- This paper consist of TWO sections A &B
- Answer ALL the questions in section A and B in the space provided.
- ALL working MUST be clearly shown.
- Mathematical tables and silent electronic calculators may be used
Take Acceleration due to gravity g=10m/s2
SECTION A (25 MARKS)
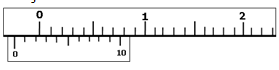
- The figure below shows parts of a vernier callipers when the jaws are closed without an object between the jaws.
- State the error of the vernier callipers. (1mark)
- A student used the vernier callipers to measure the diameter of a test tube whose actual diameter was 2.13 cm. What was the reading of the vernier callipers? (2marks)
- Explain why a hole in a ship near the surface is less dangerous than one near the bottom. (2mks)
- A block measuring 20cm by 10cm by 4cm rests on a flat surface. The block has a weight of 6N. Determine the density of the block in kg/m3 (2marks)
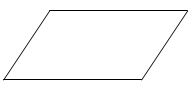
- The figure below shows a uniform cardboard in the shape of a parallelogram.
Locate the centre of gravity of the cardboard. (1 mark) - A boulder is sliding down a slope from rest, with a uniform acceleration of 3ms-2; calculate its velocity after it has slid 10m down the slope (2marks)
- Suggest a possible reason why Brownian motion is more evident in gas particles than in liquid molecules. (1mark)
- The barometer reading at the foot of a cliff of height 500m is 764mmHg. If the average density of air is 1.25kgm-3 and that of mercury is 13600kgm-3, determine the reading of the barometer at the top of the cliff. (3 marks)
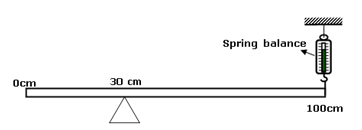
- The figure below shows a uniform metre rule which is pivoted at 30.0 cm mark. The spring balance is fastened at the 100 cm mark and it is at equilibrium when the spring balance records 1.2N. Determine the weight of the metre rule. (3 marks)
- Explain why a Bunsen burner has a wide heavy base (2marks)
- State the SI units of elastic constant of a spring (1mark)
- Two samples of bromine vapour are allowed to diffuse separately under different conditions, one in a vacuum and the other in air. State with reasons the conditions in which bromine diffuse slower. (2 marks)
- State what is meant by absolute zero temperature. (1 mark)
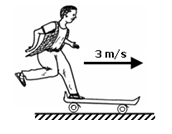
- A boy of mass 58kg jumps with a horizontal velocity of 3ms-1 onto a stationary skateboard of mass 2kg as shown below. What is his velocity as he moves off on the skateboard? (2marks)
SECTION B (55 MARKS)
-
- Define the term work as used in physics. (1 mark)
- A pulley system has two pulleys on the lower block and one pulley on the upper block. In order to raise the load of 6N, an effort of 2N is applied.
- Draw a sketch to show the pulley system. (2 marks)
- Calculate the efficiency of the pulley system (3 marks)
- In the space provided below, sketch a graph of efficiency against load for the system (2 marks)
- A workshop has a wheel and axle for lifting heavy loads; The wheel has a diameter of 30cm while the axle has a diameter of 3cm. Assuming that the machine is perfect, calculate its mechanical advantage (3 marks)
-
- What is meant by specific latent heat of vaporization? (1mark)
- In an experiment to determine the specific latent heat of vaporization of water, steam at 100oc was passed into water contained in a well lagged copper calorimeter.
The following measurements were made:
Mass of calorimeter = 50g
Initial mass of water = 70g
Initial temperature of water = 5°C
Final mass of water + Calorimeter + condensed steam = 123g
Final temperature of mixture = 30°C
Specific heat capacity of water = 4200Jkg-1k-1
Specific heat capacity of copper = 390Jkg-1k-1- Determine the
- Mass of condensed steam (1 mark)
- Total heat gained by water and calorimeter (3 marks)
- Given that L is the specific latent heat of vaporization of steam
- Write an expression for the heat given out by steam (1 mark)
- Determine the value of L (2 marks)
- Determine the
- 500g of water at 20°C is mixed with 200g of water at 55°C. Find the final temperature of the mixture. (3 marks)
-
- State the pressure law for an ideal gas (1 mark)
- An air bubble is released at the bottom of a tall jar containing a liquid. The height of the liquid column is 80cm. The volume of the bubble increase from 0.5cm3 at the bottom of the liquid to 1.15cm3 at the top. The figure below shows the variation of pressure p, on the bubble with the reciprocal of volume 1/v as it rises in the liquid
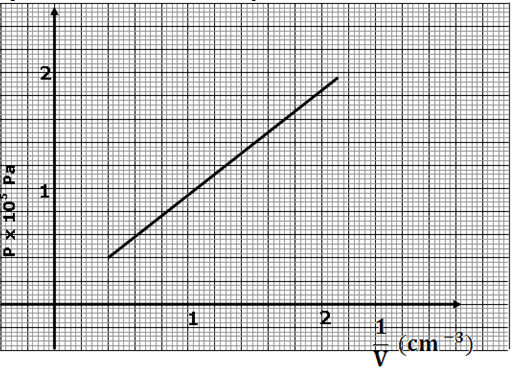
- From the graph, determine the pressure on the bubble
- At the bottom of the liquid column; (2marks)
- At the top of the liquid column. (2marks)
- Hence determine the density of the liquid in kgm-3 (3 marks)
- What is the value of the atmospheric pressure of the surrounding? (1 mark)
- From the graph, determine the pressure on the bubble
- A rubber tube is inflated to a pressure of 2.7 x 105 pa and volume 3800cm3 at a temperature of 25°C. It is then taken to another place where the temperature is 15°C and the pressure 2.5 x 105 pa. Determine the new volume. (3 marks)
-
- The mass of a density bottle is 20g when empty 70g when full of water and 60.0 g when full of liquid L. Calculate the density of the liquid L(take density of water as 1g/cm3) (3 marks)
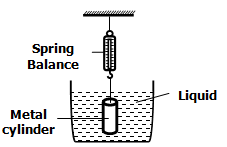
- In an experiment to determine the density of a liquid a uniform metal cylinder of cross- sectional area 6cm2 and length 4cm was hang from a spring balance and lowered gradually into the liquid as shown below.
The up thrust was calculated from the spring balance and it was found to be 0.6N when the cylinder was fully submerged. Determine:- Volume of the metal cylinder. (3marks)
- Mass of the liquid displaced by the cylinder. (2marks)
- Density of the liquid (3marks)
-
- A wet umbrella gets dried faster when its handle is rotated at high speed. Explain. (2marks)
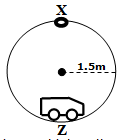
- Figure below shows a trolley moving on a circular rail in a vertical plane. Given that the mass of the trolley is 250g and the radius of the rail is 1.5m
- Determine the minimum velocity at which trolley passes point X. (3marks)
- If the trolley moves with a velocity of 4m/s as it passes point Z, Find
- angular velocity at this point. (3marks)
- The force exerted on the rails at this point. (2marks)
MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A
- The figure below shows parts of a vernier callipers when the jaws are closed without an object between the jaws.
- State the error of the vernier callipers. (1mark)
- 0.02cm
- A student used the vernier callipers to measure the diameter of a test tube whose actual diameter was 2.13 cm. What was the reading of the vernier callipers? (2marks)
Actual reading = reading of vernier calliper + zero error
reading of veriner calliper = 2.13 − 0.02
= 2.11cm
- State the error of the vernier callipers. (1mark)
- Explain why a hole in a ship near the surface is less dangerous than one near the bottom. (2mks)
- Presure at the surface is less than at the bottom ✓1 so water at the surface enters at the lower rate tahn at the bottom ✓1
- A block measuring 20cm by 10cm by 4cm rests on a flat surface. The block has a weight of 6N. Determine the density of the block in kg/m3 (2marks)
d = m = 0.6 ✓1
v 0.2 × 0.1 × 0.04
= 750kg/m3 ✓1 - The figure below shows a uniform cardboard in the shape of a parallelogram.
Locate the centre of gravity of the cardboard. (1 mark) - A boulder is sliding down a slope from rest, with a uniform acceleration of 3ms-2; calculate its velocity after it has slid 10m down the slope (2marks)
V2 = u2 + 2as
V2 = 0 + (2×3×10) ✓1
V2 = 60
V = 7.75m/s ✓1 - Suggest a possible reason why Brownian motion is more evident in gas particles than in liquid molecules. (1mark)
- Particles of gas have larger intermolecular distance between them hence they move faster ✓1
- The barometer reading at the foot of a cliff of height 500m is 764mmHg. If the average density of air is 1.25kgm-3 and that of mercury is 13600kgm-3, determine the reading of the barometer at the top of the cliff. (3 marks)
Pressure at the bottom − pressure at the top = Air pressure ✓1
Pressure at the top = (0.764 × 13600 × 10) − (500 × 1.25 × 10) ✓1
= 103,904 − 6250
= 97,654N/m2 ✓1 - The figure below shows a uniform metre rule which is pivoted at 30.0 cm mark. The spring balance is fastened at the 100 cm mark and it is at equilibrium when the spring balance records 1.2N. Determine the weight of the metre rule. (3 marks)
Sum of clockwise moments = Sum of anticlockwise moments ✓1
w × 0.2 = 1.2 × 0.7
w = 4.2N - Explain why a Bunsen burner has a wide heavy base (2marks)
- To make the burner more stable ✓1 since the heavy base lowers the centre of gravity and the wide base area provides large angle of tilt before toppling ✓1
- State the SI units of elastic constant of a spring (1mark)
- Newton per metre (N/m)
- Two samples of bromine vapour are allowed to diffuse separately under different conditions, one in a vacuum and the other in air. State with reasons the conditions in which bromine diffuse slower. (2 marks)
- Slower in air ✓1 air particles collide with bromine particcles hence low rate of diffusion ✓1
- State what is meant by absolute zero temperature. (1 mark)
- The lowest temperature that a gas can go to ✓1
- A boy of mass 58kg jumps with a horizontal velocity of 3ms-1 onto a stationary skateboard of mass 2kg as shown below. What is his velocity as he moves off on the skateboard? (2marks)
momentum before collision = momentum after collision
m1u1 + m2u2 =(m1+m2) ✓1
(58×3) + (2×0) = (58+2)V ✓1
174 = 60v
v = 2.9m/s ✓1
SECTION B (55 MARKS)
-
- Define the term work as used in physics. (1 mark)
- It is the product of force and distance moved by the object in the direction of the applied force.
- A pulley system has two pulleys on the lower block and one pulley on the upper block. In order to raise the load of 6N, an effort of 2N is applied.
- Draw a sketch to show the pulley system. (2 marks)
Blocks ✓1 Strings and direction of force ✓1
- Calculate the efficiency of the pulley system (3 marks)
M.A = L/E = 6/2 = 3 ✓1
V.R = 4 ✓1
efficiency = M.A × 100%
V.R
η = ¾ × 100%
=75% ✓1 - In the space provided below, sketch a graph of efficiency against load for the system (2 marks)
- Draw a sketch to show the pulley system. (2 marks)
- A workshop has a wheel and axle for lifting heavy loads; The wheel has a diameter of 30cm while the axle has a diameter of 3cm. Assuming that the machine is perfect, calculate its mechanical advantage (3 marks)
V.R = R/r
= 15/1.5 = 10
for the perfect machine, the efficiency is 100%
So V.R = M.A
m.A = 10
- Define the term work as used in physics. (1 mark)
-
- What is meant by specific latent heat of vaporization? (1mark)
- Quantity of heat required to convert 1kg of a liquid to vapour at constant temperature. ✓1
- In an experiment to determine the specific latent heat of vaporization of water, steam at 100oc was passed into water contained in a well lagged copper calorimeter.
The following measurements were made:
Mass of calorimeter = 50g
Initial mass of water = 70g
Initial temperature of water = 5°C
Final mass of water + Calorimeter + condensed steam = 123g
Final temperature of mixture = 30°C
Specific heat capacity of water = 4200Jkg-1k-1
Specific heat capacity of copper = 390Jkg-1k-1- Determine the
- Mass of condensed steam (1 mark)
123 − (70+50) = 3g ✓1 - Total heat gained by water and calorimeter (3 marks)
Heat gained = MCΔQ + McCcΔQ
= (0.07 × 4200 × 25) + (0.05 × 390 × 25)
= 737.5J
- Mass of condensed steam (1 mark)
- Given that L is the specific latent heat of vaporization of steam
- Write an expression for the heat given out by steam (1 mark)
Heat lost by steam = mL
= 0.003L ✓1 - Determine the value of L (2 marks)
Heat lost by steam = Heat gained by water and calorimeter
0.003L = 7837.5 ✓1
L = 2612500Jkg−1✓1
- Write an expression for the heat given out by steam (1 mark)
- Determine the
- 500g of water at 20°C is mixed with 200g of water at 55°C. Find the final temperature of the mixture. (3 marks)
Heat gained by cold wwater = Heat lost by hot water ✓1
0.5 × 4200 × (T − 20) = 0.2 × 4200 × (55 − T)
2100T − 42000 = 46200 − 840T ✓1
2940T = 88200
T = 30°C ✓1
- What is meant by specific latent heat of vaporization? (1mark)
-
- State the pressure law for an ideal gas (1 mark)
- Pressure of a fixed mass of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature at constant volume. ✓1
- An air bubble is released at the bottom of a tall jar containing a liquid. The height of the liquid column is 80cm. The volume of the bubble increase from 0.5cm3 at the bottom of the liquid to 1.15cm3 at the top. The figure below shows the variation of pressure p, on the bubble with the reciprocal of volume 1/v as it rises in the liquid

- From the graph, determine the pressure on the bubble
- At the bottom of the liquid column; (2marks)
At the bottom v = 0.5cm3 ; 1/v = 2 ✓1
p = 1.84 × 105pa - At the top of the liquid column. (2marks)
At the top v = 1.15cm3 ; 1/v = 0.87cm−3✓1
p = 1.84 × 104pa ✓1
- At the bottom of the liquid column; (2marks)
- Hence determine the density of the liquid in kgm-3 (3 marks)
Pressure difference = (1.84 × 105) − 8.4 × 104)pa ✓1
hπg = 1.0 × 105
0.8 × ρ × 10 = 1.0 × 105 ✓1
ρ = 12500kg/m3 ✓1 - What is the value of the atmospheric pressure of the surrounding? (1 mark)
4.0 × 104 pa
- From the graph, determine the pressure on the bubble
- A rubber tube is inflated to a pressure of 2.7 x 105 pa and volume 3800cm3 at a temperature of 25°C. It is then taken to another place where the temperature is 15°C and the pressure 2.5 x 105 pa. Determine the new volume. (3 marks)
P1V1 = P2V2 ✓1
T1 T2
2.7×105×3800 = 2.5×105×V2 ✓1
298 288
V2 = 3966.28cm3✓1
- State the pressure law for an ideal gas (1 mark)
-
- The mass of a density bottle is 20g when empty 70g when full of water and 60.0 g when full of liquid L. Calculate the density of the liquid L(take density of water as 1g/cm3) (3 marks)
mass of water = 70 − 20 = 50g
volume of water = 50/1 = 50cm3
volume of Liquid L = 50cm3 ✓1
mass of liquid L = (695 − 20)
= 675g
density of l = 675 ✓1
50
= 13.5g/cm3 ✓1 - In an experiment to determine the density of a liquid a uniform metal cylinder of cross- sectional area 6cm2 and length 4cm was hang from a spring balance and lowered gradually into the liquid as shown below.
The up thrust was calculated from the spring balance and it was found to be 0.6N when the cylinder was fully submerged. Determine:- Volume of the metal cylinder. (3marks)
V = Ah ✓1
= 6 × 4
= 24cm3 ✓1 - Mass of the liquid displaced by the cylinder. (2marks)
upthrust = weight of fluid displaced
= mg
0.6 = m × 10 ✓1
m = 0.06kg ✓1 - Density of the liquid (3marks)
u = vρg ✓1
0.6 = 24 × 10−6 × Ρ × 10✓1
ρ = 2500kg/m3
- Volume of the metal cylinder. (3marks)
- The mass of a density bottle is 20g when empty 70g when full of water and 60.0 g when full of liquid L. Calculate the density of the liquid L(take density of water as 1g/cm3) (3 marks)
-
- A wet umbrella gets dried faster when its handle is rotated at high speed. Explain. (2marks)
- Force of adhesion of water with the cloth provides the centripetal force necessary for circular motion ✓1
- At high speed this force gives up and water molecules fly off the umbrella which gets dried faster ✓1
- Figure below shows a trolley moving on a circular rail in a vertical plane. Given that the mass of the trolley is 250g and the radius of the rail is 1.5m
- Determine the minimum velocity at which trolley passes point X. (3marks)
At minimum velosity, T =o
mv2 = mg ✓1
r
v = √rg = √(1.5 × 10) ✓1
= 3.87 m/s ✓1 - If the trolley moves with a velocity of 4m/s as it passes point Z, Find
- angular velocity at this point. (3marks)
w = v/r
= 4/1.5
= 2.67 rad/s - The force exerted on the rails at this point. (2marks)
F = mv2 = 0.25 × 42 ✓1
r 1.5
= 2.637N ✓1
- angular velocity at this point. (3marks)
- Determine the minimum velocity at which trolley passes point X. (3marks)
- A wet umbrella gets dried faster when its handle is rotated at high speed. Explain. (2marks)
Download Physics Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Sukellemo Joint Pre Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students