SECTION A (40MKS)
- Distinguish between the following
- Olericulture and aquaculture (1mk)
- mixed cropping and inter cropping (1mk)
- State three factors that influence agriculture positivity (3mks)
- State the advantages for carrying out leveling as a tertiary operation (3mks)
- Give factors that influence the number of secondary cultivations seedbed preparation (2mks)
- State four environmental factors in Kenya (3mks)
- State four qualities for parent plant which rootstock is obtained for grafting. (3mks)
- Give four reasons why burning of land is discouraged as a method of land clearing (3mks)
- State four disadvantages of broadcasting seeds during planting (3mks)
- Outline four ideal characteristics of a dairy goat. (3mks)
- Give methods of modifying soil Ph. (4mks)
- Describe signs of good health in farm animals under the following
- Movement (½mk)
- Urine (½mk)
- Mucus membrane (½mk)
- Posture (½mk)
- Name four tools must always be used together. (3mks)
- Highlight four records you would advise a poultry farmer to keep. (2mk)
- Give four maintenance practices carried out on saws. (2mk)
- Differentiate between a nursery bed and a seedling bed. (1mk)
SECTION B
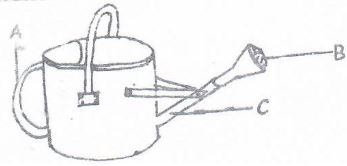
- Study the illustration below and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the equipment (1mk)
- Name the parts labeled A, B, and C (3mks)
- _________________________________
- ________________________________
- ____________________________________
- Give one use of the above equipment (1mk)
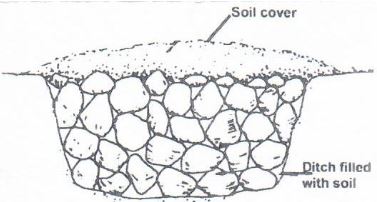
- Below is a diagram showing a method of drainage, use it to answer the questions that follows.
- Identify the above method of the method of drainage (1mk)
- State one advantage of the methods of drainage. (1mk)
- Outline three importance’s of drainage as a method of land reclamation (3mks)
-
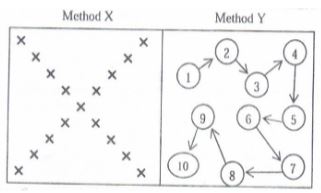
- Identify the methods of sampling down below
- Give two reasons that should be avoided during soil sampling (2mks)
- Name two sites that should be avoided during soil sampling (2mks)
- Identify the methods of sampling down below
- A farmer applied 200 kgs for CAN (20%) per Hecate maize crop. Calculate the amount of nitrogen applied on his structure crop.
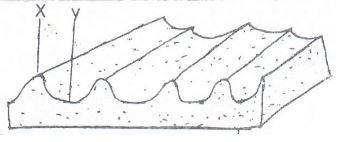
Show your workings (4mks) - The diagram below shows a territory operation carried out on a seedbed.
- Identify the operation (1mk)
- Name the parts labeled X and Y on the diagram (2mks)
- State two importance of the operation name in (a) above (2mks)
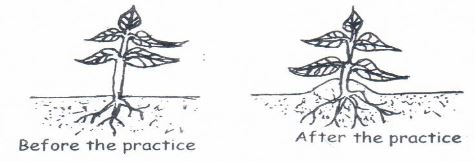
- The diagram represents a field produce. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the practice shown above (1mk)
- give a reason for carrying out the above practice on the following crops
Irish potatoes- Ground nuts
- Tobacco
- Maize (3 x 1 =3mks)
SECTION C (30MKS)
-
-
- Give three types of nursery beds used in raising seedlings (3mks)
- Give two reasons for construction a shade over nursery (2mks)
- Describe factors that should be considered when siting a vegetable nursery (5mks)
- Name any three methods of layering used in crop propagation (3mks)
- Name two methods of fertilizer applications (2mks)
-
- Name four biotic factors that affect agriculture and for each state one effect on
Agriculture (8mks) - Describe production of cabbages under the following subheadings.
- Land preparation (3mks)
- Field management practices (6mks)
MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A
- Distinguish between the following
- Olericulture – is growing of vegetables while aquaculture is rearing of dish in fishponds.
- Weed cropping is the practice of growing two or more crops in different plots while; Intercropping is the practice of growing the same crop in same plot at the same time. (2 x 1 = 2mks)
- Biotic factors that influence agriculture positivity
- Predators
- Pollination
- Decomposers
- Nitrogen fueling bacteria (4 x 1 = 4mks)
- Advantages of leveling
- Facilities uniform depth of planting
- Facilities uniform germination of seeds
- For easier germination of small seeds; grass seeds (3 x 1 = 3mks)
- Factors that influence the number of secondary cultivation
- Type of tilt required
- Topography of the slope of the land
- Moisture content to grass type of crop to grow
- Type of implement to be used. (4 x 1 = 4mks)
-
- Rainfall
- Wind
- Temperature
- Light intensity
- Relative humidity
- Type of soil (8x1=8mks)
-
- Resist to diseases
- Free from disease
- Free from pest attack
- Adapted to different soil condition e.g. soil Ph
- Complete with different scions (4 x 1= 4mks)
- Reasons why burning is discouraged as a method of land cleaning
- Kills soil organism
- Leads to loss of nutrients
- Destroys organic matter
- Leaves the land have encouraging soil erosion (4 x 1 = 4mks
- Disadvantages of broadcasting seeds during planting
- Leads to uneven germination
- Higher seed rates are used
- Leads to overcoming in some areas
- Difficult to carry out management practices like weeding
- Difficult to establish correct plant population (4 x 1 = 4mks)
- Characteristics of dairy goats
- Wedge shaped /triangular shaped
- Large stomach to store more food
- Long thin neck and small head
- Lean bodies with little small head
- Straight top line
- Long thin legs
- Prominent /viable pin bones (4 x 1 = 4mks)
- Methods of modifying soil Ph
- Apply sulphur
- Apply lime
- Apply acidic fertilizers
- Apply basic fertilizers (4 x 1 = 4mks)
-
- movement – limping /practicing (½ x 1 = ½ mk)
- Urine – different in urination, failure to urinate blood in urine (½ x ½ mk)
- Mucous membrane - pink in colur, moist and soft (½ x ½ mk)
- Posture – normal posture (½ x ½ mk)
-
- Tracer and canuls
- Hypodermic needle and syringe
- Bull ring and lead stick
- Elastration and rubber ring
- Records kept by a poultry farmer
- Breeding records
- Feed records
- Labor record
- Production records
- Health records (4 x 1 = 2mks)
- Maintenance practices carried out on saws
- Teeth setting
- Sharpening blunt teeth
- Straitening blunt blade
- Tightening loose nuts and bolts /screens (4 x 1 = 2mks)
-
- Nursery bed – special seedbed prepared for raising seedlings before transplanting
- Seed bed – a special nursery which has been uprooted from the nursery bed due to overcrowding before they are transplanted.
- (1 x 1 = 1mk)
SECTION B
-
- Identify the equipment
Watering can (1 x 1 = 1mk) - Parts labeled
- – Handle
- – Rose
- – Spout ( 3 x 1 = 3mks)
- use of the equipment
Watering seedlings in the nursery and after transplanting (1 x 1 = 1mk)
- Identify the equipment
-
- French drain
- Advantages; crops are grown normally. On the surface of the French drain
- importance of drainages
- Increases soil aeration
- Increases soil volume
- Raise soli temperature
- Reduces soil erosion
- removes toxic substances from the soil (3 x 1 = 3mks)
-
- Methods of sampling
- Method X − terrace
- Method Y – zigzag
- Reasons for soil sampling
- To rest for soil nutrients
- To rest for soil Ph
- Sites that should be avoided during soil sampling
- Dead furrows
- Terrace stands
- Old fence lines
- Old manure heaps
- Swampy areas
- Near trees and boundaries
- Where there was a boma or animal shed
- Charcoal burning sites (any 2 x 1 = 2mks)
- Methods of sampling
- 100 kg – 20kg N
1kg CAN – 20 kg N
100
200 kg CA – (20 X 2)KG n
100
40kg N per Ha
1 Ha requires 40 kg N
Therefore 5 Ha require 40 x 5 = 200 kg N
Proper working how (4mks) -
- Ridging (1 x 1 = 1mk)
-
- X – ridge
- Y – furrow
- Importance’s of the operation
- It encourages tuber expansion
- It allows early harvesting of root crops
- It helps in water conservation (2 x 1 = 2mks)
-
- Earthling up (1 x 1 = 1mk)
-
- Irish potatoes important tuber formation
- Groundnuts promote production of seeds
- Tobacco - improve drainage and prevent loading (4 x 1 4mks)
- Maize - provide support and prevent lodging (4 x 1 = 4mks)
SECTION C
-
-
- Three bypass of nursery beds
- Vegetation crop nurseries
- Tree nurseries
- Vegetation propagation nurseries (3 x1 = 3mks)
- Two reasons for constructing of shade
- To reduce the impact of rain crops
- To help in water conservation (2 x1 = 2mks)
- Factors considered when selecting sting a vegetable nursery
- Near a reliable source of rain drops
- A gentle slope to prevent flooding, erosion through run-off
- In a well secured place
- In a deep fertile and well drained soils
- Three bypass of nursery beds
- three methods of layering
- marcotting
- TP layering
- Trench layering
- Compound/serpentine layering (3 x1 = 3mks)
- Methods of fertile application
- Broadcasting
- Placement method
- Side dressing
- Folian spraying ]drip application (2 x1 = 2mks)
-
- Four biotic factors that affect agriculture and their effect
- Pests – fed on the leaves of the plants, trench diseases, injure plant paints etc.
- Parasites – absorb food substances from the digestive tract/suck blood from the animal and irritate them by biting on their skin
- Decomposers act on their skin materials causing rotting
- Pathogens transmit diseases
- Predators kills and feeds on another animal
- Pollinates transfer pollen grains from the stamens to the pistil of the flower nitrates convert nitrogen from the air into nitrates.
Naming (4 x1 = 4mks)
Explanation (4 x1 = 4mks)
- Production of cabbages
- land preparation
- Land is prepared early to allow weeds to dry and organic matter to decompose
- Dig land deeply during primary land cultivation /plough to land
- Various land/carry and secondary, cultivation to get medium tilth. (3 x1 = 3mks)
- Field management practices
- Top dressing done when the cabbages are about 20-25 cm in height using sulphate of ammonia
- To field should be kept weed free
- Control harmful pests like aphid’s cutworms
- Control diseases like damping off blackout downy mildew
- Harvest three to four months after transplanting by cutting heads when they are solid and compost (5 x1 = 5mks)
- land preparation
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Agriculture Questions and Answers - Form 2 End Term 2 Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students