Musya
People And Population - Class 8 Social Studies Revision Notes
- Theory of Human Origin
- Migration
- Settlement
- Horticultural Farming
- Fishing in Kenya
- Mining
- Forestry
- Wildlife And Tourism
- Industry
Theories of Human Origin
- Mythical Theory
- Theory of Creation
- Theory of Evolution
-
Mythical theory
- It is based on folktales told by various communities on how they originated.
Examples- Luo - Claim to be descendants of their ancestor Ramogi who lived on Ramogi hill.
- Kalenjin - Claim to be descendants of the first Orkoiyot ( medicine man) called Miot.
- Wagiriama - Claim their ancestors lived at a place called Muyeye in Malindi.They dispersed from Muyeye and formed the nine (9) sub tribes as they migrated.
- Agikuyu - Claim to have descended from Gikuyuand Mumbi Who lived at Mukurwe wa Nagathanga.
- Baganda - Claim to be descendants of Kintu who lived on Mt Elgon.
- It is based on folktales told by various communities on how they originated.
-
The Creation Theory
- It is based on Religious beliefs.
- It explains that all human beings and other creatures were created by a super natural creator, God among the Christians and Allah among the Muslims.
-
The Evolution Theory
- This is a scientific view which explains that human beings developed slowly ( evolved ) from primitive ape – like creature to what they are today. This view was first suggested by a scientist called Charles Darwin.
- Archaeology is the study of human evolution.
- To understand the evolution of man archaeologists study:-
- Tools
- Plants and animal remains (Fossils) of early creatures.
Study of Human Evolution
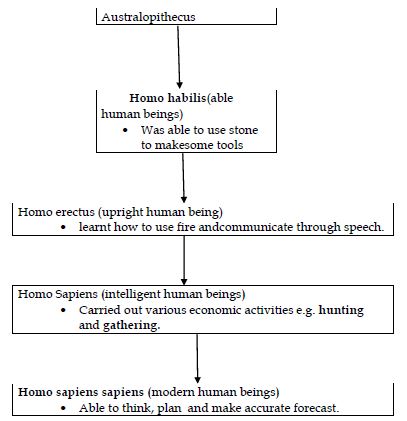
- The earliest known human-like creature was called Australopithecus.
- The period between the timeof Homo habillis and the time of Homo Sapiens is referred to as the stone age because the creatures mainly used stone tools.
- These creatures practiced the following activities:-
- Hunting and fishing.
- Gathering roots and wild berries for food.
- Painting and making ornaments.
Note
Stone age is divided into three stages:-
- Early stoneage.
- Middle stone age.
- Late stone age.
Stone age
manWhere they were found. Homo habilis
Homo erectusOlduvai Gorge.
Near Lake Turkana.
Olorgesaille in Kenya
Hadar in Ethiopia
North West shores of Lake Turkana
Isimilia in Tanzania.Homo sapiens Ngaloba in Tanzania.
Eliye springs west of Lake Turkana.
Bodo in Ethiopia.
Kanjera in Kenya.
Omo valley in Ethiopia.
Migration
- Migration is the movement of people from one place to another.
- Migration within a country is called Internal migration.
- Migration from one country to another is known as external migration.
Types of Modern Migration
- The four main types of Migration taking place in Kenya are:-
- Rural – urban migration.
- Urban – Rural migration.
- Rural – Rural migration
- Urban – Urban migration
-
Rural – Urban migration
- This is the movement of people from rural areas to urban areas.
Reason:- Search for employment.
- Shortage of farming land in some rural areas.
- Opportunity to engage actively in trading activities.
- Availability of better recreational facilities and good infrastructure.
- This is the movement of people from rural areas to urban areas.
-
Urban – Rural migration
- This is the movement of people from urban centers to rural centers.
Reasons- Retirement from employment.
- Overcrowding and high cost of living.
- Difficulties experienced in towns.
- This is the movement of people from urban centers to rural centers.
-
Rural – Rural migration
- This is the movement of people from one rural area to another.
- Note: Most rural – rural migrations are permanent especially in cases of movement to settlement schemes.
Reasons- Resettlement of people displaced by the construction of big dams which form lakes.
- Establishment of settlement schemes (irrigation schemes) which attract many people from other densely populated rural areas.
- Settlement of landless people by government .
- Seasonal migrations by nomadic pastoralists in search of pasture andwater.
- Search of employment in large plantations.
- Mining activities which may force people to move away from their original homes.
- Government actions which may force people to move away from areas where they had settled in order to conserve the environment e.g. Mau water catchment forest.
- Political unrest which may cause people to relocate from one place to another (IDPs Internally displaced persons)
- Natural disasters e.g Floods which may force people to move temporarily to safer higher grounds.
-
Urban – Urban migrations
- This is the movement of people from one urban center to another.
- Note: These migrations occur in a small scale .
Reasons- Job transfers from one town to another.
- Opportunities for business people to expand their businesses in bigger towns.
- Religious pilgrimages which may result in people settling down in the towns they visit.
Effects of Migration
Effects on urban areas
- Unemployment.
- Increase in crime.
- Increase in Immorality. Eg. - prostitution, HIV / AIDS and STIs
- Development of poor housing - slums (shanties)
- Competition (strains) for social amenities eg. Hospitals , schools etc.
- Overcrowding
- Environmental problems e.g. air pollution and water pollution.
- Increase in labour supply.
Effects on rural areas:
- Reduced pressure on land.
- Shortage of labour (negatively affecting agriculture).
- Improved economic conditions (reduction in production).
- Reversal of roles.
- Improved agricultural production (introduction of new farming methods).
NOTE:
Immigration: Is the migration of people from one country into another.
Emigration: Is the migration of people out of a country.
Positive effects of immigration
- Foreign investments which offer employment opportunities.
Negative effects of immigration
- Influx of people from war-torn countries encourages the movement of illegal arms into the countries which are used by criminals
- Refugees in our country affects the environment as they clear forests for firewood.
- The foreign cultures of these people end up affecting our cultures negatively.
Settlement
Settler Farming in Kenya
- Europeans settler farming was practiced in the white highlands(crown lands)
Examples:
| Region | Area covered. |
| Central highlands | Kiambu, Thika, Murang'a, Nyandarua, Nyeri, Kirinyaga. |
| Western highlands. | Kericho, Bureti, Sotik, Nyamira, Uasin Gishu, Kisii. |
| Central rift valley | Nakuru, Laikipia, Narok, Kajiado, Molo, Naivasha, Koibatek(Eldama Ravine). |
| Eastern | Meru , Konza, Embu, Machakos |
NB: The colonial government took away large areas of African land and allocated it to the white settlers.
Europeans settler farming in Kenya.
- The European settlers farming took African land.
- They mostly practiced large scale farming.
- They introduced cash crop farming and new livestock breed.
- Their farming methods were mechanized: they used commercial fertilizers and applied pesticides to crops.
- Africans were used as the source of labour on the settlers farms.
- rotation on their farms and divided ranching area into paddocks which helped.
- They practiced crop to control grazing.
What the settlers farmers were engaged in?
- Mixed farming (growing of crops and keeping of livestocks).
- Plantation farming (growing crops in a large scale farm). i.e. sisal, tea, coffee, wheat, maize, pyrethrum, cotton, sugarcane.
- Dairy farming, animal kept were: hare ford, Aberdeen angus, chorales, Galloway.
- Horticulture.
- Fruits grown : oranges, limes, lemons, pineapples.
- Vegetables grown:onions, carrots, tomatoes, legumes,cabbages.
- Poultry farming-chicken breed kept were; rhode island red, white leghorn light Sussex among others.
Effects of Settler Farming in Kenya
| Positive effects | Negative effects |
|
|
Settlement Schemes
Areas of settlement include:
Sotik,Endebes,Kaptagat,Matunda,Machakos,Lake,Kenyatta,Molo,Ainamoi Kitobo,Naitiri,Cherengany,Songhor/MuhoroniEldama Ravine,Chepsiri etc
Reasons for the establishment of settlement schemes in Kenya
- To settle the landless people.
- To ease congestion in the already populated areas.
- To make land ownership in Kenya fair.
- To encourage people to practice commercial farming in areas that had been occupied by settler farmers.
- To increase food production in Kenya.
- To speed up land ownership in Kenya.
- To open up areas which had not been settled in.
Benefits of settlement schemes
- Increased food and cash production in the country.
- Provision of of land to the landless (squatters)
- It has reduced congestion on land that had high population densities.
- It has helped to raise the living standards of the people.
- Agricultural exports from various settlement schemes has helped to boost the economy of our country.
- It has helped to open up the areas that had not be settled in.
Problems facing settlement schemes in Kenya
- Lack of adequate capital to invest in improved farming practices.
- Congestion in some parts of the settlement schemes due to population increase.
- Reduction in the size of land due to land fragmentation.
- People cut down trees to create room for crop growing and settlement (De-forest ration)
- Over cultivation in densely populated schemes has led to loss of soil fertility
- Poor transport network in the settlement schemes.
- Lack of adequate markets for the farm produce.
Irrigation Schemes in Kenya
Irrigation refers to the application water to crops through artificial means in
order to facilitate their growth.
Example
| MweaTebere | Perkerra |
|
|
Mwea Tebere Irrigation Schemes
- Established ii 1954. (It is the oldest in the county)
- Mainly started to settle the landless who lost their lands to the white settlers.
- Located in Kirinyaga county.
- It is the largest irrigation scheme in Kenya.
- Main crop grown is Rice.
- Sources of water for irrigation are:- River Nyamindi,River Thiba: Both are tributaries of R. Tana.
- Methods of irrigation used is Basin irrigation which involves flooding the rice plot(rice paddies)
- Canals are used to direct water from the rivers to the shallow basins
- Water flows into the basin through gravitational flow.
Perkerra Irrigation Scheme
- Located in Marigat, Baringo county.
- Mainly started to put more land under cultivation.
- Sources of water include:- River Perkera and Lake Baringo
- Methods of irrigation used isFurrow method.
- Furrows carry water from main canal to the crops which grow on the ridges
Sluice gates are used to control or regulate the flow of water into the farm.
Contributions of the scheme to the economy
| Mwea Tebere | Perkerra |
|
Note: Main problem is reduction of water into the plot during the |
Problems facing irrigation farming in Kenya
- Shortage of water during dry season.
- Siltation of the canals which reduces the amount of water that can flow to them.
- Late and irregular payments to the farmers from the irrigation board.
- Presence of weed.
- Some irrigation schemes are affected by floods during rainy seasons in places like Bunyala.
- Stagnant water is a health hazard eg. Spread of malariaand bilharzias.
- Lack of adequate capital.
- Mismanagement of finances and resources.
- Some irrigation schemes are far from the market which increases transport costs.
- Competition from imported, cheap farm produce.
- Presence of crop diseases and pests.
Horticultural Farming
- Horticulture - Is the growing of vegetables, fruits and flowers for sale.
- Viticulture - Growing of fruits only.
- Floriculture - Growing of flowers only.
Horticultural Crops Development Authority (HCDA) is a body established by the government to promote horticulture (market gardening)
The HCDA :-
- Advices the farmers.
- Provides storage facilities.
- Searches for external marks for products.
Crops grown in horticulture farming
| Flowers | Carnations , roses , lilies , orchids. |
| Fruits | Oranges, lemons, apricot, paw paws, grapes, limes, avocados, tangerines, passion fruits, peaches, apples, pears, plums, loquats, bananas, watermelons, strawberries. |
| Vegetables | Cabbages, spinach, lentils, spruce, sprouts, broccoli, peas, French beans, cauliflower, carrots, turnips, groundnuts, tomatoes, cucumber, green peas, chilies, onion, lettuce. |
Contribution of horticultural farming to the economy of Kenya
- Earning of foreign exchange.
- Creation of employment opportunities.
- Farmers earn regular income.
- Development of infrastructure.
- Availability of food.
- Crops provide raw materials for fruit and vegetable canning.
- Better use of land.
Problems facing horticultural farming in Kenya
- Bad weather.
- Poor infrastructure.
- High fees charged to farmers who export their farm produce (high tarrifs)
- High transport costs.
- High cost of farm inputs e.g. fertilizers, insecticides and pesticides.
- Lack of storage.
- Restrictions by importance
- Competition from other producers e.g. Netherlands.
- Inadequate capital to purchase farm equipment and inputs.
- Lack of co-operatives.
- Low export demand
- Poor marketing.
Horticultural farming in Kenya and Netherlands
| KENYA | NETHERLANDS |
| Most farmers are located near towns | Most farms are established on reclaimed land. |
| Most farms are small scale apart from the flower farms | Almost all the horticultural farms are large scale. |
| Poor means of infrastructure | Modernized infrastructure |
| Kenya is far from European market | Netherlands is centrally located in Europe. |
| Lack of adequate capital to promote horticultural farming | Adequate capital to scientifically manage the horticultural farms. |
| Fertile volcanic soils that are favorable for crop growing. | Sandy coastal soils are used as they drain well. |
| Little mechanization in the farms | Highly mechanized farms. |
| Labor intensive. | Capital intensive. |
| Horticultural technology is relatively new | World`s most successful horticultural producing country. |
Fishing in Kenya
- Fishing is the practice of removing or harvesting fish from water.
- Fishing is a major economic activity for those people living next to rivers , lakes or oceans which have fish.
Major fishing grounds in Kenya
Fishing grounds are places where fish are caught.
Groups of fishing grounds
- Inland fishing grounds.
- Marine / sea fishing grounds.
| INLAND FISHING GROUNDS | MARINE FISHING GROUNDS |
| Lake Turkana | Lamu |
| L. Baringo | Kiunga |
| L. Victoria | Malindi |
| L. Naivasha | Mombasa |
| L. Jipe | Kilifi |
| L. Chala | Ukunda |
| L. Masinga | Shimoni |
| Kiambere dam | Kipini |
Note:
Inland fishing is also carried out in big rivers such as:-
R. Tana,R.Sondu-Miriu,R. Yala,R.Nzoia,R. Nyando,R.Kuja.
Fish farming is the raring of fish in fish ponds and dams.
Areas where fish farming is carried out.
Sagana,Borabu,Bamburi near Mombasa,Aruba dam,Kiboswa
Types of fish caught
| Inland waters | Marine waters |
|
|
Problems facing fish farming
- Presence of predators e.g. snakes, birds, cats.
- Insufficient supply of water in ponds especially during the dry season.
- Limited market
- Presence of unwanted weeds e.g. water hyacinth in L. Victoria.
- Lack of adequate funds for most farmers.
- Use of traditional methods of harvesting.
- Inadequate refrigeration facilities.
Comparison of fish farming between Kenya and Japan
| Kenya | Japan |
| Lack of adequate capital. | There is adequate capital. |
| Most farmers use traditional methods of fishing and harvesting. | Fish farming is highly mechanized. |
| Limited market for the fish products | There is a large market for fish which encourages the industry |
| Insufficient supply of water e.g. during the dry season | Enough supply of water through out the year. |
| Fish is mainly consumed locally | Fishing is done mainly for export. |
Mining
Mining is the removal (extraction) of a mineral from where it has naturally been formed.
The main minerals in Kenya include
- Soda ash
- Gemstones
- Diatomite
- Flourspar
- Sand
- Salt
- Limestone
- Marble
| Mineral | Where mined | Uses |
| Fluorspar Method of mining: Open cast (Quarrying) |
|
|
| Limestone. Method of mining Open cast (quarrying) |
|
|
| Diatomite. Method of mining Open cast (quarrying) |
|
|
|
Gemstone. Method of mining: |
|
|
|
Marble Method of mining: |
|
|
| Salt. |
|
|
Contribution of minerals to the economy of Kenya
- Mineral exports earn Kenya foreign exchange.
- Mining is a source of employment to many people.
- It has led to the growth of towns e.g. Magadi.
- It has led to the establishment of industries that use minerals as their raw materials.
- Availability of minerals saves the country`s foreign exchange that could have been used to import them.
- Mining has led to the development of social services like schools , hospitals and sports facilities in the mining areas.
- Mining is a source of revenue to the government since the mining companies pay taxes to the government.
- It has led to the development of transport links of infrastructure.
- Mining has led to the improvement of the standards of living of people working in the mines and mineral – related industries.
Effects of mining on the environment
- Pollution of the environment.
- Land degradation.
- Destruction of vegetation during the mining process.
- Clearing of vegetation during mining leads to soil erosion.
- Open pits filled with water are a health hazards to people and animals.
- Release of harmful gases in the air may result to global warming.
- Walls of mines sometimes collapse and cause accidents to miners.
Forestry
- Forestry is the practice of establishing forests and caring for trees.
- It also involves paper harvesting and good use of trees.
Types of Forests in Kenya
There are two main types of forests found in Kenya. These are:
- Natural forests.
- Planted forests.
-
Natural forests
This are forests which have grown on their own.
They are divided as follows:- Highland rain forests.
- They grow in the high rainfall areas e.g.Slopes of mountains, Hills and highlands
Examples
Kakamega,Nyambane,Ndare,Kaimosi,Mt.Kenya,Timboroa,Nyandarua,Mau, Malava,Mt.Marsabit,Ngong hills,Mt. Elgon,Ndaragwa.
- They grow in the high rainfall areas e.g.Slopes of mountains, Hills and highlands
- Lowland rain forest.
- Found in high rainfall areas of the coast.
Examples:
Witu,Jilore,Gongeni,Boni,Arabuko – Sokoke
- Found in high rainfall areas of the coast.
- Mangrove forest
- They grow in salty waters of the Indian ocean.
- They grow along the coast in: Kwale,Kilifi,Lamu,Malindi
- Highland rain forests.
-
Planted forest
- They have been established through efforts of human beings.
- They are found in high rainfall areas where afforestration programs are being carried out.
- These forests are found in the following areas:
- Slopes of Mt. Kenya around Meru and Embu.
- Cherengani hills
- Limuru
- Elburgon
- Timboroa
- Molo
- Turbo
- Slopes of Mt Elgon
- Lari
- Njabini
- Kaptagat
- Londiani
- Moi`s bridge
- Nandi hills
Types of trees found in planted and natural forests
| Natural forest | Planted forest |
|
|
|
|
Problems Facing Forests in Kenya
- Attacks by pests and diseases which affects their rate of growth.
- Outbreaks of fires especially during the dry season.
- Deforestration due to increased demand for land for farming and settlement.
- Increased demand for forest product e.g. timber and pulp.
- Need for charcoal and firewood.
- Poor reafforestration programs.
Effects of Deforestration in Kenya
Deforestration is the cutting down of forest trees faster than they are replaced
through reafforestration.
Effects
- Deforestration affects the sources of water leading to reduced water supply.
- Cutting down of trees leads to spread of the desert.
- Reduction in forest production.
- Increase soil erosion.
- Loss of the species
- Rural communities are affected since some of them use forest products for their survival.
- Change in climate.
Forest Conservation Measures in Kenya
Forest conservation is the careful harvesting and good use of trees found in
the forest.
Conservation measures includes:
- Establishment of tree nurseries.
- Gazzetement of forest reserves by the government to protect the forests.
- Organizing and supporting tree planting activities (afforestration).
- Encouragement by the government for the public to undertake replanting activities.
- Discouraging the use of charcoal.
- Growing of trees alongside crops in the farm (Agro-forestry).
- Informing the public on the importance of trees and the and the need to plant more trees on their farms (awareness campaigns).
- Establishment of environmental clubs in schools.
- Banning tree activities.
Wildlife and Tourism
Wildlife refers to plants , birds and animals in their natural environment. (habitat).
Tourism is the travelling to other places of interest for pleasure.
Importance of wildlife
- Earns the country foreign exchange from tourists who visit the country.
- Creates jobs for many people who work in game parks, game researves ,and tourist hotels.
- Leads to economic growth of the areas they are found.
- Promotes development of local industries e.g. stone and wood curving which are mainly bought by tourists.
- Wildlife is an important national heritage.
Tourists attraction in Kenya and Switzerland
Similarities between Kenya and Switzerland
- Both countries have beautiful sceneries.
- Both countries have a rich cultural heritage which is a major tourist attraction.
- Both have good accommodation facilities for the tourists e.g. hotels.
- Both countries enjoy relative peace.
- Both countries have game parks.
Differences between Kenya and Switzerland
- Wildlife is the main tourist attraction in Kenya while Beautiful scenery is the main tourist attraction in Switzerland.
- Tourists are attracted by the warm climate ion Kenya while in Switzerland tourists are attracted by the summer and winter seasons.
- Transport and communication is highly developed in Switzerland and thus attracts tourists. In Kenya, The transport and communication is NOT highly developed.
Industries
An industry is a place where raw materials are changed from one form to another ,processed and assembled.
Types of industries
- Processing industries.
- Manufacturing industry
- Assembly industries
- Service industries.
- Processing industries
- They are also called primary industries.
- Involved in the first stage of changing raw materials from one form to another.
- Examples in Kenya : Maize, milk, fish processing etc.
- Manufacturing industries
- They are also known as Secondary industries.
- They use raw materials to make final products.
- Examples:
- Sugar from a processing industry taken to another factory to make sweets, bread or soft drinks.
- Steel rolling milk
- Glass making industry
- Insecticide industry
- Medicine making
- Cement factories
- Textile industry
- Shoe factories
- Oil refineries.
- Assembly industries
- They are also known as secondary industry.
- They put together parts that have been produced elsewhere to make new products.
- Examples include:-
- Vehicles
- Radios
- Bicycles
- Televisions etc.
- Service industry
- They are also known as tertiary industries.
- They provide services that other people and other industries need.
- Examples includes:
- Transport and communication.
- Banking
- Insurance
- Repair work
- Printing etc.
Factors Influencing Location of Industries
- Availability of raw materials.
- Availability of capital(money to start a business).
- Availability of good means of transport and communication.
- Availability of power (electricity).
- Availability of regular water supply.
- Availability of ready market.
- Government policy of location of industry.
- Availability of land.
- Personal consideration.
- Security.
- Presence of other industries.
Jua Kali Industries
- These industries are also known as cottage or fabrication industries
- It involves making simple items in the open air or under simple shade.
- They use scrap metals to fabricate different types of cheap products.
- Items made include:
- Jikos
- Jembes
- Pans
- Wheelbarrows.
- Boxes etc.
Reasons for establishment for Juakali industries in Kenya
- To create self employment opportunities.
- Products from Jua kali industries are cheap as compared to those made in manufacturing industries.
- The sale of the jua kali products earns the people income
Jua kali industries require little space to house workers. - Some Jua kali industries do not require electricity.
- ua kali industries help in cleaning up the environment as they use heap of scrap metals.
Benefits of Jua kali industries
- Creation of employment opportunities.
- Use of waste iron materials helps in recycling wastes.
- They produce many goods that are widely used in homes and schools.
- Jua kali products are cheap and long lasting.
- Jua kali helps in improving the living standards of people working in the Jua kali industry (sector)
- Jua kali is foreign exchange earner.
- The use of recycled materials helps in controlling environmental pollution.
- Jua kali reduces rural – urban migration as youths in the rural areas get employment in their rural areas.
Problems Facing Jua Kali Industries
- Inadequate space: This leads to interruption of their work.
- Competition from manufactured goods.
- Inadequate capital (cash to start and maintain the business)
- High cost of raw materials.
- Poor working conditions.
- Inadequate supply of water and electricity.
- Limited market for the products.
Contribution of Industries to The Economy of Kenya
- Creation of jobs(employment opportunities)
- Earning of income by the people.
- Earning of foreign exchange.
Making use of local resources(raw materials) - Saving on foreign exchange.
- Making it possible to have increased trade locally and with other countries.
- Promotion of agriculture due to increased demand of raw materials.
- Availability of goods.
- Growth of urban centers.
- Development of infrastructure e.g. roads.
- Increased skills by the people employed in industries.
- Encourages countries to join regional blocks.This enhances internationalrelations.
- Self sufficiency.
Physical Environment - Class 8 Social Studies Revision Notes
- Physical Environment
- Map Reading And Intepretation
- Physical Features
- Climate
- Soil
Physical Environment
What is Environment?
The things around us or in our surrounding make up the environment.
Examples
- Trees
- Animals
- Water etc.
- Grass
- Rivers
- Buildings
- Birds
Types of Environment
- Natural environment
These were things that were made by God. E.g Mountains ,Lakes, Rivers, Vegetation etc. - Human environment
These are things made through man`s efforts e.g Dams, buildings, roads, etc. - Physical environment
The non – living part of the environment which consists of Soils, air, rocks, water, hills, mountains, rivers and lakes form the physical environment.
Map Reading And Interpretation.
A map is a drawing on a flat surface that represents a whole part of the earth.
Elements of a Map
Elements of a map helps a reader to understand the information on a given
map.
The main element of a map are:
- Title
- Key
- Compress
- Frame
- Scales
Uses of Elements of a Map
| ELEMENT | USE(S) |
| Title | It is the name of the area represented by the map and the information it contains. |
| Frame | It shows the extent of the area represented by a map. It is also known as the borderline of a map. |
| Key | It contains the signs or the symbols which represents various features represented in a map. |
| Compass Direction |
Helps to find direction of a position or features in relation to others |
| Scale | Helps the map reader to know the actual distance on the earth`s surface as reprtesented on the map |
Map Reading
This is the ability to read, understand, and interpret information given on a
map.
Symbols of a map contained in the key should be fully understood and
interpreted correctly.
Features That Can be Interpreted From a Map
- Relief and drainage patterns in the area.
- Human and economic activities in the area.
- Types of climate experienced in the area.
- Transport facilities in the area.
- Vegetation found in the area.
- Human settlement pattern in the area.
- Administrative boundaries in the area.
- Social activities (services) found in the area.
Human Activities Commonly Found in a Map
Economic activities are the objectives that people carry out in order to get
income (money).
Examples
| Economic activity |
Evidence |
| Crop farming | Crops e.g coffee, tea, sisal, sugarcane, cotton, pyrethrum, wheat and cotton ginneries, factories, plantations, mills. |
| Forestry | Presence of saw mill, timber yard, forest guard, posts. |
| Livestock farming | Presence of cattle dips, butcheries, slaughter houses, cattle boma, dairy farms, creamery, veterinary offices, ranches, beef factories, trough. |
| Tourism | Presence of national parks, game reserves, camping sites, picnic sites, hotels, lodges, museums, pre-historic sites. |
| Fishing | Presence of fish ponds, fishing villages, a fish factory, fish traps, fisheries departments. |
| Mining | Presence of quarry, symbols of mines, name of the mine like Salt mining works. |
| Trade | Presence of markets, shops, trade license office, trading centers, warehouses, stores, towns, custom offices |
| Industry | Manufacturing factories, bakeries, refineries, rolling mills, ginneries, saw mill. |
| Transport and communication |
Roads, railway lines, airports, airstrips, ports, post offices, telephone lines. |
Social Activities on a Map
- Religious activities : Churches, mosques, temples, shrines.
- Medical services : Clinics, dispensaries, health centers, district hospital, provincial hospitals and National hospitals.
- Education: Schools, colleges, polytechnics, universities.
- Recreation : Cinema halls, Social halls, play grounds, theatres.
Features on a Map That Represents Administration
- Government offices e.g. Assistant chief`s offices or chief`s camp.
- Police post.
- Administrative boundaries.
Features That Show Drainage Systems on a Map
| Drainage features | Interpretation |
| Boreholes and wells | Areas of low and unreliable rainfall. |
| Permanent rivers | Areas that receive high rainfall. |
| Seasonal rivers | Areas of low rainfall. |
| Waterfall | Areas of hard and soft rocks. |
| Many swamps | Clay soils, poorly drained areas. |
| Tributaries | Direction of the flow of the river |
Human Settlement on the Map
Settlement is the pattern of population distribution in an area shown by dots and black shades.
Types of Settlement
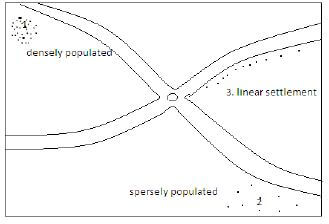
How to Identify the Functions of a Town on a Map
| Functions of the urban centre | Identification symbol |
| Administrative centre | Government offices, chief`s camp, law courts, police posts, prisons, administrative boundaries. |
| Commercial centres | Shops, markets, road functions, trading centers, towns, cities, warehouses, stores, trade licensing offices. |
| Social centres | Schools, colleges, mosque, churches, theatres, sports, grounds, hospitals, cinema halls. |
| Mining centres | Mining works, quarries, named mines. |
| Agricultural centres | Food stores, Large estates, or plantations, processing factories, dairy, creameries, cattle ranches, cattle dips, dairy farm. |
Physical Features
These are things we see on the surface of the earth. They include natural physical features and man-made(human)
Natural features: Mountains, plateaus, hills, plains, valleys, rivers, lakes, etc.
Man-made: dams, lakes etc.
The Effects of Physical Features on Human Activities
| Physical features | Human activities | |
| Lakes, oceans, rivers |
|
|
| Ocean, lakes | ||
| Snow capped mountains |
|
|
| Rift valley | ||
| Beautiful water falls | ||
| Sand beaches | ||
| Hot springs | ||
| Homa hills(limestone) |
|
|
| Lake Magadi(Soda ash) |
|
|
| Indian ocean(salt) |
|
|
Negative Effects of Physical Features
- Flooding.
- Water borne diseases e.g. Malaria and Bilharzia.
Climate
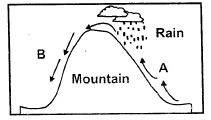
Traditional Methods of Observing Weather
- Observing the sky
- Thick grey clouds: rain.
- Certain stars arranged in a particular manner: dry spell.
- Phases of the moon
- New moon: rain.
- Full moon: It would rarely rain.
- Appearance of the rainbow
- Some communities believed that it would not rain if the rainbow appears in the sky when it was about to ran
- Condition of the environment
- Very hot and humid: Coming of the rain.
- Blowing of wind
- Strong winds blowing after a dry weather: Showed the coming of the rains
- Wind blowing during the rainy season: Meant chasing away of the rain to give way to a dry spell.
- Behavior of birds:
- Happy and playful birds in the sky would signify the coming of rains.
- Trail of ants: Signified the coming of rains.
- Croaking of frogs: Signified the coming of the rain.
- Appearance of toads: Signified the coming of the rains.
- Behavior of cattle: Coming of the rains(showing happiness by jumping up and down)
- Shedding of leaves after a rainy season: This Signified a dry spell.
Observation, Measurement and Recording of Weather Elements
What is meteorology?
It is the science of observing and measuring weather elements.
-
Wind
-
Air Pressure
-
Rainfall
The raingauge is dug into the ground as shown above. -
Temperature
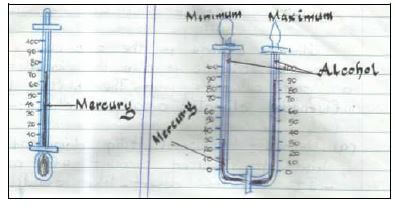
- Minimum and maximum thermometer
Used to measure temperature for the day.
It is U-shaped.
Minimum records coldest temperature.
Maximum records warmest temperatures. - Single-tube thermometer
Used to measure coldness and / or hotness of the air.
It is marked in o Celsius.
It may contain alcohol or mercury.
- Minimum and maximum thermometer
Factors Influencing Climate Change
Climate change is the occurrence of unexpected change of climatic condition in a particular region. The main factors influencing climate change include:-
- Deforestation
Cutting down of trees leads to reduced amount of rainfall.
It creates desert – like conditions in the areas previously occupied by forests.
It contributes to increased carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. - Afforestration and re-afforestration
Planting of more trees will increase the amount of rainfall.
Both afforestration and re-afforestration reduce soil erosion and evaporation, hence protecting water catchment areas. - Industrialization
Heat and smoke from industries cause pollution and increase temperature in the atmosphere. - Excess use of chemicals
Such as fertilizers causes atmospheric change due to the gasses they produce.
The growing of rice under irrigation contributes to warming of the atmosphere. The rice in water release a gas known as methane, which
contributes to global warming. The same applies to the use of fertilizers.
Global warming is also caused by the use of petroleum to run vehicles .Machines give off a gas known as carbon monoxide, which makes
the air warmer. - Clearing of vegetation for agriculture
This exposes the soil to agents of soil erosion. - Building of dams
Human-made lakes which form behind the dam modify the climate. - Ocean currents
These leads to temperature change along the coastal areas.
Impact of Climate Change on Human Activities
Positive effects
- Increase in food production due to increased amount of rainfall
- Increased generation of hidro-electric power due to high rainfall.
- Promotion of fishing due to adequate water in rivers.
Negative effects
- Low agricultural production due to lack of rains.
- Displacement of people due to floods.
- Global warming as a result of general increase in temperature worldwide.
- Increase of water-borne diseases such as malaria and bilharzias due to increased rains.
- Damage of transport systems e.g. roads.
- Migration of people migration of people to favourable climate.
- Death of human beings.
Soil
Soil is formed through a process called weathering. Soil contains:
- Organic matter
- Rock particles
- Humus
- Air
- Minerals
- Water
- Living organisms
Major Soil Types in Kenya
- Volcanic soils.
- Clay (black cotton) soil.
- Sandy soil.
- Loamy soil.
- Alluvial (young) soil.
Characteristics of Types of Soil
Volcanic Soil
- Red in colour.
- Deep fertile and well-drained.
- Occur in layers.
- Medium – sized soil particles.
- Mainly found in the highlands.
Clay( Black Cotton) Soil
- Small – sized particles.
- Dark in colour
- Deep and fertile
- Poorly drained.
- Muddy and sticky during the rainy season.
- Big cracks during dry seasons.
Sandy Soil
- Large soil particles.
- Shallow and dry.
- Contains a lot of air.
- Water seeps through them fast.
- Low water retention capacity.
- Loose nutrients mainly through leaching.
Loamy Soil
- It has a mixture of small, medium and large soil particles.
- It retains a reasonable amount of water fertile, deep and well drained.
- Appears in different colours e.g. light grey, dark brown and dark grey.
Alluvial (Young) Soil
- They are found in river valleys and flood plains.
- They are made of slits.
- Soil particles are of medium size.
- Have a smooth texture.
- They are deep and fertile.
Major Causes of Soil Erosion
Soil erosion is the natural displacement of soil from the original place of formation to another by agents of erosion like wind, water and human beings.
The major causes of soil erosion are as follows:
- Deforestation- Cutting down of trees which exposes the soil to agents of soil erosion.
- Overstocking- Keeping large herds of livestock beyond the capacity of land leading to overgrazing
- Overgrazing-Livestock grazing on all pasture (vegetation) leaving the ground bare.
- Monocropping-Growing of one type of crop on the same peace of land year after year exhausts soil fertility.
- Over-cropping-Growing of many different types of crops which compete for nutrients. The soil finally becomes loose and infertile
- Up-the-slope (hill) cultivation-This promotes gulley erosion.
- Mining and quarrying-Results to displacement of soil.
Effects of Soil Erosion on Human Activities
- Destocking (reducing the number of livestock on the farm)
- Application of fertilizers to the soil in order to increase its fertility.
- Introduction of afforestration and re-afforestrationprogrammes
- Promotion of agriculture in the flood plain where fertile soil (alluvial) is deposited.
- Adoption of good farming methods to reduce soil erosion.
- Additional expense to the government in building dams, dykes and canals.
Soil Conservation Measures
- Afforestration :
Planting of trees. - Re- afforestration:
Planting of trees where they had been cut down. - Agro-forestry:
Planting of trees together with crops. - Crop rotation:-
Growing of different crops on the same peace of land in alternate planting seasons. - Mulching: The covering of the bare ground with grass to prevent moisture loss.
- Cover cropping:
Planting of perennial crops like coffee and bananas together with food crops likepotatoes, beans and maize. - Construction of gabions:
Pilling up of stones in iron cages to prevent further movement of soil downhill. - Terracing:
Making of horizontal steps on sides of hilly areas. - Fallowing:
Leaving the land idle for some time in order to retain its fertility. - Creation of cut-off- drainage:
This is the digging of trenches to divert water from hill tops - Controlled grazing:
This is done by subdividing land into paddocks. - Use of fertilizers and manure:
This helps the soil to regain its fertility. - Contour ploughing:
This is ploughing of farm across the land guarded by the contours.
Social Studies and Religious Education - Class 8 End Term 1 Exam 2021 Set 2
STANDARD 8, END OF TERM 1
SOCIAL STUDIES AND RELIGIOUS EDUCATION
NAME....................................................SCHOOL...............................
SOCIAL STUDIES
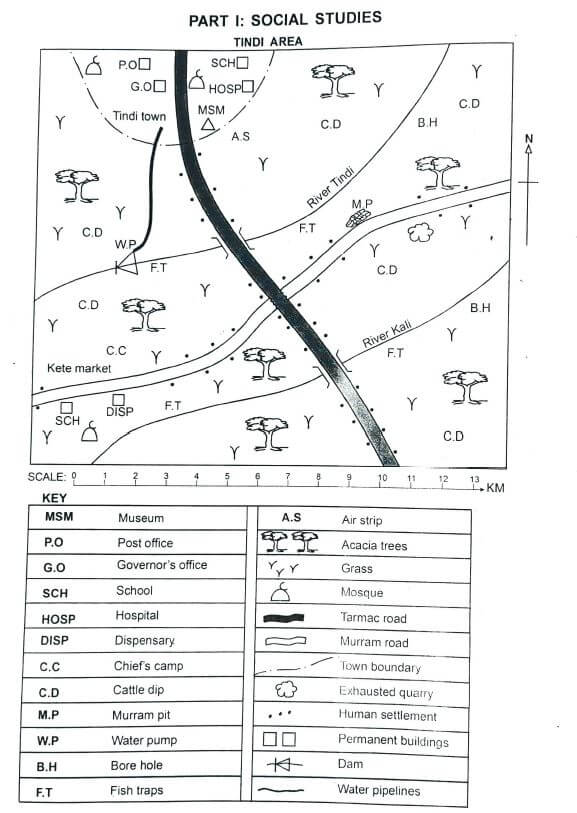
Study the map of TINDI area and wse it to answer questions 1 to 7.
- What is the approximate length of the tarmac road in Tindi area?
- 16 km
- 18 km
- 20 km
- 10 Km
- Human settlement in Tindi area is MAINLY influenced by
- drainage
- economic activities
- transport and communication
- pests and diseases
- The MAIN source water in Tindi area is
- Rivers Tindi and Kali
- the dam across River Tindi
- the borcholes
- water pans
- Which one of the following statements is NOT TRUE about Tindi town? It is
- a religious centre
- a tourist attraction centre
- an administration centre
- an agricultural collection centre
- The MAIN economic activity carried out in Tindi area is
- pastoralism
- fishing
- trading D
- mining
- The climate experienced in MOST parts of Tindi area is LIKELY to be
- hot and dry
- hot and wet
- cool and wel
- cool and dry
- The MOST widespread means of transport in Tindi area is
- waterways
- air
- road
- railway
- The MAIN factor that contributed to the rise of the kingdom of old Ghana was
- the strong Soninke army
- favoured climate that supported agriculture.
- mining activities especially walata mines.
- the Trans-saharan trade
- Which one of the following is LIKELY to be the least importance of marriage?
- Marriage helps to control the spread of HIV and AIDS.
- Marriage cnhanccs unity and cooperation in the society
- It provides an opportunity to have children and raise a family
- It encourages the development of a sense of responsibility in the society.
- The original homeland of the cushites was
- Congo forest
- Horn of Africa
- Bahr el Ghazal
- Pupungu pakwach
- Below are descriptions of an early visitor to Eastern Africa
He was Her majesty's consul for the East coast of Africa.
He navigared the Ruvuma River at the border of Tanzania and Mozambique
He met Herry Stanley in 1877 iv.
He died in Eastern Africa.
The early visitor to Eastern Africa described above is LIKELY to be- John Speke
- Henry Morton Stanley
- David Livingstone
- William Mackinnon
- Which one of the following plateaus is WRONGLY matched with the country where it is found?
- Jos Plateau - Nigeria
- Bie Plateau - Angola
- Yatta plateau - Kenya
- Fouta Djallon - Mauritania
- Which one of the following groups of communities belong to the Bantus of South Africa?
- Tsonga, Venda and Bakwena
- Bakongo, Balunda and Baluba
- Xhosa, Zulu and Sukuma
- Yao, Akamba and Nyamwezi
- Which one of the following is NOT a basic need?
- A home
- Drinking water
- Food
- Education
- Three of the following statements are TRUE about slash and burn agriculture. Which one is NOT?
- Land was used over and over again until it lost its fertility.
- Farmers practised crop rotation instead of plot rotation.
- It was a form of subsistence farming.
- Neighbours mostly produced the same types of crops.
- Which one of the following is a traditional industry?
- Bicycle assembling
- Iron smelting
- Maize milling
- The stock market
- Central Nigeria and Southern Tanzania had reduced population before the 20th century MAINLY due to
- poor drainage
- slave trade
- posts like tsc tsc flics
- unfavourable climate
- In order to communicate information to people over very long distances among traditional African communities in the past MAINLY people had to
- blow horns
- beat drums
- send messenger
- send smoke signals
- The BEST way of teaching a child to becomea traditional healer in the past was through
- observation and imitation
- story-telling
- apprenticeship
- medical colleges
- Three of the following statements are TRUE about Masaku of the Akamba. Which one is NOT? He
- was a great medicineman and a prophet.
- traded with Arabs and Coastal people.
- advised the Akamba to avoid forcigners.
- collaborated with the british colonialists.
- The Great rift valley was formed as a result of
- faulting and sinking
- volcanic activities.
- folding of sedimentary rocks
- faulting and uprifting.
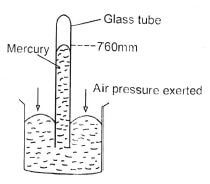
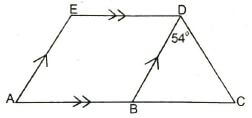
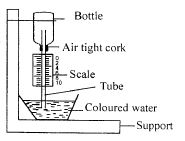
Use the diagram shown below to answer question 22
- The weather instrument shown above is referred to as
- mercury barometer
- A hygrometer
- An anemometer
- An ancroid barometer
- Which one of the following leads to lawlessness in the society
- security
- poverty
- job creation opportunities
- general elections
- Most people migrate into towns MAINLY due to
- availability of jobs in rural arcas
- better learning institutions in towns.
- lack of industries in rural areas.
- shortage of land in rural areas.
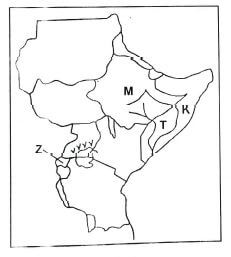
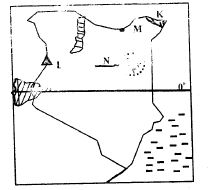
Use the map of Eastern Africa provided below to answer questions 25 to 28.
- The country marked Z is
- Uganda
- Burundi
- Djibouti
- Rwanda
- Three of the following communities are found in the country marked M. Which one is NOT?
- Amharas
- Oromo
- Falasha
- Sabaot
- The river marked K is likely to be
- Juba
- Shebelle
- White Nile
- Tana
- The MAIN crop that is grown in the area marked vvvvv is
- sugarcane
- maize
- bananas
- coffee
- Below are different types of fish
Barracuda
Herring
Trout
Mullet
Tuna
Which combination shows fresh water fish only?- i and ii
- i and v
- iv and v
- ii and iii
- The following are characteristics of a vegetation zone in Africa.
Trees have thorn and smooth barks
Trees shed leaves at different times of the year
Trees are tall and have a thick base.
Most of the plants have shallow roots.
The vegetation zone with the charateristic listed above is LIKELY to be- Tropical rainforest
- Tropical savannah
- Mediterran vegetation
- Mangrove vegetation
- Which one of the following is TRUE about wheat growing in Kenya?
- Wheat is mainly grown in Nakuru, Eldoret and Laikipia
- Kenya does not export wheat since she does not produce alot.
- Kenyan wheat is harvested using combined harvesters.
- In Kenya, the crop is grown on large scale and small scale.
- Three of the following minerals are obtained using the open-cast method. Which one is NOT?
- Soda ash
- Limestone
- Flourspar
- Diatomite
- In order to improve livestock breeds, beef farmers in Kenya and Tanzania are encouraged to practise
- group ranching
- overstocking
- in-breeding
- cross-breeding
- Which one of the following is NOT a contribution of the community in school development?
- Allowing the school to use its facilities such as fields
- Employing teachers to offer serveices to the school community.
- Feeding the school with learners and support staff.
- Providing resource persons to offer services to the school community. .
- What makes Nairobi which is near the equator cooler than Malindi which is far away from the Equator?
- Malindi has more industries than Nairobi
- Malindi receives convectional rainfall while Nairobi receives relief rainfall.
- Differences in altitude.
- Shape of the Kenyan coastline.
- Which one of the following is a similarity in the systems of government in both Kenya and Swiziland? In both countries
- civil servant implement government policies.
- political parties nominate members of parliament.
- the position of the commander-in-chief of the armed forces is hereditary.
- general elections are held after five years.
- River Ewaso Nyiro North drains its water in the
- Lake Turkana
- Indian Ocean
- Lake Victoria
- Lorian swamp
- Below were traditional methods of observing weather
A clear sky with many stars at night.
Appearance of flocks of sparrows in the sky
Presence of a full moon,
Sudden onset of high temperatures especially at night.
Smell of moist soil in the air. Which one of the following combinations showed the approach of rains?- ii, iv, v
- iii, iv, v
- i, ii, iv
- i, ii,
- Three of the following are methods of soil conservation. Which one is NOT?
- contour ploughing
- fallowin
- cultivating on steep slopes
- practising agroforestry in farms
- Ndeti, a standard eight boy on his way from school found two boys fighting. What action should he have taken?
- Report them at police station
- Call out for help from adults
- Mind his own business
- Separate the two boys.
- Three of the following are theories of human origin. Which one is NOT?
- Creation theory
- Evolution theory
- Mythical theory
- Kinetic theory
- Mwangi and Opiyo, two pupils at Masomo primary school learnt that their classmate, Mbaya has HIV and AIDS. What should they do about it?
- Tell all their classmates about Mbaya's condition
- Advise Mbaya to seck medical advice.
- Laugh at Mbaya
- Pray for Mbaya.
- The MOST effective way of protecting children from abuse is
- giving stiff punishments to child abusers
- educating the public on the right of children.
- providing counselling services to victims of abuse.
- Educating all children on their rights.
- The MAIN problem facing tourism in Kenya
- insecurity and terrorism
- culture clash
- poor infrastructur
- inadequate tourism facilities
- Which one of the following is NOT a problem facing the last Alan Community (LAC)?
- Ideological dillerences
- Lack of political will
- War in Sudan
- Labour disputes
- Below are contributions of prominent leader in Africa.
He abolished Sharia courts
He carried our land reforms
He nationalised the ownership of the Suez Canal
He was a founder member of the organisation of African Unity (OAU)
The contributions listed above were done by- Kwame Nkurumah
- Leopold Scdar Senghor
- Gamal Abdel Nasser
- Nelson Mandela
- Below are descriptions of a multi-purpose river project in Africa.
It is located at a gorge it.
It has the largest artificial lake in the world by water volume
It was completed in 1977
It was mainly constructed to provide hydo-electric power
The multi-purpose river project described above is LIKELY to be- "The volta River Scheme
- The Tana River River Projects
- Kariba Dam Project
- The Aswan High Dan
- Which system of administration did the British use in Northern Nigeri?
- Direct rule
- Indirect rule
- Assimilation
- Paternalism
- Horticultural produce in Kenya is transported to overseas markets through
- air
- roads
- the sea
- railways
- Who among the following are NOT members of the National Assembly in Kenya?
- 290 members elected directly during general elections.
- 12 members nominated by political parties.
- The speaker, who is an ex-officio member
- 16 women nominated by political parties.
- Which one of the following is a social right according to the Kenyan constitution?
- Right to work for a fair wage.
- Right to join a trade union
- Right to vote.
- Right to health care
- Ole Supeyo and Ole Kaelo are fighting over grazing land. The BEST way to resolve their conflict is through
- negotiation
- dialogue
- a mediator
- a court process
- A child of five years who is found in Kenya and whose parents are not known is taken to be a citizen by
- birth
- naturalisation
- registration
- dual-citizenship
- The MAIN factor that undermines national unity in Kenya is
- corruption
- religious differences
- tribalism
- unequal distribution of national resources
- Chief Mkwawa of the Hehe was defeated by the Germans MAINLY because
- the Germans were more organised than the Hehe people.
- the Hehe warriors were brave.
- the Germans had superior weapons.
- the Germany soldiers were more than the Hehe warriors.
- Which one of the following aspects of our culture need to be preserved?
- Wife inheritance
- Cultural heritage
- Female Genital Mutilation
- Cattle rustling
- The MAIN problem facing regional trade in Africa is
- political differences
- similarity of goods produced
- poor transport systems
- Quota system
- Mr.Lumumba, the Social studies teacher at Bidii primary school has found three pupils taking alcohol outside the school. The BEST thing that he should do is
- advise the people on dangers of alcohol abuse.
- beat the pupils immediately.
- report the matter to the headteacher.
- embarass the pupils in the presence of their schoolmates
- The MAIN duty of the police in Kenya is to
- arrest law breaker
- ensure safety on Kenyan roads
- interpret the law.
- maintain law and order.
- The highest court in Kenya is the
- High court
- Court of Appeal
- Supreme court
- Kadhi's court
PART II: RELIGIOUS EDUCATION
CHRISTIAN RELIGIOUS EDUCATION
- Which one of the following statements DOES NOT shows that human beings are special compared to other God's creation? Human beings:
- were created in God's likeness and image.
- named all animals and plants.
- were put in the garden of Eden.
- have dominion and power over God's creation.
- Which one of the following was the MAIN result of man's disobedience? Human beings
- A. were cursed by God.
- started dying.
- were made to work and sweat.
- were chased out of the garden of Eden.
- Which one of the following is the MAIN reason why Abraham is referred to as the father of faith? He
- was an old wise man.
- loved his son Isaac.
- lived with a barren wife.
- obeyed God.
- Which one of the following was the sign of the covenant made between Noah and God?
- Circumsion
- Cloud
- Rainbow
- Blood
- God asked Moses to apppoint Ohaliab and Bezalel to help him in the building of covenant box. Which one of the following abilities did he lack?
- Healing
- Weaving
- Embroidery
- Engraving
- The MAIN reason why God called Moses was to?
- Perform miracles before Pharaoh.
- Lead Israelites out of their suffering.
- Teach the Israelites about God.
- Choose the person who was to lead the Israelites.
- Which one of the following actions was carried out by Moses at Mt. Sinai?
- Getting water from the stone.
- Building an alter
- Feeding people with manna
- Performing miracles.
- According to Judges 7:20. Which one of the following was NOT given to Gideons army?
- Trumpet
- Torch
- Sword
- Jar
- "You are coming against me with sword, spear and Javelin but I came against you in the name of God Almighty "I Samuel 17:45". These words from David shows that he;
- had a lot of faith
- had a lot of strength
- was very powerful
- was ready to fight for the weak.
- All the following were done by Angel Gabriel EXCEPT? He
- appeared to Joseph in a dream.
- predicted the birth of Jesus.
- said Jesus would save mankind.
- announced the birth of Jesus.
- The following were presents given to baby Jesus by the wiseman. Which one is NOT?
- Gold
- Silver
- Myrrh
- Frankincense
- Which one of the following is the MAIN reason why King Herod wanted to kill baby Jesus?
- Jesus was born from a poor family.
- Jesus was born from the lineage of David.
- Jesus was born in Bethlehem of Judah.
- He feared that Jesus would become famous.
- By feeding five thousand people, Jesus showed one of the following character. Which one was it? He
- is powerful.
- is caring.
- is generous.
- had faith.
- "Blessed are the pure in heart for they shall see God. Matthew 5:8". These words were spoken by Jesus during?
- The sermon on the mount
- His temptation by the devil
- His transfiguration
- The miraculous catch of fish
- During the last supper Jesus took bread and broke it and shared with his disciples. The same way he took a cup of wine and gave it to his disciples. What did the bread symbolize? His
- body
- blood
- love
- saving power
- From the incident that Jesus shared a meal with Zacheus the tax collector, christians leam that they should
- condemn sinners.
- win sinnners through their deeds.
- not associate with sinners.
- deal with sinners carefully.
- Which one of the following events took place when Jesus was at the garden of Gethsemane? He was
- lifted up to heaven.
- crucified.
- transfigured
- arrested. 7
- Who among the following people helped Jesus to carry the cross?
- Joseph of Arimathea
- Simon Peter
- Simon of Cyrene
- Nicodemus
- Jesus is a sure hope of mankind. Which one of the following events marks his victory over death?
- Christmas
- Easter
- Pentecost
- Transfiguration
- Who among the following people was chosen to prepare Judas as an apostle of Christ?
- Mathias
- Barnabas
- Simon of Cyrene
- Nicodemus
- The early church prayed together, shared meals, shared their properties and shared the word of God together. All these activities symbolised?
- Charistimatic renewal
- The passover
- The holy communion
- The pentecost
- "Whatever you do, work heartily as serving the lord and not men". Colossians 3:23. Who among the following people said these words?
- James
- Peter
- Jesus
- Paul
- Which one of the following was NOT a rite of passage in African traditional communities?
- Birth
- Marriage
- Baptism
- Death
- Which one of the following ways of worship is common to both the traditional African communities?
- Reciting prayers
- Making sacrifices
- Reading scriptures
- Baptising the believers
- Which one of the following is the MAIN role of grandparents in the bring up of children in traditional African communities?
- Providing food for the children.
- Preparing them for initiation.
- unishing the evil doers
- Passing on the moral values. 8
- Wachira attended a crusade where the preacher prayed for a sick woman and she got well. Which one of the following gifts of the holy spirit did the preacher have?
- Word of wisdom
- Healing
- Preaching
- Praying
- The following are good ways in which we can use our talents. Which one is NOT?
- Participating in cleaning of the market
- Offering guidance and counselling.
- Participating in choir practice.
- Asking for money after rendering help.
- Erick a class eight boy is forced by his friends to smoke cigarettes. As a christian, what is the BEST action for him to take?
- Report the matter at the police station.
- Refuse and change his company. C
- Report his friends to the headteacher.
- Smoke and then repent later.
- On her way from school, Damaris a class eight girl meets an old lady carrying a heavy basket. Suddenly the old lady falls down. As a christian, what is the BEST action for Damaris to take?
- Run away from the scene.
- Go back to school and get help.
- Assist her to rise up.
- Tell her to rise up and go.
- In which one of the following stations was the first church established in Kenya?
- Kiambu
- Kisumu
- Malindi
- Rabai
ISLAMIC RELIGIOUS EDUCATION
- "Min Sharti Maakhalaq. Wa min Sharri ghaasigin Idhaa waqaba." This are verses from Surah
- Al-Falaq
- Al-Nasr
- Al-Kafirun
- Al-Masad
- What did AbuLahab do in the Surah Al Lahab, that made Allah (s.w) to curse him? He
- persecuted the early muslim converts
- attempted to demolish the holy kaaba
- openly called people into idol worship
- stopped the prophet from Da'awa.
- Surah Maun, promises a heavy punishment for people who commit all the following vices EXCEPT
- mistreatment of orphans
- performing prayers only to be seen by people.
- selling good with unjust measures.
- performing Swalats as you skip.
- Which one of the following characteristics describe Surah Al-Ikhlas?
- Al-Thuluithil Qur'an
- Al-Qalbul Qur'an
- Al-Fat-hul Our an
- Al-Muawidhatein
- How many chapters are there in the holy Qur'an?
- 141
- 441
- 414
- 114
- The two towns in which the holy Qur'an was revealed to prophet Muhammad (S.A.W) are
- Swafa and Sinai
- Makka and Madina
- Jerusalem and Bethlehem
- Syria and Taif
- "Visit him, never annoy him, when you prepare a broth increase the soups you mind about him" Who is this according to the hadiths?
- relative
- friend
- neighbour
- brother muslim
- Hadith. "A generous is near Allah, near paradise, near men and far from Hell. Which kind of a person is this? On
- who spends his wealth on the way of Allah.
- who gives essential services to people in need.
- receives and takes good care visitors.
- who controls his soul and docs what benefits him in the hear after
- The prophet (p.b.u.h) showed us three signs of a hypocrite. Which one on the is NOT among them? He
- betrays trust
- never fulfils a promise
- tell lies
- complains loudly
- Which one of the following values will enable a muslim to peacefully mix and interact with non-muslims even though they are annoyed
- Tolerance B
- Self reliance
- Patience
- Self discipline
- Which one among the following recitation in Swalah indicates change of a posture
- Rabbanaa Walakal-Hamd
- Allahu Akbar
- Assalaam Aleikum Warahmatullat
- Subhaan Rabi-al-Aalaa
- Zukkeina is not able to decide which high school to join after passing her KCPE exams excellently. Which Swalat should she perform to get guidance from Allah
- Swalatu Khusuf
- Swalalu Istiqa-a
- Swalat Tahajjud
- Swalatu Istikhaara
- Which form of purification is done passing dusty hands on the face
- Tayammum
- Istinjaa
- Ghusul
- Istimna-a
- Dogs and pigs, their sweat, saliva and rashes are all classified under
- Najis Mutawasit
- Najis Mukhaffafa
- Najis Mughalladha
- Najis Heidh
- The Islamic Sharia has identified and listed ______groups of people who quality to receive Zakkat.
- six
- eight
- five
- seven
- The meal prepared and feasted passed mid night by muslims in preparation for fasting that day is referred to as
- Suhuur
- Walima
- Iftaar
- Twa'am
- In which of the following places will a hujaaj put on Ihraam to start Hajj activities? At
- Arafa
- Miqat
- Muzdalifa
- Minna
- Which one of the following is NOT an obligation towards a muslim dead body?
- Dafan
- Ruqiya
- Ghusul
- Kaffan
- Which of these is a pair of vices that those who engage in them receive the curses of Allah?
- Bribe and alcohol
- Murder and theft
- Lies and falls testimony
- Apostacy and adultory
- The attribute of Allah(s.w), "Al-Mu-umin" means the
- magnificient
- sovereign
- designer
- trusted
- During the prophets ascent to the Arsh of Allah in the Miiraj trip, the prophet(p.b.u.h) used a special animal called
- Al-Baqara
- Buraq
- Al-Fiil
- Al-Qaswa
- Where was the prophet (p.b.u.h) when he received the first revelation from Angel Jibril (A.S)?
- at Aqaba
- In cave Thaur
- On Mt Swafa
- In cave Hira
- Which one among these months of the Islamic calendar is NOT an Ash-hurul Hurum?
- 9th month
- 12th month
- 1st month
- 7th month
- The two daughters of the prophet Muhammad(S.A.W) who both got married to Caliph Uthman bin Affan were
- Zainaba and Faatima
- Ummu Kulthum and Zainab
- Faatima and Ruqayya
- Ruqayya and Ummu Kulthum
- Which mistake did some army men do during Uhud that made muslims almost loose that battle to the Qufaar?
- Some army men were just hypocrites
- They disobeyed the prophet's instructions
- Some never joined the prophet in Swalat Khauf.
- When the prophet(p.b.u.h) got hurt.
- Which one among these Ummahaats were destroyed by Allah(s.w) because of injustice in measures in their businesses?
- Ummat Lut(A.S)
- Ummat Swalah (A.S)
- Ummat Shuaib(A.S)
- Ummat Nuh(A.S)
- What is Tawakkul?
- The fellowship of Allah
- Reliance on Allah
- The commitment to Allah
- The fear of Allah
- Who accompanied the prophet (S.A.W) on his Hijra trip to Madina?
- Bilaal bin Rabbah
- Uthman bin Affaan
- Abubakkar Sidiq
- Ayyub Auswari
- For how long did the prophet(S.A.W) propagate Islam secretly?
- Three years
- Ten years
- Five years.
- Thirteen years
- Muslims and the Qureish elders drafted a Hudaibiyya peace agreement that was to last for a period of
- 23 years
- 17 years
- 10 years
- 7 years
MARKING SCHEME
- B
- C
- A
- D
- A
- A
- C
- D
- A
- B
- C
- D
- A
- D
- B
- B
- B
- C
- C
- D
- A
- A
- B
- C
- D
- D
- B
- C
- D
- A
- B
- A
- D
- B
- C
- A
- D
- A
- C
- D
- D
- B
- B
- A
- C
- C
- C
- B
- A
- D
- D
- B
- A
- C
- C
- B
- B
- A
- D
- C
CRE
- C
- B
- D
- C
- A
- B
- B
- C
- A
- B
- B
- D
- B
- A
- A
- B
- C
- C
- B
- A
- C
- D
- C
- A
- D
- B
- D
- B
- C
- D
IRE
- A
- D
- C
- A
- D
- B
- C
- A
- D
- C
- B
- D
- A
- C
- B
- A
- B
- C
- A
- D
- B
- D
- A
- D
- B
- C
- B
- C
- A
- C
Science - Class 8 End Term 1 Exam 2021 Set 2
STANDARD 8, END OF TERM 1
SCIENCE
NAME....................................................SCHOOL...............................
- The following are characteristics of clouds
They are rain laden.
They have a flat base,
They are dark or grey in colour.
They bring fine weather
They are thick white feathery
Which among the above characteristics describe cumulus clouds?- (ii), (iv), (v)
- (iii), (iv). (vi)
- (ii)(iii).(v)
- (i)(iii), (iv))
- The fusion of sex cells in human being take place in the
- ovary
- uterus
- oviduct
- testis
- Which one of the following farm practices conserve soil and water?
- Terracing
- Building gabions
- Planting trees
- Mulching
- The following are signs and symptoms of certain diseases.
Skin rashes
Fever
Abdominal pains
Sore on the walls of intestines.
The disease is LIKELY to be- Bilharzia
- Typhoid
- Cholera
- Malaria
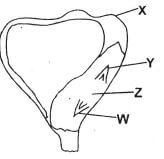
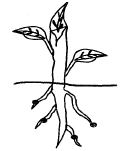
- The diagram below shows a maize seed.
Which one of the following statement is TRUE?- Part Z is the endosperm.
- Part Y forms the embryo.
- Part W forms the shoot.
- Part X store food for the young plant.
- Which one of the following pairs of materials are opaque?
- Oil and mirror
- Wood and windscreen
- Skylight and paraffin
- Frosted glass and metal
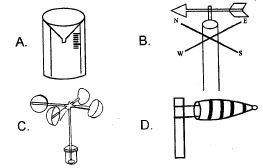
- The following are materials used to make a certain weather instrument.
Metal sheets.
Nail
Pole
Compass
The weather instrument is MAINLY used to measure- strength of wind
- amount of rainfall
- air temperature
- direction of wind
- The following are sources of electricity EXCEPT
- car batteries
- solar panel
- torch bulb
- dynamo
- Which one of the following materials is used as insulator?
- Copper wire
- Rubber band
- Iron rod
- Aluminium wire
- The BEST way of controlling the spread of HIV/AIDS among the school going pupils is by
- being faithful to one partner.
- encouraging the use of condoms.
- visiting V.C.T.
- abstaining from sex.
- Which one of the following excretory product is NOT excreted by the skin?
- Carbondioxide
- Urea
- Excess water
- Excess salt
- Which one of the following sexual transmitted infections is caused by virus?
- Syphilis
- Gonorrhoea
- Chancroid
- Genital herpes
- The following are adaptation of a certain plant.
Needlike leaves.
Thick waxy cuticle
Sunken stomata
Folded leaves
The plant growing in the same environment is also LIKELY to have- large flat leaves.
- deep root.
- air sacs
- flexible stems
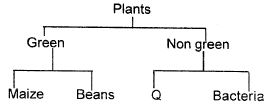
- Which of the following pairs of plants are non green and flowerless?
- Algae and bacteria
- Fern and liverworts .
- Mushroom and mucor
- Pine and cedar
- The diagram below shows an experiment on change of state on matter.
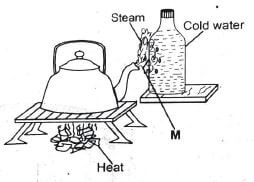
Which process take place at the point marked M?- Evaporation
- Boiling
- Condensation
- Freezing
- Which one of the following is NOT as a result of bending of light?
- A coin in water appear raised.
- Formation of images on mirrors.
- Swimming pools appears raised.
- Formation of the rainbow.
- The following are effects of drug abuse.Which one is an economic effect?
- Loss of income.
- Accident
- Poor health
- Marital conflicts
- Birds that feed on flesh have
- short, straight, thick beak
- strong, curved beaks
- flat, serrated beaks
- long, slender beaks
- Which one of the following is NOT a sign of ill health in livestock?
- Rough coat.
- Reduced yields.
- Stunted growth
- Lower yields.
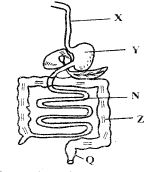
- In which of the following parts of digestive system is food NOT digested?
- Small intestine
- Stomach
- Mouth
- Large intestines
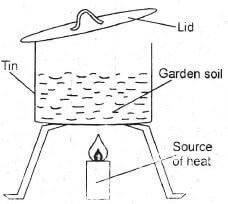
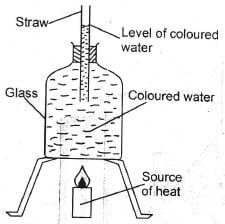
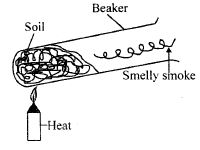
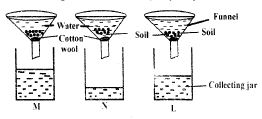
- The set up below can be used to investigate the presence of a certain component of soil.
Which two components soil can be investigated by the set up shown above- Water and humus
- Mineral particles and organic matter.
- Water and living organism.
- Ilumus and air
- The following are examples of straight fertilizer EXCEPT
- Munate of potash
- CAN
- Diammonium Phosphate
- Double supersphosphate
- The body require enough mineral salts for
- energy
- good health
- growth and repair
- muscle development
- The following animals lay unfertilized eggs and live partially in water EXCEPT
- salamander
- toads
- crocodile
- news
- Which one of the following pairs of plants have the same root system?
- Onions and sisal
- Coconut and mango
- Grass and beans
- Cowpeas and sorghum
- Which one of the following statement is NOT TRUE about all arteries?
- They carry blood rich in oxygen.
- They carry blood away from the heart.
- They have thick walls.
- Blood pressure in them is high.
- Which two form of energy. DOES NOT require medium for transmission
- Electricity and light
- Heat and light
- Sound and light.
- Sound and heat
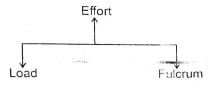
- The diagram below represent the arrangement of the parts of a lever.
The lever illustrated above is LIKELY to be- spade
- wheelbarrow
- claw hammer
- crowbar
- Which one of the following is NOT a way of reducing friction? Using
- ball bearing
- rubber
- lubricants
- roller
- The diagram below shows a food chain
Maize → rat → snake → vultures
Which one of the following animal is in the same level with the vultures?- Duck
- Goat
- Hyena
- Lion
- The following are properties of matter
Have definite volume
Have definite muss.
Change state when heated
Occupy space.
Which substance given below bave the above characteristics?- Milk and water vapour
- Salt and ice
- Oxygen and nitrogen
- Water and milk
- Which one of the following immunizable diseases are immunized at 10 weeks and immediately after birth to young infants?
- Polio, Tetanus, Tuberculosis
- Whooping cough, Tetanus, Diptheria
- Tuberculosis, Measles, Polio
- Yellow fever, Polio, Fertusis
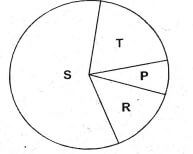
- The chart below represent approximate percentage of the component of air.
Which portion represent the gas that is NOT used by living things?- S
- T
- P
- R
- Oil and grease are used in some simple tools to
- reduce opposing force
- make them more durable.
- increase friction.
- make them more attractive.
- Which of the following feeds provide livestock with protein?
- Maize germ
- Lucem
- Cotton seed cake
- Mollasses
- One of the following is NOT in the same group as a tick. Which one?
- Spider
- Scorpion
- Mite
- Crab
- The diagram represents a set up that was used to demonstrate a certain property of matter
The aspect of matter demonstrated is that- liquid expand and contract.
- gases expand and contract.
- water exert pressure
- air occupies space.
- Pre-test counselling is given
- after the result of the test are released.
- after the test is done.
- before one takes an HIV test.
- before results are released to the person who is tested.
- Which one of the following foods will help boost the immune system of the body?
- Egg, milk, bacon
- Carrot, rice, cassava
- Onions, spinach, tomatoes
- Peas, beans, greengrams
- When tea leaves is put in a glass of cold water and heated at the bottom, the tea leaves are observed to rise and fall. This is because tea leaves
- are carried by hot water which come down on cooling.
- and water rise when heated and come down on cooling.
- becomes lighter than water when heated.
- rise when heated and come down on cooling
- Which one of the following is a MAJOR non living component of environment?
- Animal
- Buildings
- Plant
- Soil
- Which one of the following is NOT a use of water in factory?
- Making fountains.
- Surfing
- Mixing chemicals
- Cleaning equipments.
- Which one of the following activities is water conserved by re-using?
- Using domestic water for washing toilets.
- Treating sewage water.
- Turning off taps after use.
- Harvesting rain water from roofs.
- During pregnancy period, the placenta has all the following functions EXCEPT
- facilitates the exchange of foods from the mother to the foetus.
- allow the mother's blood to mix with foetus blood
- facilitates the exchange of gases between the mother.
- allows the passage of waste from the foetus to the mother.
- During the investigation of soil water retention all the following materials need to be the same EXCEPT
- size of the funnel.
- time allowed for the experiment.
- types of soil
- amount of water added.
- A flower which has long feathery stigma and loosely held anthers is also LIKELY
- produce nectar.
- have sweet scent
- have brightly coloured petals.
- produce many pollen grains
- A beam balance is used fo
- comparing mass of different objects.
- measuring volume of objects.
- comparing size of different objects.
- measuring height of objects.
- Study the diagram below
Which pair of blood vessels above carry blood that is bright red in colour?- W.X
- W.S
- ST D
- T.X
- Carnassial teeth found in the carnivorous animals are modified
- canine and premnolars
- pre molars and molars
- canine
- incisors
- The diagram below shows a method of separating mixture
The method can be used to separate- coarse and fine sand
- salt and iron filling
- sugar and water
- maize and beans
MARKING SCHEME
- A
- C
- D
- B
- B
- A
- D
- C
- B
- D
- A
- D
- B
- C
- C
- B
- A
- B
- D
- D
- A
- C
- B
- C
- A
- A
- B
- A
- B
- C
- D
- A
- B
- A
- B
- D
- B
- C
- C
- A
- D
- B
- A
- B
- C
- D
- A
- C
- B
- A
Kiswahili - Class 8 End Term 1 Exam 2021 Set 2
DARASA LA 8, MWISHO WA MUHULA WA 1
KISWAHILI
JINA....................................................SHULE...............................
Soma vifungu vifuatavyo vina nafasi 1 mpaka 15. Kwa kila nafasi umepewa majibu munne hapo. Jaza pengo kwa kuchagua jawabu lifaulo zaidi.
1 marafiki wote 2 kuwa nao, siwezi kumsahau Tito asilani. Yeye 3 kuainisha aina mbalimbali 4 maneno. 5 alinifahamisha kwamba maneno kama vile 6 huitwa vielezi. Isitoshe, 7 ya kushirikiana na wengine katika shughuli za kimasomo kwani 8 , 9 nilifaidika sana kutokana na urafiki wetu.
- A. Baadhi ya B Miongoni mwa C. Fauka ya D. Licha ya
- A. niliyewahi B. aliowahi C. niliyowahi D. niliowahi
- A. ndiye aliyenifunza B. ndio alionifunza C. ndivyo alivyonifunza D. ndiye alionifunza
- A. ya B. na C. za D. wa
- A. Mathalan B. Ihali C. Kwani D. Kumbe
- A. mbali, ila. njema B. tamu, nzuri, bora C. hizo, vile, tena D. taratibu sana, vizuri
- A. alinivunja moyo B. alinitia shime C. alinipiga kumbo D. alinionea gere
- A. Mchumia juani hulia kivulini
B. Jirani ni akiba
C. Kofi hazilii ila kwa viganja viwili
D. Jua vimeundwa - A. Yakini B. Katu C. Kamwe D. Asilani
Elimu ina manufaa 10 Mtu 11 elimu ya kumfaa, maisha yake hugubikwa na giza 12 . Kwa mfano, kupitia elimu ya mazingira, tunajifunza jinsi 13 kuongeza 14 katika mazingira yetu. Vijana nao hufunzwa kutumia vipawa 15 kujikimu kimaisha
- A. anuwai B. nyingi C. mingi D. kiasi
- A. asiopata B. asingepata C. asipopata D. asikopata
- A. tiriri B. totoro C. kochokocho D. furifuri
- A. tunaoweza B. tunayoweza C. tunaweza D. tunavyoweza
- A. thamani B. dhamani C. ridhaa D. riba
- A. zao В yao C. vyao D. chao
Kuanzia nambari 16 mpaka 30, chagmujawahu lifaalo zaidi kwa kila swali
- Bainisha matumizi ya kiambishi-ka kwenye sentensi.
Mwalimu alituita akatushauri- Kuonyesha masharti
- Kuonyesha hali ya kuendelea
- Kuonyesha kutegemeana kwa vitendo
- Kuonyesha kufuatana kwa matukio
- Chagua maelezo ambayo ni sahihi.
- Kikuku ni pambo la shingoni.
- Kipuli huvaliwa upande wa kushoto wa pua
- Kishaufu ni pambo la puani.
- Bangili ni pambo la mviringo la shingoni.
- Tunasema jua, juza na nawa
- navya
- nawia
- nawishwa
- nawika
- Andika katika wingi. Jirani ameniazima uteo wake.
- Jirani wamelazima uteo wao.
- Jirani wametuazima teo zao.
- Majirani wametuazima teo yao.
- Majirani wametuazima teo zao.
- Kamilisha: Mgonjwa alibebwa na wauguzi kwa _____ hadi kwenye wodi.
- ambulensi
- machela
- toroli
- nyoka
- Kanusha: Mtoto alipoangukaaliumia.
- Mtoto alipoanguka hakuumia.
- Mtoto hajaanguka wala hakuumia
- Mioto asipoanguka hataumia.
- Mtoto hakuanguka na kuumia.
- Kutokana na kitenzi tii tunapata sifa gani?
- Utiifu
- Katii
- Mtiifu
- Tiliwa
- Geuza sentensi ifuatayo katika hali ya udogo.
Mtoto alifurahi aliponunuliwa mkoba- Kitoto alifurahi aliponunuliwa kikoba
- Toto lilifurahi liliponunuliwa koba.
- Vitoto vilifurahi viliponunuliwa vikoba.
- Kitoto kilifurahi kiliponunuliwa kikoba
- Tegua kitendawili kifuatacho.
Mlima wa Kwale hupandwa kwa kucha.- Kula sima.
- Kusuka nywele
- Muwa
- Jiwe
- Sentensi gani kati ya hizi ni tashbihi?
- Sikio la kufa halisikii dawa.
- Jina jema ni hazina maishani.
- Mikono yake ni baridi kama barafu
- Wezi wale walikimbia mkiki mkiki.
- Fahali ni kwa mtamba kama ilivyo kipora kwa
- jogoo
- tembe
- beberu
- kuku
- Andika katika usemi halisi.
Kaka aliniambia kuwa tungeenda shambani siku ambayo ingefuata.- "Utaenda shambani kesho" Kaka aliniambia.
- "Kesho wanaenda shambani" Kaka aliniambia
- "Tungeenda shambani kesho", Kaka aliniambia.
- "Mtaenda shambuni kesho," Kaka aliniambia.
- Msemo 'kuwa na kichwa kizito' una maana ya,
- kuwa na usingizi
- kutosikia
- kuwa na kichwa kikubwa
- kuwa mwerevu
- Kamilisha: Angalijua huko kulikuwa na wezi _______mlango.
- angefunga
- asingefunga
- hangalifunga
- angalifinga
- Chagua methali nyingine yenye maana sawa na hii.
Akutanguliaye chanoni hukuzidi tonge.- Mwenda mbio subiri achoke.
- Ukiona vyaelca jua vimcundwa.
- Atanguliaye kisimani hunywa maji mengi.
- Mchimba kisima huingia mwenyewe.
Soma kifungu kifuatacho kisha ujibu maswali kuanzia 31 mpaka 40.
Hakuna kitu muhimu maishani kuliko afya ya akili. Kwa hakika afya hii ya akili ndiyo humwezesha mtu kutenda mambo jinsi anavyotakikana. Mtu mwenye afya ya akili huweza kutangamana vyema na wenzake bila kuwabughudhi kwa lolote. Aghalabu mtu huyu huwa mfurufu wakati wote, jambo ambalo humsaidia kudumisha hata afya ya mwili.
Matendo ya watu wengi katika siku za hivi karibuni yanadhihirisha kuwa afya ya akili inazidi kudorora. Imekuwa kawaida kama sheria kusikia kuwa mtu fulani amechukua silaha na kumwumiza mwenzake vibaya. Wengine wanatumia silaha za maangamizi ya halaiki pasi na kisa wala sababu. Baadaye watu hawa wakipelekwa mbele ya sheria huonekana kuchanganyikiwa; yaani hawajijui hawajitambui.
Je, ni nini hasa kinachochangia kuvurugika kwa afya ya akili? Kwanza, binandamu anapokabiliwa na hali ngumu ya maisha kila uchao, hujipata akihangaika kimawazo. Hali hii ikiendelea kwa muda mrefu pasipo kushughulika ipasavyo, akili ya mhusika huweza kuenda tenge. Watu wengi, wakubwa kwa wadogo wanaendelea kuhangaika kwa sababu mbalimbali.
Matumizi mabaya ya vileo yamewafanya baadhi ya watu kuwa punguani. Kwa mfano, uvutaji wa bangi ni sababu kuu ya vijana wengi kurukwa na akili. Ni vyema tujitenge na waraibu wa mihadarati kwani niazi mbovu ni harabu ya nzima.Kwa hakika dawa hizi hazina manufaa yoyote.
Ili kudumisha afya ya akili, ni lazima ushauri nasaha uimarishwe katika sekta zote za kijamii. Kupitia ushauri walmarika shuleni kwa mfano, vijana watashauriwa kuhusu madhara ya kuandama sana starehe vilevile, watajifunza kuratibu muda wao na kuutumia kwa njia ya manufaa. Vilevile, wataelekezana kutambua mbinu mwafaka zaidi za kuepuka vishawishi vinavyoambatana na ujana.
Serikali haina budi kukabiliana na ulanguzi wa dawa za kulevya. Hili halitafanyika kwa kuwatia nguvuni waraibu tu. Huku ni kama kupogoa matawi ya mti na kuutarajia ukauke. Biashara hii sharti ikomeshwe kuanzia kwa wauzaji wa humu nchini na hata magenge ya kimataifa.
Mtu anapokabiliwa na tatizo, ni vyema kuwaendea washauri ili aongozwe kwa njia ifaayo. Wale walioathirika nao wajikubali na kutafuta matibabu kabla hali zao hazijazorota zaidi. Taifa halitaweza kupiga hatua bila raia wake kuwa razini.
- Chagua maelezo yanayolingana na aya ya kwanza.
- Afya ya akili ndicho kitu muhimu pekee maishani.
- Mtu akiwa na matatizo ya akili huoneakana waziwazi.
- Mtu asiye na afya ya akili ni mwendawazimu.
- Utendaji wa mtu huweza kuathiriwa na afya ya akili.
- Wanajamii wakiwa na afya ya akili,
- hudumisha uhusiano mwema baina yao.
- huvuruga maingiliano miongoni mwao.
- hawakabiliwi na shida zozote maishani.
- hukabiliwa na changamoto nyingi maishani.
- Kulingana na aya ya pili,
- malezi mabaya ya watoto yamewafanya wengi kupotoka.
- maovu yameongezeka kutokana na kuzorota kwa afya ya akili.
- matumizi ya silaha yanavuruga afya ya akili.
- si kawaida kwa watu siku hizi kuumizana kwa silaha.
- Maneno hawajijui hawajitambui yametumia tamathali gani ya usemi?
- Sitiari
- Tanakali za sauti
- Vielezi ya kutilia mkazo.
- Tashbihi
- Chagua jibu lililo sahihi.
- Wote wanaohangaika hupata shida za kiakili.
- Kukosa kusaidiwa husababisha matatizo ya akili.
- Kuhangaika kwa muda mrefu huathiri afya ya akili.
- Hali ngumu ya maisha ni mfano wa shida za kiakili.
- Hali anayopinga mwandishi hasa katika aya ya nne ni,
- hali ya vijana kurukwa na akili.
- madhara ya mihadarati hasa katika familia.
- watu wanaotumia pesa kununua mihadarati.
- matumizi mabaya ya vileo.
- Methali 'Nazi mbovu harabu ya nzima' ina maana kuwa,
- Ukifuatana na watu wabaya watakupotosha.
- Ukitumia mihadarati vibaya utahasirika.
- Vijana wakitumia mihadarati watakuwa punguani.
- Watu wazima wakiingilia ulevi vijana watawaiga.
- Yapi ni manufaa ya ushauri wa marika?
- Vijana huonyeshwa jinsi ya kuandama starehe.
- Vijana walioshauriwa hawapatani na vishawishi vyovyote.
- Vijana hujifunza kutumia muda wao ipasavyo.
- Vijana hushauriwa kuhusu dawa zifaazo.
- Kupogoa matawi ya mti kumelinganishwa na
- kuwanasa walanguzi wa mihadarati.
- kuwashika wanaotumia mihadarati.
- kukabiliana na magenge ya kimataifa.
- kumaliza kabisa biashara ya mihadarati.
- Kichwa kifaacho zaidi kwa makala haya ni
- Madhara ya mihadarati.
- Umuhimu wa ushauri nasaha.
- Umuhimu wa afya ya akili.
- Serikali kupunguza shida za maisha.
Soma makala yanayofuata kisha ujibu maswali kuanzia 41 - 50.
Msenangu alifahamika katika kijiji chao na takriban kila mtu. Watoto walimfahamu kutokana na mtindo wake wa kutembea. Alitembea wima kama askarijeshi na kila alipokwenda kupiga chupa zake, alikuwa na mazoca ya kupiga kwata kama mwanajeshi gwarideni. Sababu nyingine iliyomfanya Msenangu afahamike ni ucheshi wake. Aliwasimulia vijana hadithi za kila aina na kuwavunja mbavu kwa umahiri wake wa kuzitamba hadithi zenyewe.
Ingawa Msenangu alikuwa na umri mpevu sana, alikuwa mmoja kati ya wazee wachache wa kwao waliojua kusoma. Idadi ya waliojua kusoma wakati huo ilikuwa akali sana na mzee huyo aliona fahari kuwa miongoni mwa hao wachache. Habari za kuandikwa kwa katiba mpya zilipofika kijijini, Msenangu alifurahi na kuchanua uso. Hii ni nafasi ya kuhakikisha kuwa nimewaeleza yote yanayohitajika kufanywa : alijitapa Msenangu. Wanakijiji walitaka kuteua vijana wawawakilishe ambapo tume ya kuandika katiba ampya ingefika pale kijijini. Hata hivyo, Msenangu alikazania kuwa ni lazima angekuwa mmoja wao. Licha ya uwezo wake wa kusoma, wanakijiji wengi hawakuamini kuwa alijua lolote kuhusiana na katiba.
Siku yenyewe, vijana walioteuliwa walitumia lugha ya kisheria ambayo ni dhahiri wanakijiji wengi hawakuielewa. Muda is muda, watu walianza kuondoka ukumbini mmoja mmoja. Ndipo bila kungoja aalikwe, mzee Msenangu alisimama. Watu waliokuwa nje ya ukumbi waliambiana, "Haya Msenangu huyo!' Alianza kuongea," Ndugu wanakamati, nimcisubiri fursa hii kwa hamu kubwa. Maneno yangu mimi si mengi kwani sikusoma mambo hayo ya "yesi" "yesi". Lakini ningependa kusema machache niliyo nayo moyoni. Nataka iandikwe katiba itakayoiendesha nchi yetu, kwa njia nzuri, kwa miaka mingi ijayo.Katiba hiyo ni lazima iwalinde raia wote, walemavu na wasio walemavu waonao na wasioona, waumini na walevi' alianza Msenangu. Watu walimtazama kwa mshangao mkubwa.
"Tulieni tumsikilize!” Wengine walisema. Wale waliokuwa wakiondoka ukumbini walirudi haraka kuketi. iangu akaendelea, “Katiba inayoifaa nchi ni ile isiyozingatia matakwa ya kundi moja la jamii tu... zima ziwepo njia za kuwadhibiti viongozi hawa kuhakikisha kuwa wanapotwaa madaraka hawatugeuzi sisi wanyonge kuwa wanase sere wao wa kuchezea, "alisema Msenangu na kutua. Ukumbi mzima sasa ukawa umemtegea sikio ndi!
Wanakumati walikuwa wakiandika huku wakiitikia kwa vichwa vyao. "Sisi wanyonge tunaoishi huku mashambani tuna shida. Wahenga walisema "Sheria ni msumeno hukata mbele na nyuma" Lakini kwetu huku haikati, inakala nyuma tu. Wenye vyeo wanapotamani vikataa vyetu wanavitwaa tu kwa njia rahisi wakitumia vyeo vyao. Tunaposhindwa kulipa pesa za michango ambazo hatuna, machifu wanaamuru mifugo yetu isombwe. Pawepo na sheria za kuwadhibiti watu kama hao. Kwa kifupi, iwe sheria inayotetea tajiri na maskini, mr yonge na mwenye nguvu, aliye nacho na asiye nacho.
Wanakamati wapendwa, usalama umeadimika kama mito jangwani. Sisi wenyewe tumegeuka walinda usalama. Lakini jambo la kushangaza ni kwamba tuwatiapo wahuni hao mikononi mwa walinda usalama wanazunguka mbuyu na kuwa huru.
Katika nchi inayothamini raia wake, bei za bidhaa haziongezeki shaghalabaghala tu. Ningetaka katiba iangalie jambo hili."
Baada ya kusema haya Msenangu akachukua mkongojo wake na polepole akatoka ukumbini na kuuacha umati umeduwaa. Kisha ukumbi ukalipuka pu kwa makofi na vigelegele ukimshangilia Msenangu ambaye alikuwa tayari ameshaondoka.
- Chagua jibu lisilo sahihi
- Watu wote walimfahamu Msenangu.
- Msenangu alikuwa na tabia ya ulevi,
- Msenangu alizoca kuwafurahisha watu.
- Watoto walimfahamu Msenangu kwa kutembea kijeshi.
- Maana ya kuwavunja mbavu ni
- kuwaumiza mbavuni
- kucheka kisirisiri
- kuwachekesha sana
- kuwashangaza watu
- Ni jambo lipi alilojivunia Msenangu?
- Kupendwa na watu wengi.
- Elimu aliyokuwa nayo.
- Kuwashinda vijana kiclimu.
- Kuwa na wasomi kijijini.
- Msenangu alifurahishwa na habari za kuandikwa kwa katiba mpya kwa sababu,
- angeonyesha ubingwa wake kwa wale wasiomjua.
- angeshindana na vijana katika maarifa yao.
- aliwachukia viongozi waliokuwa mamlaka
- angependekeza njia za kuboresha utawala.
- Kwanini wanakijiji walianza kutoka ukumbini?
- Muda ulikuwa umeyoyoma.
- Hawakuzielewa hotuba ya wazungumzaji.
- Walikerwa na maneno ya Msenangu.
- Walipuuzwa na waandishi wa katibampya.
- Watu walishangazwa zaidi na Msenangu kutokana na,
- umaarufu wake wa kusema
- kupinga maovu ambayo hawakuyajua.
- kupigana na serikali iliyokuwa mamlakani.
- kuchangia hoja nzito zenye umuhimu.
- Sheria ni msumeno hukata mbele na nyuma kwani,
- haipendelei wala kumbagua yeyote.
- sheria haina manufaa kwa mtu yeyote.
- sheria wakati wote huwabagua wanyonge.
- huwaumiza watu wote katika jamii.
- Kulingana na maneno aliyoyasema Msenangu
- usawa ulikuwa ukizingatiwa huko zaidi.
- katiba ya zamani ilikuwa bora zaidi.
- wanyonge walikuwa wakidhulumiwa katika jamii.
- viongozi wa jamii walionyesha uzalendo.
- Nini kilichangia zaidi kudorora kwa usalama?
- Wananchi kukosa kushirikiana.
- Uhaba wa kazi katika jamii.
- Kukosa sheria za kuwahukumu wahalifu.
- Ufisadi uliowafanya wahalifu kuachwa huru.
- Kilingana na aya ya mwisho
- Hotuba ya Msenangu ilikatizwa kwa makofi.
- Msenangu hakuwepo aliposhangiliwa.
- Bei za bidhaa zilikuwa juu sana.
- Msenangu alituzwa kwa mkongojo.
INSHA
Wewe ni mmojawapo wa wanafunzi wa darasa la nane shuleni mwako. Andika hotuba utakayowatolea wanafunzi wengine shuleni kuhusu jinsi ya kuimarisha matokeo yao katika mitihani.
MAAKIZO
- B
- D
- A
- C
- A
- D
- B
- C
- A
- A
- C
- B
- D
- A
- C
- D
- C
- A
- D
- B
- A
- C
- D
- A
- C
- B
- D
- A
- D
- C
- D
- A
- B
- C
- C
- D
- A
- C
- B
- C
- A
- C
- B
- D
- B
- D
- A
- C
- D
- B
English - Class 8 End Term 1 Exam 2021 Set 2
STANDARD 8, END OF TERM 1
ENGLISH
NAME....................................................SCHOOL...............................
Read the passage below It contains blank spaces mumhered 1 to 15. For each blank space, choose the BEST alternative from the choices given
People usually feel like taking some time 1 to sit alone and 2 some personal decisions. This requires a quiet place without any noise. 3 the background. Such places 4 have become very 5 due to urbanisation and industrialisation. Even if 6 was to get into a 7 forest, far away from the road, he 8 only succed in keeping off noise from machine-related sources as there are animals and birds which 9 in the forest and communicate to one another by the noises they make. A monkey, for example, will 10 to pass information to other monkeys. 11 at night, complete silence is impossible to achieve as there are some birds, insects 12 wild animals which hunt at night. They make noise to tell the others 13 where they are or where danger they should avoid has been 14 . It is therefore only 15 to achieve some reasonable amount of silence but almost impossible to achieve complete silence.
- A away B. off C. out D.about
- A. take B. plan C. bring D. make
- A at. B. in C. by D. on
- A. therefore B. moreover C. however D. consequently
- A rare B.special C. strange D. clear
- A be B. one C. she D.it
- A green B. tall C. wide D. thick
- A should B would C. might D. could
- A move B. remain C. stay D. live
- A trumpet B chatter C. howl D.scream
- A Even B. Now C. so D. Likewise
- A of B. also C. and D. then
- A either B both C. neither D.only
- A defeated B detected C. dejected D. suspected
- A known B. easy C. believed D. possible
For questions 16 la 18 cheese the alternativ That means the SAME AS the underlined wory
- The hardworking teacher was promoted
- Strict
- Clever
- Industrious
- Energetic
- You will finally get your destination if the vehicle does not break down.
- lastl
- immediately
- really
- actually
- You have to be smart in your work to achieve your aim
- intelligent
- neat
- attractive
- clean
For each of the questions 19 to 21, choose from the alternative given the statement which when combined with the phrase makes a complete and sensible sentence
- Susana will only be treated
- because she reaches the hospital on time.
- as she reaches the hospital on time.
- after she reaches the hospital on time.
- if she reaches the hospital on time.
- If I had time, I
- should visit my grandmother
- could visit my grandmother.
- would visit my grandmother,
- might visit my grandmother.
- It was until the rains started
- that the farmers started planting their crops.
- when the farmers started planting their crops.
- as the farmers started planting their crops.
- before the farmers started planting their crops.
For questions 22 and 23, choose the BEST arrangement of the given sentences to make sensible paragraphs
- Use of written or oral language should be effective
it is importance to communicate in order to be understood
The response too will help you know whether you communicated or not
If the language is too high or too low, you may not achieve your aim- ii, iv. iii, i
- ii, i, iv, iii
- ii, iii, iv, i
- ii, i, iii, iv
- However, the water has to be clean to keep you healthy.
Water is essential for life.
This could change depending on the type of food eaten and the day's weather
You need to drink an average of eight glasses of water per day:- iv, i, ii,iii
- iv, ii, iii, i
- ii, iii, iv. i
- ii, iv, iii, i
In questions 24 and 25, choose the correct alternative that means the SAME AS the given sentence.
- Hardly had the cock crowed than we woke up.
- We woke up when the cock crowed.
- The cock crowed and immediately we woke up.
- The cock crowed as soon as we woke up
- We woke up then the cock crowed.
- "What have you been doing since morning?" her mother asked.
- Her mother asked if she had been doing anything since morning.
- Her mother asked her what she was doing since morning.
- Her mother asked her what she had done since morning
- Her mother asked her what she had been doing since morning
Read the passage below and then answer questions 26 to 38.
When Tolo arrived back, he was not in a talking mood. He looked tired, worn out, hungry and moody. His clothes too, looked torn, dirty and it was obvious wherever he had been to was hell on carth. It took a few days then he gathered courage to take a few trusted friends who remained glued next to him, especially in the evenings.
Tolo was at home and like other hunters, he decided to go and inspect his traps. The first two had caught nothing and so he proceeded to the third one which was located near the riverbank. It was a forested area and thus, having a panga in the hand was essential.
He was lucky! A deer had been trapped and it looked either dead or dying from a distance. llowever, when he moved closer, he realized its eyes were wide open although it made no attempt to Ilee. lle knew it was just waiting to be carried away but how wrong it was! The poor creature had been struggling for hours and hours and upon realizing it couldn't flee itself, decided to save the little energy left for any opportunity of escape ifit ever came. So when Tolo cut off the rope it had entangled itself in. the deer made a leap into the air and its first landing was four metres away
Tolo was shocked and surprised but he picked his panga and went after the creature. Due to his speed and undergrowth, he lost it. Knowing that it couldn't cross he adjacent river that fast, he decided to keep going after it; sooner or later, he would get it.
It was not long when he reached it but what he saw almost made him faint. The deer was in the claws of a ferocious-looking leopard, with teeth dripping fresh blood, glared and glowled at him, he found himself climbing the closest tree. It was the safest thing he could do but it was the gravest mistake that landed him in trouble.
The went up the tree with the heart beating fast but hopeful to get the safety he was very much wanted. For some time, it remained so but at around eight o oclock, he heard some noise and looked down. Tulis utter surprise, the Icopard, with the deer's neck in the jaws, was struggling up the tree! This shocked him and made him climb to even higher branches. It was then that he realized that he was 100, was trapped! The leopard settled on a thick branch, just below him and started eating its meal probably aware of his presence.
It's this meal that lasted a whole two days and within those two days. lolo learnt that one can actually stay for two days and nights without food, drink and very little sleep lle vowed to abandon trapping animals and ventured into crop cultivation.
- Tolo was not in a talking mood because
- he had just arrived back
- many people had talked ill about him.
- what he had undergone was still tormenting him.
- he did not find the right people to address
- From the way Tolo looked, it is possible to suggest that he
- knew little about good grooming,
- decided to change his appearance completely
- he intended to attract the villages attention.
- he had not had time for good grooming.
- What does the writer mean by describing where Tolo had been as hell on earth?
- The conditions there were undesirable.
- No one else had been there
- He had been to hell and saw for himself
- lt took him a long time to return.
- When Tolo left home that evening.
- he was accompanied by other hunters.
- it was a routine he always did.
- he expected to catch a trapped animal
- he was in too much of a hurry
- The item Tolo carried as he inspected his traps can BEST be described as
- Weapon
- equipment
- instrument
- tool
- As soon as Tolo saw the trapped deer, he
- became curious to acertain its state.
- wondered how to carry it away.
- suspected it would cause trouble
- doubted if he was truly lucky
- The MAIN reason why the deer leap into the air is
- it was alarmed by Tolo's arrival.
- it had been resting all along
- its life depended on it.
- it had just opened its eyes.
- Which of the four words below describe what made Tolo to follow the fleeing deer?
- concentration
- determination
- curiosity
- anxiety
- What made Tolo realise that the deer wouldn't go far?
- Knowledge of how deer behave.
- The speed at which it had left.
- This experience as a hunter
- The time the deur had taken in the trap
- By climbing the nearest tree, Tolo wanted to
- frighten the leopard off its prey.
- see if the antelope was actually dead.
- hide from the leopard then take the antelope
- save himself from danger.
- Why does the writer describe climbing the true the gravest mistake?
- it almost made him lose his life.
- the tree was not strong enough for him and the leopard.
- leopards normally hunt their prey up the tree
- he should have climbed a different tree
- The leopard settled only two branches away from Tolo because
- it had no business following Tolo.
- it felt comfortable there.
- the upper branches were weak
- it was tired because of the load it had.
- The BEST summary for this passage would
- it's unwise to venture out alone.
- We have to be selective on where to go.
- you can lead yourself into serious trouble
- your company can discourage you from talking.
Read the passage below and then answer questions 39 to 50
Speaking up is important, especially when addressing people who are senior to you. It is the best ever thing to do as it leaves no doubt to your listener that you know what you are saying and are confident. Mental toughness sometimes requires you to say 'No' even when given a command. In the Special Forces, it is called 'Chinese Parliament'. This is where all of us are able to talk very leely with one another, with complete disregard to positions others hold. It's common to hear one say, 'I'm going to be part of the mission and I'm not going to lose my life' If such a person thinks it is dangerous, it's wise for him to say so at once without mincing his words.
In the forces, it's difficult to go direct to the commander and tell him that the plan can't work and it's loaded with big risks. This, however, should be acceptable especially when one has read intelligence reports on the possible danger. It could make the commander think of a different way, of attacking the enemy. Options are usually many, not one. This only happens when you don't have mental toughness to question things or give suggestions.
If you fail to talk to your seniors and instead have the Big Boss mentality, with an assumption that the commander knows it all, you may die alongside the same commander or he might live after you're gone. This only happens when you don't have mental toughness to question things or give suggestions
In the army, however much you have trained and have expertise in a certain area, it is necessary to be flexible. This means that although rules are laid down to be followed, at times, they could be bent". It doesn't make sense to stick to laid down procedures when it looks obvious that it's leading you into a disaster. Sadly, at times, such actions end up affecting a specific individual who then is blamed for it.
If you are not flexible, you could end up gencrating lower results. This is because it kills creativity and innovation. Conditions and situations keep changing and this should make every single and individual by shifting the mindset. Creativity is vital for the growth and development because things, people, time and circumstances change.
- What does the writer mean by saying speaking up is importance?
- It shows the speaker a lot of respect
- Speaking up makes it easy to identify seniors from juniors.
- It makes one develop confidence when talking.
- It ensures the communication is effective.
- By saying 'No' When given a command, it shows that
- your state of mind is acceptable.
- you don't easily take in instructions.
- you think faster than others.
- no one is clever as you are.
- For your listeners to confirm that he had been paying attention,
- only your seniors should get you
- statements said should be repeated.
- you should be loud enough.
- there must be many questions asked.
- In a Chinese parliament, one is expected to
- pay attention when being spoken to
- speaking loudly and clearly
- remember the positions people hold.
- express himself freely to all others.
- How do people in the forces pass information to their seniors?
- After getting intelligence reports,
- By talking politely to their commanders.
- If everybody is aware of the danger.
- By asking their seniors for solution problems
- The MAIN use of the intelligence is that
- his commander uses it to win the war
- it could safeguard the soldiers
- No soldier can go to fight without it
- Identifying the soldier to be promoted becomes easy.
- The Big Boss mentality is discouraged because
- both soldiers and the commander are at risk
- the commanders do not like it.
- only the commaders give orders to soldiers.
- it relies on a lot of assumption
- What is the opposite of the word flexible as used in the fourth paragraph?
- Tough
- Rigid
- Brave
- Strong
- By bending rules, the writer means that
- doing the opposite of what the rule says.
- there are rules to be followed.
- not following the rules exactly as expected
- the decision to follow the rules or not to is optional
- Some people are blamed for causing disasters
- as they obviously caused them.
- since they have got injured in the accidents
- as someone has to take the blame anyway.
- they had the capacity to avert it.
- Why would people be flexible in decision making?
- Many decisions are eratic.
- Situations are not stati
- No one knows everything
- Many decisions are not popular
- The BEST title for this passage would be
- Communication within the armed forces
- How commanders intimidate their juniors
- The operation of the Chinese Parliament
- The blame game within the armed forces
COMPOSITION
Below is the beginning of a story. Complete it in your own words, making it as interesting as you can
We were at the parade in the morning when we saw two cars driving into the schol compound. They were parked near the head teacher's office and immediately we dispersed.....
MARKING SCHEME
- B
- D
- B
- C
- A
- B
- D
- C
- D
- B
- A
- C
- A
- B
- D
- C
- B
- A
- D
- C
- A
- B
- D
- B
- D
- C
- D
- A
- B
- D
- A
- C
- B
- C
- D
- A
- B
- A
- D
- A
- C
- D
- A
- B
- A
- B
- C
- D
- B
- A
Mathematics - Class 8 End Term 1 Exam 2021 Set 2
STANDARD 8, END OF TERM 1
MATHEMATICS
NAME....................................................SCHOOL...............................
- What is 8 346 524 in words?
- Eight million three hundred and forty six thousand, five hundred and twenty four.
- Eighty three million forty six thousand five hundred and twenty four
- Eight hundred and thirty four thousand six hundred and fifty two and four tenth.
- Eighty three million four hundred and six thousand and twenty four.
- What is the value of
- 1
- 9
- 12
- 60
- What is 4 899.84 rounded off the nearest whole number?
- 4899
- 4 899.8
- 7890
- 4 900
- What is the LCM of 18, 24 and 36?
- 6
- 72
- 144
- 108
- What is the sum of the total values of digit 2 and digit 7 in the number 4 265 785?
- 200 000
- 700
- 200 700
- 265 700
- Hassan bought the following items from a shop.
3 packets of maize flour at sh. 110
2kg rice for sh. 210 1 1/2kg of ndengu at Sh. 140
2 loaves of bread at sh. 55
If he paid using 2-500 shilling notes, how much balance did he get?- Sh. 140
- Sh. 860
- Sh. 199
- Sh. 805
- What is the value of x in the equation?
- 4
- 2
- 3
- 1
- The area of a square is 3 364m2. What is the length of one side of the square?
- 1 682
- 58
- 841
- 52
- What is the CORRECT order of writing the fractions 2/3, 1/2, 3/5, 4/7 from the smallest to the largest?
- 2/3 , 3/5 , 4/7 , 1/2
- 1/2 , 2/3 , 3/5 ,4/7
- 1/2 ,4/7 , 3/5 ,2/3
- 4/7 ,3/5 , 2/3 ,1/2
- In the triangle ABC below, draw a bisector of angle ABC and angle BCD. Join the two bisectors and let them meet at x. Let point x be the centre of the circle and draw a circle touching the sides ABC. What is the length of the radius?
- 2.5cm
- 5c
- 42cm
- 8.4c
- A rectangular picce of land measures 215m by 65m. Fencing posts are put at an interval of 5m. How many posts are required to fence?
- 56
- 280
- 560
- 112
- Okello bought a jacket for sh. 1 350 after getting a 10% discount. What was the marked price of the jacket?
- Sh. 1 215
- Sh. 1 650
- Sh. 1 500
- Sh. 1 800
- The table below shows the number of crates of a soda delivered in a depot for six days.
Days Mon Tue Wed Thur Fri Sat No of crates 24 32 18 25 27 33
What was the median sale in that week?- 27
- 18
- 33
- 26
- Nyar Gem and Jar Kisumu shared some money in the ratio 2:3. How much more money did Jar Kisumu get than Nyar Gem if they shared Sh. 8 400 in total?
- Sh. 3 360
- Sh. 1 680
- Sh. 5 040
- Sh. 4 200
- What is the value of 0.6+0.4+0.25
0.2- 2.2
- 4.4
- 11
- 3.6
- Which of the following statement is NOT TRUE about a square?
- All sides are equal.
- Has two pairs of parallel sides.
- All interior angles are equal.
- Diagonals are not equal.
- Kamau had the following denominations of money.
2 - 1000 shillings notes
12- 500 shilling notes
8 - 200 shilling notes.
12 - 100 shilling notes
He decided to change all the money into fifty shilling notes How many notes did he get in total?- 408
- 216
- 10 800
- 108
- On a map a road of 12km is represented by 6cm. What is the scale used?
- 1:2 00
- B. 1: 20 000
- 1:200 000
- 1:2 000 000
- What is the simplest form of
- 8x +2y
- 6x
- 4.x + 2y
- 8x
- A rectangular plot has a diagonal of 170m. If the lenth is 150m, how long is the width?
- 120m
- 160m
- 80m
- 270m
- The triangle PQR below is drawn to scale.
What is the size of angle QPR?- 55°
- 74°
- 68°
- 52°
- Ogello is paid sh. 14 375 after working for 25 day's How much does he carn for working 12 days?
- Sh. 575
- Sh. 6000
- Sh 11 500
- SHS 750
- A meeting was attended by 600 people. Out of these 0.14 were men, 0.2 were women and the rest were youth How many youths were there?
- 84
- 204
- 120
- 396
- Terry is twice as old as Tracy but eight years younger than Iriza, If Tracy is y years old. what will be the sum of their ages in 6 years lo come?
- 5y +26
- 5y + 8
- 4y + 26
- 4y + 18
- A family uses 2 - 500ml packets of milk daily. How many litres of milk does the family consume in the month of January. February and March of a leap year?
- 92 litres
- 90 litres
- 89 litres
- 91 litres
- What is the square root of 0.0016?
- 0.0004
- 0.004
- 0.04
- 04
- Kiprono ran round the track 7 times.
How many kilometres did he cover?- 3
- 30
- 300
- 3 000
- Wanjala bought a cow at Sh. 14 000. During the dry season he sold-it making a 15% loss. At what price did he sell the cow?
- Sh 11 900
- Sh. 16 100
- Sh. 2 100
- Sh. 12 150
- A wheel of radius 28cm makes 2 000 revolutions. How many kilometres docsit cover?
- 325 000km
- 3 520km
- 352km
- 3.52km
- What is the value of
1/2 + 1/2(1/3 - 1/6) of 2/3 ÷ 1/4?- 13/18
- 5/18
- 13/24
- 12/17
- Kawira bought 60 mangoes @ sh. 5 each. She spent sh. 100 on transport. During transportaion, 10 mangoes got spoilt and sold the rest at sh 12 each. How much profit did she make?
- Sh. 300
- Sh. 200
- Sh. 150
- Sh. 400
- Line AB below is part of a Rhombus. Angle ABC 65° Complete the Rhombus. What is the length of diagonal BD?
- 5.8cm
- 4cm
- 10.3cm
- 8.6cm
- A bus left Mombasa on Tuesday at 8:30pm. It took 8 hours 45min to reach Nairobi. On what day and time did it get to Nairobi?
- Wednesday 0515hrs
- Wednesday 1715hrs
- Tuesday 1515hrs
- Tuesday 0315hrs
- The pie chart below shows how Mkulima spent his sh. 36 000 salary
How much did he save?- 6 000
- 4 000
- 2 000
- 24 000
- A car travelled a distance of 216km in 3 hours hours and later covered another 144km in 2 hours. What was the average speed in km per hour.
- 72km/h
- 60km/h
- 80km/h
- 90km/h
- The diagram below shows a cuboid.
Calculate the surface area.- 220cm2
- 196cm2
- 168cm2
- 112cm2
- A carton contains 36 - 500g tins of blueband. How many tonnes does such 12 cartons carry?
- 216
- 21.6
- 2.16
- 0.216
- The diagram below sows a Trapezium ABCD
What is the area of the trapezium?- 840cm2
- 420cm2
- 510cm2
- 255cm2
- A tank had water upto 4 full. When 120 litres of water were drawn from the tank, it became 1/2 full. What was the capacity of the tank?
- 160 litres
- 480 litres
- 360 litres
- 340 litres
- At a prayer rally 2 800 men attended. The number of women was 1 800 more than that of men but 3 200 less than that of children. How many people attended the rally?
- 15 200
- 10 600
- 7 400
- 7800
- In the figure below ABCDE is a rhombus and BCD is a triangle. Angle BDC = 54° and line BD = line BC.
What is the size of angle DEA?- 63º
- 68°
- 117°
- 78°
- The table below shows the charges of sending money via money order.
Range Charged upto - 1000 110 1001 - 2500 165 2501 - 5000 225 5001 - 10000 285 10001 - 20000 355
Njagi sent two money orders one of sh. 12 000 and another one of sh. 7 500. How much money in total did he pay at the post office?- Sh. 19 500
- Sh.20 040
- Sh. 640
- Sh. 20 140
- Kirinkai is paid a basic salary of sh. 18 000 and a commission of 4% on all the sales he makes. How much money did he earn in a month he sold goods worth sh. 480 000
- Sh. 19 200
- Sh. 18 000
- Sh. 37 200
- Sh. 19 920
- What is the sixth number in the pattern
1, 4, 9, 16,_____?- 25
- 36
- 49
- 29
- The marked price of a generator is sh. 36 000 but a discount of 20% is given on cash payment. On hire purchase a deposit of sh. 6 000 and monthly instalment of sh. 3 000 for 12 months. How much more is the hirepurchase price than cash price?
- Sh. 42 000
- Sh. 28 800
- Sh. 12 000
- Sh. 13 200
- The table mat below is made up of rectangular cloth joined to a semi-circular ones.
What is the area of the table mat?- 12 712cm2
- 8808cm2
- 4 704cm2
- 8 710cm2
- The table below shows the number of crates of broad sold by a supplier.
DAY MON TUE WED THUR FRI SAT SUN No. of crates sold 16 15 7 6 13 8 12
If a crate holds 15 breads, how many breads did he sell that week?- 77
- 1155
- 1005
- 67
- The mass of an empty lorry is 7.2 tonnes. When loaded with 60 bags of maize each with a mass of 90kg and 45 bags of rice each of mass 50kg. What is the mass of loaded lorry in tonnes?
- 14.85 tonnes
- 7650 tonnes
- 7.65 tonnes
- 14 850 tonnes
- The number of road accidents recorded in the country in the year 2019 was 17 000.In the year 2020 the number decreased to 14 450. What was the percentage decrease?
- 1712%
- 85%
- 15%
- 20
- The graph below shows the journey by Kipkewewe from Kapchorua to Kiplagich and back.
What was the average speed for the whole journey?- 12km/h
- 30km/h
- 24km/h
- 40km/h
MARKING SCHEME
- A
- B
- D
- B
- C
- A
- D
- B
- C
- A
- D
- C
- D
- B
- C
- D
- B
- C
- D
- C
- A
- B
- D
- A
- D
- B
- D
- A
- D
- A
- B
- B
- A
- B
- A
- A
- D
- B
- B
- A
- C
- D
- C
- B
- D
- A
- B
- D
- C
- C
Social Studies and Religious Education - Class 6 End Term 1 Exam 2021 Set 2
STANDARD 6, END OF TERM 1 EXAM
SOCIAL STUDIES AND RELIGIOUS EDUCATION
NAME....................................................SCHOOL....................................
SECTION A
SOCIAL STUDIES
Study the map of N. ere area and answer questions 1 - 7
- What is the direction of the quarry from the National park?
- North East
- South West
- North West
- South East
- The peoplee of Ndere area are mainly
- Christians
- Traditionalists
- Pagans
- Hindus
- What is the climate of the North Western part of Ndere Area?
- Cool and wet
- Hot and wet
- Hot and dry
- Cool and dry
- Which one of the following economic activities is NOT carried out in Ndere area?
- Tourism
- Lumbering
- Crop farming
- Fishing
- What feature is found at the part marked M on river Kembo?
- Tributary
- Estuary
- Delta
- Confluence
- The administrative head of Ndere area is likely to be
- a senator
- a member of county assembly
- a governor
- the president
- Which type of vegetation is found at the South Eastern part of Ndere area?
- Grassland vegetation
- Mountain vegetation
- Riverine vegetation
- Papyrus reeds
- The following Kenyan communities belong to the Western Bantus. Which one does NOT?
- Abaluhyia
- Abakuria
- Abagusii
- Ameru
- Which one of the following is the most widespread means of sending messages to large number of people. Use of
- newspapers
- television
- radio
- messengers
- Which one of the following weather instruments is used to measure both the strength and direction of wind?
- Which of the following is the most expensive way of preserving fish?
- Smoking
- Using a refrigerator
- Sun drying
- Salting
- The largest relief region in Kenya is the
- plateau
- lake basin
- Rift valley
- highlands
- The following rivers drain into lake Turkana except
- River Omo
- River Turkwel
- River Kerio
- River Ewaso Nyiro North
- Kenya is divided into constituencies.
- 47
- 68
- 290
- 350
Use the diagram below to answer questions 15 - 16.
- The side marked B is known as
- leeward side
- rainshadow
- Windward side
- convectional side
- Which economic activity cannot be carried out in the region marked A?
- Cash crop farming
- Dairy farming
- Pastoralism
- Fish farming
- Which one of the following is NOT among the Kalenjin age sets?
- Chumo
- Nyong
- Maina
- Mwangi
- General elections are held in Kenya after every _______ years.
- 5
- 10
- 20
- 1
- Jamhuri day is celebrated on ________ year.
- 12th December
- 1st June
- 1st May
- 20th October
- The road sign shown below means
- road junction ahead
- hospital ahead
- right bend ahead
- no entry
- Which of the following factors mainly influences the way penple are distributed in an area?
- Climate
- Soil
- Relief
- Latitude
- Which one of the following is the main line of latitude?
- The Greenwich Meridian
- The Tropic of cancer
- The Tropic of capricon
- The Equator
- In which year did Kenya become a British colony?
- 1895
- 1920
- 1952
- 1963
- What was the main economic activity of the Semites who settled at the Coast of Kenya?
- Cattle Keeping
- Hunting and gathering
- Trading
- Crop farming
- Which one of the following countries in Eastern Africa does not have a coastal plain?
- Eritrea
- Uganda
- Djibouti
- Somalia
- What is the main function of the judiciary?
- It makes laws
- It interprets the laws
- It implements government policies
- It arrests criminals
- Lawlessness can lead to all the following except
- slow development
- loss of property and life
- civil wars among communities
- rapid development
- Who among the following traditional Kenyan leaders did not resist the British?
- Nabongo Mumia
- Koitalel Arap Samoei
- Mukite wa Nameme
- Mekatilili wa Menza
- Which of the following countries border Kenya to the North West
- Ethiopia
- Sudan
- Uganda
- South Sudan
- Acacia and baobab trees are mainly found in the
- mountain vegetation
- desert vegetation
- Savannah vegetation
- riverine vegetation
- A group of people who are related by blood, marriage or adoption form:
- a family
- a clan
- an age set
- a community
- Education in the past was passed through the following methods except
- riddles
- books
- proverbs
- songs
- Planting of trees where some have been cut is known as
- afforestation
- deforestation
- agro forestry
- re- afforestation
- Which one of the following is NOT a human right?
- Right to education
- Right to life
- Right to safe environment
- Right to mob justice
- A good citizen is the one who does the following except
- fights corruption
- pays taxes
- practices honesty
- practices nepotism
- The exchange of goods and services for other goods and services is called
- currency trade
- monetary trade
- traditional trade
- barter trade
- Which one of the following is NOT a product of traditional industries?
- Vest
- Spear
- Cowbell
- Drum
- Three of the following are species of trees found in natural forests. Which is NOT?
- Mvule
- Camphor
- Pine
- Mahogany
- The walls of the Rift Valley are called
- ranges
- faults
- escarpments
- Drifts
- The first prime minister of Kenya was
- Jomo Kenyatta
- Eliud Mathu
- Raila Odinga
- James Gichuru
- Which one of the following Kenyan communities does not belong to the Mijikenda?
- Agiriama
- Wataita
- Ribe
- Chonyi
- Carrying of goods from one place to another is called:
- communication
- transport
- trading
- tourism
- Debates in the County Assembly are chaired by
- the Governor
- the Member of County Assembly
- the Speaker
- the County Commission
Us the map below to answer quesjons 44 - 47
- The tourist attraction marked K is
- Sibiloi National park
- Malka Mari National park
- Awara plains
- Lotikipi plains
- The border town marked M is likely to be
- Moyale
- Lodwar
- Mandera
- Wajir
- The river marked N is
- River Kerio
- River Turkwel
- River Ewaso Nyiro North
- River Yala
- The mountain marked L was formed through
- volcanicity
- faulting
- folding
- erosion
- Which one of the following is a manufacturing industry?
- Cement making
- Fruit canning
- Printing
- Banking
- The practise of growing fruits, vegetables and flowers is called
- horticulture
- viticulture
- floriculture
- market gardening
- The following are conditions favouring the growing of a certain crop
Fertile soils
Heavy rainfall
Well drained, slightly acidic soils
Cool temperaturesWhich crop requires the above conditions?- Maize
- Cotton
- Wheat
- Sugarcane
- Which body in Kenya is in-charge of managing the National Games Parks?
- The Kenya Wildlife Services
- The County Government
- The Kenya Defence Forces
- The Kenya Forestry Department
- Which one of the following is the main function of schools?
- To prepare learners for future life
- To equip learners with knowledge and skills
- To educate learners on good morals
- To help learners on good morals
- Which means of transport is used to transport petroleum from Mombasa to Kisumu?
- Pipeline
- Cable
- Railway
- Road
- What is another name for alluvial soil?
- Loam soil
- Red volcanic soil
- Young soil
- Black cotton soil
- Which one of the following activities does not cause soil erosion?
- Overgrazing
- Monocropping
- Deforestation
- Afforestation
- Which one of the following mountains in Eastern Africa is NOT correctly matched with the country where it is found?
- Ras-Dashan - Ethiopia
- Meru - Tanzania
- Elgon - Sudan
- Ruwenzori -- Tanzania
- Rusinga Island is found in
- lake Victoria
- the Indian Ocean
- Lake Turkana
- Lake Baringo
- The Turkana, Maasai, Njemps and Samburu are
- Plain Nilotes
- Highland Nilotes
- River Lake Nilotes
- Western Bantus
- The following are factors that promote peace in the society except:
- increased corruption among leaders
- respect for human right
- religious tolerance among people
- respect for the rule of law
- The Independent Electoral and Boundaries Commission (IEBC) is headed by
- the President
- the Returning Officer
- the Elections Officer
- the IEBC Chairman
SECTION B
CHRISTIAN RELIGIOUS EDUCATION
- The book in the Bible wnion talks about the story of creation is
- Exodus
- Genesis
- Leviticus
- Mathew
- Who was the first person to lead the Exodus of the Israelites from Egypt?
- Moses
- Aaron
- Joshua
- Caleb
- Which one of the following was NOT a responsibility given to both the man and the woman that God created?
- To make money
- To have many children
- To care for all the things that God had made
- To have power over the fish, birds and all the animals.
- The Israelites first celebrated Passover while in: -
- Canaan
- Jerusalem
- Galilee
- Egypt
- Joseph was able to overcome the temptations from Potiphar's wife mainly he was
- forgiving
- hardworking
- faithful
- humble
- In Genesis 1:26, which creatures were created last?
- Fish
- Birds
- Human beings
- Animals
- Among the three kings of Israel, who among them was being tormented by evil spirits?
- David
- Saul
- Solomon
- Jeroboam
- Which one of the following parables of Jesus talks about repentance? The parable of:
- the sower
- the lost son
- the lost coin
- the judge and the widow
- Jesus washed the disciples' feet to demonstrate
- love and hate
- pride and love
- humility and love
- selfishness and humility
- Who among the following was forced to carry the cross for Jesus?
- Simon of cyrene
- Simon Pete
- John the Baptist
- Joseph of Arimathea
- Jesus performed his first miracle at a wedding at
- Cana
- Capernaum
- Jericho
- Jerusalem
- All the following women went to the tomb where Jesus had been buried EXCEPT:
- Mary Magdalene
- Joanna
- Salome
- Mary the mother of James
- Which is the third book in the four Gospels in the New testament?
- Mathew
- Mark
- Luke
- John
- "Salvation has come to this house today, for this man also is a descendant of Abraham. (Luke 19:1-10) Jesus was referring to which one of the following people?
- Judas
- Paul
- Zacchaeus
- Simon Peter
- All the following activities were done by the early believers EXCEPT
- learnt from the Apostles
- shared meals and prayers
- praised God and prayed together
- organised harambee meetings
- In Gen. 12: 1-9 who obeyed and trusted God and God blessed him?
- Abraham
- Moses
- Joshua
- Caleb
- Jesus shared the Last Supper with His disciples before His
- Death, crucifixion and arrest.
- Arrest, death and crucifixion
- Arrest, crucifixion and death
- Crucifixion, baptism and death
- Which one of the following is NOT a name that refers to the Eucharist?
- the Holy Communion
- the Manna
- the Holy mass
- the Lord's table
- The disciples received the gift of the Holy Spirit on:
- Christmas
- Pentecost
- Easter
- Good Friday
- According to Ephesians 4:11. God gave different gifts to people Which gift did he not give among the following?
- singers
- Apostles
- Prophets
- Evangelists
- African traditional communities believed that when a person died, he/she joined the
- pastors
- friends
- medicinemen
- ancestors
- One of the following was NOT an activity conducted by the ancestors in African traditional societies. Which one is it?
- They began a clan
- They solved disagreements
- They made sure that families lived together in peace
- They forced children to go to school
- What name do the Bukusu call their God?
- Ngai
- Were
- Nyasaye
- Mulungu
- Which one of the stages in traditional African communities did NOT mark new life?
- Birth
- Initiation
- Marriage
- Baptism
- Which one of the following practices can end a friendship?
- Love
- Gossip
- Kindness
- Thankfulness
- Who among the following people are NOT needy?
- The orphans
- The wealthy
- The aged
- People living with HIV/AIDS
- Christians can live the new life well by the help
- friends
- parents
- teachers
- The Holy Spirit
- Christians believe that they can get new life when they
- believe in the priest
- believe in the ancestors
- believe in Jesus Christ
- believe in the trinity
- Christians share new life with others by
- reading the Bible only
- doing good and helping one another
- helping the rich
- preaching the word of God to the poor
- Mary's father wants her to drop out of school and get married to a rich man. As a Christian, Mary should
- accept to get married
- talk arrogantly to her fathe
- run away from home
- report the matter at the chiefs office.
MARKING SCHEME
- A
- C
- A
- D
- D
- C
- D
- D
- C
- D
- B
- A
- D
- C
- B
- C
- D
- A
- A
- A
- A
- A
- B
- C
- B
- B
- D
- A
- D
- C
- A
- B
- D
- D
- D
- D
- A
- C
- C
- A
- B
- B
- C
- B
- A
- C
- A
- A
- A
- C
- A
- A
- A
- C
- D
- C
- A
- A
- A
- C
CRE
- B
- A
- A
- D
- C
- C
- B
- B
- C
- A
- A
- B
- C
- C
- D
- A
- C
- B
- B
- A
- D
- D
- C
- D
- B
- B
- D
- C
- B
- D
Science - Class 6 End Term 1 Exam 2021 Set 2
STANDARD 6, END OF TERM 1 EXAM
SCIENCE
NAME....................................................SCHOOL.............................
- The diagram below is a weather instrument.
It is used to measure- the direction of wind
- the speed of wind
- the direction of speed of wind
- the strength and direction of wind.
- The other name for asymptomatic stage of HIV/AIDS is
- full blown stage
- incubation stage
- window stage
- symptomatic stage
- Which one of the following is NOT a physical change in girls during adolescence?
- Onset of menstruation
- Broadening of shoulders
- Enlargement of breasts
- Growth of pubic hair
- Which statement is NOT TRUE about the tooth drawn below?
- They are part of the milk teeth
- They are eight in each jaw
- They are used for grinding food
- It is called premolars
- Which one of the following is a common characteristic to both a chameleon and a salamander?
- Their bodies are covered with scales
- They lay unfertilised eggs
- They give birth to live young ones
- They have varied body temperatures
- The following are characteristics of a certain matter
It has a definite mass
It changes state when cooled
It does not have a definite shape
It does not have a definite volume.
The substance described above is likely to be- water
- sand
- flour
- oxygen
- Three of the following plants have the same characteristics except
- fern
- lichen
- liverwort
- mould
- Which bottle will produce the highest sound when hit with a nail?
- The tooth problem that is associated with a hole in the tooth is known as
- tooth cavity
- tooth decay
- bad breath
- bleeding gum
- Which one of the following animals are vertebrates?
- Rabbits and earthworm
- Snakes and frogs
- Spiders and fish
- Snails and ducks
- The diagram below shows a child suffering from a certain decrease.
The child is likely to suffer from- Kwashiorkor
- rickets
- anaemia
- marasmus
- Green plants make their own food in the presence of all the following except
- water
- sunlight
- chlorophyll
- oxygen
- Which one of the following is NOT a form of medicine?
- Powder
- Tablets
- Syrup
- Liquids
- The diagram below shows a germinating bean seed.
The part marked N helps in the absorption of- oxygen and carbondioxide
- water and oxygen
- chlorophyll and air
- sunlight and water
- HIV/AIDS is spread through all the following ways except
- sexual intercourse
- blood transfusion
- shaking hands
- sharing piercing objects
- The chart below shows classification of plants.
Which of the following plants cannot fit at the part marked Q?- Mould
- Mushroom
- Toadstool
- Lichen
- The part of the breathing system that makes the lungs to expand and contract when breathing is the
- bronchus
- ribs
- diaphragm
- trachea
- The following are parts of the male reproductive system except
- testis
- urethra
- penis
- uterus
- The rising of water in soil is known as
- capillarity
- drainage
- soil profile
- leaching
- The diagram below shows a root system.
The following plants have the same root system as the one shown above except- groundnut
- rice
- green gram
- blackjack
- Medicines used to treat known diseases are called
- antibiotics
- vaccines
- painkillers
- sedatives
- The set up below was carried out by std. 5 pupils of Ojwando primary school.
Which component of soil were they investigating?- Organic matter
- Water
- Air
- Mineral particles
- Which one of the following factors does not affect sinking and floating?
- Shape
- Size
- Material
- Weight
- Which one is NOT a source of light?
- Moon
- Stars
- Candle
- Sun
- Which one of the followng materials has a definite mass, shape and volume?
- Wood
- Milk
- Water vapour
- Paraffin
- Which phase of the moon cannot be seen at all?
- The following are characteristics of certain clouds:
Feathery
Found high in the sky
Cover the whole sky
A flat base Which one shows a characteristic of nimbus clouds?- (iv)
- (ii)
- (ii)
- (i)
- Std. 5 pupils at Rapogi Primary School carried out an experiment as shown below.
Heat travelled from point Q to R through- conduction
- convection
- radiation
- melting
- Lack of vitamin D in the diet causes a deficiency disease known as
- marasmus
- kwashiorkor
- anaemia
- rickets
- A material that does not allow heat to pass through it is known as
- a conductor
- a metal
- opaque
- an insulator
- Three of the following are uses of light except
- warming the house
- reading comfortably
- discouraging pests
- avoiding accidents
- Std. 6 pupils did the experiment below ta investigate a certain property of soil.
The type of soil marked N is likely to have:- air spaces
- large air spaces
- big particles
- the best capillarity
- Which process in the change of state in matter takes place when temperature is decreased?
- Freezing
- Evaporation
- Melting
- Expansion
- The following are characteristics of a certain vertebrate
Warm blooded
Can fly
Has fur and hair on the body
Gives birth to live young ones
The above animal is likely to be- kangaroo
- bat
- ostrich
- seal
- Which one of the following animals moves by galloping?
- Snake
- Tortoise
- Horse
- Elephant
- The following are all tuber crops. Which one is NOT?
- Yams
- Cassava
- Wheat
- Arrowroots
- The removal of undigested food from the body is called
- egestion
- ingestion
- digestion
- excretion
- The following are functions of plant leaves. Which one is NOT?
- Transpiration
- Photosynthesis
- Absorption
- Food storage
- The experts who study the stars and other heavenly bodies are called
- forecasters
- meteorologists
- astronomy
- astronomers
- The transfer of heat without a medium takes place through
- conduction
- convection
- radiation
- contraction
- Which one of the following is NOT a characteristic of animals?
- They die
- They feed
- They reproduce
- They make their own food
- Which one of the following group of food constitute a balanced diet?
- Cabbage ugali salad
- Beans, rice, kales
- Meat, chapati beans
- Water meion spinach ripe bananas
- The weather instrument works under one of the following principles. Which one?
- liquids expand on heating and contraction on cooling
- air expands on heating and contracts on cooling
- Air in motion
- Matter occupies space
- Clothes dry fastest when the weather is
- rainy and cloudy
- windy and sunny
- sunny and calm
- sunny and cloudy
- Which one of the following is measured using a beam balance?
- Weight
- Volume
- Mass
- Friction
- Which one of the following is NOT a recreational use of water?
- Surfing
- Making fountains
- Boat racing
- Swimming
- Which one of the following is NOT a poultry?
- Goose
- Turkey
- Duck
- Ostrich
Use the diagram below to answer questions 48-49
- The absorption of digested food takes place in the part marked:
- N
- Z
- Y
- Q
- What are the names of the parts X, Y, Z and Q respectively?
- Rectum, stomach, illeum, colon
- Gullet, stomach, illeum rectum
- Trachea, stomach, coion, rectum
- Oesophagus stomach, colon rectum
- The ability of the body to defend itself
against diseases is called- immunity
- immunisation
- syndrome
- immunodeficiency
MARKING SCHEME
- D
- B
- B
- B
- D
- D
- D
- C
- A
- B
- A
- D
- A
- B
- C
- D
- C
- D
- A
- B
- A
- A
- B
- A
- A
- A
- B
- A
- D
- D
- A
- A
- A
- B
- C
- C
- A
- C
- D
- C
- D
- B
- B
- B
- C
- B
- D
- A
- D
- A
Kiswahili - Class 6 End Term 1 Exam 2021 Set 2
DARASA LA 6, MWISHO WA MUHULA 1
KISWAHILI
JINA....................................................SHULE.............................
Soma vifungu vifuatavyo. Kina nafasi 1 hadi 15. Kwa kila nafasi, umepewa maneno manne hapo. Chagua jibu lifaalo zaidi kati ya yale uliyopewa
Mtoto 1 aliacha mchezo 2 aliokuwa nao na akafuata maneno 3 akiambiwa afuate na baba yake. Alitokea 4 mtoto 5 6 wote 7 darasani 8 , kwa hivyo mtihani 9 yeye ndiye 10 wa kwanza.
- A. ule B. yule C. wale D. vile
- A. yake B. zake C. wake D. lake
- A. aliyokuwa B. aliokuwa C. alizokuwa D. alilokuwa
- A. kua B. kuka C. kuwa D. kukuwa
- A. mhodari B. hodari C. mbora D. mshujaa
- A. kumliko B. kuwaliko C. kuliko D. kukiliko
- A. huo B. hilo C. hiyo D. humo
- A. mwao B. lao C. yao D. nao
- A. ulikuja B. ulipokuja C. uliyekuja D. ilipokuja
- A. atakayekuwa B. aliyekuwa C. angekuwa D. angalikuwa
Ama kweli, elimu ni bahari 11 haina mwisho. Kila siku, mja 12 jambo 13 ambalo hakulijua. Nayo elimu humfaa mmiliko wake kwa 14 na marefu. Mtu aliyesoma, kwa mfano, hupata kazi nzuri na hujua 15 na watu.
- A. ambalo B. ambao C. ambaye D. ambayo
- A. amejifunza B. anajifunza C. hujifunza D. atajifunza
- A. mpya B. jipya C. mapya D. lipya
- A. mapana B. mengi C. machache D. mageni
- A. Kutengana B. kutengemana C. kutangamana D. kutegana
Kutoka swali la 16 mpaka 30, chagua jibu lililo sahihi
- Kitenzi 'choka katika kauli ya kutendesha ni
- chokesha
- choza
- chosha
- chokea
- Tumia kiunganishi mufti kujaza pengo
Niliweza kumwua ndovu ______ swara- laiti
- ilhali
- sembuse
- lakini
- Udogo wa neno 'mwana' ni
- jijana
- jana
- Kimwana
- kijana
- Chagua kinyume cha neno lililopigiwa mstari katika sentensi ifuatayo
Baada ya kutabasamu, alianza kuhutubia hadhira- kucheka
- kununa
- kughafilika
- kulia
- Kamilisha methali ifuatayo
Dua la kuku halimpati- mjinga
- ndege
- mbwa
- mwewe
- Sehemu ya chini ya sikio huitwa
- ndewe
- masharubu
- paji
- mashavu
- Andika wingi wa sentensi ifuatayo.
Mti uzaao embe unaitwa mwembe.- Miti zizaazo miembe zinaitwa maembe.
- Miti izaayo miembe inaitwa maembe.
- Miti izaayo maembe huitwa myembe.
- Miti izaayo maembe inaitwa miembe.
- Jaza pengo kwa kivurishi kilaache
Mtoto _____ alianguka vibaya sana- mwenye
- wenyewe
- mwenyewe
- enyewe
- Mtu anayefanya kazi ya kujenga kwa mawe huitwa
- sonara
- mwashi
- hamali
- nokoa
- Tegua kitendawili hiki
Njoo umwone umpendaye.- Kioo
- Picha
- Runinga
- Filamu
- Malipo ya kuolewa huitwa
- nauli
- koto
- mahali
- mahari
- Kanchiri, shimizi, kaptura na kocho kwa jina moja ni
- nguo
- mavazi
- mapambo
- maumbo
- Bainisha akisami inayoonyesha subui
- 1/7
- 1/3
- 1/8
- 1/9
- . Tumia '-ingine kwa usahihi:
Mama amenunua nguo _______ nyingi- zingine
- ingine
- nyingine
- mengine
- Tumia 'amba' kwa usahihi
Mwalimu aliyeingia na vitabu ni Bwana Mirobi.- Mwalimu ambaye anayeingia na vitabu ni Bwana Mirobi
- Mwalimu ambaye aliyeingia na vitabu ni Bwana Mirobi
- Mwalimu ambaye aingiaye na vitabu ni Bwana Mirobi
- Mwalimu ambaye aliingia na vitabu ni Bwana Mirobi.
Soma kifungu kifuatacho kisha ujibu maswali 31-40
Adili alijiandaa kwa safari ya kuitikia wito wa mfalme.
Farasi watatu walitandikwa matandiko mazuri. Yeye alipanda farasi mmoja, na mmoja kwa kila nyani. Ikibali alipanda farasi wake mwenyewe. Farasi wa Adili na yule wa Ikibali walikwenda sambamba njiani. Nyuma yao waliandamana nyani juu ya farasi. Kila mtu aliyeona nyani wamepanda farasi alistaajabu. Mnyama kupandwa na mnyama! Ulikuwa mpeo wa miujiza kwa watu.
Vinywa vya umati wa watu vilikuwa wazi kwa kivumo cha lo salala! Wakati umefika wa mawe kusema, miti kujibu na wanyama kuwa watu! Ikibali aligeuza uso wake kwa Adili akasema kwa ucheshi, "Mbwa wanatubwekea kama walionusa kundi la wanyama wanaowindwa." Adili alikubali kwa kuinamisha kichwa akitabasamu. Walisafiri hivi mpaka nchiya mfalme. Baada ya kutua, Adili alipelekwa mbele ya mfalme na manyani wake.
- Adili alijizatiti kwenda
- kumsalimia mfalme
- kuonana na mfalme
- kumwua falme
- kuwatandika farasi
- Farasi watatu waliandikwa matandiko walikuwa ni wa kuwabeba
- Mfalme, Adili na Ikibali
- Adili, Ikibali na mfalme
- Ikibali, Adili na nduguze
- Adili na nyani wawili
- Farasi wa Ikibali na wa Adili walikwenda sambamba. Maana yake ni kuwa walikwenda
- mmoja mblele mwingine nyuma
- karibu karibu
- unyounyo mwendo wa asteaste
- sawasawa ubavu kwa ubavu
- Manyani waliandamana nyuma ya Ikibali na Adili. Ndiko kusema Adili na Ikibali waliandamana na nyani
- sambamba
- unyounyo
- mkabala
- chapuchapu
- Kilichowashangaza watu zaidi katika habari hii ni
- Adili kuongozana na ikibali
- Adili kupanda farasi.
- Nyani kupanda farasi
- Mawe kusema, miti kujibu na wanyama kuwa watu
- kibali aliposema kwa ucheshi, bila shaka
- alinuna
- alighadhabika
- alinong'ona
- alitabasamu
- Mbwa alibweka. Je, wangekuwa fahali wangefanyaje?
- Wengeroroma
- Wangenguruma
- Wangekoroma
- Wangetetea
- Ikibali alipogeuza uso wake kwa Adili, bila shaka
- alimtazama Adili
- alimpa Adili kisogo
- alimkabidhi Adili
- hakumwangalia ana kwa ana
- Walipofika na kuwasili ughaibuni
- mfalme waliwalaki
- nyani walichoka
- Adili na Ikibali waliagana
- Adili alifikishwa maskanini pa mfalme
- Kauli ipi si sahihi kulingana na makara haya?
- Watu walishangazwa na nyani waliopanda farasi
- Watu walishangilia ili nyani wapande farasi
- Mbwa nao waliobweka walipowaona Ikibali na Adili
- Adili na nyani waliitwa na mfalme
Soma barua ifuatayo kisha ujibu maswali 41 hadi 50
Zera Ahmed.
S.L.P 27001,
MOMBASA
27-01-2001
Meneja wa Benki Kuu,
S.L.P 20101
NAIROBI.
KUH: OMBI LA KAZI
Mimi nina umri wa miaka thelathini, nimesomea kazi hii ya kufanya kazi kwenye benki kama mhasibu. Niliupata waraka mliokuwa mmetuma mkitafuta mhasibu. Mimi ni mmoja wa wahasibu wale bora na maarufu zaidi nchini.
Nimeisomea kazi hii katika mojawapo wa vyuo vikuu nchini. Nilikuwa katika chuo kikuu kisha nikajaribu kufanya kazi kwa miaka miwili kwani nilikuwa nikijua kuwa, haba na haba hujaza kibaba.
Mimi ni stadi katika hisabati na lugha nyingine nyingi kama vile Kiswahili, King'eng'e, Kifaransa, Kijerumani pamoja na lugha nyingine nyingi.
Sipendi mapendeleo labda katika kabila, aila au hata rangi ya sura.
Huu ndio mwanya peke yake ninao wa kupata kazi hii ya uhasibu. Tafadhali ninakusihi unipe kazi hii.
Wako mwaminifu,
Zena Ahmed.
- Barua ya aina hii huitwa
- barua ya kindugu
- barua ya kirafiki
- barua rasmi
- barua kuu
- Anwani ya pili katika barua hii ni ya
- mwandishi
- mwandikiwa
- Zena
- mhasibu
- Barua hii iliandikwa mwezi gani?
- Februari
- Machi
- Juni
- Januari
- Nia ya mwandishi huyu kuandika barua hii ni
- Kuwa meneja
- kuenda chuo kikuu
- kuwa tarishi wa benki
- ombi la kazi katika benki
- Mwandishi amesomea kasi ya
- utabibu
- uhasibu
- ualimu
- ukadamu
- Kazi ya uhasibu ni ipi?
- Kazi ya kuhesabu pes
- Amali ya kuchunga pesa
- Riziki ya upelelezi
- Kazi ya ufundi
- Baadhi ya mapendeleo ambayo mwandishi hayapendi na yametajwa ni kama vile
- ukabila
- jinsia
- lugha
- elimu
- Mwandishi wa habari hii amesoma hadi
- shule ya msingi
- chuo kikuu
- shule ya upili
- chekechea
- Zena Ahmed alisomea kazi hii ya uhasibu wapi?
- Chuo kikuu
- Shule ya upili
- Shule ya msingi
- Chuo cha ufundi
- Mwandishi wa habari aliandika barua akiwa wapi?
- Makerere
- Mombasa
- Benki
- Nairobi
INSHA
Andika insha kuhusu: SHEREHE YA SIKU YA KUZALIWA KWANGU
MARKING SCHEME
- A
- C
- A
- C
- B
- C
- D
- A
- B
- B
- D
- C
- B
- A
- C
- C
- C
- D
- B
- D
- A
- D
- C
- B
- A
- D
- B
- A
- C
- D
- B
- D
- D
- B
- C
- D
- A
- A
- D
- B
- C
- B
- D
- D
- B
- A
- A
- B
- A
- B