QUESTIONS
SECTION A (40 marks)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided.
- State four factors to consider when choosing building materials.(4 marks)
-
- List four defects that are commonly found in timber on a construction site.(2 marks)
- State four factors to consider when setting up a site for construction.(2 marks)
- State two purposes of stripping the top soil.(2 marks)
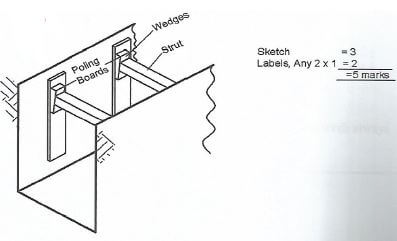
- Sketch and label an open timbering to a shallow trench.(5 marks)
-
- Explain the meaning of the term "efflorescence" as used in buildings.(2 marks)
- Describe the tamping method of compacting concrete. (2 marks)
-
- List four methods of curing concrete.6.(2 marks)
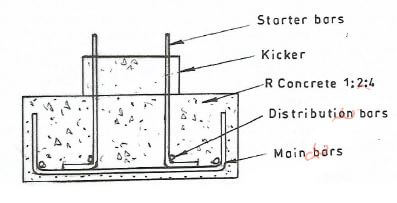
- Explain the purpose of using starter bars in reinforced concrete works.(2 marks)
-
- Define the term "damp proofing as used in construction(2 marks)
- List two materials used as damp proof membrane.(1 marks)
-
- State two factors that affect the selection of foundations for buildings,(2 marks)
- Sketch and label a cross section through a pad foundation (4 marks)
- Explain four reasons for site investigation. (4 marks)
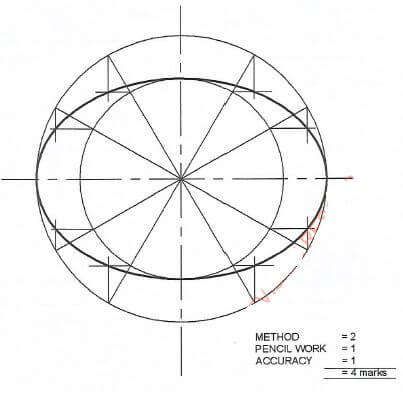
- Figure 1 shows a shape to be moulded to form the top of a table.
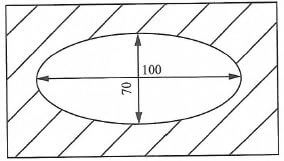
Figure 1
Using the concentric circles method, construct the shape. (4 marks)
SECTION B (60 marks)
Answer question 11 on the A3 paper and any other three questions from this section in the spaces provided. Candidates are advised to spend not more than 25 minutes on question 11.
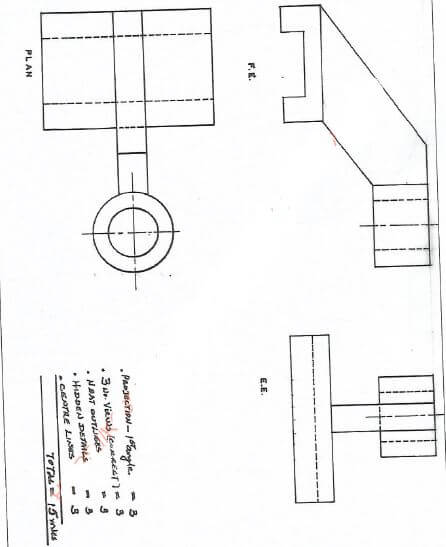
- Figure 2 shows a machine part drawn in isometric projection.
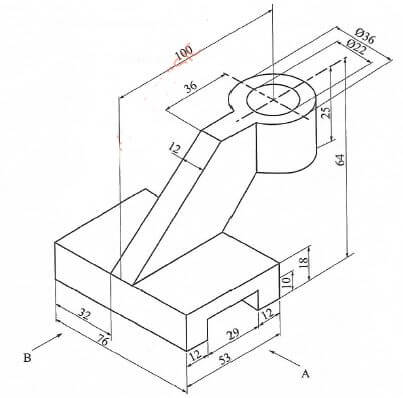
Draw Full Size, the following views in first angle projection:(15 marks)- Front elevation in the direction of arrow A.
- End elevation in the direction of arrow B.
- The plan.
-
-
- Define the term "lintel" as used in building construction.(2 marks)
- Draw and label a cross section of concrete lintel over a brick wall.(4 marks)
- State four factors that influence the method of excavation for foundation walls.(4 marks)
- Draw and label a cross-section through a honey-comb sleeper wall.(5 marks)
-
-
-
- Define the term "scaffold" as used on construction sites.(2 marks)
- With the aid of labelled sketches, show how the following parts of a scaffold are assembled:(6 marks)
- Standard to base plate
- Joining two standards to increase height
-
- Define the term "flat roof".(1 mark)
- State four functions of a roof on a building.(4 marks)
- List two methods of strengthening the joints of rafters (2 mark)
-
-
- State five functions of a floor screed.(5 marks)
- State five functions of paints on buildings. (5 marks)
- Describe the direct hot water supply system. (5 marks)
-
- State five requirements of formwork in construction. (5 marks)
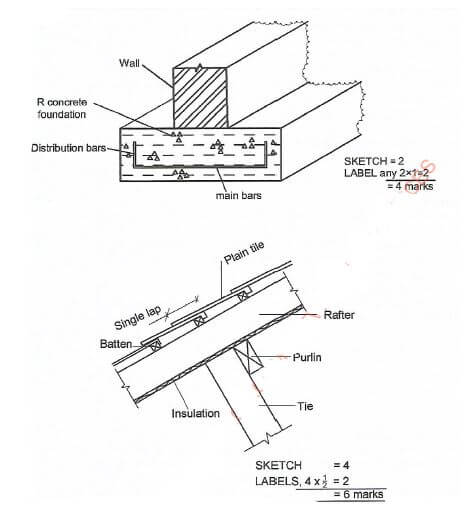
- Sketch a pictorial view of a reinforced strip foundation(4 marks)
- With the aid of a cross section, show the details of a single lap tile roof to include the purlin, rafter, tie and batten as the structural members.(6 marks)
MARKING SCHEME
- Factors to consider when choosing building materials
- Cost: Consider lifespan or value of product.
- Aesthetics : Consider the looks you want.
- Availability: Readily available, more affordable.
- Durability: Lasting longer than others.
- Maintenance : Easy to maintain at low cost.
- Performance : Structural strength to support building loads.
- Installation/construction: Ease of installation process.
-
- Defects in timber that become common issues on site:
- End splitting
- Decay
- Discoloration
- Shrinking/expansion causing warping
- Staining
- Cupping/bowing
- Factors to consider when setting up a site.
- History of site-underground rails and fills.
- Previous/current use.
- Access/egress.
- Overhead and buried services.
- Restriction of the area.
- Topography and ground condition
- Telephone and water services.
- Defects in timber that become common issues on site:
- Purpose of stripping the top soil.
- To remove the top 150mm deep vegetable soil.
- To attain a reduced level.
- To reach a firm base particularly in hard soils.
-
-
- Efflorescence:
Soluble salts, commonly white, deposited on the surface of stone, brick, plaster, or mortar; usually caused by free alkalis from mortar or adjacent concrete as moisture moves through it. - Tamping concrete.
This is done using a hand held tamping equipment. Wet concrete is tamped repeatedly on the surface until satisfactory compaction is achieved. The surface of concrete remains rather rough and will require to be finished off with a wooden float.
- Efflorescence:
-
- Methods of curing concrete
- Providing shades
- Covering the surface with hessian mats or gunny bags
- Sprinkling water on the surface
- Ponding
- Membrane curing
- Steam curing
- Chemical application
- Starter bars
Starter bars are mostly used in reinforcement of columns and other structural materials that have short steel bars to be continued at a later date e.g. as used in pad foundations. They enable correct fixing of column reinforcement bars.
- Methods of curing concrete
-
- Damp proofing
This is the application of damp proof course or membranes to stop the entry of moisture into buildings and other structures. - Materials for damp proof membrane
- Vapour barrier used in roof decking.
- Mastic asphalt used in flat roof covering.
- Bitumen felts
- Polythene Tanking
- Damp proofing
-
- Factors that affect selection of foundations
- The total loads expected on the building.
- The nature and bearing capacity of the subsoil.
- Underground services on site and type of structures in the neighbourhood
- Topography and ground conditions.
-
- Factors that affect selection of foundations
- Reasons for site investigation
- Safe and economical design of foundations and temporary works.
- To know the nature of each stratum and engineering properties of the soil and rock, which may affect the design and mode of construction of proposed structure and foundation.
- To foresee and provide against difficulties that may arise during construction due to ground and other local conditions.
- To investigate the occurrence or causes of all natural and manmade changes in conditions and results arising from such changes.
- To ensure safety of surrounding existing structures.
- To locate the ground water levels and possible corrosive effect of the soil and water on foundation materials.
-
-
-
-
- Lintel
A lintel is a structural horizontal member that spans the opening between two vertical supports. -
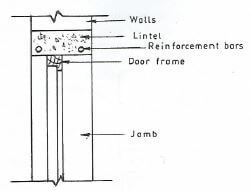
sketch = 2 marks
label, any 2 x 1 = 2 marks
- Lintel
- Factors influencing the method of excavation
- Surrounding existing buildings.
- Availability of equipment and machines.
- Speed required/expected to do the work.
- Existing underground services.
- Access to the site.
-
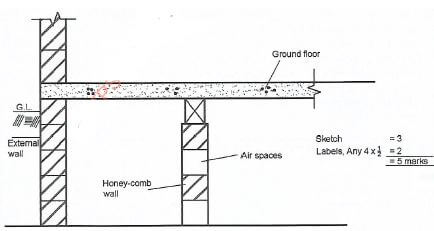
Accept raised timber floor if given.
-
-
-
- Scaffolding
Scaffolds are temporary platforms that are erected to enable the workers access higher heights off the ground during construction -
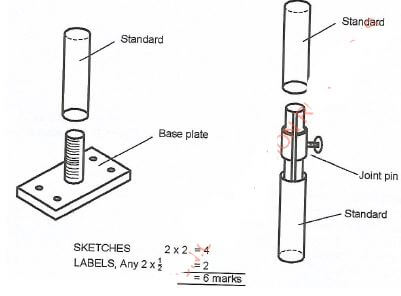
Accept other correct methods
- Scaffolding
- Flat roof
This is a low pitched roof with a pitch 10° or less to the horizontal.
Functions of roofs on buildings:- To keep out rain, wind, snow and dust.
- To prevent excessive heat loss in winter.
- To keep the interior of the building cool in summer.
- Designed to accommodate all stresses encountered on a building.
- Designed to accept movement due to changes in temperature and moisture content.
- Methods of treating joints of rafters for strength.
- Timber connectors with bolts.
- Truss plates with nails.
- Truss plates with spikes.
- Plywood gusset plates.
-
-
- Functions of screed
- Provide a smooth surface on which to lay a floor finish.
- Provide falls to the surface.
- Conceal services, such as electricity cables in conduit, hot and cold water pipes, gas pipes etc.
- Provide thermal insulation by the use of lightweight aggregates in the screed.
- Provide sound insulation by constructing a floating floor.
- Protection of damp proof membrane where the membrane is placed on the concrete slab.
- Provide a hard wearing surface finish in high-traffic areas.
- Functions of paints
- To protect surfaces from rain, sunlight, abrasion, chemical, insect, fungi and fire.
- To provide decoration in the form of colour and use of different colours.
- To provide hygienic surfaces that can be easily cleaned.
- To provide antistatic properties. For proper identification of the premises e.g butchery.
- To prevent rusting or corrosion of metallic materials like iron sheets, gates and window or door frames.
Accept any other correct response.
- Direct hot water supply
- Cold water flows through the water jacket in the boiler where its temperature is raised and convection currents are induced which causes hot water to raise and circulate.
- The hot water leaving the boiler is replaced by colder water descending from the hot water cylinder or tank by gravity thus setting up the circulation. The hot water supply is drawn off from the top of the cylinder by a horizontal pipe at least 450mm long.
- Functions of screed
-
-
- Requirements of formwork in construction
- Strength
- Rigidity
- Tightness
- Good alignment
- Surface finish
- Durability
- Ease of placing concrete
- Ease of stripping
- Economy
- Requirements of formwork in construction
-
Download KCSE 2018 Building Construction Paper 1 with Marking Scheme.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

