INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- State the functions of the following organelles (3marks)
- Lysosomes
- Golgi apparatus
- Chloroplast
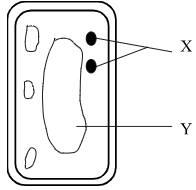
- The diagram below represents a cell
- Name the parts labeled X and Y (2marks)
- State why the structures labeled X would be more on one side than the other side. (1mark)
- Write the role of the following parts of microscope. (2marks)
- Mirror
- Diaphragm
- Explain why plant cells do not burst when immersed in distilled water. (1mk)
- An experiment was carried out to investigate the rate of reaction shown below
Sucrose →Fructose +Glucose
For the products; Fructose and Glucose to be formed, it was found that substance K was to be added and the temperature maintained at 37°C.When another substance L was added, the reaction slowed down and eventually stopped.- Suggest the identity of the substances K and L (2marks)
- Explain how substance L slowed down the reaction. (1mark)
-
- State two roles of light in the process of photosynthesis. (2marks)
- Name one product of dark phase reaction in photosynthesis. (1mark)
- A solution of sugarcane was boiled with hydrochloric acid; sodium carbonate was added; cooled and Benedict’s solution was added then boiled. An orange precipitate was formed.
- Why was the solution boiled with hydrochloric acid? (1mark)
- Why was sodium carbonate added? (1mark)
- Name the type of reaction that takes place when simple sugars combine to form complex sugar. (1mark)
- .
- State two functions of bile juice in the digestion of food? (2marks)
- How does substrate concentration affect the rate of enzyme reaction? (1mark)
- A certain animal has no incisors, no canines, six premolars and six molars in its upper jaw, in the lower jaw there are six incisors, two canines, six premolars and six molars. Write its dental formular? (2marks)
- Name the physiological process by which gas exchange takes place at the respiratory surface of animal and plants. (1mark)
-
- The action of ptyalin stops at the stomach. Give a reason. (1marks)
- State a factor that denatures enzymes (1mark)
- Name the features that increase the surface area of small intestines. (2marks)
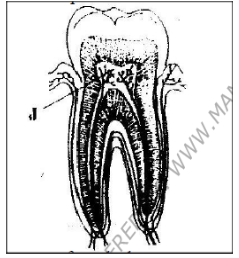
- The diagram shown below shows a section through a human tooth.
-
- Identify the type of teeth. (1mk)
- Give a reason for your answer in 12(a) i) above. (1mk)
- How is the part J important in the functioning of the tooth? (2mks)
-
- Name the functions of the following apparatus.
- Pitfall trap (1mk)
- Bait trap (1mk)
- State any two functions of lipids in the body. (2mks)
- The scientific name for cat is Canis Domestica.
- Identify two mistakes made in writing the name above. (2mks)
- State two reasons why latin language are preferred when writing the above name. (2mks)
- State two factors that increase the rate of photosynthesis. (2mks)
- Raymond observed eight epidermal cells across the field of a light microscope. If the diameter of the field of the field of view is 4mm, estimate the average size of each cell in micrometer. Show your working. (3mks)
- Give the reason for carrying out the following procedures when preparing wet mounts of plant tissues.
- Making very thin sections (1mk)
- Adding water on the plant section (1mk)
- Placing cover slip over the plant section (1mk)
- Give three roles of active transport in living organisms. (3mks)
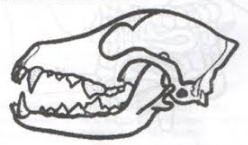
- The diagram below represents the lower jaw of a mammal.
- Name the mode of nutrition of the mammal whose jaw is shown. (1mk)
- Give two observable reasons for your answer in 20 i.) above (2mks)
- Label the incisor tooth in the diagram. (1mk)
-
- Define the term photosynthesis. (1mk)
- Name three photosynthetic cells in a leaf. (3mks)
- The diagram below shows what happens to red blood cells when it was put in a solution.
- Name the type of solution in which the cell was put. (1mk)
- Name the process demonstrated in the diagram. (1mk)
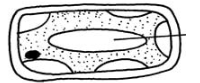
- The cell shown below was obtained from a piece of potato that was immersed in 20% salt solution. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Name the process shown in the diagram above. (1mk)
- Account for the observation above. (3mk)
- Study the table below and answer the questions that follow.
Identify the physiological process responsible for the absorption of the following substances through the roots of plants in this habitat:Sodium ion concentration Iodide ion concentration Sea water 250 35 Cell sap 100 550 - Sodium ion (1mk)
- Iodide ion (1mk)
- Give three enzymes that are produced in the small intestine. (3mks)
- Name the mineral or vitamin necessary for the following; (3mks)
- Blood clotting
- Nerve impulse transmission
- Night vision
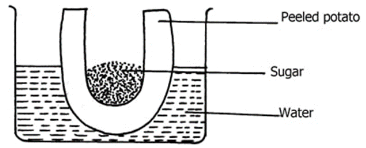
- An experiment was set-up as shown below and left for one hour
- State the expected result at the end of one hour (1mk)
- Explain the observations made in this experiment. (2mks)
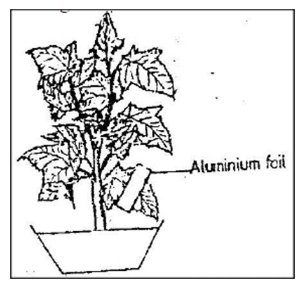
- The diagram below shows a leaf of a growing plant partly covered with aluminium foil. The plant was placed in the sun from morning to midday and then tested for starch.
- What was the aim of the experiment? (1mk)
-
- State the observation made when the leaf was tested for starch (1mk)
- Account for the observation in 28 b(i) above. (2mks)
MARKING SCHEME
-
- Lysosomes
- Destroy old and worn out cells;
- Destroy foreign bodies;
- Golgi apparatus
- packaging and transport of glycoprotein;
- Secrete lysosomes;
- Chloroplasts-photosynthesis ; (3mks)
- Lysosomes
-
-
- X-Chloroplasts;
- Y-Vacuole(s);
- Move to upper part of the cell in order to receive maximum light for photosynthesis ( in dimlight); (3mks)
-
-
- Acts as a light reflector, allowing the observer to see the specimen more clearly.
- To control the amount of light that reaches the specimen
-
- Plant cells have cell wall; cell wall is rigid/cellulose cell wall is strong and rigid to withstand turgor pressure;
- water is absorbed by osmosis; cells become turgid; cell wall create inward pressure that prevent cell from bursting;
-
-
- K-Enzyme;
- L-Inhibitor; (2mks)
- Compete for the active site of the enzyme; (1mk)
-
-
- Split water molecules/photolysis;
Produce ATP; (2mks) - Glucose;
- Split water molecules/photolysis;
-
- To hydrolyze/breakdown double sugars into simple sugars;
- Neutralize the (unused) acid;
- Condensation; (3mks)
-
- Has alkaline salts which create alkaline media/neutralize acidic food from the stomach
Emulsification of fats into droplets; - As the substrate concentration decreases the rate of enzyme action decreases; Ac. the converse. (3mks)
- Has alkaline salts which create alkaline media/neutralize acidic food from the stomach
- i 0 c 0 pm 3 m 3 lower case letters (2mks)
3 3 3 3
demarcation included - Diffusion; (1mk)
-
- In stomach there is acid medium/ and ptyalin only acts at slightly alkaline medium; (1mk)
- High temperatures above 40°c; (1mk)
-
- Villi;
- Microvilli;
- Long (2mks)
-
-
- Molar/ Premolar (1mk)
- Has two roots/ cusps/ Ridges (1mk)
- Has nerve fibres that detect changes/ Has blood capillaries that supply Oxygen and nutrients/ remove metabolic wastes from the tooth cells
-
-
- To catch / trap crawling animals
- Attract and trap small animals (2mks)
-
- Insulation
- Shock absorber
- Source of energy
- Source of metabolic water
- Structural compounds (First two pts)
-
- Not underlined separately
Species name started with a capital letter/ upper case (2mks) - Universally accepted by scientists acc. Uniformity
Is a ‘dead’ language i.e lacks indigenous speakers
- Not underlined separately
-
- Optimum temperature
- Optimum light intensity
- Increase in CO2 concentration
- Increase in amount of water (First two pts)
- Diameter of one cell = Field of view Diameter
Number of cells
= 4mm
8
= 0.5 mm;
1mm = 1000 micrometers
0.5 mm = ( 0.5 x 1000);
1
= 500 micrometers; -
- Enhance/ easy diffusion/ absorption of iodine solution
- For the section/ cells not to dry up/ die/
Keep the section/cells alive/ Maintain the shape of cells/ section - Hold the specimen in position (3mks)
-
- Absoption of mineral salts by plants roots from soil
- Absoption of soluble products of digestion in the gut
- Excretion of metabolic waste products through the skin/ kidney
- Accumulation of mineral in the body of marine organisms to offset osmotic imbalance (3mks)
-
- Carnivorous Rj. Carnivore
- Presence pointed/ large canines
Presence of carnassial teeth (2mks) - Incisor correctly labeled in the diagram. (1mk)
-
- Process by which green plants manufacture food from Carbon (IV) oxide and water in the presence of light (1mk)
-
- Palisade cell
- Guard cells
- Spongy mesophyll cells (3mks)
-
- Hypertonic (1mk)
- Crenation (1mk)
-
- Plasmolysis (1mk)
- The plant cell lost water by osmosis since it was placed in a hypertonic solution causing the cell membrane to detach from the cell wall (3mks)
-
- Diffusion
- Active transport (2mks)
- Peptidase/ lipase/ lactase/ maltase/ sucrose (First 3pts)
-
- Calcium ions/ Vitamin K
- Sodium ions/ Potassium ions/ Chloride ions
- Vitamin A
-
- The potato cup will be filled with solution;
- The solution in the potato cells is hypertonic to the water; hence water moves into the cell by osmosis; this makes the solution in the neighbouring cells to be hypertonic to the outer cells; hence water moves from cell to cell until it eventually enters the potato cup;
-
- To show that light is necessary for photosynthesis;
-
- Only the uncovered areas turned blue- black with iodine;
- The part covered with aluminum foil did not receive light; and thus could not carry out photosynthesis ;
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Biology Questions and Answers - Form 1 End Term 3 Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students