INSTRUCTIONS TO STUDENTS:
- Write your name and adm in the spaces provided above.
- Sign and write the date of examination in the spaces provided above.
- Answer ALL the questions in the spaces provided.
- All working must be clearly shown where necessary
- Candidates should check the question paper to ascertain that all the pages are printed as indicated and that no questions are missing
- Candidates should answer the questions in English.
For Examiner’s Use Only
|
Questions |
Maximum Score |
Candidate’s Score |
|
1 – 29 |
80 |

QUESTIONS
- The diagram below shows part of Solvay process.
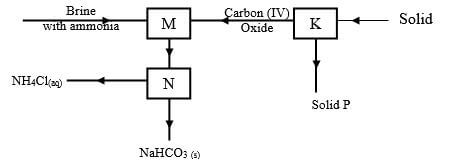
- Name solid P ( 1 Mark)
- State the process taking place in chamber N. ( 1mark)
- State two uses of calcium chloride which is a by-product in this process.( 1 mark)
- 100cm3 of methane gas diffused through a porous partition in 40 seconds. How long would it take 90cm3 of ozone gas to diffuse through the same partition? C = 12, H = 1, O = 16 (3marks)
- Ammonia is produced in large scale by Haber process.
- Write an equation for the formation of ammonia gas. (1 mark)
- State two optimum conditions for obtaining a high yield of ammonia in the process. (2 marks)
- The scheme below shows some reactions starting with ethyne. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
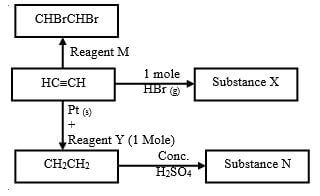
- Name substance X and N (1mark)
- Name reagent M (1 Mark)
- Ethene undergoes polymerization to form a polymer. Give an equation for the reaction and name the product.
- Equation; (1 mark)
- Name: (1mark)
- The curves below represent the volume of carbon (IV) oxide gas evolved once 2M(concentrated) hydrochloric acid was reacted with 100g of powdered calcium carbonate and also when 1M concentrated hydrochloric acid was reacted with the same quantity of carbonate.
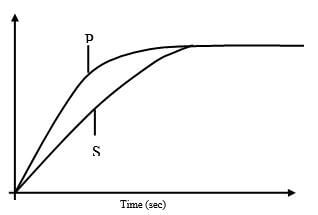
- Which of the two curves represents the reaction of 2M concentrated HCl with powdered calcium carbonate. Give a reason. (2 marks)
- Why do the two curves flatten at the same level of production of CO2 (1 mark)
- Study the following equilibrium equation.
2X2(g) + Y2(g) ⇌ 2X2Y(g) ΔH = -197Kj/mol
Suggest two ways of increasing the yield of X2Y. (1 mark) - The table below gives some elements in the periodic table. Use it to answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements.
Which of the above letters represent:Element
A
B
C
D
E
Atomic number
12
13
14
15
16
- A metallic element which forms ions with the smallest ionic radius? Explain(2 marks)
- A non metallic element with the largest atomic size? Explain. ( 1mark)
- The diagram below shows a burning jiko. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
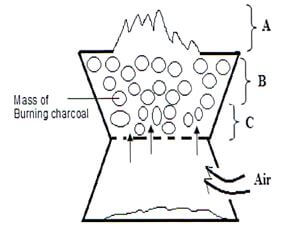
- Write the equation for the reaction taking place in region A. (1 Mark)
- Name the gas produced at region B. (1 Mark)
- State ONE use of the gas named in (b) above. (1 Mark)
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow.
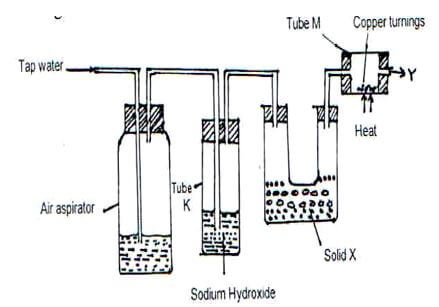
- What is the purpose of passing tap water through the air aspirator? (1 Mark)
- State and explain the observation that would be made in tube M after sometime.(1 Mark)
- 15g of sodium chloride was dissolved in 120cm3 of distilled water. Calculate the concentration of the resulting solution in moles per litre. (Na = 23, Cl = 35.5) (3Marks)
-
- State Boyle’s Law. (1 Mark)
- The volume of a gas at 30ºC and 780mmHg is 400cm3. What will be its volume at 50ºC at 600 mmHg. (3marks)
- Sulphur exhibits allotropy.
- What is allotropy? (1 Mark)
- Name the two allotropes of sulphur. (2 Marks)
- Sulphur powder was placed in a deflagrating spoon and heated on a Bunsen Burner.
- State the observation made. (1 Mark)
- The product obtained was dissolved in water. Comment on the PH of the solution formed.(1 Mark)
- 0.318g of an oxide of metal M was completely reduced by hydrogen gas to 0.254g of metal. Calculate empirical formula of the metal oxide. (M = 63.5, O = 16) (3 Marks)
- Given the following reagents: Solid sodium Carbonate, water, solid Lead (II) nitrate. Describe how a sample of Lead (II) Carbonate can be prepared in the laboratory.(3 Marks)
- Volume of liquids can be measured using a pipette; measuring cylinder or burette. Explain which one would be best for measuring 29.1cm3 of liquid. (1 Mark)
- Study the information in the table and answer the questions below.
Describe how a solid sample of substance V could be obtained from a solid mixture of V and W.(2 Marks)Substance
Solubility g/100g water
V
126
W
2
- Use the bond energies given below to calculate the heat of reaction for; (3 marks)
H2(g) + Cl2(g) → 2HCl (g)
Bond
Energy (Kj/Mol)
H – H
435
Cl – Cl
243
H – Cl
431
- The PH of a soil sample was found to be 5.7. An agricultural officer recommended addition of lime.
- State two functions of the lime. (2 Marks)
- Give the name of the process applied in (a) above. (1mark)
- The electronic configuration of ions X2+ is 2.8 while that of ion Y- is 2.8.8.
- Write down the electron arrangement of the atoms of X and Y (2 Marks)
- Compare the atomic radii of the two elements. (1 Mark)
- Give the name of the chemical family to which element X belongs (1 Mark)
- Use the information below to answer the questions that follow.
C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) ΔH1 = -393 KJ/mol
H2(g) + ½ O2(g) → H2O(l) ΔH2 = -286 KJ/mol
C4H10 + 6 ½ O2(g) → 4CO2(g) + 5H2O(l) ΔH3 = -2877KJ/mol- Calculate the molar enthalpy of formation of butane (C4H10) from its elements in their normal states. (3mks)
-
-
- A student found a colourless liquid in the laboratory which he suspected to be water. Describe a chemical test the could have performed to confirm that the liquid is water.(2 Marks)
- What other test could he have done to prove that the liquid is pure water?(1 Mark)
-
- The diagram below shows that the set-up that was used to prepare and collect a sample of nitric acid
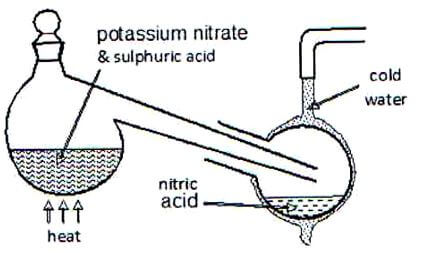
- Give a reason why it is possible to separate nitric acid from sulphuric acid in the set-up. (1 Mark)
- Name another substance that can be used instead of potassium nitrate.(1 Mark)
- Give one use of nitric acid.(1mark)
- The structure of water molecules can be represented as shown below.
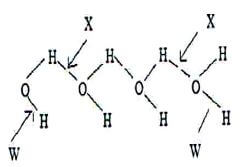
- Name the bond type represented by letter X and W. (1 Mark)
- Relative molecular mass of methane and water are almost similar, however the boiling of water is 100ºC while that of methane is -161ºC. Explain. (1 Mark)
- Diamond and graphite are allotropes of carbon. In terms of structure and bonding, explain why?
- Diamond is used in drilling of hard rocks. (1 Mark)
- Graphite is a lubricant. (1Mark)
- The set up was used to prepare dry hydrogen gas. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
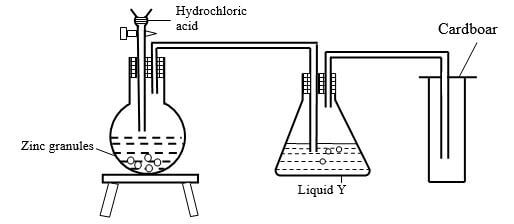
- Is set-up used to prepare the gas correct? Give reason. (1 Mark)
- What would be liquid Y?(1mark)
- Give two physical properties of hydrogen gas (1 Mark)
- Given element W has atomic number 14 and consists of isotopes as shown below.
Isotope A B C
Isotope mass 28 29 30
Percentage abundance 92.2 4.7 3.1
Determine the relative atomic mass of W (2 Marks) - The diagram below represents a set up used for the large scale manufacture of hydrochloric acid.
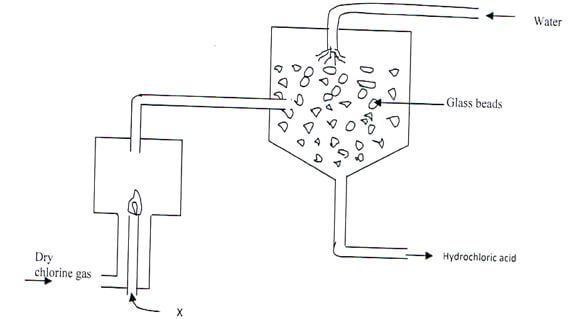
- Name substance X ( 1Mark)
- What is the purpose of the glass beads? ( 1 Mark)
- Give one use of hydrochloric acid ( 1Mark)
- A mixture contains Iron (III) Chloride, calcium chloride and iron filings. Describe how one can separate and recover the substances in the mixture.(3marks)
- The structure below represents two cleansing agents A and B. Which cleansing agent would be suitable for washing in water containing calcium chloride? Give a reason.(2marks)
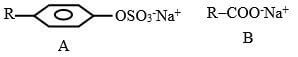

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Calcium oxide//Quickline 1 Mark
- Filtration//Fractional crystallization 1
-
- In the extraction of sodium metal
- Pickling
- As a drying agent
- Anti microbial agent
- Anti cracking agent
(Any to correct answers award 2 mark each)
- Rate of diffusion of methane gas = 100cm 3/40 sec = 2.5cmsec-1 ½ mark
Let rate of diffusion of ozone be 90/t = R
Molar mass of CH4 = 12 + 4 = 16 ½ mark
Molar mass of O3 = 16 x 3 = 48
∴ Rmethane/ROzone= √(〖MMO〗_3 )/√(〖MMCH〗_4 )
2.5/R = √48/√16 ½ mark
∴R = (2.5 x √16)/√48 = 1.4434cm3/sec ½ mark
∴ 90/t = 1.4434 ½ mark
∴ t = 90/1.4434
= 62.3528sec ½ mark -
- N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g)
Pressures of 200 atms
Temperature of 450 ℃ to 500℃
Finely divided iron (any two)
- N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g)
-
- X – Bromo ethene 1 mark
N – Ethyl hydrogen sulphate 1 mark- M – Bromine gas 1 mark
Polyethene 1 mark
- X – Bromo ethene 1 mark
-
-
- P 1
- It reacts with the carbonate faster ½ and the reaction ends earlier. ½
- The same quantities of reactants ½ have been used hence total volume of gas ½ evolved is the same.
-
-
- Lowering the temperature ½
- Increasing pressure ½
-
- B 1mk - It looses 3 electrons and the remaining electrons are strongly held than before due to less repulsion. (1 Mark) total (2marks)
- C 1mark - It has the weakest nuclear charge among the non-metals given (1 Mark) total 2marks
-
- 2CO(g) + O2(g) → 2CO2(g)
- Carbon (II) Oxide
- Extraction of metals
-
- To displace/drive out the air in the aspirator
- A black solid ; copper (II) oxide is formed // copper is oxidized to copper (II) oxide
- No. of moles = m
R.f
= 15/58.5
= 0.25641 moles
Molarity = 0.25641/0.12
= 2.13675M -
- Boyles law states that the volume V1 of a fixed mass of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure P1 when temperature is kept constant.
- (P1 V1)/T1 = (P2 V2)/T12
(780 X 400)/303 = (600xV_2)/323
⇒ V2 = (323 x 780 x 400)/(303 x 600)
= 554.3234cm3
-
- Allotropy – existence of an element in more than one structural form in the same physical state.
- Rhombic/ 1mk
Monoclini// 1mk -
- Blue flame (1 mk)// pungent smell
- Acidic (1 mk)//low pH
- Ratio M O
Moles 0.254/63.5 0.64/16 ½
Ratio 0.04 : 0.04 ½
1 : 1
E.F = MO 1 -
- Add water to Lead (II) nitrate to obtain Lead (II) nitrate solution. ½
- Add water to sodium carbonate to obtain sodium carbonate solution. ½
- Mix the solutions to ppt Lead (II) carbonate. 1
- Filter to obtain Lead (II) carbonate as a residue. ½
- Was the residue and dry between filter paper ½
- Burette 1 has accuracy of 0.1 cm3
- Add water to the solid mixture.
- V dissolves while W will not.
- Filter to obtain W as residue.
- Heat the filtrate to evaporate the water.
- Bond breaking
= H - H + Cl - Cl
= 435 + 243
= +678 kJ mol-1
Bond formation energy
= 2 × H - Cl
= 2 × 431
= -862 km mol-1
Heat of reaction
= Bond breaking energy + Bond formation energy
= +678 + -862
= -184 kJ mol- -
- Adding calcium ions to soil
Raise PH of soil/Neutralize soil - liming
- Adding calcium ions to soil
-
- X – 2.8.2
Y – 2.8.7 - Atomic radii of x is larger than that of y
- Alkaline earth metals
- X – 2.8.2
- 4C(s) + 5H2(g) …………ΔHf(CH4)……………………..>C4H10(g)
4CO2(g) + 5H2O(l)
4(-393) + 5 (-286) = ΔHf + (-2877)
ΔHf(CH4) = 2877 – 1572 – 1430
= -125 Kj/mol (3mks -
- By putting a few drops of the liquid to anhydrous copper (II) sulphate, which would change from white to blue. Cobalt (II)chloride paper (anhydrous (II) chloride changes from blue to pink on adding the liquid. (2 mks)
- By determining its boiling point, has b.p of 1000 at sea level/determining freezing point which is 00 at sea Level / determining its density which is 1g/cm3. (1 mk)
-
- It has a low boiling point (it is volatile)
- Sodium nitrate (1 mark)
- Manufacture of fertilizer(1mark)
-
- X – Hydrogen bond
Y – Covalent bond - Water contain hydrogen bonds holding the molecules together which are stronger than van der waals forces whereas CH4 has only van der waals forces holding molecules together.
- X – Hydrogen bond
-
- In diamond all carbon atoms are joined together by covalent bonds in three dimensional structure//or tetrahedral structure thus very hard.
- The carbon atoms are bonded in layers/or hexagonal layers which are held by weak forces of attraction// or Van der waal’s forces these layers slide over one another easily.
-
- NO (1) Mark
The gas is less dense ( ½ Mark) hence can’t be collected by downward delivery.(1/2mk) - Concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid ( ½ Mark) Reject if “concentrated” is missing
- It’s colourless
Odourless
Less dense than air
Any two for ( ½ mark) each
- NO (1) Mark
- ((92.2 x 2.8)+ (4.7 x 29)+ (3.2 x 30))/100
= (2581.6+136.3+93.0)/100 -
- Hydrogen
- They increase the surface area over which the gas dissolves in water.
-
- Give one use of hydrochloric acid
- Treatment of water at the water works.
- Sewage treatment
- Manufacture of dyes, drugs etc
- To clean metal surfaces to remove rust
- Place the mixture on a piece of paper and put a magnet above the mixture to attract iron filings
- Heat the remaining part of the mixture for Al2Cl3 to sublime and collect sublimate.
- Calcium chloride will remain at the bottom of the tube
- A - does not form scum with hard water.
Download Chemistry Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Form 4 Term 2 Opener Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

