Musya
Conserving our Environment - CBC Grade 5 Agriculture Revision Notes
Soil Conservation
Soil recovery
- Soil is important in a number of ways. They Include:
- It’s our life support system
- It provides anchorage for plant roots
- It holds water and nutrients
- It’s a home for various micro-organisms
- We build on soil.
- Therefore soil plays a vital role in our environment. As without soil human life would be very difficult.
- It’s therefore a resource that should be guarded with a lot of caution. This is why to keep this resource in good we should limit chances of various factors doing away with it.
- Soil erosion is the removal of the top soil from one place to another by means of water, wind, or animal activities.
- Eroded soils by water are deposited to other places by siltation.
- Silt is the deposited soil and is rich in humor such soil very fertile. It comprises of organic matter and can be recovered. Silty soil is slippery when wet, not grainy or rocky
Soil recovery/restoration
- This is the process of collecting eroded soil from its deposition back to the farm for farming.
Importance of soil recovery
- Soil conservation is key to environmental sustainability
- It helps protect natural resources and watersheds,
- restores habitats for plants and wildlife,
- Improves water quality, and makes soil healthier.
- Soil conservation also creates economic opportunity.
- We should therefore look for eroded places and recover the soil and conserve our environment for the future.
- Runoff water is the water that runs on the ground at high speed and it removes the soil from its path leaving behind a gully.
- Soil eroded by runoff are deposited at the river banks, on the sides of the roads or in places where there are cover crops.
- Recovering soil is important to crops because it is very fertile, comprising of decomposed organic matter.
- Runoff water has the energy to detach soil particles by scour and to transport entrained soil materials either in suspension or by pushing or rolling larger particles.
(Runoff)
( soil deposition site)
Soil Improvement
- Soil improvement is the addition of soil nutrients to poor and non-productive soils. This can be done by addict organic manure.
Methods of soil conservation
- These include fallowing,
- using compost, manure, crop residues,
- Using fertilizer trees (e.g Calliandra and Pygeum africana),
- intercropping legumes with cereals and including the principles of conservation agriculture (crop rotation, ensuring permanent cover for the soil and no disturbing of the top soil layer).
- Organic manure can be prepared by the use of organic materials such as plants materials, animal waste, food remains or kitchen wastes.
- This can be done by the method of hip compost or pit compost.
- With hip compost, the organic materials are hipped on the ground and left to decompose for some time and then transported to the farm where planting takes place.
- In the absence of compost pit or residue pit, we may use drum or wood pallet as compost bin.”
- On the other hand, pit manure is prepared by digging underground and dumping all organic waste materials inside. These materials are left for sometimes to decompose then are used in the farm to improve soil.
(compost pit building)
(wooden compost)
(drum compost)
(compost heap)
(compost garden)
- Once the waste materials have decomposed fully we can plant a suitable crop in the waste pit.
- Dumping green and dry plant remains, food remains and kitchen wastes in a pit situated on a poor soil site is a god farming practice.
- This is because once the organic waste materials decay, they release nutrients that are required for the growth of pants.
- Therefore if an area has poor soil, it can be improved using organic manure, a crop can be grown successfully.
Importance of conserving soil
- The soil is literally the foundation of plant life. A tree will not be a tree without soil. While there are some plants that can live in water or air, most plants need to be rooted to the ground. It is the soil that provides nutrition to this plant life. It is through this vegetation that nourishes the humankind and the animal kingdom. Plants are important resource of food and fuel and of wood and other by-products that make our other life functions possible.
- The soil additionally supports the animal kingdom. Our agriculture also relies on soil, for its location and for other functions to be derived from its existence. It will be almost impossible to support the animal and human life without land.
- The soil is necessary for water supply. This is the magic of nature. The land is also necessary to ensure the quality of water we derive from our earth. Soil and water co-exist. So do we and soil co-exist? Taking good care of our soil equates to taking care of our water supply.
Water Conservation
- Water conservation is the process of retain water in the soil for planting. Water conservation can be done through mulching, shading, and cores cropping.
- Mulching
- Is the process of soil water conservation by spreading dry leaves or planting on the ground surface where the crops are planted.
- The dry leaves are called mulch where they are used to conserve soil water/moisture.
- Mulching prevents direct sunshine to the soil surface which lowers the rate or evaporation.
- Shading
- This is done by constructing a shade structure and covering its top with dry leaves.
- This is usually constructed on top of seedbeds to protect the seedling from the scotching sun and also to protect the soil from losing water through evaporation.
- Cover Cropping
- Cover cropping is the process of soil water conservation through planting short crops that spread wide on the ground.
- Plants used for cover cropping are bean plants, peas and green grams.
- Water just like soil, is an important resource in our environment for farming practices. We can use mulching, cover cropping and shading to conserve soil moisture.
- These farming practices reduce loss of water from the soil.
- Conserving water ensures that water in our farms is well used throughout the growing season
- It is important to conserve water because it is an important resource for farming in our homes. Without water, the plants will not grow to produce food for us.
- Mulching
Importance of water conservation
- Without fresh water you will die in just a few days.
- Conserving water is important because it keeps water pure and clean while protecting the environment
- Water conservation reduces energy use and can even save your household money.
Living better with wild animals
- Wild animals are very useful to use. Some are dangerous like the leopard and the lion.
Importance of wild animals
- Wildlife provides nutrients to humans
- People depend on wildlife for their livelihoods
- Wildlife has cultural significance
- Wildlife is important for the economy
- Protecting wildlife creates more jobs

- Wild animals generate revenue through local and international tourism. Some animals destroy our crops and some kill our domestic animals.
- We can scare and keep away wild animals without killing them.
- We can keep away animals by the use sounds, using smells and use of smelly and bitter tasting plants.
- Use of Sounds
- Some animals are often scared by sounds made by people talking or shouting. Animals like monkeys and squirrels can be scared away by the use of sounds made by radio. A radio is switched on and put in a plantation to scare wild animals’ away.
- Using Smells
- Some wild animals are repellant to bad smells. Smells can be produced by burning items such as rugs, plastics or tires. This smell is used to keep away animals such as rodents.
- Use of Smelly and bitter tasting plants
- Some animals avoid smelly and bitter tasting plants. This method keeps away root eaters (rodents) such as the mole from destroying farm plants, and digging holes in the farm.
- Care and Safety from Wild Animals
- Some wild animals can be dangerous. They can attack us or even kill us, they include the wild dog, wild cat and monkeys. Such animals can also transmit dangerous diseases such as rabies. We should always keep a safe distances from wild animals. We should not touch or provoke wild animals.
- Use of Sounds
Growing Climbing fruit Plants
- Fruits are source of food rich in vitamins.
- They are important for our bodies for growth vitamins are nutrients needed by the body to repair warm out tissues.
- Climbing fruits plants have a stem called a vain. Vains are weak and therefore are needed to be supported using wood or wires.
- Such fruits plants can also be made to climb along the fence. They include the passion fruits, grapes, blackberries, kiwi fruits, raspberry fruits and gooseberry fruits.
How to Plant
- Climbing fruit plants can be planted from seeds or from stem cutting. Fruits seeds can be found from the market or can be prepared at home for planting.
- To prepare fruits seeds, get a fruit from a tree or from the market, extract seeds from it and wash.
- Dry the seeds on the sunlight and select the best seeds for planting. Prepare a seedbed and plant your seeds.
- Always water your seeds regularly until the seeds germinate. After germinating and the seedlings are strong, you can transfer them to their place of planting.
- This process of transferring seedlings from the seedbed to their place of planting is called transplanting.
Passion fruit seeds
- To prepare stem cutting select a sweet able fruit plant to get the stems form. Using a knife, cut the stem into small pieces of about one feet.
- Insert the cuttings into a planting site such as a container or a socket. Take care of the planted cutting by watering them, shading and removing weeds. When the cuttings start to develop leaves and roots, you can transplant them to their new places.
stem cuttings
(stem cutting)
- Young climbing fruits plants should be taken care of. We should make a shade of them to prevent them from direct sunlight.
- We should also construct a support structure using strong poles and wires for the fruit plant to support itself on.
- We also need to guide the plant along wires the process of guiding a climbing fruit plant along a wire is called Training.
Ways of training a plant
- A grower trains plants to:
- Improve flower or plant appearance and management,
- improve flower and fruit size and quality and
- to protect plants from damage.
- Training plants is done by:
- supporting,
- thinning,
- stopping,
- disbudding and
- pruning.
- Water the young fruit plant regularly and apply manure at its roots. Artificial fertilizer can also be used at minimal quantities to ensure safe food, protect the plant from any weeds by weeding them regularly by uprooting weeds from the stem.
Managing Climbing fruit plants
- This is taking care of the plant to ensure that it grows until the harvesting stage. The process of managing fruits plant include, watering, weeding, manure application, training and harvesting.
- This can be well achieved by developing a project schedule.
- The planted climbing fruit plant should be watered regularly on the established site.
- Weeding should be done to reduce competition from weeds for nutrients, water and light.
- It is important to make a shade over the young plants. The shade protects them from direct heat of the sun. It is important to make a fence around them.
- A fence protects them from being damaged by animals.
- Well-rotted manure should be applied from time to time to ensure that the fruit plants grow healthy.
- Climbing fruit plants also need to be supported so that they grow well and receive adequate light.
Harvesting
- Fruits can be harvested at their right time of harvest. Once the fruits are mature, they should be harvested. The right time for fruit harvesting can be determined by observing the colour of the fruit.
- Some fruits like the yellow passion fruit turn their colour to yellow and become a bit softer, smoother and sweet smelling. Some fruits such as the passion fruits fall of from the tree when they are ready for harvesting.
Harvesting Process
- Climbing fruit plant can easily be damaged during the harvesting process. We should take care not to pull the fruits from climbing fruit plant.
- Pulling the fruits can damage both the fruit and the plant. Tender fruits such as berries should be placed in small container immediately after harvesting to prevent damage.
Earth And Space - Grade 5 Science and Technology Revision Notes
Moon
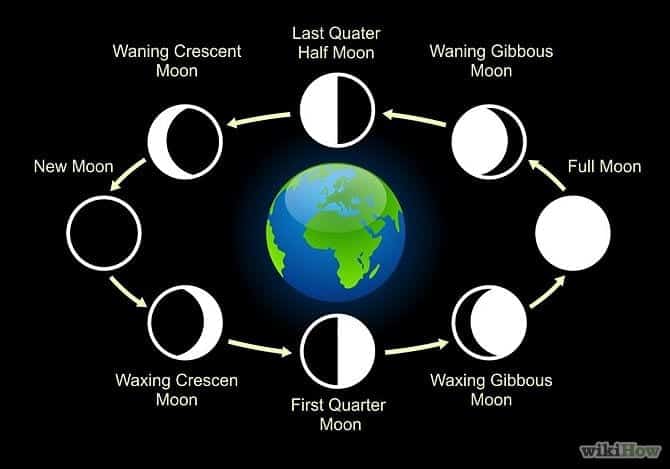
Observing different phases of the moon.
- The phases of the moon are the different shapes of the moon we can see from over a month.
- This can be observed at night during the month of the moon.
Identifying different phases of the moon
- There are eight phases that the moon goes through. Each phase repeats itself every 29.5 days. The following are the phases of the moon
using the real moon as an example, here is how they look like: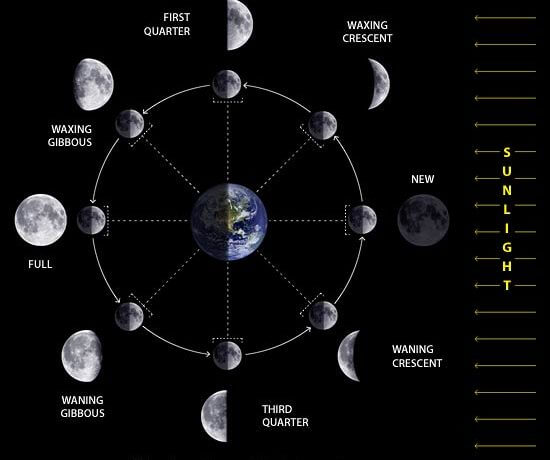
Force and Energy - Grade 5 Science and Technology Revision Notes
Gravity
Demonstrating Gravity
- Hold and suspend erasers in the air. Release them and tell what happens.
- Identify what causes the objects to act as they do. Name and define the cause.
- The fruits and leaves fell to the ground due to a force acting on them. The erasers dropped to the ground due to a force acting on them. This force is known as gravity.
- Gravity is defined as the force acting on objects pulling them down.
Effects of gravity on an object.
- The force that pulls down things is called the force of gravity.
- When you throw a ball into the air, gravity pulls it back down. When you release a stone suspended in the air, gravity pulls it down to the ground.
- When the books are tipped at the edge of the desk, the fall down due to gravity.
- Gravity causes fruits and leaves to fall from trees.
- Gravity is a force that pulls things down. It is also called the normal force.
Application of Gravity.
- The force of gravity enables the following in our lives:
- Gravity causes a ball you throw in the air to come down again
- It cause a glass to drop down and fall onto the floor
- It causes us to move down and slide
- It causes apple to fall down from apple tree
- It keeps us firmly on earth, otherwise we would float away into space.
- It causes a pen that rolls off your desk to fall onto the floor
- It causes water to move down a river and waterfall.
- It causes a rock to roll downhill.
Sound
Energy Producing sounds
- Sounds are produced when we the following
- Clap our hands
- Stamp our feet
- When we whistle.
- When we hot a drum
- Playing guitar
- Sound is the energy that things produce when they vibrate.
Loud and soft sounds
- Volume is the amount of sound something produces.
- It is the measure of the loudness of sound. Loud sounds are produced by big vibrations, while low sounds are produced by small vibrations.
- The energy of a sound determines its loudness. The greater the energy the greater the sound.
- Whispering makes a soft sound while shouting to a friend across a playground makes a loud sound.
- Fire alarms and car’s horn are examples of loud sounds, while whispering to a friend and the sound of blowing wind are examples of soft sounds.
Identifying areas with loud sounds
- Areas that produce loud sound in the environment include:
- Industries
- Music shops
- Markets
- Stadia (plural for stadium)
Sound pollution
- Sound pollution is defined as sounds or noises that are loud, annoying and harmful to the ears.
Effects of sound pollution
- The effect of sound pollution on human health and behaviour include the following:
- Loss of hearing - the immediate effect of noise pollution to a person, over a period of time is reduced hearing ability. Over a time a person may completely lose his or her hearing.
- Poor concentration - loud and continuous noise makes a person lose concentration on any activity that they are carrying out.
- Irritability - loud and continuous noise at home and at school may result in irritability which lead to aggressive behaviour.
- Sleep disturbances - loud noise disturbs your sleep and keeps you awake.
- Interferences with communication - loud noise makes people unable to communicate freely. You may find it difficult to understand or even hear what someone else is saying.
Protecting self from loud sound
- Turning down devices producing loud sound
- Using hearing protection devices when in a place with loud sound.
- Avoid areas with loud sound.
- Staying in houses with soundproof walls.
Heat Transfer
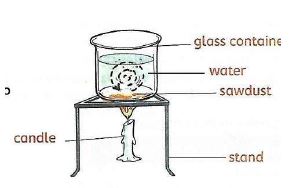
Demonstrating Transfer of heat in liquids
- Materials
- Sawdust
- A glass container
- A stand
- Water
- A matchbox
- A source of heat (a candle)
Procedure
- Fill in the glass container with water
- Place a small amount of sawdust in the water
- Allow the sawdust to settle at the bottom of the container
- Place the glass container on the stand
- Heat the container using candle as the source of heat
- Observe what happens.
- As the water continues to heat, a steady rise of sawdust is observed. This is because the water at the bottom of the glass container gets hotter, expands and rises.
- The cold water at the top then moves downwards and takes the place of the risen hot water.
- The cycle repeats itself. The sawdust particles show a movement in the water called convection currents.
- Therefore, heat is transferred in liquids through convection.
(convection currents in liquids)
(heating water via convection)
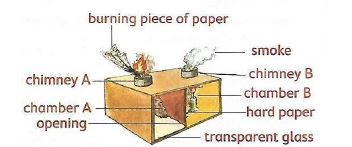
Demonstrating transfer of heat in gases
- Materials
- A small carton box with a top
- Hard paper or piece of carton
- A piece of paper
- A short candle
- A matchbox
Procedure
- Make a chimney on each end of the top of the box
- Divide the box with hard paper or a piece of carton to make two chambers A and B. place the transparent glass on the side of the box for viewing.
- Light up a candle. Put the lit candle below the chimney B on the box. Close the box.
- Place a burning piece of paper over chimney A as shown in figure 6
- Observe chimney B and tell what you see.
- Record your observations.
- The burning paper produces smoke that moves from chamber A to Chamber B through the opening.
- The candle in chamber b heats the smoke coming from chamber A, which becomes lighter and rises.
- As the smoke rises up it moves up through chimney B. Cooler air enters Chamber A through chimney A, creating a circular motion known as convection currents.
- These currents can be viewed through the transparent glass.
- The transfer of heat in gases is known as Convection
(convection in gases)
Application of convection in everyday life
- Convection of heat is used in everyday life by many ways. These ways include:
- Ventilating buildings
- Inflation of hot air balloons
- Heating of food in a microwave
- Formation of land and sea breezes
- Boiling of water in a sufuria or kettle
- Vehicle engines
Transfer of heat by radiation
- When you stand in the sunlight, you can feel the warmth of the sun. The heat energy from the sun is transferred to your skin through radiation.
- When you sit beside a fire, you feel warm. The warmth of the heat from the fire is transferred from the fire to you through radiation.
Application of radiation in everyday life
- Radiation is used in everyday life in many ways. These ways include:
- Warming ourselves using electric heaters
- Using solar heaters in the house
- Drying clothes and grains
- Using greenhouses to aid growth of plants
Matter - Grade 5 Science and Technology Revision Notes
Change of state
Effects of heating matter.
- Matter - everything around us. All materials and substances that exist and occupy space.
- States of matter - different forms of substances, that is solids, liquids and gases.
- Change of state - to turn from one form to another, for example from solid to liquid. It occurs when matter absorbs or loses energy.
- When solids are heated, they change their states of matter. Some solids such as candle wax and cookin fat, melt into liquid, while ice cubes melt into water (liquid)
- The process in which a solid changes to a liquid is called melting.
- There are some solids that change to gases when heated, for example mothballs. The process in which a solid changes directly to a gas is called sublimation.
Heating Liquids.
- Some liquids change their state of matter through heating.
- Water (liquid) changes to water vapour (gas) when heated.
- The process in which a liquid boils and changes to a gas is called evaporation.
Effects of cooling matter.
Cooling water vapour
- When vapour is cooled it changes to liquids. This means that it has changed its state from gaseous state to liquid state.
- The process in which a gas changes to a liquid is called condensation. Cooling Liquids
- When liquids such as water, melted fat and melted candle wax are cooled, they harden and become solids.
- They change from liquid state to solid state.
- The process in which a liquid changes to a solid is called freezing.
- When gases such as mothball vapour are cooled, they become solids without forming liquids first. A mothball is made up of a substance known as naphthalene whose vapour changes from gaseous state to solid state on cooling.
- The process in which a gas changes directly to a solid without going through the liquid state is known as deposition.
Application of change of state of matter.
- Heating is used to dry grains, fish and other foods to preserve them. It also dries clothes and salt through evaporation.
- Heating of water bodies causes evaporation and cooling of air forms rain through condensation.
- Cooling preserves food and also makes ice through freezing. Solid metal melts into liquid on heating.
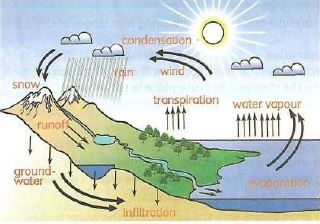
Water cycle
- A cycle is something that happens over and over again. It has no beginning and no end. The following are the water cycle stages:
Stage 1: Evaporation and Transpiration.
- The water cycle begins with the sun heating the water bodies. As the water heats up, it evaporates.
- In addition, green plants also release water vapour into the air in a process called transpiration. The vapour rises up into the sky.
Stage 2: condensation
- High up in the sky, the temperatures are cool. Water vapour in the clouds cool down and becomes liquid water. This liquid water is stored in clouds. The process of water vapour turning back into liquid is called condensation.
Precipitation
- The water falls from the sky in the form of rain, snow or hail through precipitation.
Runoff and infiltration
- As the water fall on the ground, the water forms streams and rivers and collects in lakes and oceans. This is known as run-off. Besides runoff, water is also absorbed into the soil.
- This is called infiltration. The water get stored as groundwater. The cycle then continues.
Acids and Bases
Identifying acids and bases
- Most substances are both acids and bases in nature.
- However, we cannot taste each and every substance to tell whether it is an acid or a base.
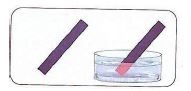
- In order to taste whether it’s an acid or base we use a litmus paper to find out whether a substance is acidic or basic in nature.
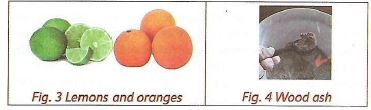
- The litmus paper is known as an indicator. Indicators change their colour when they are dipped in a solution containing an acidic or a basic substance. Lemon juice turns the blue litmus paper red. This means that lemon juice is an acidic
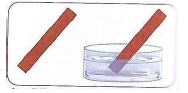
- Wood ash solution turns red litmus paper blue. This means that the wood as solution is a base.
- Common substances used as acids and bases
- Blue litmus paper turns red when dipped into:
- Lemon juice
- Grape juice
- Orange juice
- Sour milk
- Therefore, soap, antacid tablets, baking soda and wood ash are bases.
Physical properties of acids and bases
Acids
- They have sour taste
- They turn blue litmus paper red.
(testing acid using blue litmus paper)
Bases
- Have bitter taste
- They are slippery when touched
- Turn red litmus paper blue
(testing base using
Uses of acids and bases
Acids
- Acids in fruits such as lemon and orange is used to enhance taste in drinks and to flavor
- Lemon acid is used in some cultures to make milk sour
- Vinegar contains acid that is used for cooking purposes and it is also used to give salads a delicious taste.
- Vehicles have batteries that have an acid which is used to produce electricity.
Bases
- There are various items used on a daily basis that contain bases. They include:
- Baking powder is used to bake bread, burns and doughnuts
- Antacid tablets are used to relieve heartburn.
- Soap is used for bathing. We use detergents to wash our clothes
- We clean our teeth using toothpaste.
Coding - Grade 5 Science and Technology Revision Notes
Patterns and games
Simple programming using Scratch.
- The scratch language has similarities to children’s building brick toys.
- It uses a simple structure of graphical bricks or blocks of computer code.
- They snap and interlock together to build and control sound, music and images.
Main parts of Scratch
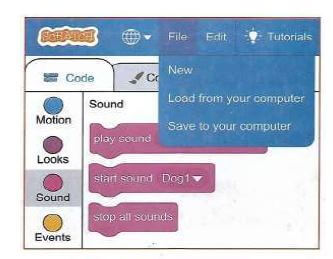
- Menus - this part contains the file menu used to save or load your projects.
- Main tabs - this part helps a user switch between different activities, such as coding, drawing or adding sound.
- Blocks categories (Blocks Palette) -this part contains a coloured set of code blocks that are used to program the sprite and give actions to it.
- Code blocks -these are blocks that are shaped differently and are used to create code in scratch. The blocks connect to each other vertically like a jigsaw.
- Coding area (sprite area) - this is the place where you create a code (script) for a sprite to do a specific action. You drag and drop the code here and snap them together to create your programme.
- Start and stop - you click the green flag to start your code or the stop sign to stop the code.
- The stage: this is the main working area where the sprite moves and performs as per the given code of instruction.
- Sprite - this is a small graphic character that performs actions, such as moving around in the stage.
- Sprite info - this part of scratch shows information about each sprite, such as how big it is.
- Sprite list - this part displays all the sprites in your project.
- The selected sprite has a blue border around it.
- Choose a backdrop - this part is used for adding a new background to your project.
- Choose a sprite - this part is used for adding a new sprite to your project.
- Tutorials - this part contains some help videos. Click the white X to close it.
Sprites
- The sprite info is where scratch displays icons of the sprites that are being used in the current project.
- A sprite is an animated character or object in your program.
- Sprites can move around, be active or be objects that stay still. These actions are determined by the scripts that your create.scripts tell the sprites what to do and what actions to perform.
- The cat sprite called Sprite1 always appears by default when you create a new project.
- To add a new sprite to a scratch project, you use the icon in the button right-corner of the pane.
- Clicking this button allows you to choose from a library of already existing sprites offered for free on the scratch program.
- Moving the mouse over this reveals more options, as shown
- The options include the following
- Upload sprite
- this button allows you to upload a sprite from your computer.
- Surprise
- this button randomly selects a sprite from the scratch library and inserts it into your current project.
- Paint
- this paint brush button creates a blank sprite with an empty costume.
- Choose a sprite
- this button allows you to choose a sprite from the library.
Creating animation using scratch.
- Start the scratch 3.0 from your desktop by clicking the icon below.
- At the moment we only have one sprite, a cat named scratchy labelled sprite1.
- By placing blocks in the coding area, we give instructions to the sprite.
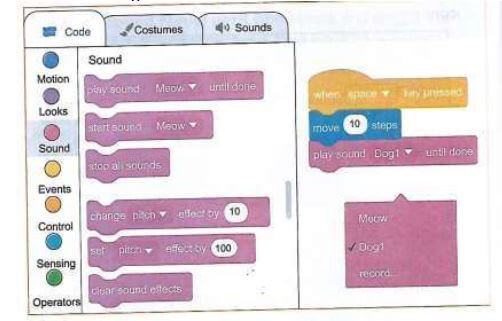
- first , go to the blocks Category section located at the lefthand side of the scratch interface which contains thematic folders of blocks of code such as the following:
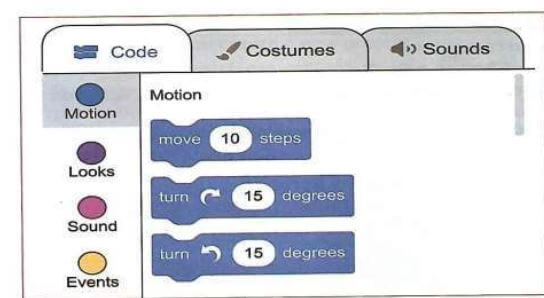
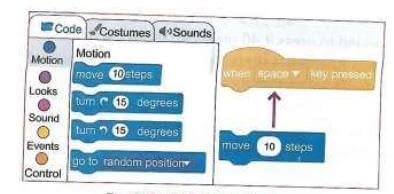
- Motion - these blocks of code control the movement of the sprite
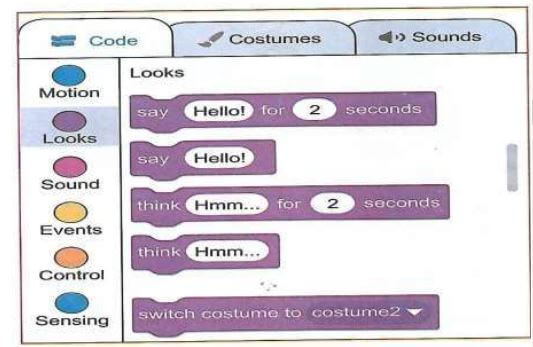
- Looks - these blocks of code change the appearance of a sprite.
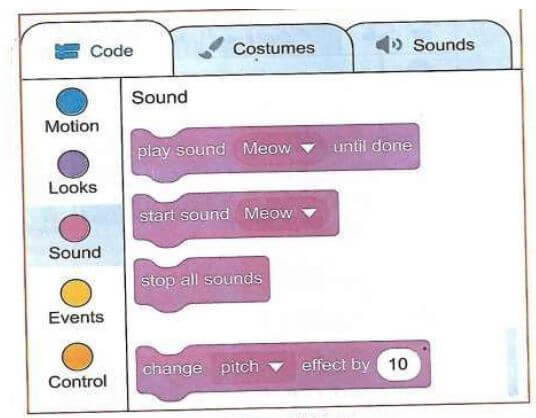
- Sound - these blocks of code add and control sound in your scratch project.
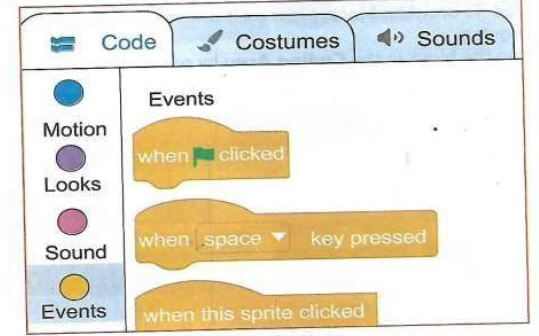
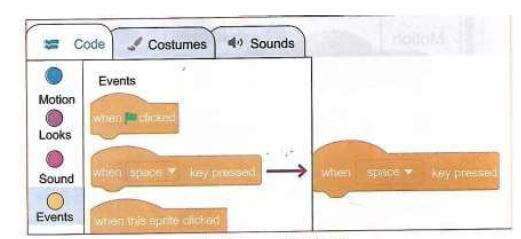
- Events - these blocks of code control when and how the scripts or codes are activated.
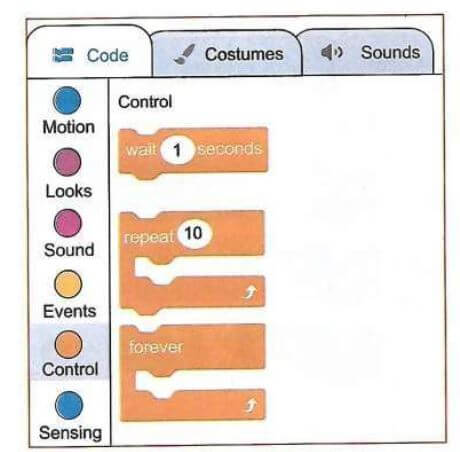
- Control - these blocks of code control how the scripts or codes run.
- Motion - these blocks of code control the movement of the sprite
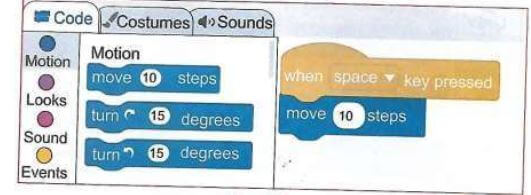
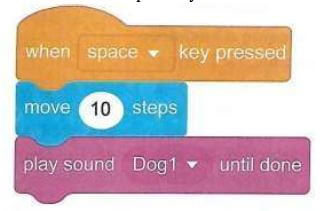
- Now let us make a scratchy run. On the main tabs, click on the events from the blocks categories. Select when the space key pressed block and drag it from the code blocks to the coding area. To drag the block, press on it and hold the space key while dragging.
- Drop the block in the coding area by releasing the mouse button as shown below
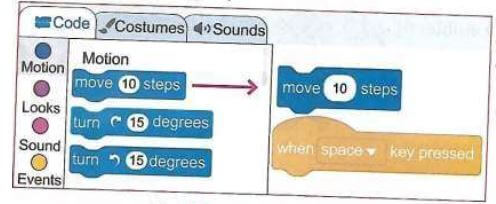
- Next, switch from events to motion in the blocks categories. Select move 10 steps block and drag it from the code blocks to the coding area
- Position the block under the events block by pressing the space key.
- Release the mouse and the motion block will attach and fix itself under the events block.
- You have managed to create your first code. Press the space key and watch how scratchy moves. If you keep pressing the space key, scratchy will go to the edge of the stage. The tail will still be visible
- To bring scratchy back, press on its tail, and drag the cat back to the center of the stage. You can press the space key again to move scratchy to the right. Drag it once more to the left side of the stage.
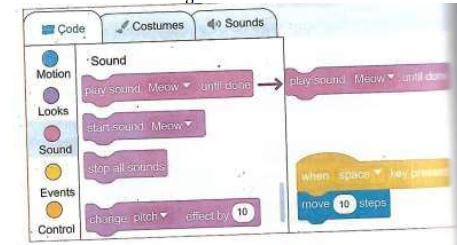
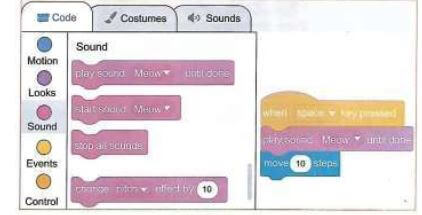
- Next, give sound to the source code. Make the scratchy Meow. Switch from motion to sound in the blocks categories.
- Select play sound Meow until done block and drag it from the code blocks to the coding area.
- Fix it under the motion block. Scratchy is now moving and meowing when you press the space key.
- If scratchy meows too loudly, adjust the volume by going to the main tabs, then clicking on sounds tab. Then reduce the volume by continuously clicking on the softer sound icon.
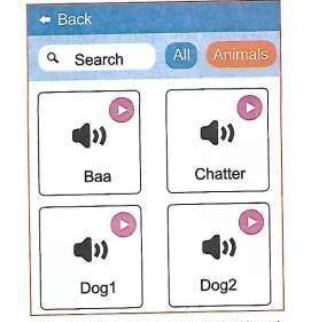
- If you tire with meowing, you may add new sounds. Let us make scratchy bark. Go to main tabs, click sounds tab. Click on the choose a sound icon. It will open the sound library. This contains different types of sounds. Select animal.
- Click on the Dog 1 sound. Now, we can use two different sounds for scratchy. Go to the code tab, then the code blocks section.
- On the play sound meow until done block, click on the drop-down menu. Select Dog1 sound.
- Press the space key. Watch the cat walking and barking.
- Save your project. Click file. Next, click save to your computer. You will see the save window where you enter a file name.
Computing Devices - Grade 5 Science and Technology Revision Notes
- Handling data - word processing
Handling data - word processing
- A word processor is computer software used to compose, format, edit and print documents. Examples include:
- Microsoft word
- Open office .org Writer
- Word pad
- Word perfect
- Open office writer
Creating a word document
- Open Microsoft word 2010 by searching through windows “Microsoft word”
- Launch Microsoft word 2010 by double clicking.
- On the landing page (immediate page) click blank and Microsoft word 2010 document will open
Components of A word document
- They include:
- Title bar
- Ribbon
- Horizontal scroll bar
- Status bar
- Typing area
- Vertical scroll bar
Keying information (typing)
- Create a word document
- Key in the information by doing the following:
- Type on the keyboard to create text
- Use the mouse to move the insertion point (blinking line - indicates where you can enter or key in text on the page) to a specific place in your document. Click the location in the text where you want to place it.
- Press the spacebar on the keyboard to add space after a word or in between text.
- Press enter on the keyboard to move the insertion point to the next paragraph.
Editing a word document.
- Click and drag across the text you want to select.
- You can select any amount of text with this method, from a single character to your entire document.
- Here are some other ways to select text you’ll find useful:
- Press and hold down the Shift key, and move the insertion point either with your mouse or the arrow keys to select text.
- Double-click a single word to select it.
- Press the Ctrl key and click in a sentence to select it.
- Triple-click in a paragraph, or double-click in the left margin next to a paragraph, to select it.
- Click in the left margin to select an entire line, or click and drag in the left margin to select multiple lines.
- Press Ctrl + A to select everything in the document
Edit Text
- Select the text you want to replace, then start typing the new text.
Changing font size
- Create a word document
- Type a short essay on good citizenship
- Select the text you want to edit
- left - click or long press the drop-down arrow next to the font size box on the home tab.
- Move your cursor over the various font sizes
- Left-click the font size you want to use. The font size will change on the document.
Changing font style
- Use the text you typed on good citizenship. Select the text you want to edit.
- Left-click the drop-down arrow next to the font style box on the home tab.
- Move your cursor over the various font styles
- Left-click the font style you want to use. The font style will change in the document.
Changing font colour
- Use the text you typed on good citizenship. Select the text you want to edit
- Left-click the drop down arrow next to the font colour box on the home tab.
- Move your cursor over the various font colours.
- Left-click the font colour you want to use. The font colour will change in the document.
Changing text into bold, italic and underlining
- Open an existing word document or start a new document and type your text.
- Change some of the text that you have already types to a different font
- Select the text that you wish to edit or change for the formatting.
- To change the selected font to bold, click B in the formatting ribbon at the top of the document
- To change the selected font to italics, click I in the formatting ribbon at the top of the document
- To change the selected so that it is underlined, click U in the formatting ribbon at the top of the document
Changing Text Case
- Select the text you want to edit
- Click the change case command in the font group on the Home Tab.
- Select one of the case options from the list.
- Write down the different options on the case list.
Changing text alignment
- Open an existing word document or start a new document and type your text. The default layout is left align, where text will be aligned to the left margin of the document.
- To change the layout of your text, select the text that you wish to change using the mouse.
- To center the selected text, click on
icon in the formatting ribbon at the top of the document.
- To right align the selected text, click on
icon in the formatting ribbon at the top of the document.
- To left align the selected text, click on
icon in the formatting ribbon at the top of the document.
- To justify text so that it is aligned both right and left, click on
icon in the formatting ribbon at the top of the document.
Inserting Text
- Create a new word document
- Type some text into the document
- Move your mouse to the location where you want text to appear in the document.
- Left-click the mouse. The insertion point appears.
- Type the text you want to appear.
Deleting text
- Create a new word document
- Type some text into the document
- Place your cursor next to the text you want to delete
- Press the backspace key on your keyboard to delete text to the left of the cursor.
- Press the Delete key on your keyboard to delete text to the right of the cursor.
Selecting text
- Create a new word documentb.
- Type some text into the document
- Place the insertion point next to the text you want to select.
- Left-click your mouse. While holding it down, drag your mouse over the text to select it.
- Release the mouse button. You have selected the text
- A highlighted box will appear over the selected text.
Copying and pasting
- Create a new word document
- Type some text into the document
- Select the text you want to copy
- Click the copy command on the Home Tab.
- Place the insertion point where you want the text to appear.
- Click the paste common on the Home tab. The text will appear.
Saving a document
- When saving the document for the first time:
- Choose file. Then save from the menu bar. The save as dialog box appears
- Another option is clicking the save button on the standard toolbar.
 Then save as dialog box appears.
Then save as dialog box appears. - There as a last option of choose file, the save as from the menu bar. The save as dialog box appears.
- Before clicking save button in the save as dialog box, first name your file with a descriptive name that you will remember.
- To name you file, once the save as dialog box is open, the current file name appears highlighted, ready for you to change it.
- Type a short descriptive name in the file name box. File names can include spaces and capital letters but not special
characters. - If you do not choose a file name, word program will assign a file name for you. It assigns the first line of text in your document. If you save a blank document, the file will be saved as Doc1, Doc2 and so forth.
- After you name your file, choose a file location. This will keep your files orderly and easy to find. My documents is the default file location in word program.
- To save a file in My documents, make sure My documents is the current file location in making sure the left column and save in drop-down box state my documents.
- Click save button.
NOTE
- Save - is used when saving file for the first time, it doesn't matter if you choose to save it using save or save as.both commands open the save as dialog box.
- Save as - lets you save an existing file under a new name, allowing you to create a new file.
Retrieving documents
- Open a Microsoft word
- Click file in the upper left-hand corner of the screen.
- Click open
- An open dialog box will pop up. From this, find your way to the file in which your document is saved. Files that are on your computer can be located by clicking browse.
- Once you have located your document and clicked on it to select it, its name will be shown in the file name box at the
bottom of the dialog box. - Click open. The document will then be opened.
Safety when using computer devices
- Turn on the computer correctly. Follow the right process.
- Respect yourself by not giving your name and password.
- Prepare early for each task. Using time wisely
- Respect others by sharing computer devices.
- Report problems with the computer devices. It saves time and energy.
- Take responsibility for your actions.
- Log off and leave the computer station ready for the next person to use.
Environment - Grade 5 Science and Technology Revision Notes
Solid waste management
Identifying solid waste
- Solid waste is a type of waste that consists of everyday items that are thrown away by people.
- Solid waste is also known as rubbish, garbage or trash
- Solid waste comes from our offices, homes, schools, industries and hospitals among other places.
- Solid waste management is the process of collecting, treating and disposing of solid waste. It's about how solid waste can be changed and used as a valuable resource.
Classifying waste.
- Wastes are classified as both those that decompose easily and those that do not decompose.
- For example:
- Tomato fruit brakes down and starts to rot and eventually becomes part of soil. This is called decomposition.
- The plastic bottle did not show any change after a week. Therefore, the plastic bottles do not rot. It cannot decompose.
Ways of managing solid waste
- Different types of waste are managed differently. These ways include the 3Rs - Reusing, Recycling and Reducing.
- Reusing
- Some solid waste can be used again for their original purpose or for different work. For instance, discarded bottles can be cleaned and used for bottling drinks, or used at home for other tasks.
- Other reusable solid waste include boxes, bags, old clothes, books, old newspapers and wood.
- Recycling
- Recycling solid waste means that the material is reprocessed before being used to make new products. All types of organic waste can be recycled by composting. Other solid wastes that can be recycled include paper, waste metals, glass and plastic bottles, among others.
- Reducing
- Waste reduction is a set of processes and practices intended to reduce the amount of waste produced. It is a way of preventing materials from ending up as waste. This can be done by buying products with less packaging, making use of reusable rather than disposable items, using your own shopping bags, minimizing food waste and repairing and maintaining items such as clothing, so that they last long. Solid waste can be reduced through the following ways
- Avoiding using plastic bags to carry items. Instead use baskets.
- Using reusable (canvas) bags for buying items
- Borrowing, renting or sharing items that are not regularly used.
- Using sponges or dish clothes instead of paper towels.
- Using plug-in appliances instead of battery 0perated gadgets.
- Buying durable and repairable products.
- Waste reduction is a set of processes and practices intended to reduce the amount of waste produced. It is a way of preventing materials from ending up as waste. This can be done by buying products with less packaging, making use of reusable rather than disposable items, using your own shopping bags, minimizing food waste and repairing and maintaining items such as clothing, so that they last long. Solid waste can be reduced through the following ways
Project
- Making dustbins using locally available materials
- Make a toy car
Health Education - Grade 5 Science and Technology Revision Notes
- Water borne diseases
- External Body parasites
- Internal Body parasites
Water borne diseases
- Diseases- illnesses that affect our health.
- Waterborne diseases - are diseases that are spread by contaminated water or food.
They include:- Typhoid
- Bilharzia
- Cholera
- Dysentery
Typhoid
- It is caused by bacteria that are spread through eating contaminated food and drinking contaminated water
Signs and symptoms
- Body weakness
- Headache
- Rash on neck and abdomen
- Fever
- Vomiting and diarrhoea
Prevention of typhoid
- Washing hands and utensils before handling or eating food.
- Washing fruits before eating and washing vegetables before cooking.
- Cooking food well before eating. Always cover food.
- Boiling water before drinking
- Spraying the house and the toilet with an insecticide to kill flies.
Bilharzia
- Bilharzia, also known as snail fever, is a disease caused by a parasitic worm. A person becomes infected when he or she comes into direct contact with fresh water that has snails carrying the parasitic worm.
Signs and symptoms of bilharzia
- Body rashes
- General body weakness
- Headache
- Fever
- Vomiting and diarrhoea
Prevention of bilharzia
- Cleaning and disinfecting swimming pool water.
- Draining stagnant water. Avoid walking in stagnant water.
- Drinking safe and clean water
- Bathing or showering using clean water
- Weaving gloves and gumboots when working in waterlogged areas.
Cholera
- Cholera is caused by bacteria that spread through eating contaminated food and drinking contaminated water.
Signs and symptoms of cholera
- Body weakness
- Headache
- Fever
- Vomiting and watery diarrhoea
- Loss of fluids and severe dehydration.
Prevention of cholera
- Washing hands before handling or eating food.
- Washing fruits and vegetables before eating or cooking.
- Cooking food well before eating. Always cover food.
- Boil water before drinking it.
- Spraying the house and the toilet with an insecticide to kill flies.
Dysentery
- Is caused by bacteria that are spread through food and drinking water that is contaminated.
Signs and symptoms of dysentery
- High fever and chills
- Abdominal pains
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Vomiting
- Dehydration
- Severe diarrhoea
Prevention of dysentery
- Washing fruits and vegetables before eating or cooking
- Boiling water before drinking
- Spraying the house and the toilet with an insecticide to kill flies
- Washing hands before handling or eating food.
External Body parasites
- Include parasites such as fleas, jiggers and mites that live on the
- outer surface of the body especially the skin.
- Soil transmitted diseases.
Lice
- Lice are tiny parasitic insects that live in the clothing and bedding of an infected person. Lice travels to the skin of
the infected person several times a day to feed on blood. - The most common places for bites are around the neck, shoulders, armpits, waist and groin. These are places where clothing seams are most likely to touch the skin.
Signs and symptoms of lice
- Intense itching
- Rash caused by an allergic reaction to body lice bites
Red bumps on the skin - Thickened or darkened skin, usually near the waist or groin on the bed.
- Itching of the head or scalp caused by lice found on the head.
- Tiny red sores from scratching the scalp caused by lice found on the head.
Prevention and management of Lice
- Improve personal hygiene and regular changing into clean, washed clothing.
- All clothing, bed linens and towels used by the infected person should be washed with hot water and then dried.
- Medicines that kill lices may be used to get rid of body lice.
- Head lice treatment requires thorough combing of the hair to remove lice eggs.
- Avoid sharing brushes or combs.
- Shave hair.
Scabies
- It's a skin disease caused by a mite. The mite causes an itchy, red rash to form on the skin. The mite can be transmitted
through infected clothing or bedding.
Signs and symptoms of scabies
- Severe and intense itching that gets worse at night
- Continuous scratching of the infected area
- Rashes and blisters on the skin
- Sores in areas where a person has scratched the skin.
Prevention and management of scabies
- Wash or dry-clean all clothes, towels and bed linens. When washing, use hot, soapy water. Dry the washed
clothes. - Clean and vacuum carpets and rugs
- Treat scabies with medication.
Jiggers
- A jigger is a small, pinhead-sized parasitic insect. Jigger larvae live in the soil and feed on organic matter. Jiggers usually attack the feet and toes. Sometimes they attack the hands and fingers.
Signs and symptoms of jiggers
- The affected part itches
- The infected person feels a lot of pain in their feet, making it difficult to walk.
- The parasite may cause ulcers on the feet.
- The feet of the infected person may swell
- The toenails of the infected person may fall off
- The parasite can cause deformed toes and fingers.
Prevention and management of jiggers.
- Observe general cleanliness
- Smear the floor and walls of mud houses with cod dung.
- Avoid close and frequent interaction with animals that host the fleas, for example dogs.
- Wear shoes whenever possible.
- Use antiseptics and petroleum jelly to treat jiggers. Use gloves when treating jiggers and the wash your hands when done
Internal Body parasites
Common internal parasites
- They are parasites such as roundworms that live within the body, especially in the intestines.
Roundworms
- A roundworm is an internal body parasite that infects the small intestine of a human being. It gets nutrients from the small intestine of the infected person.
- It is a soil- transmitted parasite. Human faeces can cause contamination if an infected person passes faeces on soil or near a source of water.
- A person gets infected if he or she eats or drinks contaminated food or water.
Signs and symptoms of roundworm infection
- Abdominal pain
- Worms visible in faeces Slow growth in children
- Diarrhoea
- Loss of appetite
- Vomiting
- Weight loss
Prevention and management of roundworm infection
- Wash food properly before cooking. Also wash hands after using the toilet
- Wash any utensils and cooking surfaces after using them.
- Filter and boil water before drinking it
- Wash hands with soap and warm water before handling or eating food.
- Avoid common bathing areas, especially if they are dirty.
- Clean hands with soap and water after playing outside
- Roundworms are treated with medicine.
Pinworms
- Swallowing pinworm eggs causes a pinworm infection.
- The eggs are found in contaminated food or drink. If you do not wash your hands well, your fingers can carry pinworms.
- The eggs then hatch in the intestines. Female pinworms move to the anal area to lay their eggs, which often results in anal itching.
- When you scratch the itchy area, the eggs cling to your fingers and get under your fingernails.
- The eggs then get transferred to other surfaces, such as toys, bed linens or toilet seats. The eggs can also be transferred from contaminated fingers to food, liquids, clothes or other people.
Signs and symptoms of pinworm infection
- Disturbed sleep
- Loss of appetite
- Itching of the anal area, especially at night
- Severe irritability
- Abdominal pain
- Weight loss
Prevention and management of pinworm infection
- Take a bath in the morning and wash the anal area
- Change underwear and bed sheets daily
- Wash bed sheets, night clothes, underwear and towels in hot water to kill pinworm eggs.
- Avoid scratching the anal area. Trim your nails so eggs do not collect. Avoid biting your nails.
- Thoroughly wash your hands after visiting the toilet and before eating
- Visit the doctor for treatment.
Tape worms
- Tapeworms are intestinal parasites that are shaped like a tape measure.
- Tapeworm eggs normally enter the human
- Body from animals through food, especially raw or undercooked meat.
- People can also become infected if there is contact with animal faeces or contaminated water.
Signs and symptoms of tapeworm infection
- Abdominal pain
- Vomiting
- Inflammation of the intestines
- General weakness
- Diarrhoea and weight loss
- Lack of appetite and feeling dizzy
- Eggs, larvae or segments from the tapeworm in stool.
Prevention and management of tapeworm infection
- Visit a doctor for treatment
- Thoroughly wash your hands with soap and water after visiting the toilet and before eating.
- Always wash all vegetables with clean water
- Always wash all fruits with clean water
- Properly dispose of animal and human faeces
- Cook meat properly. This will kill larvae or eggs of tapeworms
- Do not eat raw or uncooked mean
- Treat pets, such as dogs for tapeworms
- Make sure all work surfaces, especially in the kitchen, are regularly cleaned and disinfected.
Hookworms
- Hookworms are soil transmitted parasites. Human faeces can cause contamination if an infected person passes faeces on soil.
- When a person comes into contact with this soil, hookworm larvae can pass through the skin of the person.
- This can happen if the person walks barefoot on soil that contains the larvae or swallows contaminated soil particles for example on unwashed vegetable leaves.
Signs and symptoms of hookworm infection
- A skin rash that is red and itchy
- Fever
- Stomach pain and diarrhoea
- Anaemia
- Loss of appetite and weight loss
- Tiredness and weakness
- Stunted growth
- Malnutrition
Prevention and management of hookworm infection
- Visit a doctor for treatment
- Wear shoes, especially in areas with soil
- Avoid eating unwashed foods that may be contaminated with hookworms
- Pass faeces in toilets and latrines
- Do not use fertilizer made from raw human faeces
- Wear gloves and gumboots when gardening
- Treat pets for hook work
Human Beings - Grade 5 Science and Technology Revision Notes
- Sense Organs
- Skeleton and Muscles
- Types of Muscles
- Breathing system
Sense Organs
- Human have five basic senses, namely sigh, smell, taste and feeling or touch
- The organs associated with each senses send informations to the brain to help us understand and perceive the world around us.
Functions of sense organs
- These organs include;
- Tongue - for taste
- Ears for hearing
- Nose for smell
- Skin – for feeling or touch
Cares for various sense organs
- Bathing daily with soap and clean water
- Applying oil to keep the skin moist
- Brushing tongue and teeth when cleaning the mouth
- Keeping the nose clean by using the handkerchief.
- Clean the ears using cotton buds.
- By no putting sharp objects into the nose or ears.
Skeleton and Muscles
Parts of a human skeleton
- The human body is a complex design made of various system and structures
- The parts that make the human skeleton are the skull, the rib cage and the smooth muscles.
Functions of human skeleton
- This is the structure made of bones, cartilages and connective tissues; it serves the following functions;
- The skull protects the brain from injuries
- Backbone provides support to the body and helps the body to remain upright
- It also makes the person flexible.
- It is also known as human spine
- It is made up of 33 bones called the vertebrae . these bones stretches from the neck to the pelvis and protect the spinal cord.
- The backbone provides support to the body,allowing the body to stand , bend or twist.
- The backbone also protect the brain and the body
- The rib cage protects the heart and the lungs
- It is made up of curved bones called lungs
- It is found in the chest area
- It protects a person’s internal organs from damage and gives structures to the test.
- Most human beings have 12 pairs of rib bones
- The limbs bones support the weight of the human body.
- They also help a person to move
- There are 30 bones in each lower limps(leg) these are,
- Femur – is a single bon of the thigh, its rounded head connects with the hip socket to form the hip join. There are 30 bones in each upper limb (arm)
- The humerus is the single bone of the upper arm and the ulna and the radius are the paired bones of the forearms. Other bones include:
- Tibia
- Fibula
- Seven tarsal bones
- Five metarsal bones and 14 phalanges
Types of Muscles
- It is a tissue that functions as a source of power
- It is a bundle of fibrous tissue in a human or animal body that can contract, producing movements in the body maintaining the position of the part of the body.
- The human body has three types of muscles
- Cardiac muscles – these muscles make up the mass of the heart and are responsible for the heart’s rhythmic contractions.
- Skeleton muscles - they connect to and control the motions of the human skeleton. They are found between the bones and use tendons to connect to bones. They are controlled voluntarily and are concerned with movement, posture and balance of human body.
- Smooth muscles – are control involuntarily. They are found in the walls of blood vessels ,urinary bladder , the intestine and stomach
Functions of Skeleton Muscles (Voluntary muscles)
- support and help the body move
- Control the body temperature
- Keep the body upright
- Protect the organs of the body
Breathing system
Parts of human breathing system
- System – the human body is like a factory that is made of many parts. These parts work in groups called system
- The breathing system has both visible parts such as the nose, internal parts such as the trachea, lungs and diaphragm. These parts work together to enable human being to breathe.
Functions of breathing system
- Breathing – this is the mechanism of taking air and blowing out air.\
- Air blow from outside into the nose through nostril. The nose has tiny hairs that clean the air by trapping dusts. At the back of the nose these is membrane that produces mucus which makes the air moist, warm and clean.
- The trachea is called windpipe, it receives air from the nose,it has C- shaped ring that keep it strong and open. The walls of the windpipe have mucus and tiny hairs that filter air and keep it clean. The trachea acts as a passage for air from the nose into the lungs
- A human being has two lungs
- Membrane that produces mucus, which makes the air moist, warm and clean.
- The trachea is also called the windpipe. It receives air from the nose. It has C-shaped rings that keep it strong and open. The walls of the windpipe have mucus and tiny hairs that filter the air and keep it clean. The trachea acts as passage for air, from the nose into the lungs
- A human being has two lungs located inside the chest. The lungs are a pair of airfilled organs. The lungs take in the oxygen in the air and take out carbon dioxide that the body does not need.
- The diaphragm is located under the lungs. It controls breathing. It separates the chest from the abdomen. It helps to fill the lungs with air when breathing in.
- It also helps to take out air when breathing out.
- Breathing is essential for the living process of human beings to continue.
Diseases that affect the human breathing system
- The human breathing system is affected by many diseases. They include:
Tuberculosis (TB)
- Is a disease that affects the breathing system. It mainly affects the lungs. TB is caused by bacteria. It spreads from one person to another
through sneezing, coughing or spitting.
- Night sweats
- Coughing up blood
- Unintentional weight loss
- Coughing that last for three or more weeks
- Chest pain or pain when breathing or coughing
- Staying dust free, well-ventilated rooms
- Vaccinating infants
- Covering the mouth when sneezing
- Wearing a mask in public if you are already infected
- An infected person should finish his or her entire course of medication
Pneumonia
- Is caused by germs such as bacteria and viruses. It can also be called fungi.
Signs and symptoms of Pneumonia
- Chest pains when breathing or coughing
- Cough that may produce mucus
- Sweating and shaking
- Nausea, vomiting or diarrhoea
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Fever
- Vaccination against pneumonia
- Keeping immune system strong
- Practicing good hygiene
- Not smoking
Colds
- Colds are caused by a virus. The virus affects the nose and the throat.
- Children under the age of six years are at greatest risk of getting it.
- Running or stuffy nose
- Congestion in the nose
- Sneezing
- Mild fever and generally feeling unwell
- Sore throat and cough
- Mildhead.
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and clean water.
- Disinfecting items
- Covering the mouth when coughing or sneezing
- Avoid sharing utensils
Asthma
- Is a disease that narrows and swells the airways in the lungs, producing extra mucus. This makes breathing difficult. Being exposed to substances such as pollen, dust mites, infections such as common cold, cold air, pollutants such as smoke, strong emotions and some kinds of medications can cause asthma.
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pains
- A whistling sound when breathing out
- Getting vaccinated for influenza na pneumonia
- Identifying and avoiding asthma triggers
- Monitoring your breathing
- Treating early attacks
- Taking medication as prescribed by the doctor.
- Carefully following your medication plan.
Coughs
- Can be caused by smoke exposure, infections, asthma and presence of mucus in the throat.
- Frequent throat clearing and sore throat
- Wheezing and shortness of breath
- Persistent coughing
- Running nose
- Hoarse voice
- Avoiding smoke particles and dusty places
- Avoiding smoking
- Drinking a lot of water
- Avoiding unhealthy surroundings and crowded places
Influenza
- It is commonly called the flu. It is caused by a virus. The flu is transmitted through the air in droplets when someone with the infection coughs, sneezes or talks.
Signs and symptoms of influenza
- A high fever
- Chills and sweats
- Dry and persistent cough
- Nose congestions
- Aching muscles
- Headache
- Fatigue and weakness
- Sore throat
- Yearly flu vacation for any person who is six months old and above.
- Thorough and frequent hand-washing
- Covering your mouth and nose when sneezing or coughing
- Avoiding crowds during peak flu season.
Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID - 19)
- COVID-19 is a disease of the breathing system. It is caused by a virus, known as coronavirus. The virus looks like a round ball with
a spiky crown. - When an infected person sneezes or coughs, tiny droplets are spread into the air. These droplets contain the virus.
- One can get infected if he or she touches a surface with the virus. The virus enters a person’s system if one touches their nose, eyes or mouth
Signs and symptoms of COVID-19
- Fever
- Dry cough
- Sore throat
- Headache
- Tiredness
- Loss of taste or smell
- Wash your hands well frequently for at least 20 seconds withsoap and running water. If soap and water are not available, use an alcohol- based hand sanitizer.
- Use a handkerchief or tissue when sneezing or coughing. If you do not have one, sneeze or cough into your elbow.
- Avoid touching your eyes, nose and mouth
- Clean and disinfect surfaces and objects.
- During an outbreak, stay home. If you need to go out put on the right face mask
- During an outbreak, keep social distance of about 2 metres from other people
- If you feel sick, tell your parents or guardians. You will be taken to see a doctor. You will be put on treatment.
Living Things - Grade 5 Science and Technology Revision Notes
Plants
Classification of plants
- Plants are living things
- Classifications - is the act or the process of dividing plants in groups, according to the given features.
- In grade 5 plants are groups into two categories which include
- Flowering plants – these are plants that produce flowers for examples maize, pawpaw and beans.
- Non – flowering plants - these are plants that do not produce flowers for examples mosses, fern and algae.
Safety precautions when handling harmful plants
Precautions – are measures taken in advance to prevent harm to the learners when carrying out different
activities. They include
- Wearing protective cloths
- Washing hands after handling plants
- Not eating or tasting or smelling poisonous plants
Importance of flowering plants
- Flowering plants are very useful
- They give food
- They give shelter
- They give medicine
- They add beauty to the environment
Fungi
- They are neither plants nor animals
- They grow on dead and decaying plants and obtain their food from them
- They include bread mould, yeast and mushroom
- The black or green patches on the slice of bread are called mould
- Fungi grow on soil and water. They also grow on decaying food or rotting plants,
Safety precautions when handling fungi.
- Precautions – these are measures taken in advance to prevent harm to the learners when carrying out
different activities. They include;- Wearing protective gears
- Washing hands after handling plants
- No eating or tasting or smelling poisonous plants
Importance of fungi to human beings
- Fungi are useful.
- Some fungi are used as food e.g. Mushrooms
- Some fungi are used in the process of cooking e.g yeast. It is used in the baking industries .
- Some fungi are used in making medicines
- Some are use in the processing some beverages e.g in fermenting milk
Economic importance of fungi to the environment.
- It’s a source of food
- Yeast used in baking
- Pesticides used in controlling insect and pest
- Mushrooms farming is both for food and for export
Animals
Vertebrates
- Animals are divided into two groups, vertebrates and invertebrates
- Vertebrates have vertebral column also called backbone. The backbone runs from the skull, joining the upper limbs and the ribcage to the lower limbs
- There are 5 classes of animals in the vertebrates groups
- Mammals
- Birds
- Fish
- Reptiles
- Amphibians
- Mammals and birds are warm blooded, meaning their body temperatures are constant
- Fish and reptiles and amphibians are cold blooded meaning their body temperature changes according to the surrounding
Characteristics of mammals
- They have memory glands
- They range in different sizes
- They have backbones
- They give birth to young on while other lay eggs e. the duck bill platypus and spiny ant eater.
- They live in land
- Body covered with far or hairs
- They are warm blooded
Characteristics of birds
- These are animals with have feathers and can fly, however some do not fly e.g ostrich which can just run fast.
- They have the following characteristics
- They are warm blooded
- They have backbone
- Body covered with feathers
- Birds lay eggs
- They have wings
Characteristics of fish
- These are animals which live in water
- They have backbones
- They live in water
- They are cold blooded
- They breathe through gills
- Move by swimming
- Their bodies are covered with scales
Characteristics of reptiles
- They have backbones
- They are cold blooded
- Their bodies are covered with scales
- They breathe through lungs
- Most reptiles lay eggs
Characteristics of Amphibians
- These are animals that spend their lives in water and on land
- They have the following characteristics;
- They have backbones
- They have moist skins
- Live partly in water and partly on land
- They breathe through gills when young and through lungs when mature
- They are cold blooded
- Most amphibians lay eggs