QUESTIONS
SECTION A (30 marks)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided
- Give two disadvantages of intensive system of farming. (1mk)
- List four methods of farming. (2mks)
- Give the meaning of the following terms:
- nitrogen fixation into the soil; (1mk)
- phosphorus fixation in loss of soil fertility. (1mk)
- Give four reasons for keeping livestock health records on the farm. (2mks)
- Explain the relationship between scarcity and choice as used in agricultural economics. (2mks)
- Sate two reasons for land fragmentation in Kenya. (1mk)
- Give four advantages of individual owner operator tenure system as practiced in Kenya. (2mks)
- Sate four features that should be considered when choosing water pipes for use on the farm. (2mks)
- Give four reasons for treating water for use on the farm. (2mks)
- Name four statutory boards that are involved in the marketing of crop produce in Kenya. (2mks)
- State four marketing functions of Kenya Co-operative Creameries 9K.C.C.). (2mks)
- Give two reasons for carrying out each of the following operations in land preparation:
- rolling; (1mk)
- leveling. (1mk)
- Name three recommended practices that should be carried out when clearing the bush during land preparation. (11/2 mks)
- State five advantages of zero grazing. (21/2 marks)
- Give four factors that would determine the stage at which a crop is harvested. (2mks)
- Name two classes of weeds on the basis of each of the following:
- growth cycle; (1mk)
- plant morphology. (1mk)
SECTION B (20 marks)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided.
- Below is a diagram of a weed. Study the diagram carefully and answer the questions that follow.
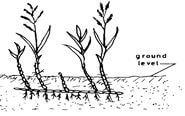
- dentify the weed illustrated above. (1/2mk)
- Why is the weed illustrated above difficult to control? (1mk)
- State four ways in which the weed can be controlled in a field of maize.(2mks)
- The table below shows pH values of different soil samples. Study it and answer the questions that follow.

- Which soil sample has the highest acidity? (1/2mks)
- State two ways in which the pH value of sample S8 can be lowered.(1mk)
- Which of the above soil samples is suitable for growing tea? (1/2mk)
- Explain how agroforestry tree seeds should be prepared after collection in readiness for planting. (4mks)
-
- The diagrams below represent two ways in which a crop was pruned.
Study them carefully and answer the questions that follow.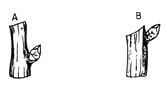
- Which diagram represents the correct way of pruning? (1/2mks)
- Give a reason for your answer in (i) above. (1mk)
- State two ways in which pruning assists in controlling crop diseases. (1mk)
- The diagrams below represent two ways in which a crop was pruned.
- On 1st January 2009, Kaburu Farm started farm operations with Ksh 30,000 cash. During the month, the farm made the following transactions. Study the transactions and prepare a cash analysis for Kaburu Farm for the month of January. (51/2 mks)
Date Transaction Amount (Ksh)
05/0109 Livestock sales 80,000
08/01/09 Crop sales 50,000
15/01/09 Bought seed for planting 7,000
20/01/09 Paid K.F.A. for fertilizer 16,400
25/01/09 Bought livestock feeds 50,000
30/01/09 Paid wages for planting & weeding 56,000
31/01/09 Received cash from K.C.C for milk delivery 120,000
31/01/09 Paid transport charges for milk delivery 9,000 -
- What do the figures 18:46:10 on a fertilizer bag represent? (1½ mks)
- Calculate the quantity of filler materials in the fertilizer in (a) above.(1mk)
SECTION C (40 marks)
Answer any two questions in this section in the spaces provided after question 25.
-
- Explain eight factors that can encourage soil erosion. (8 mks)
- Describe the seven management practices that should be carried out on a vegetable nursery after sowing seeds until the seedlings are ready for transplanting. (7 mks)
- State five soil factors that should be considered when selecting a crop to grow in an area. (5mks)
-
- Outline five ways in which high temperature affects agricultural production in Kenya. (5mks)
-
- Explain four presentations that should be observed when harvesting cotton. (4mks)
- Describe the harvesting of sugar cane. (3mks)
- Explain eight factors that should be considered when planning to set up a farm business. (8mks)
-
- Explain six physical methods that can be used to control crop pests on the farm. (6mks)
- Describe the production of bulb onions under the following sub-headings:
- field management; (4mks)
- harvesting. (3mks)
- Explain seven factors that influence seed rates in crop production.(7mks)
Marking Scheme
- Disadvantages of intensive system of farming.
- Requires high initial capital/Expensive
- Is labour expensive
- Requires high level of management/skilled labour (2 x 1/2 = 1 mark)
- 4 methods of farming.
- Shifting cultivation
- Nomadic pastoralism
- Organic farming
- Mixed farming
- Agroforestry (4 x 1/2 = 2 marks)
-
- Nitrogen fixation
- Process in which atmospheric nitrogen is converted to nitrates for plant uptake. (1 x 1 = 1 mark)
- Phosphorous fixation
- Process in which phosphorous combines with other elements to form compounds that cannot be absorbed by plants. (1 x 1 = 1 mark)
- Nitrogen fixation
- 4 reasons for keeping livestock health records.
- Help in calculation of treatment and health costs
- Help in culling/selecting livestock
- Help in future diagnosis treatment and control measures
- Help determine the common diseases and parasites/prevent diseases and parasites
- Help to support livestock insurance claims (4 x 1/2 = 2 marks)
- Relationship between scarcity and choice.
- Scarcity is where production resources are limited in supply relative to demand; therefore a choice has to be made on which enterprise(s) to allocate the limited resources. (2 marks - mark as a whole)
- 2 reasons for land fragmentation.
- Buying/selling/paying debts/compensation
- Inheritance
- Settlement and resettlement
- Gift/donations
- Shifting cultivation (2 x 1/2 = 2 marks)
- Advantages of individual tenure system.
- Easy to acquire credit.
- Land disputes are minimized
- Long term investment is encouraged
- Incentive to conserve and improve land
- Easy to plan and make decisions
- Easy to sell/lease whole or part of the land. (4 x 1/2 = 2 marks)
- 4 features for choosing powers
- Durability
- Strength/ability to withstand pressure/thickness of the wall of the pipe
- Diameter/size of the pipe
- Workability/manoeverability of the pipe
- Colour (4 x 1/2 = 2 marks)
- 4 reasons for treating water.
- Remove chemical impurities/softening of water
- Kill disease causing organisms/kill germs/pathogens
- Remove bad smells and taste
- Remove impurities of solid particles (4 x 1/2 = 2 marks)
- 4 Statutory Boards
- Kenya Sugar Board/Authority (KSB/KSA)
- Kenya Tea Development Authority/Agency/Tea board of Kenya (KTDA, TBK)
- National Cereals and Produce Board (NCPB)
- Coffee Board of Kenya (CBK)
- Pyrethrum Board of Kenya (PBK)
- Cotton Lint and Seed Marketing Board/Cotton Board of Kenya (CLSMB, CBK)
- Horticultural Crop Development Authority (HCDA)
- Kenya Sisal Board (KSB) (4 x 1/2 = 2 marks)
- 4 marketing functions of KCC
- Buying and assembling milk/collection
- Processing milk
- Market research
- Advertisement/promotion of milk/milk products
- Strategic storage of milk products
- Distribution of milk/transportation
- Selling milk
- Marketing and packaging
- Risk bearing
- Financing - related to marketing function
- Grading/standardization
- Rej: Marketing alone (4 x 1/2 = 2 marks)
-
-
- Increases seed soil contact
- Compacts soil/seed to protect it against agents of erosion
- Crushing large soil clods
- Soil levelling (2 x 1/2 = 2 marks)
- Levelling
- Ensures uniform depth of planting/uniform germination/uniform fertilizer application
- Ensures uniform water level in paddy
- Rice fields
- To remove depression which collect water leading to rotting of seeds.(2 x 1/2 = 1 mark)
-
- 3 activities in clearing land
- Tree felling
- Stumping/removal of stumps/destumping
- Slashing/mowing (3 x 1/2 = 11/2 marks)
- 5 Advantages of zero grazing
- Requires little land
- Quick accumulation of manure
- Easy to control diseases and parasites
- Less wastage of feeds
- Has high stocking rate
- High milk yield
- Efficient use of fodder (5 x 1/2 = 21/2 marks)
- 4 factors determining stage of crop harvesting.
- Intended use of the crop
- Chemical concentration of the produce/stage of maturity/change in colour
- Prevailing weather conditions
- Market demand for the produce/market price (4 x 1/2 = 2 marks)
-
- Growth Cycle
- Annual weeds
- Biennual weeds
- Perennial weeds (2 x 1/2 = 1 mark)
-
- Broad leaved weeds
- Narrow leaved weeds (2 x 1/2 = 1 mark)
- Growth Cycle
-
- Weed
- Couch grass/Digitaria scalarum (1 x 1/2 = 1/2 mark)
- Why its difficult to control.
- Presence of underground stems/rhizomes which are difficult to control/underground storage structure (1 x 1 = 1 mark)
- 4 control
- Uprooting
- Cultivation
- Slashing
- Use of herbicides
- Mulching
Rej: Rogueing (4 x 1/2 = 2 marks)
- Weed
-
- Soil Sample with highest acidity
- Sample S1 (1 x 1/2 = 1/2 mark)
- Lowering pH
- Application of acidic fertilizers: Accept S/A; ASN; DAP; MAP
Rej: Nitrogenous fertilizers - Application of sulphur (2 x 1/2 = 1 mark)
- Application of acidic fertilizers: Accept S/A; ASN; DAP; MAP
- Soil sample suitable for tea growing
- S2
- S3
- S4
- Soil Sample with highest acidity
-
- Extraction to remove seeds from pods/fruits
- Drying to reduce seed moisture content
- Testing to verify seed quality
- Treatment to break dormancy/helps improve germination/soaking in water
- Seed dressing to control pests and diseases
- Seed innoculation to improve nitrogen fixation
- Washing/cleaning to remove mucilage (4 x 1 = 4 marks)
No procedure
-
-
- Correct pruning
- B
NB: Wrong identity
Wrong reason (1 x 1/2 = 1/2 mark)
- B
- Reason
- Slant cut is a few centimetres above the bud/leaf (1 x 1 = 1 mark)
- Correct pruning
- 2 how pruning controls diseases
- Removes diseased parts
- Creates unfavourable conditions/environment for disease agents
- Facilitates penetration of chemical sprays. (2 x 1/2 = 1 marks)
-
-
- KABURU FARM CASH ANALYSIS FOR JANUARY 2009
No marks for title
NB: Check for double entryRECEIPTS (SALES AND RECEIPTS) EXPENDITURE(PURCHASESAND EXPENSES) DATE DESCRIPTION TOTAL CASH LIVESTOCK CROP DATE DESCRIPTION TOTAL CROPS LIVESTOCK Ksh Ksh Ksh Ksh Ksh Ksh Ksh 01/1/09 cash in hand 30,000 30,000 15/1/09 seeds for planting 7,500 7,500 05/1/09 livestock sales 80,000 80,000 20/1/09 paid KFA for fertiliser 16,400 16,400 08/1/09 crop sales 50,000 50,000 25/1/09 bought livestock feed 50,000 50,000 31/1/09 cash for milk delivery to KCC 120,000 120,000 30/1/09 paid wages for planting & weeding 56,000 56,000 31/1/09 transport charges for milk delivery 9,000 9,000 TOTAL 280,000 30,000 200,000 50,000 TOTAL 138,900 79,900 59,000 CLOSING BALANCE 141,100 TOTAL 280,000 TOTAL 280,000 - Correct labelling of expenditure and receipt columns 1 x 1/2 = 1/2 mark
- Correct entries by dates 9 x 1/2 = 41/2 marks
- Balancing 1 x 1/2 = 1/2 mark
Closing balance
Cash at hand i.e 141,000
- KABURU FARM CASH ANALYSIS FOR JANUARY 2009
-
- Figures 18:46 on a fertilizer bag mean
- 18% Nitrogen (NO
- 46% phosphorous pentoxide (P2O5)
- 10% Potassium oxide (K2O) (3 x 1/2 = 11/2 marks)
- Filler material
- = 100 - (18 + 46 + 10)
= 100 - 74
= 26kg or 26%
Ignore working
Mark answer only i.e 26
Unit must be therefore a score. 1 x 1 = 1 mark
- = 100 - (18 + 46 + 10)
- Figures 18:46 on a fertilizer bag mean
-
- 8 Factors that encourage soil erosion.
- Lack of ground cover exposes soil to agents of soil erosion/removal of cover crops
- Steep slopes increase the speed of surface run-offs hence erosive power of water
- Light/sandy soils are easily carried away by agents of soil erosion.
- Shallow soils are easily saturated with water and carried away
- High rainfall intensity on bare ground/leads at detachment of soil hence run off
- Frequent cultivation/over cultivation pulverizes the soil making it easy to detach and carry away.
- Overstocking leads to overgrazing which destroys ground cover exposing it to agents of erosion.
- Burning/deforestation destroys vegetation cover and exposes soil to agents of erosion.
- Ploughing up and down the slope creates channels which speed up and increases the erosive it to agents of water.
- Cultivation of river banks destroys riverine (Viparia) vegetation & destroys soil structure exposing it to agents of erosion.
- Cultivating the soil when too dry destroys soil structure making it easy to be eroded.
- Long slopes increases volume speed of run off hence increasing erosive power of water.
Question if filter not qualified = No mark
Factor & effect - High rainfall amount increase saturation of soil hence increase in soil erosion.
-
- Mulching to conserve moisture
- Erection of shade to minimize evapotranspiration
- Weed control to reduce competition with seedlings for nutrients, light, space etc
- Pest and disease control to ensure healthy and vigorously growing seedlings
- Pricking out/thinning to minimise competition for growth elements
- Fertilizer application to supplement nutrients in the soil
- Watering to ensure adequate moisture supply
- Hardening off/removing shade/reducing watering to acclimatize the seedling to conditions in the field.
- Removal of mulch immediately after germination
NB: Correctly stated (7 x 1 = 7 marks)
- 5 soils factors that determine a crop growth in an area.
- Soil drainage/rate of water infiltration and percolation through the soil
- Soil structure/arrangement of soil particles or aggregates/water holding capacity
- Soil nutrient content/variety and quantity of mineral nutrients in the soil/Soil fertility
- Soil profile/soil depth/depth and arrangement of soil horizons in relation to the rooting systems of the crop
- Soil pH/chemical properties of the soil/degree of acidity or alkalinity of the soil solution
- Soil borne pests and diseases/the prevalent pests/diseases in the soil
- Water holding capacity
5 correctly stated (5 x 1 = 5 marks)
- 8 Factors that encourage soil erosion.
-
- 5 effects of high temperature
- Increases incidences of some pests/parasite and diseases
- Improves quality of certain crops e.g fruits, pineapples, papaws’
- Lowers quality of certain crops e.g pyrethrum
- Increases rate of evapotranspiration/wilting in plants
- Increases rate of growth for early maturity in crops
- Limits distribution of exotic livestock breeds
- Lowers production in livestock
- Influences design of farm buildings and structures
- Lowers labour productivity (5 x 1 = 5 marks)
- 4 precautions observed in cotton harvesting
- Sisal bags/gunny bags should not be used to prevent mixing of lint and sisal fibres which causes ginning problems
- Hands should be cleaned to avoid staining of the lint
- Picking should be done when the lint is dry to prevent fibres from sticking together
- Use clean containers for picking
- Use different containers for AR (Safi) and BR (fifi) gardens of cotton to ensure quality/separation
- Picking should be done immediately the bolls open/split to prevent staining by dust/dirt
- Avoid picking leaves & twigs to avoid (containers)1 x 4 = 4 marks
- Sugar cane harvesting
- Harvest at the correct age / 13 -22 months for plant crop/ 12 - 18 months for rotation
- Take sugar can samples of testing to determine maturity.
- Cut the mature cane at the base/near the ground
- Cut off the green tops
- Strip off green leaves/burn the cane
- Deliver the cane to the factory within 48 hours/immediately after cutting
- Use a cane harvesting machete. (6 x 1/2 = 3 marks)
- 8 factors considered in farm planning
- Risk and uncertainties: enterprises should be analysed to determine the risks and uncertainties involved.
- Security: enterprises which require more security should be sited near the farm house/provision of adequate security
- Land size: a large number of enterprises can be established on a large scale compared to a small scale farm.
- Current trends in labour market: to determine availability and cost of labour especially during peak period.
- Farmers objectives and preferences: to ensure the farmer who is the operator has a sense of ownership of the plan and brings about motivation
- Current market trends and prices of outputs: to ensure consideration of enterprises with high profits returns.
- Availability and cost of farm inputs: to identify enterprises that are affordable and whose inputs are readily available.
- Government policy/regulation: to seek permission for enterprises undertaken on quota system e.g coffee growing and avoid enterprises and farming systems prohibited by the government
- Environmental factors: soil, climate and topography should be analysed to determine livestock crop enterprises that are suitable to the local ecological conditions.
- Communication and transport facilities and facilitate movement of outputs to the market and supply of inputs. Also helps in conveying improved methods of farming and market trends.
- Availability of capital: to acquire farm inputs
- Possible production enterprises: should be identified and analysed so that suitable and profitable enterprises are selected
Wrong factor
Award for explanation
1/2 mk - stating the factor = 1/2 x 8 = 4
- 5 effects of high temperature
-
- 6 physical methods of controlling crops pests
- Trapping/picking and killing the pests
- Use of lethal temperature to kill the pests
- Flood the suffocate and kill the pests
- Use of physical barriers e.g fences, rat guards, etc to keep the pests away from the crop/produce
- Proper drying to make penetration difficult
- Use of explosive to destroy breeding grounds and the kill the pests
- Suffocation: carbon dioxide build up to suffocate pests in stores especially cyprus bins. (6 x 1 = 6 marks)
-
- Field management of bulb onions
- Weed control through shallow cultivation to avoid damage to the shallow inion roots
- Remove excess soil around the roots gradually to facilitate bulb expansion
- Water regularly at the early stages to ensure adequate moisture supply
- Top dress with nitrogenous fertilizer at appropriate rates
- Control pests e.g thrips using appropriate pesticides
- Control diseases e.g rusts, mildews using appropriate method. (4 x 1 = 4 marks)
- Harvesting of bulb onions
- Is done 4 -5 months after planting/when leaves wither/turn brown
- Cut break and bend this tops at the neck
- Harvesting is done by lifting/pulling/digging out the crop
- Leave the bulbs on the ground/undershade to dry for 3 days and turn frequently to ensure uniform drying.
3 x 1 = 3 marks
- Field management of bulb onions
- 7 factors influencing seed rate
- Intended use of the crop e.g fodder maize requires high seed rate than grain maize.
- Germination percentage - high speed rate is required for seeds with low germination percentage
- Method of planting: Broadcasting requires high seed rate than row planting.
- Number of seeds per hole: two or more seeds per hole requires more seed rate than one seed per hole.
- Soil fertility: poor/infertile soils require low seed are because crops are widely spread compared to fertile soils.
- Growth characteristics of the crop: tall/tillering/indeterminate varieties require low seed rate compared to short/less tillering/determinate varieties
- Spacing: High sped rate is required in closer spacing than wider spacing
- Seed purity: Impure seed/containing chaff and foreign materials will lead to high seed rate compared to pure seed
- Pure/mixed stand
High seed rate for pure stand and low seed rate for mixed stand.
1/2 mk for stated factor = 1/2 x 7 = 31/2 mk
1/2 mk for explanation given = 1/2 x 7 = 31/2 mk
- 6 physical methods of controlling crops pests
Download KCSE 2010 Agriculture Paper 1 Questions with Marking Scheme.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

