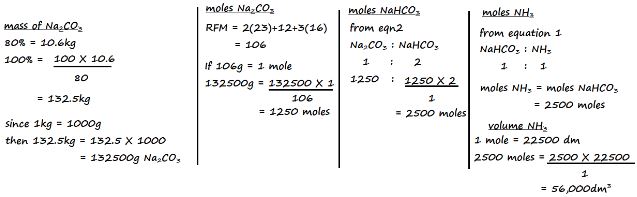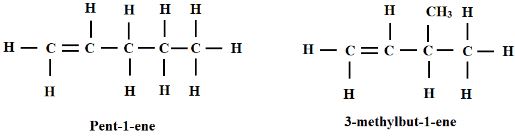Instructions to candidate
- Answer ALL questions
- All working MUST be clearly shown where applicable
- KNEC mathematical tables and silent non-programmable electronic calculators may be used
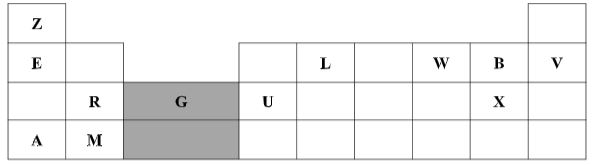
- The grid below represents part of the periodic table. Study the information and answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent actual symbols of elements
- Which element would form a trivalent cation? (1 Mark)
- Write the equation for the reaction that would occur between R and B (1 Mark)
- What is the name of the elements that are found in the region labelled G? (1 Mark)
- Which is the most reactive non-metallic element in the table above? Explain (2 Marks)
- How does the atomic radius of L compare with that of B? Explain (2 Marks)
- The table below shows some properties and electron arrangement of ions of elements represented by letters D to K which are not actual symbols of elements. Study the information and answer the questions that follow.
Ion Electron arrangement of ion Atomic radius of element (nm) Ionic radius of element (nm) D- 2.8 0.072 0.136 E+ 2.8.8 0.231 0.133 F3+ 2.8 0.143 0.050 G2+ 2.8.8 0.133 0.074 H2+ 2.8 0.160 0.064 I+ 2.8 0.186 0.095 J3- 2.8.8 0.110 0.190 K- 2.8.8 0.099 0.181 - State the atomic numbers of elements F and G (1 Mark)
- Select two metals that belong to period 3 (1 Mark)
- Element I reacts violently with water. Write the equation for this reaction (1 Mark)
- Why is the ionic radius of G smaller than its atomic radius? (1 Mark)
- Compare the reactivities of elements G and H. Explain (2 Marks)
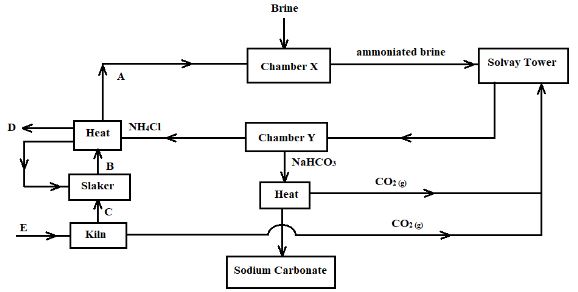
- The flow chart below represents the main steps in the industrial manufacture of sodium carbonate. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- What is the name given to this process? (1 Mark)
- Name the substances labelled A, B, C, and D. (2 Marks)
- Identify substance E and write a chemical equation for the process it undergoes to produce C (2 Marks)
- Name the process that takes place in the chamber marked Y (1 Mark)
- The process taking place in the chamber marked X requires the industry to be located near a large water body. Explain (2 Marks)
- Name two by-products that are recycled in this process (1 Mark)
- Ammonia is a raw material in the industrial manufacture of sodium carbonate. Write the chemical equations for the processes taking place in the carbonator and roaster
Carbonator: (1 Mark)
Roaster: (1 Mark) - Considering the two reactions, and assuming that there was no recycling process, calculate the volume of ammonia at s.t.p. that would be required to produce 10.6kg of sodium carbonate if the factory is operating at 80% efficiency (3 Marks)
(C = 12.0, O = 16.0, H = 1.0, Na = 23.0, N = 14.0, molar gas volume at s.t.p. is 22.4dm3) - Sodium carbonate may be prepared using the double salt, trona (Na2CO3•NaHCO3•2H2O). Why is it difficult to show that trona contains water of crystallization by heating? (1 Mark)
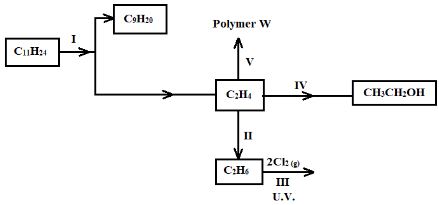
- Study the flow chart below and use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Name the process labelled I (1 Mark)
- Describe how acidified potassium manganate (VII) solution can be used to distinguish between C2H4 and C2H6. (2 Marks)
- State one industrial application of the process in step II (1 Mark)
- Write an equation for the reaction in step III (1 Mark)
- The compound C10H22 is cracked to obtain an alkane X and another hydrocarbon. The cracking takes place according to the following equation
C10H22 → C5H10 + X- Write down the formula of substance X (1 Mark)
- The cracking process requires the use of a catalyst. State two reasons why a catalyst is used in this reaction (2 Marks)
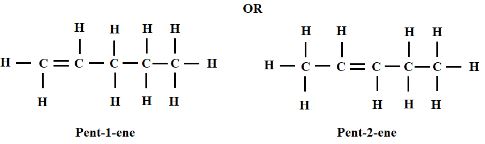
- Draw and name the compound C5H10 (2 Marks)
- Name the type of reaction that takes place when C5H10 reacts with chlorine gas (1 Mark)
- Draw the structure of the main product of this reaction (1 Mark)
- What are structural isomers? (1 Mark)
- Draw and name any two structural isomers of C5H10 (2 Marks)
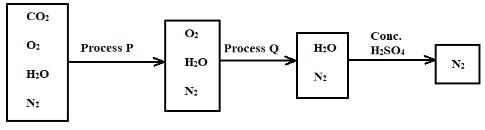
- The flow diagram below shows the process of obtaining nitrogen from a sample of air. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
- What is the purpose of processes P and Q? (2 Marks)
Process P
Process Q - Identify the reagents used in the processes P and Q (2 Marks)
Process P
Process Q - Write equations for the reactions taking place during processes P and Q (2 Marks)
Process P
Process Q - Comment on the purity of the nitrogen gas collected (2 Marks)
- A student categorised air as a compound and not as a mixture. Give two reasons as to why the student was wrong (2 Marks)
- What is the purpose of processes P and Q? (2 Marks)
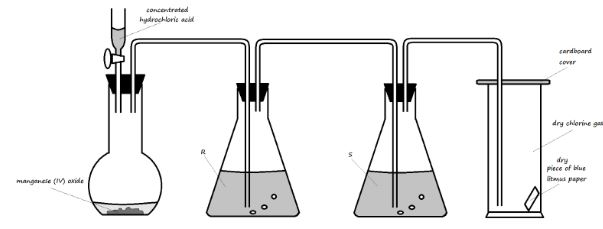
- The diagram below illustrates an experiment setup used for the preparation of dry chlorine in the laboratory
- State one mistake that is in the setup (1 Mark)
- Write an equation for the reaction that would occur in the flask (1 Mark)
- What is the role of manganese (IV) oxide in the setup? (1 Mark)
- State the identity and roles of the following in the setup:
- Solution R (2 Marks
- Solution S (2 Marks)
- State and explain one important precaution that should be observed when carrying out this experiment (2 Marks)
- State and explain the observation made on the blue litmus paper in the gas jar (2 Marks)
- State three uses of chlorine gas (3 Marks)
-
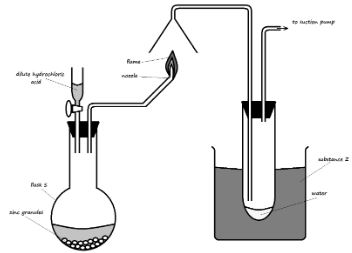
- Study the setup below and use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Identify substance Z and state its purpose in the experiment (2 Marks)
- Write an equation for:
The reaction in the flask (1 Mark)
The reaction at the nozzle (1 Mark) - Describe a test for the product formed in flask S (2 Marks)
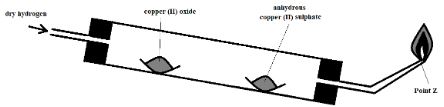
- The diagram below was used to study a property of hydrogen gas. Study it and use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Name the missing condition in the setup (1 Mark)
- State two observations that may be made in the combustion tube (2 Marks)
- What is the importance of the reaction at the nozzle? (1 Mark)
- What would be observed if the copper (II) oxide were replaced with zinc oxide? (1 Mark)
- Why is it important to tilt the combustion tube as demonstrated in the diagram? (1 Mark)
- State one other use of hydrogen apart from that demonstrated by the reaction in the setup (1 Mark)
- Study the setup below and use it to answer the questions that follow.
MARKING SCHEME
- the grid below represents part of the periodic table. Study the information and answer the questions that follow. The letters don't represent actual symbols of elements.
- Which element would form a trivalent cation? (1 Mark)
- Element U
- Write the equation for the reaction that would occur between R and B (1 Mark)
- R (s) + B2 (g) → RB2 (s)
- What is the name of the elements that are found in the region labelled G? (1 Mark)
- Transition metals [Reject Transition elements]
- Which is the most reactive non-metallic element in the table above? Explain (2 Marks)
- Element B. It has the smallest atomic radius thus gains an electron most easily//It has the highest effective nuclear force of attraction among the elements that can react, thus gains electrons most easily.
- How does the atomic radius of L compare with that of B? Explain (2 Marks)
- L is larger than B. L has fewer protons for the same number of energy levels as B hence experiences a weaker effective force of attraction that holds its energy levels loosely.
- Which element would form a trivalent cation? (1 Mark)
- The table below shows some properties and electron arrangement of ions of elements represented by letters D to K which are not actual symbols of elements. Study the information and answer the questions that follow.
Ion Electron arrangement of ion Atomic radius of element (nm) Ionic radius of element (nm) D- 2.8 0.072 0.136 E+ 2.8.8 0.231 0.133 F3+ 2.8 0.143 0.050 G2+ 2.8.8 0.133 0.074 H2+ 2.8 0.160 0.064 I+ 2.8 0.186 0.095 J3- 2.8.8 0.110 0.190 K- 2.8.8 0.099 0.181 - State the atomic numbers of elements F and G (1 Mark)
- F3+ → 2.8 thus F →F3+ + 3e- hence F → 2.8 + 3e- thus 2.8.3 hence atomic number 13
- G2+→ 2.8.8 thus G → G2+ + 2.8 hence G → 2.8.8 thus 2.8.8.3 hence atomic number 21
- Select two metals that belong to period 3 (1 Mark)
- F, H, and I [the first two written by the candidate are considered]
- Element I reacts violently with water. Write the equation for this reaction (1 Mark)
- 2I (s) + H2O (l) → 2IOH (aq) + H2 (g)
- Why is the ionic radius of G smaller than its atomic radius? (1 Mark)
- The ion is formed through the loss of an electron, which results in the loss of an entire energy level. The ion has fewer occupied energy levels than the atom.
- Compare the reactivities of elements G and H. Explain (2 Marks)
- Element G is more reactive than element H. Element G has more occupied energy levels than element H hence its valence electrons experience a weaker effective nuclear force, allowing them to be more easily lost.
- State the atomic numbers of elements F and G (1 Mark)
- The flow chart below represents the main steps in the industrial manufacture of sodium carbonate. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- What is the name given to this process? (1 Mark)
- Solvay process
- Name the substances labelled A, B, C, and D. (2 Marks)
- A - Ammonia gas
- B - Calcium hydroxide
- C - Calcium oxide
- D - Calcium chloride
- Identify substance E and write a chemical equation for the process it undergoes to produce C (2 Marks)
Limestone.
heat
CaC03(s) → CaO(s) + C02(g) - Name the process that takes place in the chamber marked Y (1 Mark)
- Filtration
- The process taking place in the chamber marked X requires the industry to be located near a large water body. Explain (2 Marks)
- The reaction between ammoniated brine and carbon (IV) oxide produces a lot of heat. The industry needs to be located near a large water body to provide water for cooling the chamber.
- Name two by-products that are recycled in this process (1 Mark)
- Ammonia
- Carbon (IV) oxide
- Ammonia is a raw material in the industrial manufacture of sodium carbonate. Write the chemical equations for the processes taking place in the carbonator and roaster
Carbonator: NH3 (g) + NaCl (aq) + H2O (l) + CO2 (g) ? NH4Cl (aq) + NaHCO3 (s) (1 Mark)
heat
Roaster: 2NaHCO3(s) → Na2CO3(s) + CO2(g) + H2O (1 Mark) - Considering the two reactions, and assuming that there was no recycling process, calculate the volume of ammonia at s.t.p. that would be required to produce 10.6kg of sodium carbonate if the factory is operating at 80% efficiency (3 Marks)
(C = 12.0, O = 16.0, H = 1.0, Na = 23.0, N = 14.0, molar gas volume at s.t.p. is 22.4dm3)
- Sodium carbonate may be prepared using the double salt, trona (Na2CO3•NaHCO3•2H2O). Why is it difficult to show that trona contains water of crystallization by heating? (1 Mark)
- Sodium hydrogen carbonate in trona decomposes to form water as one of its products
- What is the name given to this process? (1 Mark)
- Study the flow chart below and use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Name the process labelled I (1 Mark)
- Cracking [of long chain alkane] (accept cracking)
- Describe how acidified potassium manganate (VII) solution can be used to distinguish between C2H4 and C2H6. (2 Marks)
- Put equal volumes of acidified potassium manganate (VII) into two separate boiling tubes. Bubble some C2H4 into the first boiling tube and some C2H6 into the second boiling tube. The colour of potassium manganate (VII) changes from purple to colourless in the tube through which C2H4 is bubbled but remains purple in the boiling tube through which C2H6 is bubbled.
- State one industrial application of the process in step II (1 Mark)
- Manufacture of margarine from vegetable oils
- Write an equation for the reaction in step III (1 Mark)
- The compound C10H22 is cracked to obtain an alkane X and another hydrocarbon. The cracking takes place according to the following equation
C10H22 → C5H10 + X- Write down the formula of substance X (1 Mark)
- C5H12
- The cracking process requires the use of a catalyst. State two reasons why a catalyst is used in this reaction (2 Marks)
- It speeds up the rate of reaction
- It lowers the cost of production since less energy is used
- Reaction runs at lower temperatures
[first two of the candidate’s answers are marked]
- Draw and name the compound C5H10 (2 Marks)
The correct name must be assigned to the correct structure
The structure should be a fully open structure. - Name the type of reaction that takes place when C5H10 reacts with chlorine gas (1 Mark)
- Addition reaction
- Draw the structure of the main product of this reaction (1 Mark)
- Write down the formula of substance X (1 Mark)
- What are structural isomers? (1 Mark)
- These are organic compounds with the same molecular formula but with different structural arrangement.
- Draw and name any two structural isomers of C5H10 (2 Marks)
- Name the process labelled I (1 Mark)
- The flow diagram below shows the process of obtaining nitrogen from a sample of air. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
- What is the purpose of processes P and Q? (2 Marks)
- Process P Removing carbon (IV) oxide from the air sample
- Process Q Removing oxygen from the air sample
- Identify the reagents used in the processes P and Q (2 Marks)
- Process P - Concentrated potassium hydroxide solution
[must be concentrated] [conc. Sodium hydroxide may also work] - Process Q - Heated copper turnings may be used
[metals high in the reactivity series like potassium, sodium, calcium, and magnesium may not be used]
- Process P - Concentrated potassium hydroxide solution
- Write equations for the reactions taking place during processes P and Q (2 Marks)
- Process P - 2KOH (aq) + CO2 (g) → K2CO3 (aq) + H2O (l)
- Process Q - 2Cu (s) + O2 (g) → 2CuO (s)
- Comment on the purity of the nitrogen gas collected (2 Marks)
- It is impure. It contains noble gases that were not removed during the separation process.
- A student categorised air as a compound and not as a mixture. Give two reasons as to why the student was wrong (2 Marks)
- The components of air retain their physical and chemical properties
- The components of air can be separated by physical means
- The components of air are not in fixed proportions
[the first two answers written by the candidate]
- What is the purpose of processes P and Q? (2 Marks)
- The diagram below illustrates an experiment setup used for the preparation of dry chlorine in the laboratory
- State one mistake that is in the setup (1 Mark)
- There is no heat on the manganese (IV) oxide
- Write an equation for the reaction that would occur in the flask (1 Mark)
- 4HCl (aq) + MnO2 (s) → MnCl2 (aq) + Cl2 (g) + 2H2O (l)
- What is the role of manganese (IV) oxide in the setup? (1 Mark)
- It oxidises the concentrated hydrochloric acid to chlorine gas
- State the identity and roles of the following in the setup:
- Solution R (2 Marks)
- To absorb excess hydrogen chloride fumes from the concentrated hydrochloric acid
- Solution S (2 Marks)
- To dry the gas
- Solution R (2 Marks)
- State and explain one important precaution that should be observed when carrying out this experiment (2 Marks)
- The experiment should be done in a fume chamber. The chlorine gas produced is poisonous/toxic.
- State and explain the observation made on the blue litmus paper in the gas jar (2 Marks)
- The blue litmus paper remains blue. Dry chlorine gas has no effect on dry litmus paper.
- State three uses of chlorine gas (3 Marks)
- Used in the manufacture of bleaching agents
- Used in water treatment to kill bacteria
- Used in the large-scale manufacture of hydrochloric acid
- Used in the manufacture of polyvinylchloride (pvc)
[any first three answers the candidate writes]
- State one mistake that is in the setup (1 Mark)
-
- Study the setup below and use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Identify substance Z and state its purpose in the experiment (2 Marks)
- Ice-cold water. It condenses water vapor from the candle flame
- Write an equation for: The reaction in the flask (1 Mark)
- Zn (s) + 2HCl (aq) → ZnCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
The reaction at the nozzle (1 Mark) - 2H2 (g) + O2 (g) ? 2H2O (l)
- Zn (s) + 2HCl (aq) → ZnCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
- Describe a test for the product formed in flask S (2 Marks)
- Insert a burning splint into flask S. The flame extinguishes with a ‘pop’ sound.
- Identify substance Z and state its purpose in the experiment (2 Marks)
- The diagram below was used to study a property of hydrogen gas. Study it and use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Name the missing condition in the setup (1 Mark)
- Heat on copper (II) oxide
- State two observations that may be made in the combustion tube (2 Marks)
- The copper (II) oxide changed from black to a blue appearance
- What is the importance of the reaction at the nozzle? (1 Mark)
- It prevents the gas from accumulating in the room, as the gas may explode.
- What would be observed if the copper (II) oxide were replaced with zinc oxide? (1 Mark)
- The solid would change colour from yellow to a grey substance.
- Why is it important to tilt the combustion tube as demonstrated in the diagram? (1 Mark)
- To prevent the water formed from flowing to the hot parts of the tube to cause breakage of the test tube.
- State one other use of hydrogen apart from that demonstrated by the reaction in the setup (1 Mark)
- Manufacture of margarine from vegetable oils
- Used as fuel in rocket engines
- Mixed with oxygen to form the extremely hot oxy-hydrogen flame that is used for welding.
[only the first answer from the candidate]
- Name the missing condition in the setup (1 Mark)
- Study the setup below and use it to answer the questions that follow.
Download Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Form 3 End Term 3 Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students