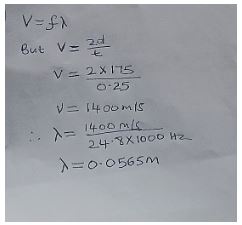- Attempt ALL questions in sections A and B.
- All working must be clearly shown
SECTION A: (25 MARKS)
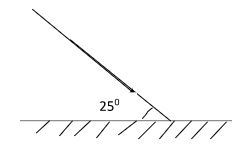
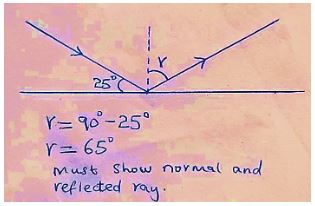
- An incident ray makes an angle of 25° to the mirror as shown below.
Fig 1
Complete the diagram to show how the ray is reflected after striking the mirror hence calculate angle of reflection. (2 mks) - Give the reason why insulators do not conduct electric current. (1 mk)
- A positively charged glass rod is brought near the brass cap of a negatively charged electroscope. Explain why the leaf falls. (2 mks)
- What causes a freely suspended magnetic needle to always point in the north south direction? (1 mk)
- A ray of light travelling towards a concave mirror passes through its centre of curvature. State how the ray is reflected after striking the mirror. (1 mk)
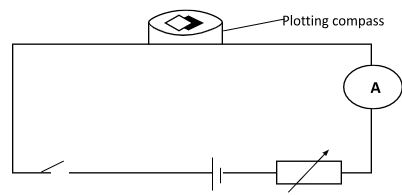
- Fig 2 below shows a magnetic compass placed near a conductor in an electric circuit.
- State what happens to the magnetic needle when the switch is closed. (1 mk)
- Explain why the needle behaves as described in (a) above. (1 mk)
- What are longitudinal waves. (1 mk)
- An echo sounder in a ship produces a sound pulse of frequency 24.8 KHZ. An echo is received from sea bed at a depth of 175m after 0.25 seconds. Calculate the wave length of sound in water. (3 mks)
- The critical angle of a ray of light travelling from medium A to air is 44°.
- Define the term critical angle. (1 mk)
- Calculate the angle of refraction, when the angle of incidence is decreased to 400 (give your answer to 3 decimal places.) (3mks)
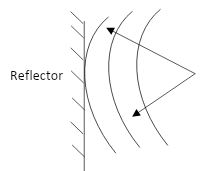
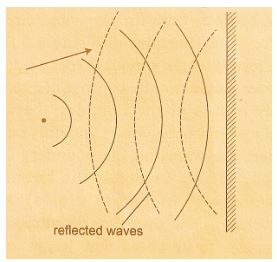
- A circular wave is incident on a straight reflector as shown in fig 3 below.
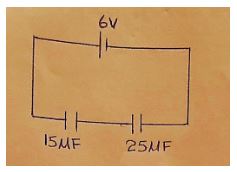
Complete the diagram to show how the wave is reflected. (2 mks) - Fig 4. Below shows a circuit consisting of capacitors and a battery
Determine the charge stored in the circuit (3mk) -
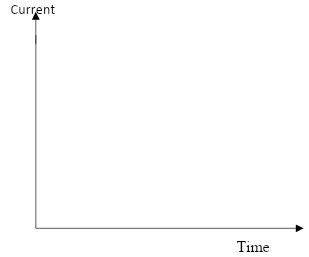
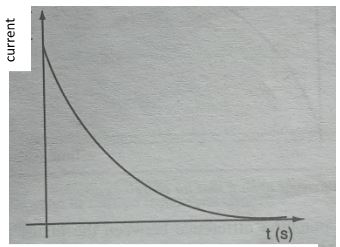
- Sketch a graph to show the variation of the current against time for a discharging capacitor in axis below. (1 mk)
- State two ways of increasing the capacitance of a capacitor. (2mk)
- Sketch a graph to show the variation of the current against time for a discharging capacitor in axis below. (1 mk)
SECTION B (55 MARKS)
-
- State two factors that determine the heat produced by a conductor when connected to an electric circuit. (2mks)
- The electrical power is given by
P = V I where V = Pd across a conductor
I = Current through a conductor.
Show that electrical power can also be given by
P = V2/R where R=resistance. (3 mk) - What property does a fuse wire have that makes it suitable for its use in a circuit. (1 mk)
- An electric heater rated 1.2 KW, 240V supplies 5.5 x 105 joules of heat energy to water in an insulated container.
- For how long is the heater switched on.(Give your answer in minutes and to 2 decimal places) (3 mks)
- Determine the resistance of the heater coil (2 mks)
-
-
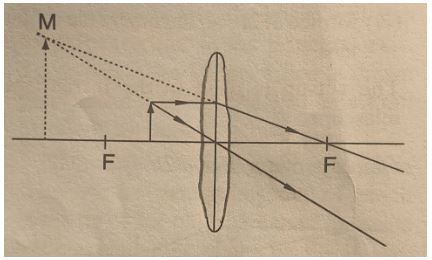
- Using a ray diagram show how a convex lens forms an image when an object is placed between it and its focal point. (3 mks)
- Name one optical device that makes use of the above set up. (1 mk)
- In an experiment to determine the focal length of a converging lens, several values of image distance V and corresponding values of object U were obtained.
Object distance (U) cm 10 15 20 25 Image distance (V) cm 40.0 17.1 13.3 11.8 1/U x 10-2 (cm-1) 1/v x 10-2 (cm-1) - Complete the table. (2 mks)
- Plot a graph of 1/v against 1/U and produce it to cut both axis (4 mks)
- Find the intercepts at 1/u. = _______________ (cm-1) (1 mk)
1/v = ______________ (cm-1) (1 mk) - Determine the average value of focal length of the lens from the graph (2 mks)
-
-
- The table below shows an arrangement of electromagnetic spectrum.
Radio waves Micro waves A Visible light B X rays Gamma rays - Name the radiation represented by B. (1mk)
- Name the human organ that detect radiation A. (1mk)
- State one application of gamma rays. (1mk)
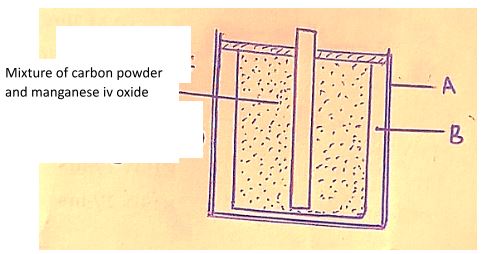
- Fig 5. Shows a dry cell (the paper that covers the dry cell is not shown)
- Name the parts labelled A and B
- ( 1mk)
- ( 1mk)
- State and explain the importance of manganese (iv) oxide in the cell (2mks)
- Explain why large currents should not be drawn from the cell for a long time (2mks)
- Name the parts labelled A and B
- State with reasons whether the dry cell is classified as primary or secondary type of cell (2mks)
- The table below shows an arrangement of electromagnetic spectrum.
-
- Explain what is meant by non-Ohmic conductors (2mks)
- State the reason why electromotive force of a cell is always higher than the potential difference (terminal voltage) (1mk)
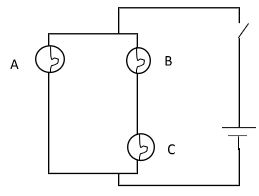
- Fig 6, below shows three identical bulbs A, B, and C connected in a series – parallel circuit.
- State the bulb with the highest potential difference. (1 mk)
- If current through Bulb B is 0.85A, determine the current through bulb A. (2 mks)
- State two factors that affect a resistance of a metal conductor (2mks)
-
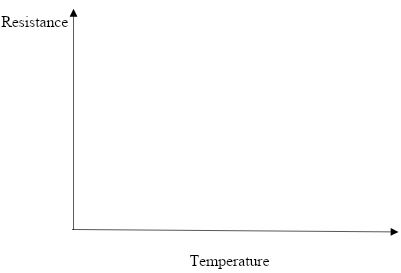
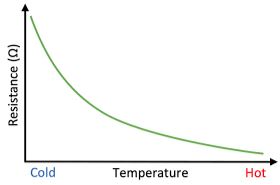
- In the axis provided below sketch a graph to show the relationship between the resistance( R) and temperature of a thermistor (1mk)
- Explain the curve of your graph in (e) (i) above. (1mk)
- In the axis provided below sketch a graph to show the relationship between the resistance( R) and temperature of a thermistor (1mk)
-
- What is meant by the term diffraction of a wave (1mk)
- State two factors that determine the extent of diffraction of a given wave (2 mks)
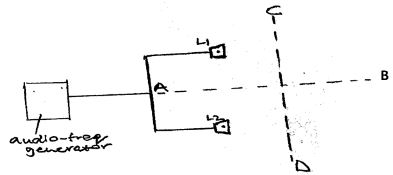
- Two identical loudspeakers connected to the same audio-frequency generator are placed some distance away from each other as shown below.
- Briefly describe the sound experienced by:
- An observer moving along line AB. (1mk)
-
- An observer moving along CD. (1mk)
- Explain the sound experienced by the observer in (b (i)) above (2mks)
-
- State with reason the effect of increasing the frequency of the audio generator on the sound heard along line CD (2mks)
- Briefly describe the sound experienced by:
MARKING SCHEME
- Fig (1)
- Because their electrons are tightly bound to the nuclei of the atoms and are not free to move.
- The positively charged glass rod attracts some electrons from the leaf and metal plate towards the brass cap hence decreasing the charge at leaf and plate.
- Because of earths magnetic field. / The earth behaves as though it has a magnet inside.
- The ray is reflected along the same path.
-
- The magnetic needle gets deflected.
- When current passes through the conductor magnetic field forms around it which interacts with that of magnetic needle causing a deflection.
- They are the waves in which the direction of the particles is parallel or along the direction of wave travel.
-
-
- The angle of incidence in the denser medium for which the angle of refraction in the less dense medium is 90° .
- refractive index = 1/sin c
= 1/sin 44°
= 1.44
When, i = 40°
Refractive index = sin 40° /sin r
Sin r = sin 40°/1.44
= 0.446
r = 26.5°
-
-
Q = CV
Q = (25 x 15)/ (25 + 15) µF x 6V
Q = 56.25µC -
-
-
- Decreasing of distance of separation of plates.
- Increasing of area of overlap of plates.
-
SECTION B
-
-
- Amount of current
- Resistance of conductor
- Time taken. (any 2)
- P = VI
But I =V/R
Therefore P = V (V/R)
P = V2 /R - Low melting point.
-
- Heat = power x time
5.5 x105 J = (1.2 x 1000) W x t
t = 458.33 s
t = (458.33/60) minutes
t = 7.64 min - P = V2/R
R = 2402/( 1.2 x 1000)
R = 48 Ω
- Heat = power x time
-
-
-
- Magnifying glass/microscope
-
-
Object distance (U) cm 10 15 20 25 Image distance (V) cm 40.0 17.1 13.3 11.8 1/U x 10-2 (cm-1) 10.0 6.7 5.0 4.0 1/v x 10-2 (cm-1) 2.5 5.8 7.5 8.5 -
- Labelling axis --- (1 mk)
- Scale ---- (1 mk)
- Plotting points--- (1 mk)
- Straight line --- (1 mk)
- 1/u. = 12.2 x 10-2 (cm-1)
1/v = 12.3 x 10-2 (cm-1) - Average focal length = (f1 + f2)/2
But, f1 = 1/ (12.2 x 10-2 )
f1 = 8.2 cm
f2 = 1/(12.3 x 10-2 )
f2 = 8.13 cm
average focal length = (8.2 + 8.13)/2
= 8.165 cm
-
-
-
-
- ultra violet radiations
- skin
- To kill tumors and cancerous cells
- Zinc can
- Ammonium chloride jelly( or paste)
-
- Its importance is to depolarize.
- It removes hydrogen gas around the carbon rod by reducing it to water.
- The process of depolarization is slow hence some hydrogen is left at the carbon rod causing insulation.
-
- It’s is a primary cell
- It cannot be recharged
-
-
- The materials in which voltage across is not directly proportional to current flowing since they do not obey Ohms law.
- Some of the cells energy is used to drive current through the internal resistance of the cell.
-
- Bulb A.
- Current = 0.85 A x 2
= 1.7 A
-
- cross section area
- length of conductor
- nature of the material
- temperature (any 2)
-
-
- The resistance of a thermistor decreases with increase in temperature
-
-
- speading of a wave after passing through a gap or an obstacle.
-
- size of wavelength.
- size of gap
-
- The observer hears loud sound all through
-
- The observer hears alternating loud and soft sound
- A loud is heard when there is constructive interference and a soft sound when there is destructive interference.
-
-
- Distances between the points of constructive interferences (loud sound) is reduced and also those of destructive interferences (soft sound) are reduced.
- Because higher frequency signal has shorter wavelength.
Download Physics Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Lainaku 1 Joint PreMock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students