- Answer all questions in section A.
- In section B, Answer question 6 and any other two questions from the remaining questions.
- Answer all questions.
SECTION A
Answer all questions in this section
-
- What is geography? (2marks)
- Give three proofs that the earth is almost spherical in shape. (3marks)
-
- Differentiate between weathering and mass wasting. (2marks)
- State three causes of landslides. (3marks)
-
- Differentiate between a watershed and a catchment area? (2marks)
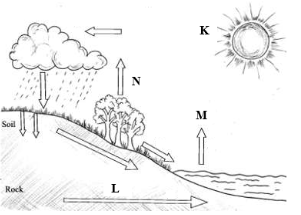
- The diagram below shows a hydrological cycle.
What processes do the arrows labelled K, L and N represent? (3marks)
- The diagram below shows a coastal landform.
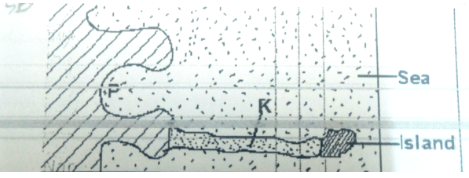
- Name the features marked P and K. (2marks)
- List down three types of ocean tides. (3marks)
-
- Name the types of earth movements that occur within the earth’s crust. (2marks)
- Describe the origin of continents according to the theory of continental drift. (3marks)
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other two questions in this section
- Study the map of Nyeri (East Africa 1:50,000) to answer questions that follow.
-
- what is the sheet number of the map extract. (1 mark)
- Give the longitudinal extent of the area covered by the map extract. (1 mar
-
- Give two reasons which show that the area receives high rainfall. (2 marks)
- Name two physical features found in the grid square 6246 (2 marks)
- Draw a rectangle 4 cm by 6 cm to represent the area north of Northing 60 and between Eastings 64 and 68. On it mark and label
- River Amboni(Honi)
- Road B5
- Mweiga township (5 marks)
- Describe the drainage of the area covered by the map (4 marks)
- Students of Njogu-ini school wanted to do a field study on vegetation on the area covered by the map.
- Identify two means of transport they are likely to use. (2 marks)
- Name three types of vegetation they are likely to identify (3 marks)
- State three preparations they could make. (3 marks)
- Identify two problems they are likely to encounter. (2 marks)
-
-
- Name two instruments kept in a Stevenson screen. (2 marks)
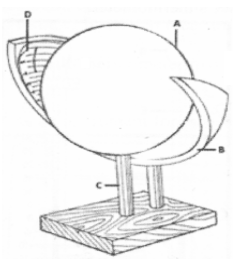
- The diagram below shows a weather measuring instrument. Use it to answer the questions below.
- Name the parts marked A and D. (2Marks)
- Describe how the instrument works. (4 marks)
- The table below shows climatic figure for station Q. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
Months J F M A M J J A S O N D Temp in °C 30 31 31 29 27 27 28 29 28 28 27 30 Rainfall in mm 257 246 231 234 207 201 218 227 234 240 235 230 - Calculate the annual range of temperature for station Q. (2 marks)
- Give four characteristics of climate for station Q. (4 marks)
- With the aid of a well-labelled diagram, describe the formation of cyclonic rainfall. (6 marks)
- You intend to carry out a field study of a weather station in your school.
- Give two methods of recording data that you are likely to use. (2 marks)
- State three reasons why the recording of data at a school weather station may be inaccurate. (3 marks)
-
- Name three types of faults: (3 marks)
-
- With the aid of well labeled diagrams explain how compressional forces can lead to the formation of a rift valley. (7 marks)
- Give two examples of Horst Mountains in east Africa: (2 marks)
- Describe two ways in which faulting may influence drainage systems. (4 marks)
- A part from the Rift Valley name two other relief features that were formed as result of faulting. (3 marks)
- Explain three ways in which features resulting from faulting are of economic importance: (6 marks)
-
- Define soil (2 marks)
- Explain how the following factors influence soil formation;
- Parent material (4 marks)
- Human activities (2 marks)
- The diagram below shows a soil profile. Use it to answer question (i) and (ii).
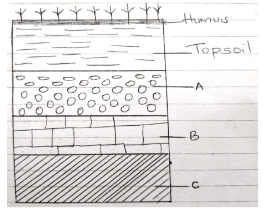
- Name the parts marked A, B and C. (3 marks)
- Describe the characteristics of the top soil (4 marks)
-
- Explain three causes of physical soil degeneration. (6 marks)
- State four ways of conserving soils (4 marks)
-
- Describe plucking as a process in glacial erosion. (4 marks)
- Explain three conditions that lead to glacial deposition. (6 marks)
- The diagram below shows features resulting from glacial deposition in a lowland area.
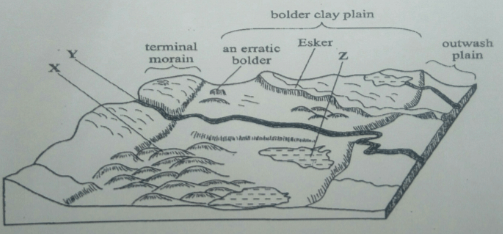
- Name the features marked X, Y, and Z. (3 marks)
- Describe how terminal moraine is formed. (4 Marks)
- Explain four positive effects of glaciation in low land area. (8 marks)
MARKING SCHEME
-
- What is Geography? (2 Mks)
- Geography is the study of the distribution and interrelationships of natural and human phenomena in relation to the earth’s surface/It is the study of the earth as a home of human kind.
- Give three proofs that the earth is almost spherical in shape. (3 Mks)
- Circumnavigation of the earth. When one sails or flies along a straight path without changing direction, he or she comes back to the starting point.
- The earth’s horizon appears spherical when observed from a high point.
- Rising and setting of the sun, since people living in the east see the sun earlier than those in the west.
- When a ship is approaching the land from the sea, an observer standing on a high cliff first sees the smoke, then the mast and finally the rest of the ship’s body.
- During the eclipse of the moon, (lunar eclipse), a spherical shadow of the earth is cast on the moon.
- All other planets are spherical, hence the Earth being a planet, is not an exception.
- Photographs of the earth taken from the space by satellites show that the earth has a spherical shape.
(Any 3x1mk = 3mks)
- What is Geography? (2 Mks)
-
- Differentiate between weathering and mass wasting. (2 marks)
- Weathering is the breakdown/disintegration/decomposition of rocks at or near surface of the earth in situ by physical/chemical processes while mass wasting is displacement/movement of weathered materials down a slope under the influence of gravity.
- State three causes of landslides. (3 marks)
- Steep gradient of the slope.
- Nature of the materials on the slope.
- High amount of precipitation.
- Occurrence of earth movements such as earthquakes.
- Rise in temperature in glaciated highlands.
- Clearing of vegetation cover on the steep slopes.
- Human activities on steep slopes such as mining and construction.
- Differentiate between weathering and mass wasting. (2 marks)
-
- Differentiate between a watershed and a catchment area. (2 marks)
- A watershed is a ridge line boundary separating drainage basins or rivers systems while a catchment area is a wetland which a river draws its waters from.
- The diagram below shows the hydrological cycle.
What processes do the arrows labelled K, L and N represent? (3 marks)- K - Radiation/insolation/sun’s rays
- L – Percolation
- N – Evapotranspiration
- Differentiate between a watershed and a catchment area. (2 marks)
- The diagram below shows a coastal landform.
- Name the features marked P and K. (2 Mks)
- P – Bay
- K – Tombolo
- List down three types of ocean tides. (3 Mks)
- Perigian tides.
- Apogean tides.
- Spring tides.
- Neap tides.
(Any 3x1mk = 3mks)
- Name the features marked P and K. (2 Mks)
-
- Name the types of earth movements that occur within the earth’s crust. (2 Mks)
- Horizontal earth movement/ Lateral/ erogenic
- Vertical earth movement/ Epeirogenic
- Describe the origin of continents according to the theory of continental drift. (3 Mks)
- There was initially one super continent/Landmass known as Pangaea
- It was surrounded by large water mass known as Panthalassa.
- Later Pangaea broke into two continents namely Laurasia (Northern continent) and Gondwanaland (Southern continent).
- The two were separated by a narrow ocean called Tethys.
- Laurasia split into the current Northern continents: North America, Europe and Asia, while Gondwanaland split to the current Southern continents: Africa, South America, India, Australia, New Zealand and Antarctica.
NB: Follow the sequence. Last point must be mentioned to score 3 max points
- Name the types of earth movements that occur within the earth’s crust. (2 Mks)
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other two questions in this section
- Study the map of Nyeri (East Africa 1:50,000) to answer questions that follow.
-
- what is the sheet number of the map extract. (1 mark)
- 120/
- Give the longitudinal extent of the area covered by the map extract. (1 mark)
- From 36°45’E to 37°00’E
- what is the sheet number of the map extract. (1 mark)
-
- Give two reasons which show that the area receives high rainfall. (2 marks)
- Presence of forests
- Coffee production
- Presence of many permanent rivers/streams (Any 2x1mk =2mks)
- Name two physical features found in the grid square 6246 (2 marks)
- River valley
- Steep slope
- spurs
- Give two reasons which show that the area receives high rainfall. (2 marks)
- Draw a rectangle 4 cm by 6 cm to represent the area north of Northing 60 and between Eastings 64 and 68. On it mark and label
- River Amboni(Honi)
- Road B5
- Mweiga township (5 marks)
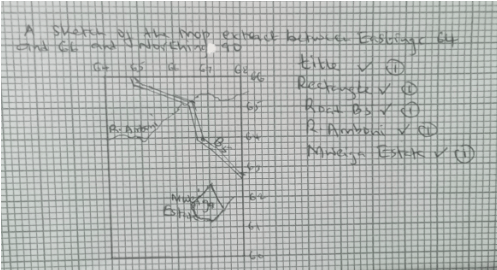
- Describe the drainage of the area covered by the map (4 marks)
- There are many permanent rivers
- The main drainage pattern is dendritic
- There are water holes
- There are many dams
- The main rivers are Amboni, Muringato,Chanya
- Most rivers are flowing from west to east (Any 4x1mk = 4mks)
- Students of Njogu-ini school wanted to do a field study on vegetation on the area covered by the map.
- Identify two means of transport they are likely to use. ( 2 marks)
- Roads
- water
- Name three types of vegetation they are likely to identify (3 marks)
- Bamboo
- Scrub
- Thicket
- Forest
- Woodland (Any 3x1mk = 3mks)
- State three preparations they could make. (3 marks)
- conduct pre-visit/ reconnaissance
- Draw a route map
- Prepare working schedule
- Seek permission from school management
- Gather all the necessary tools
- Identify two problems they are likely to encounter. (2 marks)
- Difficult to access some areas due to thick vegetation (2mks)
- They might be scared/attacked by dangerous wild animals in the thickets
- Heavy downpour which might have interrupted the field study
- Fatigue
- Accidents from falls
- Uncooperative respondents
- Unable to identify some vegetation (Any 2x1mk = 2mks)
- Identify two means of transport they are likely to use. ( 2 marks)
-
-
- Name two instruments kept in a Stevenson screen. (2 marks)
- Hygrometer
- Maximum thermometer
- Minimum thermometer
- The six’s thermometer
(Any 2x1mk = 2mks)
- The diagram below shows a weather measuring instrument. Use it to answer the questions below.
- Name the parts marked A and D. (2 marks)
- A - Spherical glass lens
- D - Sensitized card
- Describe how the instrument works. (4 marks)
- The glass sphere focusses the sun’s rays on a sensitized card which is graduated in hours and minutes.
- The heat burns the paper/card as the sun moves across the sky.
- The unburnt sections in the card indicates when there was cloud cover.
- At the end of the day, the card is removed and the number of hours that the sun shone are obtained by adding the burnt sections on the card.
- Name the parts marked A and D. (2 marks)
- The table below shows climatic figure for station Q. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Calculate the annual range of temperature for station Q. (2 marks)
= 31°C − 27°C
= 4°C - Outline four characteristics of climate in station Q. (4 marks)
- The station experiences high temperatures.
- Highest temperature is 31°C/the lowest temperature is 27°C.
- The annual range of temperature is 4°C/the station has a low range of temperature.
- The station experiences high rainfall/2760mm.
- The station experiences rainfall throughout the year/there is no dry month.
- Lowest rainfall is experienced in May and July when temperature is also lowest.
- The station has one rainfall maxima regime. (Any 4x1mk =4mks)
- With the aid of a well-labelled diagram, describe the formation of cyclonic rainfall. (6 marks)
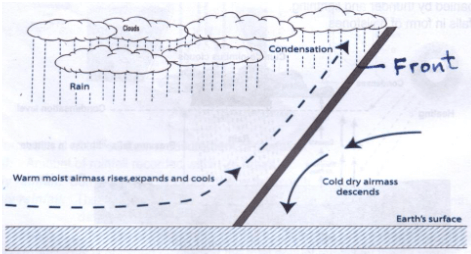
Text - 4 marks
Diagram - 2 marks
Total - 6 marks
- It occurs where two airmasses meet one warm and moist and the other cold and dry.
- It is the meeting point of cold, heavy dry polar easterlies and warm, light and moist north/south westerlies.
- The meeting of the air masses forms a front.
- When the two air masses meet along the front, the warm lighter westerly, winds rises over the cold polar air.
- Since it is moist, the air condenses forming clouds.
- The clouds become heavy enough, eventually falling as cyclonic rain through the cold air.
- Calculate the annual range of temperature for station Q. (2 marks)
- You intend to carry out a field study of a weather station in your school.
- Give two methods of recording data that you are likely to use. (2 marks)
- Filling in questionnaires
- Labelling of samples
- Note taking
- Taking photographs
- Sketching diagrams
- Tabulation (Any2x1mk = 2mks)
- State three reasons why the recording of data at a school weather station may be inaccurate. (3 marks)
- Human error.
- Interference with the instruments by animals and people.
- Poor siting of a weather station.
- Extreme weather conditions.
- Natural calamities i.e. landslides.
- Use of defective instruments. (Any 3x1mk = 3mks)
- Give two methods of recording data that you are likely to use. (2 marks)
- Name two instruments kept in a Stevenson screen. (2 marks)
-
- Three types of faults (3marks)
- Normal
- Reverse/ thrust/ low angle over thrust
- Tear / shear / transform
- Anticlinal fault (Any 3x1mk = 3mks)
-
- How compressional forces can lead to the formation of a rift valley
Diagram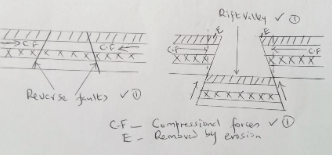
Diagram=3mks
Text 4 x 1 = 4 mks
Total = 7 mks
Explanation;- Layers of crustal rocks are subjected to compressional forces
- Two almost parallel reverse faults develop
- Outer blocks are thrust upwards and pushed over the middle block
- Middle block sinks / remains at a lower level forming the floor of a rift valley
- The overhanging parts are eroded by erosion / collapse
- Two examples of Horst Mountains in east Africa (2 marks)
- Pare
- Usambara
- Ruwenzori (Any 2 x 1 = 2 marks)
- How compressional forces can lead to the formation of a rift valley
- Describe two ways in which faulting may influence drainage systems. (4 marks)
- If rift faulting occurs in an enclosed area, a basin may be formed. When riversflow into the basin, a lake may be formed. This basin may become an area of inland drainage.
- Some rivers may end up flowing along fault lines, thus forming a fault-guided drainage pattern.
- Uplifting of land which follows faulting may block a river. This may cause it to reverse or change its direction of flow.
- When faulting occurs across a river valley, it may cause the river to disappear into the ground through a fault line.
- When faulting occurs across a river valley, vertical displacement of land may occur.
- The river forms a waterfall where it descends the newly formed escarpment.
- Faulting may lead to the formation of escarpments with springs forming at the base due to exposure of the water table.
(Any 2x2mks = 4mks)
- A part from the Rift Valley name two other relief features that were formed as result of faulting. (2marks)
- tilt block
- escarpment / scarp slope
- block mountains / horsts
- fault steps
- depressions
- Explain three ways in which features resulting from faulting are of economic importance: (6 marks)
- Blocks / horst mountains are a source of rivers which provide water for industrial/ domestic, agricultural, HEP production.
- Rift valley formation has led to exposure of minerals such as diatomites/ soda ash which are mined on the rift valley floor.
- Mountains formed through faulting attract rain on the wind sides which favour agriculture activities / settlements
- Rift valley lakes are important fishing grounds, provide water for irrigation, transportation.
- Faulted features such as rift valleys provide beautiful scenery which promotes tourism industry.
(Any 3 x 2 = 4 marks)
- Three types of faults (3marks)
-
- Define soil (2 marks)
- It is the accumulation of rock particles, minerals, organic matter, water and air found on the surface of the earth on which plants grow
- Soil is a thin layer of unconsolidated loose rock materials and decayed organic matter on the earth’s surface in which plant grow (Any 1x2mks = 2mks)
- Explain how the following factors influence soil formation
- Parent material (4marks)
- Hard rocks are weathered slowly because they are more resistant. This slows down soil formation process. /Soft rocks are weathered faster because they are less resistant. These speeds up the soil formation process.
- Large grained rocks are weathered down to form coarse soils. /Small grained rocks are weathered down to form fine soils.
- The texture of the rocks determines the type of soil e.g. Sandy, loamy or clay.
- Mineral of parent rock are transferred to the soil during weathering. (Any2x2mks =4 marks)
- Human activities (2 marks)
- Human activities like grazing, cultivation, use of fertilizer and construction can change the nature of the soil.
- Human beings through activities like mining, construction works and quarrying aid in weathering processes which is the initial soil forming process.
(Any 1x2mks = 2mks)
- Parent material (4marks)
- The diagram below shows a soil profile. Use it to answer question (i) and (ii).
- Name the parts marked A, B and C. (3 marks)
- A – sub soil/horizon B
- B – weathered parent materials/ horizon C
- C – parent rock/ Horizon D
- Describe the characteristics of the top soil (4 marks)
- Dark in colour,
- Some are light in colour
- Contains humus,
- Has true soils – solum,
- A zone where leaching occurs – eluviation
- Divided into A00, A0,A1,A2,A3
- Name the parts marked A, B and C. (3 marks)
-
- Explain three causes of physical soil degeneration (6 marks)
- Overgrazing leads to removal of vegetation exposing soil to agents of erosion and excessive evaporation from soil (water loss)
- Overgrazing results in loose and fine textured soils due to rock pounding by animals.
- Frequent ploughing weakens soil structure making it easy for agents of soil erosion to carry away the top fertile soils.
- Heavy rainfall washes down the top soil leading to thin / shallow soil,
- Heavy rainfall may also alter the structure of soils from crumb to blocky / columnar which are unsuitable for cultivation on
- Heavy rainfall may result in water logging in flat and lowland areas making the soils unsuitable for plant growth.
- Prolonged drought causes the soils to lose water to become dry thus become susceptible to wind erosion.
- Prolonged drought causes the soil to lose water / moisture thus soil particles held together become loose / disintegrate.
(Any 3x2mks = 6mks)
- State four ways of conserving soils (4marks)
- Crop rotation
- Mixed farming
- Application of chemical fertilizers
- Creation of drainage ditches / trenches
- Intercropping
- Mulching
- Bush fallowing
- Ploughing along the contours
- Controlled grazing
- Strip cropping
- Construction of cut off drains
- Terracing on steep slopes
- Afforestation/reafforestation/agroforestry
- Explain three causes of physical soil degeneration (6 marks)
- Define soil (2 marks)
-
- Describe plucking as a process of glacial erosion. (4 Mks)
- Pressure from the overlying mass of ice causes freeze thaw action.
- Melting water fills the cracks/joints in the bed rock.
- As water freezes it exerts pressure on the cracks enlarging them.
- The enlarged cracks lead to disintegration of the rock.
- The disintegrated rocks eventually get embedded within the mass of ice.
- As the ice moves, it pulls out or gorges out the embedded rock from the mother rock. This process is called plucking.
NB: The last point must be mentioned to score max 4 mks (4mks)
- Explain three conditions that lead to glacial deposition. (6 Mks)
- Rising temperature lead to melting of ice thereby causing the ice to deposit its load.
- Change of gradient to relatively flat surface will reduce the velocity of the glacial movement which will subsequently lead to deposition of glacial materials.
- Alternating warm and cold periods lead to seasonal melting of ice which allows materials embedded in the ice to be released and deposited.
- Stagnation/accumulation of glaciers leads to pressure at the base of the glacier which in turn leads to melting of ice at the base. The melt water then carries and deposits materials underneath which loosens the heavy materials beneath the mass ice and is subsequently deposited.
- Friction at the base and sides of a glacier and a rough surface leads to melting of ice, causing the ice to deposit its load. (Any 3x2mks = 6mks)
- The diagram below shows features resulting from glacial deposition on a lowland area.
- Name the features marked X, Y and Z. (3 Mks)
- X - Drumlins
- Y – A river/melt water
- Z – kettle lake/lake
- Describe how terminal moraine is formed. (4 Mks)
- Moving ice carries solid materials/moraines
- Moving ice stagnates and ice at the snout melts.
- Melting ice releases its load
- Gradually the load piles into a ridge
- Over time the ridge forms a horse shoe shape/block of solid materials called terminal moraine
NB: follow the sequence (4mks)
- Name the features marked X, Y and Z. (3 Mks)
- Explain four positive effects of glaciations in lowland areas. (8 Mks)
- Glacial till provides fertile soils which are suitable for arable farming.
- Ice sheets in their scouring effect may expose the minerals making them easy to extract.
- Out wash plains comprise of sand and gravel which are used as building/construction materials.
- Glacial lakes found in lowland areas can be exploited for various economic uses such as fishing and transportation.
- Glaciation forms features such as drumlins, eskers which are tourists attraction hence foreign exchange earnings.
- Glaciated lowlands are generally flat and ideal for establishment of settlements/development of transportation network.
(Any 4x2mks = 8mks)
- Describe plucking as a process of glacial erosion. (4 Mks)
Download Geography Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Form 4 Term 3 Opener Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students