-
-
- Increase the radius of rotation
- Reduce the angular velocity/speed of rotation
Download Physics Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Arise and Shine Pre Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
