INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- This paper consist of three sections A, B and C
- Answer ALL he questions in section A and B and ANY TWO questions in section C in the spaces provided
SECTION A: Answer all the questions in this section (30 Marks)
- Name three branches of horticulture (1 ½ marks)
- List three aspects of light that influence crops growth (1½ marks)
-
- What is mixed farming (1 mark)
- Give three disadvantages of mixed farming to a small scale farmer (1½ marks)
- Give two ways how hard pans would be caused by cultivation (1 mark
-
- Give a reason why nitrogenous fertilizer should: (2 marks)
- Be stored under dry condition
- Be applied in most soils
- Be applied to an established crop
- Be applied frequently
- Distinguish between complete compound fertilizer and incomplete compound fertilizer (1 mark)
- Give a reason why nitrogenous fertilizer should: (2 marks)
- State two mechanical methods of separating soil particles according to size during soil analysis (2 marks)
- Give two methods of controlling stalk borer in maize production (1 marks)
- State two reasons why too much air in the silo is undesirable in the process of silage making (1 mark)
- State three ways of controlling weeds in pure grass pastures (1 ½ marks)
- Give four advantages of title deed to a farmer (2 marks)
- Outline four advantages of a mixed-legume pasture over a pure-grass pasture (2 marks)
- Give four management practices that promote high herbage yields in pasture Production (2 marks)
- Give four factors that a farmer should consider in siting a nursery (2 marks)
- Give four benefits of using vegetable propagation in orange production (2 marks)
-
- What is micro-catchment? (1 mark)
- List any four types of micro-catchments (2marks)
- List four common bacterial diseases that affect crops (2 marks)
SECTION B: Answer all the questions in this section (20 Marks)
- Study the diagram below.

- Name the process above used to prepare Irish potatoes in readiness for planting (1 mark)
-
- Which of the two potatoes is suitable for planting? (1 mark)
- Give a reason for your answer in (b) (i) above (1 mark)
- Give two reasons why maize needs to be earthed (2 marks
- A farmer growing maize on 10 hectares is to dress it with sulphate of ammonia (20%N) at the rate of 120kg of S.A per hectare. At the local market S.A is available in 50kg bags selling at Ksh. 1500 per bag.
- Calculate the amount of S.A the farmer needs to top-dress his crop of maize (3 marks)
- Calculate the amount of money he will use on fertilizer (2 marks)
- The diagram below illustrates a type of soil erosion. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow.
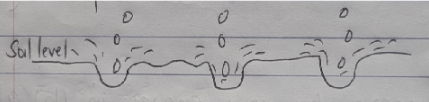
- Identify the type of erosion above (1 mark)
- Give two factors that may accelerate the rate of the type of erosion above (2 marks)
- Give two effects of the type of soil erosion shown above on the farm (2 marks)
- Study the diagrams labelled G and H
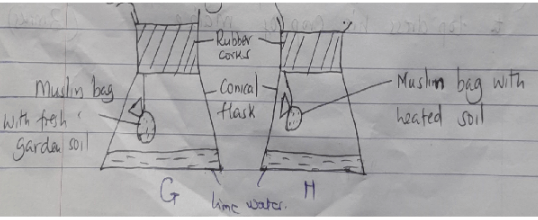
- Give one use of setting up such an experiment (1 mark)
- Give two reasons why the garden soil in the experiment H is heated (2 marks)
- Briefly explain what happens to the lime water in both experiment G and H
- Experiment G (1 mark)
- Experiment H (1 mark)
SECTION C: Answer TWO questions only in this section (40 Marks)
-
- Discuss ten cultural practices of controlling pests in a crop field (10 marks)
- Outline five factors a farmer should consider before deciding on the type of irrigation in crop production (5 marks)
- Describe the qualities of the mother plant that should be considered when selecting vegetative material for planting (5 marks)
-
- Discuss the factors considered when drawing a crop rotation programme (10 marks)
- Explain the precautions that should be observed during harvesting of tea (5 marks)
- Describe reasons for drainage as a method of land reclamation in crop production (5 marks)
-
- Describe production of onions under the following subheadings
- Ecological requirement (3 marks)
- Land preparation (4 marks)
- Harvesting and marketing (3 marks)
- Breaking the tops in onions (1 mark)
- Two pests in onions (2 marks)
- Explain seven ways soil fertility is maintained (7 marks)
- Describe production of onions under the following subheadings
MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A
-
- Olericulture
- Pomoculture/ pomology
- Floriculture. (3 x ½ = 1½ marks )
-
- Light duration
- Light wave
- Light intensity (3 x ½ = 1½ marks)
-
- Practice of growing crops and keeping livestock in the same piece of land at the same time. (1mark)
-
- Requires high level of management.
- Labour intensive
- If not well confirmed, livestock can damage crops (3 x ½ = 1½ marks )
-
- Use of heavy machinery on wet soil
- Ploughing at the same depth continuously. (2 x ½ = 1marks )
-
- Because nitrogenous fertilizers are hygrocopic i.e. to absorb moisture from the atmosphere.
- Because they are highly volatile i.e. change into gaseous form in dry conditions and escape.
- Because they are easily leached behold root zones of crops.
- Because they have a short residual effect. (4 x ½ = 2 marks)
-
- Sieving methods using various sizes.
- Seiver / mechanical methods
- Sedimentation method. (2 x 1 = 2 marks )
-
- Hand picking and killing
- Use of appropriate pestcide (2 x 1 = 2marks )
-
- It can lead to rotting
- It promotes aerobic respiration which can result in loss of nutrients. (2 x ½ = 1 mark )
-
- Uprooting
- Use of herbicides
- Cover cropping
- Slashing (3 x ½ = 1½ marks )
-
- Reduces land disputes
- It is official prove / security for loan
- Encourages farmers to carry out long term investment on the land. (4 x ½ = 2 marks )
-
- More palatable than pure grass
- Reduces soil erosion
- Has better weed control effect
- creases soil fertility because of nitrogen fixation
- Economy in use of fertilizer
- Better distribution of growth
- Makes maximum use of soil nutrients
- More nitration’s
- Tighter yields per unit area of land.
- Security against tatol loss due to attack by pest. (4 x ½ = 2 marks )
-
- Weeding
- Re – seeding
- Fertilizer application
- Topping
- Mixing with legumes. (4 x ½ = 2 marks )
-
- Gentle slope
- Nearness to permanent source of water
- Well secured place
- Fertile soil
- Well sheltered place. (4 x ½ = 2 marks )
-
- Early maturity of the crop
- Plants assume desired size and shape
- Possible to obtain two more varieties of oranges on one rootstock.
- High yielding
- Maintains parental genetic characteristics
- Possible to propagate seedless orange varieties (4 x ½ = 2 marks )
-
- A micro catchment is a rainwater harvesting system which involves the collection of runoff water for productive use. (1 x 1 = 1mk)
-
- Control bunds
- Contour ridges
- Semi-circular bunds
- Trapezoidal bunds
- Contour –stone bunds
- Permanent rock dams
- Water spreading bunds (4 x ½ = 2 marks )
-
- Bacterial blight of coffee
- Bacterial wilt of potatoes
- Bacterial wilt of tomatoes
- Black arm of cotton
- Black rot of cabbage
- Halo bright of beans. (4 x ½ = 2 marks)
SECTION B
-
- Chitting (1mark)
-
- B (1mark)
- Presence of sprouted auxiliary buds (1mark)
-
- extra support
- prevent lodging
- Proper nutrients utilization by the roots. (1mark)
-
- Size of land 10 hectares
(SA suphate of ammonia 20% N
Route of 1500/= per bag (50 kg)
1ha - 120kg
10ha 120 x 10 = 1,200kgs
1200kg /50 = 24 bags (3marks) - 1500 x 24bags = 36,000/= (2marks)
- Size of land 10 hectares
-
- splash / rain drop erosion. (1marks)
-
- High amount and intensity of rainfall.
- Slope of land (topography/ sleep slope)
- Type of soil
- Shallow soil depths
- Lack of vegetation cover
- Clean weeding (2 x 1 = 2marks)
-
- Exposes shallowly planted seeds
- Hollow cut soil exposing underlying layers. (2 x 1 = 2marks)
-
- To test presence of living organisms in the soil. (1marks)
-
- To kill all living organisms.
- To remove moisture. (2 x 1 = 2marks)
-
- G - Lime water turned milky due to carbon dioxide produced by living organism in fresh garden soil. (1mk)
- H- Limewater remained clear with no noticeable change (1mk)
-
-
- Timely planting.
- Proper tillage
- Close season
- Trap cropping
- Planting resistance crop varieties
- Field hygiene
- Alteration of environmental conditions,
- Destruction of alternate host.
- Proper spacing
- Uses of organic manure
- Irrigation (1 x 10 = 10marks)
-
- Type of soil
- Type of crop to be grown
- Source of water / quality of water
- Size of land to be irrigated
- Capital available
- Topography of land
- Profitability /viability of enterprises. (1 x 5 = 5marks)
-
- High yield
- Resistant to pest
- Resistant to diseases
- High quality produce
- High rooting ability
- Early maturing (1 x 5 = 5marks)
-
-
-
- Crop depth ; deep rooted crops alternate with shallow rooted
- Weed control - crop of same families alternated
- Pest and diseases control - with different families to break cycles;
- Soil fertility – heavy feeders alternated with shallow / lighter feeders
- Soil structure; grass leys included at the end of programme to improve soil structure.
(5 x 2 = 10 marks)
-
- Plucked tea leaves should be put in woven baskets to allow free air circulation to prevent fermentation.
- Keep plucked tea cool and shaded place
- Plucked tea should be delivered to the factory the same day.
- Plucked tea should not be compressed to prevent heating up and browning lowering quality
-
- Increase soil aeration
- Increase soil volume
- Raise soil temperatures
- Increase microbial activities
- Reduce soil erosion
- Remove toxic substances.
-
-
-
- Ecological requirement
- Altitude - 2100MA sea level
- Rainfall 100mm P.a
- Irrigation during dry period
- Soil should be fertile, well drained soil ph 6.0 - 7.0
- Temperature - warm hot climates core suitable. (3mks)
- Land preparation
- Cultivate the land during dry period and is prepared to a fine titth
- Remove all for good start
- Apply phosphate fertilizer at rate of 250kg.ha. (4marks)
- Harvesting
- Breaking the tops quickens withering. (1mk)
- Thrips; onion fly ; leaf minor
- Ecological requirement
-
- Crop rotation - makes maximum utilization of soil nutrients.
Control of soil erosion - soil erosion carry’s the top fertile soil. - Application of organic manure
- Planting leguminous , crops to fix nitrogen in soil.
- Control of weed – weeds compete with crops for nutrients
- Planting cover crops - help to prevent soil erosion.
- Crop rotation - makes maximum utilization of soil nutrients.
-
Download Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Chogoria Murugi Zone Pre Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
