SECTION A: (25 Marks)
Answer all the questions in this section in the sapces provided
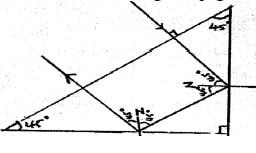
- Figure 1 shows a ray of light incident on a mirror at an angle of 45°. Another mirror is placed at an angle of 45° to the first one as shown.
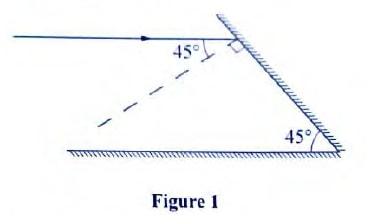
Sketch the path of the ray until it emerges. (2 marks) - An un-magnetized steel rod is clamped facing North-South direction and then hammered repeatedly for some time. When tested, it is found to be magnetized. Explain this observation. (2mks)
- The mechanical disturbance due to hammering aligns the domain with the earth’s magnetic field causing magnetization
- Figure 2 shows a solenoid carrying an electric current.
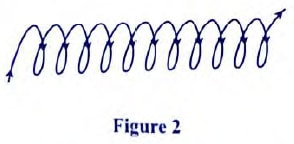
Sketch the magnetic field pattern inside and at the ends of the solenoid (1 mrk) - Figure 3, shows how the displacement of a point varies with time as a wave passes it.
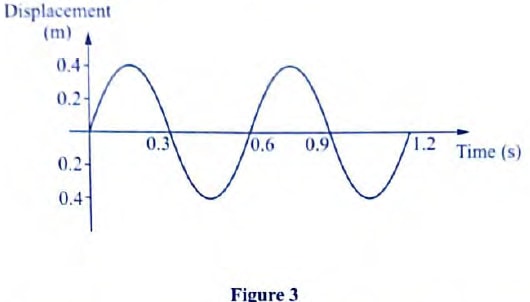
On the same diagram, draw a wave which passes the point with half the amplitude and twice the frequency of the one shown. - State the reason why a convex mirror is preferred over a plane mirror for use as a driving mirror. (1 mark)
- Figure 4 shows straight waves incident on a diverging lens placed in a ripple tank to reduce its depth.
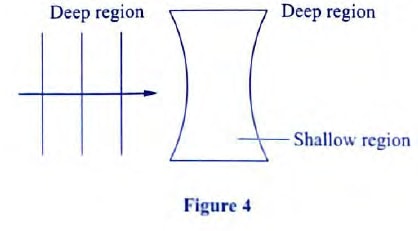
Complete the diagram to show the waves in both the shallow region and beyond the lens. (2 marks) - Figure 5 shows the cross-section of a dry cell. Use the information on the figure to answer questions below
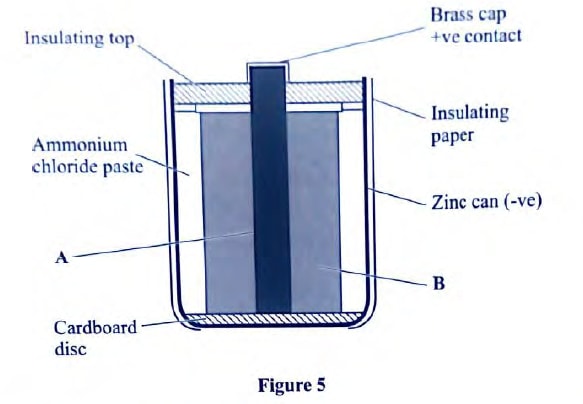
- Name the parts labeled A and B. (2 marks)
- State the use of manganese (IV) oxide in the cell. (1 mark)
- The following is part of radioactive decay series Determine the values of a and b (2 marks)
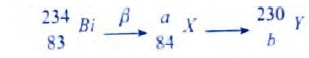
- Draw a ray diagram to show how a ray of light may be totally internally reflected two times in an isosceles right - angled glass prism. (Assume that the critical angle of glass is 420(2 marks)
- Figure 6 shows a narrow beam of X-rays passing between two metal plates in air. The plates are connected in series with a switch, a cell and a milliameter. It is observed that when the switch is closed a current flows in the milliameter.
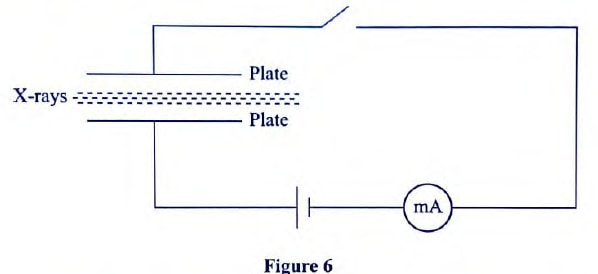
Explain this observation. (2 marks) - A heater of resistance R1 is rated P watts, V volts while another of resistance R2 is rated 2P watts, V/2 volts. Determine R1 / R2 3 marks)
- When germanium crystal is doped with arsenic, it becomes an N-type semiconductor. Explain how this change occurs. (2mks) (Number of electrons in the outermost shell for germanium =4, arsenic =5)
- A boy standing in front of a cliff blows a whistle and hears the echo after 0.5s. He then moves 17 metres further away from the cliff and blows the whistle again. He now hears the echo after 0.6s. Determine the speed of the sound.
SECTION B: 55 Marks
Answer all questions in this section
-
- Figure 7 shows a simple electric bell circuit
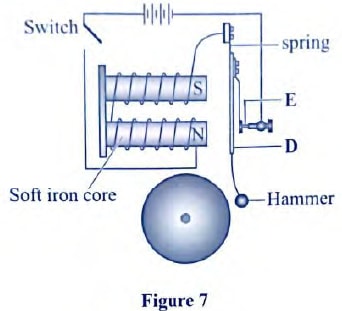
- Name the parts labeled
- D
- E
- When the switch is closed, the hammer hits the gong repeatedly. Explain why:
- the hammer hits the gong. (2 marks)
- the hammer hits the gong repeatedly. (3 marks)
- Name the parts labeled
- An electric bulb is rated 60 W, 240 V. Determine:
- the current that flows through it when it is connected to a 240 V supply.(3 marks)
- the resistance of the bulb. (3 marks)
- Figure 7 shows a simple electric bell circuit
- Figure 8, shows two coils A and B placed close to each other. A is connected to a steady D.C. supply and a switch, B is connected to a sensitive galvanometer.
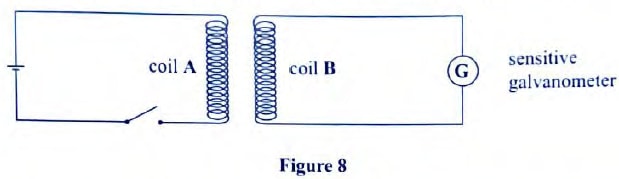
-
- The switch is now closed, state the observation made on the galvanometer. (2marks)
- Explain what would be observed if the switch is then opened. (2marks)
- The primary coil of a transformer has 1000 turns and the secondary coil has 200 turns. The primary coil is connected to a 240V ac. Mains supply.
- Explain how an e.m.f is induced in the secondary coil. (2marks)
- Determine the secondary voltage. (3marks)
- Determine the efficiency of the transformer given that the current in the primary coil is 0.20A and in the secondary coil it is 0.80A. (3marks)
-
-
- Figure 9, shows a cicuit that may be used to charge a capacitor.
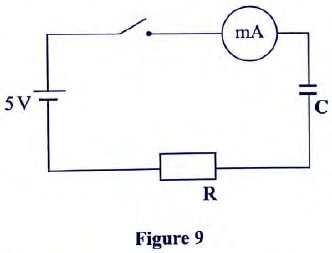
- state the observation on the milliameter when the circuit is switched on:
- explain the observation in (i) above.
- The circuit in figure 8 is left on for some time. State the value of p.d. across:
- the resistor R;
- the capacitor C;
- sketch the graph of potential difference (V) across R against time.
- Figure 10 shows three capacitors connected to a 10V battery
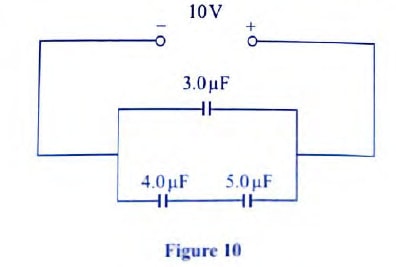
Calculate:- the combined capacitance of the three capacitors
- the charge on the 5.0 juF capacitor.
- Figure 9, shows a cicuit that may be used to charge a capacitor.
-
- When a radiation was released into a diffusion cloud chamber, short thick tracks were observed. State with a reason, the type of radiation that was detected. (2 marks)
- The half-life of an element X is 3.83 days. A sample of this element is found to have an activity rate of 1.6 x 103 disintegrations per second at a particular time. Determine its activity rate after 19.15 days. (2 marks)
- State what is meant by an extrinsic semiconductor. ( 1 mark)
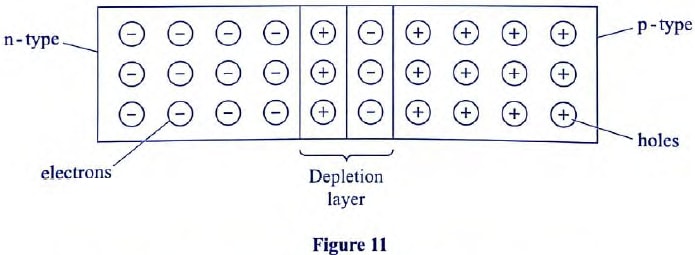
- Figure 11, shows a depletion layer in an unbiased p-n junction. State how a battery can be used to make the depletion layer narrower. ( 1 mk)
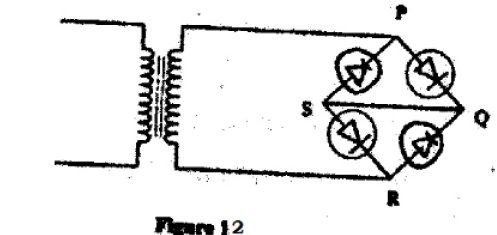
- Figure 12, shows an incomplete circuit of a full wave rectifier.
- Draw in the figure two more diodes to complete the circuit. (2 marks)
- Show on the figure 12 the points across which the output of the rectifier should be obtained. (1 mark)
-
- State one factor that affects the speed of sound in a solid.(1mk)
- An observer stands half-way between two vertical cliffs that are L metres apart.He strikes a gong and measures the time interval, t, between the echoes heard from the two cliffs. He moves a further 10m and again strikes the gong and measures the time interval between the echoes. The process is repeated several times. The graph in Figure 13 shows the relation between the time interval, t and the distance, x from the centre.
- From the graph, determine the value of x for which the time interval was 0.55. (1mk)
- Given that t = where v is the speed of sound in air, determine the value of v from the graph. (3mks).
- If the maximum time measured by the observer was t=4.7s, determine the distance L between the cliffs. (3mks)
- A search boat uses a signal of frequency 6.0 x 104 Hz to detect a sunken ship directly below. Two reflected signals are received; one after 0.1 seconds from sunken boat and the other after 0.14 seconds from the sea bed. If the sea bed is 98 m below the boat, determine:
- The speed of the signal in water. (3mks) You may use the value of v from (ii) above.
- The depth of the sunken ship below the boat (2 mks)
MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A: (25 Marks)
Answer all the questions in this section in the sapces provided
- Figure 1 shows a ray of light incident on a mirror at an angle of 45°. Another mirror is placed at an angle of 45° to the first one as shown.

Sketch the path of the ray until it emerges. (2 marks)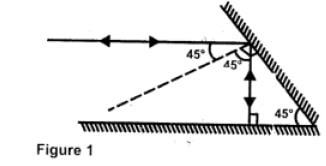
- An un-magnetized steel rod is clamped facing North-South direction and then hammered repeatedly for some time. When tested, it is found to be magnetized. Explain this observation. (2mks)
- The mechanical disturbance due to hammering aligns the domain with the earth’s magnetic field causing magnetization
- Figure 2 shows a solenoid carrying an electric current.

Sketch the magnetic field pattern inside and at the ends of the solenoid (1 mrk)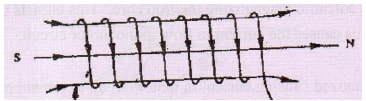
- Figure 3, shows how the displacement of a point varies with time as a wave passes it.

On the same diagram, draw a wave which passes the point with half the amplitude and twice the frequency of the one shown.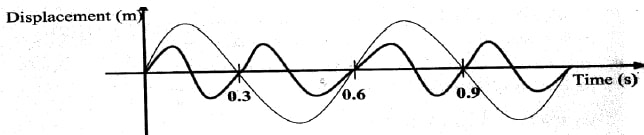
- State the reason why a convex mirror is preferred over a plane mirror for use as a driving mirror. (1 mark)
- It has a wide field of view / wide angle of view / wider range of view
- Figure 4 shows straight waves incident on a diverging lens placed in a ripple tank to reduce its depth.

Complete the diagram to show the waves in both the shallow region and beyond the lens. (2 marks)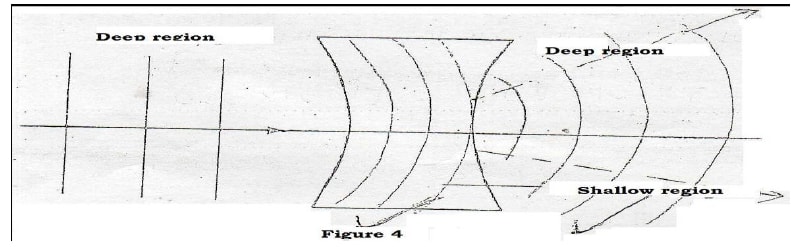
- Decreased in shallow region
- Diverging after refraction to the deep region must be complete
- Figure 5 shows the cross-section of a dry cell. Use the information on the figure to answer questions below

- Name the parts labeled A and B. (2 marks)
- A – Carbon rod or graphite rod
- B – Mixture of Manganese (IV) oxide with carbon powder
- State the use of manganese (IV) oxide in the cell. (1 mark)
- Manganese (IV) oxide is a depolarizer or oxidizing agent. It is used to oxidize hydrogen to water
- Name the parts labeled A and B. (2 marks)
- The following is part of radioactive decay series Determine the values of a and b (2 marks)
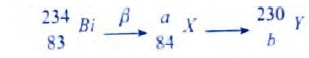
- a = 234
- b= 82
- Draw a ray diagram to show how a ray of light may be totally internally reflected two times in an isosceles right - angled glass prism. (Assume that the critical angle of glass is 420(2 marks)
- Figure 6 shows a narrow beam of X-rays passing between two metal plates in air. The plates are connected in series with a switch, a cell and a milliameter. It is observed that when the switch is closed a current flows in the milliameter.

Explain this observation. (2 marks)- X-rays cause ionization of air molecules between the plates. The ions move to plates of opposite charge.
- A heater of resistance R1 is rated P watts, V volts while another of resistance R2 is rated 2P watts, V/2 volts. Determine R1 / R2 3 marks)
- R1 = V2/P
R2 = V2/8P
R1/R2=(V2x8P)/PV2
=8
- R1 = V2/P
- When germanium crystal is doped with arsenic, it becomes an N-type semiconductor. Explain how this change occurs. (2mks) (Number of electrons in the outermost shell for germanium =4, arsenic =5)
- Arsenic shares four electrons with germanium leaving a free electron for conduction.
- A boy standing in front of a cliff blows a whistle and hears the echo after 0.5s. He then moves 17 metres further away from the cliff and blows the whistle again. He now hears the echo after 0.6s. Determine the speed of the sound.
2d/05 = 2d/0.6 + 34
D = 17/0.2 = 85 m
Speed = (2 x 86)/0.5
= 340m/s
OR V = d/t
= (17 x 2)/0.1
= 340 m/s
SECTION B: (55 marks)
Answer all the questions in this section
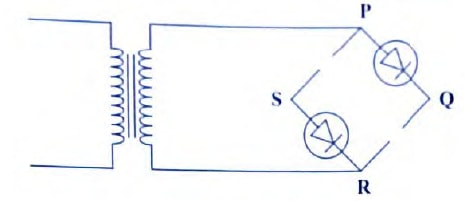
- Figure 7 shows a simple electric bell circuit

- Name the parts labeled
- D
- Soft iron armature
- E
- Contact screw
- D
- When the switch is closed, the hammer hits the gong repeatedly. Explain why:
- the hammer hits the gong. (2 marks)
- Soft iron core is magnetized
- It attracts the armature
- the hammer hits the gong repeatedly. (3 marks)
- Contact is broken
- The core then loses magnetism
- Armature spring back making contact again
- the hammer hits the gong. (2 marks)
- Name the parts labeled
- An electric bulb is rated 60 W, 240 V. Determine:
- the current that flows through it when it is connected to a 240 V supply.(3 marks)
- I = P/V = 60/240 = 0.25A
- the resistance of the bulb. (3 marks)
- R = P/I2 = 60/0.252 = 960Ω or R = V/I = 240/0.25 = 960Ω
- the current that flows through it when it is connected to a 240 V supply.(3 marks)
- Figure 7 shows a simple electric bell circuit
- Figure 8, shows two coils A and B placed close to each other. A is connected to a steady D.C. supply and a switch, B is connected to a sensitive galvanometer.

-
- The switch is now closed, state the observation made on the galvanometer. (2marks)
- The galvanometer will be deflected to one side and then back to zero.
- Explain what would be observed if the switch is then opened. (2marks)
- A greater deflection will be obtained in the opposite direction as the current takes less time to die off than to build up
- The switch is now closed, state the observation made on the galvanometer. (2marks)
- The primary coil of a transformer has 1000 turns and the secondary coil has 200 turns. The primary coil is connected to a 240V ac. Mains supply.
- Explain how an e.m.f is induced in the secondary coil. (2marks)
- The changing current in the primary coil induces a current in the secondary coil due to changing magnetic field of the primary current
- Determine the secondary voltage. (3marks)
Ns/Np = Vs/Vp hence Vs = (240 x 200)/1000
= 48V - Determine the efficiency of the transformer given that the current in the primary coil is 0.20A and in the secondary coil it is 0.80A. (3marks)
Efficiency = power output x 100
Power input
4.8 x 0.8 x 100
240 x 0.2
= 80%
- Explain how an e.m.f is induced in the secondary coil. (2marks)
-
-
- Figure 9, shows a cicuit that may be used to charge a capacitor.

- state the observation on the milliameter when the circuit is switched on:
- Current falls off to zero.Falling to zero deflects to maximum then zero.
- explain the observation in (i) above.
- Current flows when the capacitor is charging. When fully charged no current flows and potential difference (p.d.) is equal to charging voltage
- state the observation on the milliameter when the circuit is switched on:
- The circuit in figure 8 is left on for some time. State the value of p.d. across:
- the resistor R;
- VR = 0 volts
- the capacitor C;
- Vc = 5 Volts
- the resistor R;
- sketch the graph of potential difference (V) across R against time.
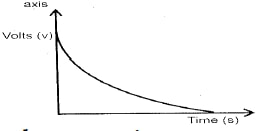
- Figure 10 shows three capacitors connected to a 10V battery

Calculate:- the combined capacitance of the three capacitors
- Parallel capacitance ,Cp
- the charge on the 5.0 juF capacitor.
- Charge on series section Q = CV
- = 2.22× 10 = 22.2
- the combined capacitance of the three capacitors
- Figure 9, shows a cicuit that may be used to charge a capacitor.
-
- When a radiation was released into a diffusion cloud chamber, short thick tracks were observed. State with a reason, the type of radiation that was detected. (2 marks)
- Alpha radiation. This radiation has a short range with intense ionization hence thick tracks
- The half-life of an element X is 3.83 days. A sample of this element is found to have an activity rate of 1.6 x 103 disintegrations per second at a particular time. Determine its activity rate after 19.15 days. (2 marks)
- Number of half lifes = 19.15/3.83 = 5
- N = N(½)T/t = 6 x 103 (½)5 = 50 days/sec
- State what is meant by an extrinsic semiconductor. ( 1 mark)
- It is a semiconductor in which impurities have been added to change conductivity
- Figure 11, shows a depletion layer in an unbiased p-n junction. State how a battery can be used to make the depletion layer narrower. ( 1 mk)

- By connecting it in a forward biased mode
- Figure 12, shows an incomplete circuit of a full wave rectifier.

- Draw in the figure two more diodes to complete the circuit. (2 marks)
- Show on the figure the points across which the output of the rectifier should be obtained. (1 mark)
- Across QS
- Draw in the figure two more diodes to complete the circuit. (2 marks)
- When a radiation was released into a diffusion cloud chamber, short thick tracks were observed. State with a reason, the type of radiation that was detected. (2 marks)
-
- State one factor that affects the speed of sound in a solid.(1mk)
- Temperature
- Density
- An observer stands half-way between two vertical cliffs that are L metres apart.He strikes a gong and measures the time interval, t, between the echoes heard from the two cliffs. He moves a further 10m and again strikes the gong and measures the time interval between the echoes. The process is repeated several times. The graph in Figure 13 shows the relation between the time interval, t and the distance, x from the centre.
- From the graph, determine the value of x for which the time interval was 0.55. (1mk)
- 47 metres
- Given that t = where v is the speed of sound in air, determine the value of v from the graph. (3mks).
From t = 4/Vx, 4/v = gradient hence v = 4/gradient
Gradient = (4.7 – 2) x 10-1/(40 – 17)
= 0.01174
V = 4/0.01174 = 340.715 m/s2 - If the maximum time measured by the observer was t=4.7s, determine the distance L between the cliffs. (3mks)
- Distance = speed x tim
- 2D = distance to and from the cliff
- 2D = 340.715 x 4.7
- D = 800.68 metres
- From the graph, determine the value of x for which the time interval was 0.55. (1mk)
- A search boat uses a signal of frequency 6.0 x 104 Hz to detect a sunken ship directly below. Two reflected signals are received; one after 0.1 seconds from sunken boat and the other after 0.14 seconds from the sea bed. If the sea bed is 98 m below the boat, determine:
- The speed of the signal in water. (3mks) You may use the value of v from (ii) above.
- Distance moved by sound from sea bed = 98 x 2 m
- V = 98 x 2/0.14
- = 1400 m/s
- The depth of the sunken ship below the boat (2 mks)
- Distance = v x t
- = 1400 x 0.10/2
- = 70 m
- The speed of the signal in water. (3mks) You may use the value of v from (ii) above.
- State one factor that affects the speed of sound in a solid.(1mk)
Download KCSE 2016 Physics Paper 2 Questions with Marking Scheme.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students