QUESTIONS
-
- An atom Q can be represented as
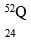
What does the number 52 represent? (1mk) - Study the information in the table below and answer the equations that follow
(Letters are not the actual symbols of the elements)
Element
Electronic arrangement of stable ion
Atomic Radius
(nm)
Ionic Radius
(nm)
N
2.8.8
0.197
0.099
P
2.8.8
0.099
0.181
R
2.8
0.160
0.065
S
2.8
0.186
0.095
T
2
0.152
0.068
U
2.8
0.072
0.136
- Write the formula of the compound formed when N reacts with P
(Atomic numbers are N = 20; P = 17) (1mk) - Identify the elements which belong to the third period of the periodic table Explain (2mks)
- Which of the element identified in b (ii) above comes last in the third period? Explain (2mks)
- Select two elements which are non- metals (1mk)
- Write the formula of the compound formed when N reacts with P
- The table below gives some properties of substances I, II, III, and IV
Study it and answer the questions that follow
Substance
Electrical conductivity
M.P (0C)
B.P (0C)
Solid
Molten
I
Does not conduct
Conducts
801
1420
II
Conducts
Conducts
650
1107
III
Does not conduct
Does not conduct
1700
2200
IV
Does not conduct
Does not conduct
113
440
- What type of bonding exists in substances I and II (1mk)
I
II - Which substances is likely to be sulphur? Explain (2mks)
- What type of bonding exists in substances I and II (1mk)
- An atom Q can be represented as
-
- State two differences between chemical and nuclear reactions (2mks)
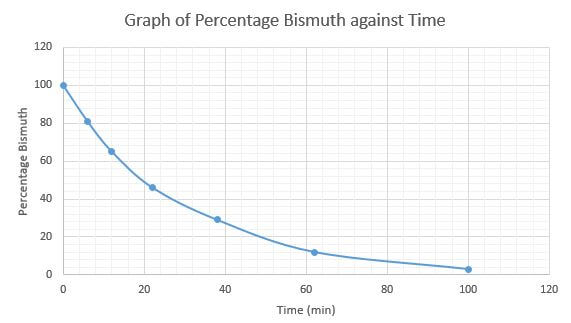
- The table below gives the percentages of a radioactive isotope of Bismuth that remains after decaying at different times
Time (min)
0
6
12
22
38
62
100
Percentage of Bismuth
100
81
65
46
29
12
3
- On the grid provided, plot a graph of the percentage of Bismuth remaining
(Vertical axis) against time (3mks) - Using the graph, determine the:
- Half – life of the Bismuth isotope (1mk)
- Original mass of the Bismuth isotope given that the mass that remained after 70 minutes was 016g (2mk
- On the grid provided, plot a graph of the percentage of Bismuth remaining
- Give one use of radioactive isotopes in medicine (1mk)
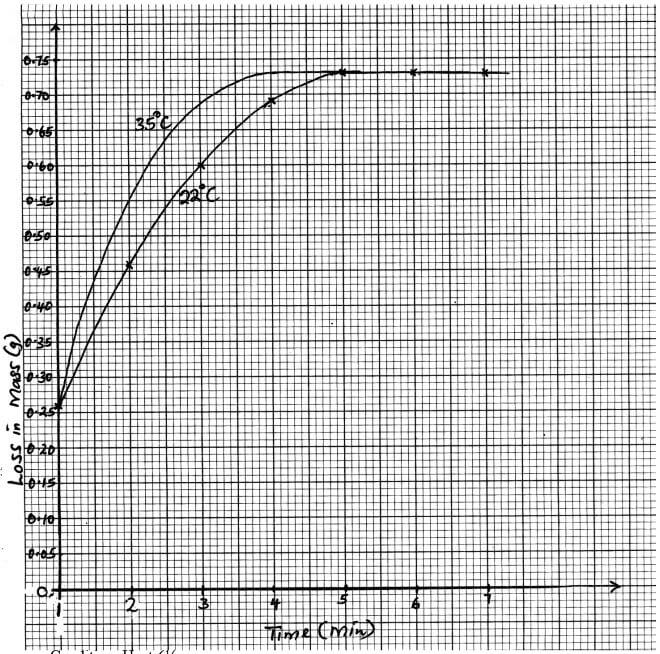
- The set up below is used to measure the change in mass during the course of the reaction between 7dilute hydrochloric acid (excess) and marble chips at 22°C
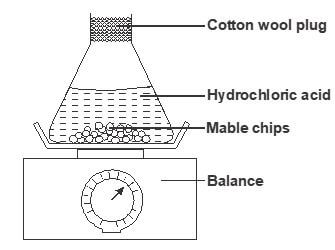
Changes in mass were noted at one minute intervals and were as follows- Give an equation for the reaction taking place in the flask (1 mark)
- Why did the mass of the flask change with time? (1 mark)
- What is the role of cotton wool at the mouth of the flask? (1 mark)
- Plot a graph of loss in mass (Y-axis) against time (X-axis) Label the curve 22°C (3 marks)
Time (min)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Loss in mass(g)
0.26
0.46
0.60
0.69
0.73
0.73
0.73
- On the graph same axis as in (d) above, sketch the graph you would expect to obtain if the experiment was repeated at 35°C Label the curve 35°C (2 marks)

- State what would happen if the marble chips were replaced with the same mass of marble powder Explain (2 marks)
- Why is it not advisable to use sulphuric (VI) acid in place of hydrochloric acid in this experiment? (1 mark)
-
- Study the table below and answer the questions that follow
Bond type bond energy kJmol-1 C-C 346 C = C 610 C-H 413 C-Br 280 Br-Br 193 - Calculate the enthalpy change for the following reaction (3 marks)
C2H4(g) + Br2(g) → C2H4Br2(g) - Name the type of reaction that took place in (a) above (1mark)
- Calculate the enthalpy change for the following reaction (3 marks)
- Butane C4H10 cannot be prepared directly from its elements but its standard heat of formation (∆Hʄθ) can be obtained indirectly
The following heats of combustion are given
∆HCθ (Carbon) = -393kJ/mol
∆HCθ (Hydrogen) = -286kJ/mol
∆HCθ (Butane) =-2877kJ/mol- Draw an energy cycle diagram linking the heat of formation of butane with its heat of combustion and the heat of combustion of its constituents elements (1mark)
- Calculate the heat of formation of butane ∆Hʄθ (C4H10) (2marks)
- Given that the lattice enthalpy of potassium chloride is +690kJ/mol and hydration enthalpies of K+ and Cl- are -322kJ and -364kJ respectively Calculate the enthalpy of solution of potassium chloride (3 marks)
- Study the table below and answer the questions that follow
- The scheme below shows a series of reactions starting with ethanol Study it and answer the questions that follow
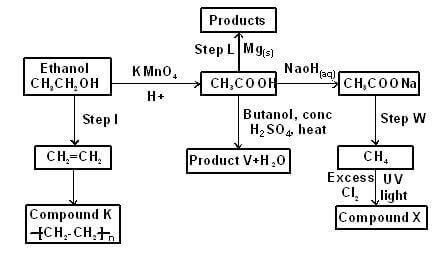
- Give the type of reaction, the reagent(s) and the condition(s) necessary for step 1 to take place (1 mark)
- Write the equation for the reaction that takes place in step L (1 mark)
- Name product V and give the equation responsible for its formation (2 marks)
- Give the reagent(s) and condition(s) necessary for step W to take place (1 mark)
- Give the IUPAC name and structural formula of compound X (1 mark)
- Name compound K and state the type of reaction involved in its formation (2 marks)
- If the relative molecular mass of K is 44800, determine the value of n (C = 12, H = 1) (2 marks)
- Draw an energy cycle diagram linking the heat of formation of butane with its heat of combustion and the heat of combustion of its constituents elements (1mark)
- Calculate the heat of formation of butane ∆Hʄθ (C4H10) (2marks)
- Given that the lattice enthalpy of potassium chloride is +690kJ/mol and hydration enthalpies of K+ and Cl- are -322kJ and -364kJ respectively Calculate the enthalpy of solution of potassium chloride (3 marks)
MARKING SCHEME
-
- Mass number√/sum of number of protons and neutrons in an atom of element
-
- NP2 √
- P, R, √ S√
- P. √
P is nonmetal√½ while R and S are metals.
Metal come first before non-metals across a period√½ - P and U√
-
- I Ionic/electrovalent. √
II Metallic√ - IV. √
Is made of simple molecular structure√ with low boiling/melting point and a poor electrical conductor.
- I Ionic/electrovalent. √
-
-
No change in mass
change in mass
-
-
Smooth curve – 1mkCorrect plots – 7 points -1mk5 or 6 points – ½mkBelow 5 points – 0mkScale – Consistent scale on both axis – ½mk-Labeling of axis – ½mk(Penalize 1mk if the axis are inverted)
-
- From correctly plotted graph t ½ = 20 minutes√
- From correctly plotted graph at 70minutes = 9%√
=> Original mass = 0.16 x 100 √ = 1.7778 g
9
-
- Treatment of cancer√
Detection of uptake of iodine in kidneys√
Regulation of heart pace maker√
Sterilization of surgical instruments√
-
-
- CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → CaCl2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
- The carbon (IV) oxide formed escaped into the atmosphere
- To prevent acid from spraying out
- In the graph paper (3mks)
- 1mk for curve 35°C
-
- The reaction rate would increase
- Marble powder offers a larger surface area than chips, which causes the rate of reaction to increase
- There would be formation of insoluble calcium sulphate that would coat calcium carbonate (Marble chips) stopping the reaction
-
- Type of reaction: Dehydration
Reagent : Concentrated Sulphuric (VI) acid
Condition: 170oC - 180°C (single value in that range) - Mg(s) + 2CH3COOH(aq) → (CH3COOH)2Mg(aq) + H2(g)
- V - Butylethanoate
CH3COOH(aq) + CH3CH2CH2CH2OH(l) → CH3COOCH2CH2CH2CH3(aq) + H2O(l) - Reagent: Soda lime
Condition: Heat - Name: Tetrachloromethane/ carbon tetrachloride
Structure: - Name: Polyethene/polythene
Type of reaction: Addition reaction/Addition polymerization - Molecular mass of -CH2 - CH2 - = 14 + 14
= 28
n = 44800 = 1600
- Type of reaction: Dehydration
Download Chemistry Questions and Answers - Form 4 Mid Term 2 Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

