- State the name given to the study of (2mks)
- The cell
- Micro-organisms
- Name the organelle that performs each of the following functions (2mks)
Protein synthesis
Transport of cell secretions
- A student drew a 6cm long diagram of a plant flower. If the actual length of the flower was 12cm, calculate the magnification of the drawing made by the student. Show your working. (2mks)
- What is the name given to organisms whose bodies are made up of (2mks)
- One cell……………………………………..
- Many cells…………………………………..
- State two functions of placenta in mammals (2mks)
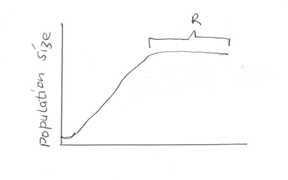
- The graph below shows growth rate of a certain organism.
List down three factors that could have caused limited population growth at R. (3mks)
- Members of the same species of organisms tend to differ due to variation. State three causes of variation in organisms. (3mks)
- The equation below represents oxidation of a certain food substrate
C57H04O6 + 80 O2 →57CO2 + 52CO2 + 52 H2O + Energy- Calculate the respiratory quotient. (2mks)
- Which type of food substrate is being oxidized (1mk)
- What is the importance of bile in human digestive system (2mks)
- Give three adaptations of the xerophytic leaves to transpiration. (3mks)
- State two examples of sex-linked traits found on the Y- chromosome in human. (2mks)
- With reference to the gill of tilapia explain: (2mks)
- Why the gill bar is curved.
- Why gill filaments are highly vascularised?
- Why would carboxyhaemoglobin lead to death? (2mks)
- State the importance of osmosis in plants (3mks)
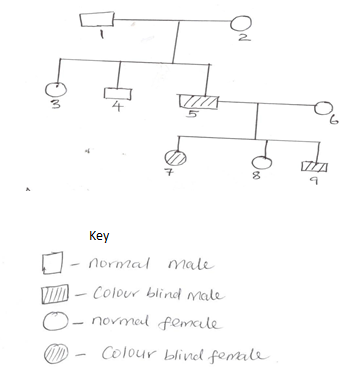
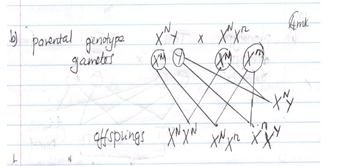
- The figure below is a pedigree showing the inheritance of colour blindness, a disease transmitted through a recessive gene located on x – chromosome.
- Using the symbol N for normal gene and n for colour blind gene, write down the genotypes of parents 1 and 2 (2mks)
- Work out the possible genotypes of the children 3, 4 and 5 (4mks)
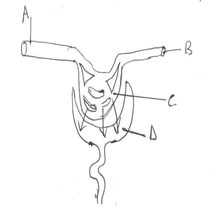
- Apart of the nephron is shown in the diagram below.
- Name the parts labeled A, B, C and D. (2mks)
- Name the process by which fluid in D is formed. (1mk)
- What is osmoregulation (1mk)
- Name the components of blood that does not diffuse into the region D (2mks)
- A patient was found to produce a lot of dilute urine and complained of thirst most of the time. The urine was found not to have glucose after a laboratory test.
- Which disease was the patient suffering from (1mk)
- Name the hormone likely to be deficient in the patient’s body. (1mk)
- What effects does the hormone have on the kidney? (1mk)
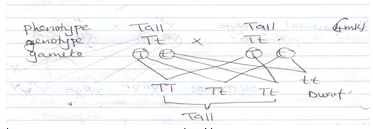
- In a biological experiment, a cross was made between a tall pea plant and dwarf plant. Their progeny was selfed and the resulting plants were a mixture of tall and dwarf in the ratio 3: 1 respectively.
- Using letter T to represent the gene for tall, work out the F2 generation (4mks)
- State the genotypic ratio of the F2 generation (1mk)
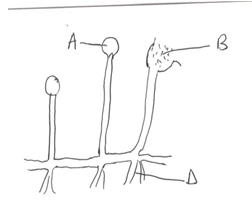
- The figure below shows the structure of a common mould.
- Name the parts A, B and D. (3mks)
- Name the type of nutrition exhibited by the mould (1mk)
- In which kingdom does the mould belong to? (1mk)
-
- Name any three processes in living things that depend on diffusion (3mks)
- Name three factors that affect the rate of diffusion (3mks)
-
- State two physiological changes that take place in human skin in order to facilitate heat loss from the body (2mks)
- Name the fluid that is produced by sebaceous glands. (1mk)
-
- What are the two end products of anaerobic respiration in plants (2mks)
- What is the end product of respiration in animals when there is insufficient oxygen supply (1mk)
-
- What is meant by the term sex linked genes (1mk)
- Name two disorders due to gene mutation (2mks)
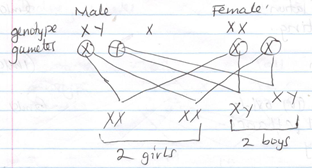
- How is sex determined in man? (4mks)
-
- State two adaptations of the xylem vessels to their functions (1mk)
- State two forces that are involved in transport of water in xylem (2mks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Cytology
- Microbiology (2mks)
- Ribosomes
Endoplasmic reticulum (2mks) - Magnification = Length of diagram
Length of object
= 6cm = x0.5
12cm (2mks) -
- Unicellular
- Multicellular
-
- facilitate transfer of nutrients from mother to foetus
- Facilitate transfer of metabolic wastes from foetus to mother
- Facilitate exchange of gases between foetal and maternal blood
- Secrets progesterone
- Protects the foetus from pathogens and toxins from maternal blood.
-
- Competition for limited resources
- Predation
- Emigration
- Social stress
- Diseases and parasites
-
- Gamete formation accept crossing over/Independent assortment
- Fertilization
- Mutation (3 mks)
-
- RQ = Volume of Co2 produced
Volume of O2 consumed
RQ = 57 = 0.7
80 (2mks) - Fats/lipids (1mk)
- RQ = Volume of Co2 produced
- Emulsification
Neutralizes acidic chyme to provide alkaline medium for pancreatic enzymes. (2mks) -
- Reduced leaf size
- Thick waxy cuticle
- Sunken stomata
- Stomata on the lower surface only
- Small intercellular spaces
-
- Premature baldness
- Tuft of hair in pinna
- Tuft of hair in nose
-
- To increase surface area for attachment of gill filaments.
- For efficient transport/exchange of respiratory gases.
- Does not easily dissociate; therefore reduce capacity of haemoglobin in transport oxygen to the tissues (1mk)
-
- Absorption of water from soil by plant roots
- Support(in seedlings and herbaceous plants)
- Opening and closing of stomata
- Feeding in insectivorous plants
-
- Parent 1 - XNY
Parent 2 - XNXn -
- Parent 1 - XNY
-
- A - Afferent arteriole/ vessel
B - Efferent arteriole/vessel
C - Glomerulus
D - Bowan’s capsule - Ultrafiltration (1mk)
- Control of salt and water balance in the body maintenance of appropriate osmotic pressure for proper cell functioning. (2mks)
- Blood cells
Plasma proteins
- A - Afferent arteriole/ vessel
-
- Diabetes inspidus (1mk)
- Antidiuretic Hormone/vasopressin (1mk)
- Makes the distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct more permeable to water hence more water reabsorbed into the body by the kidney tubules (1mk)
-
- ITT:2Tt:Itt (1mk)
-
-
- A - Sporagium
B - Spores
D - Rhizoids - Saprophytism (1mk)
- Kingdom Fungi
- A - Sporagium
-
-
- Gaseous exchange in plants and animals (3mks)
- Absorption of materials
- Removal/excretion of metabolic wastes
- - Diffusion gradient
- Temperature
- Thickness of tissue/membranes
- Size of molecules
- Surface area
-
-
-
- - Vasodilation (2mks)
- Sweating - Sebum
- - Vasodilation (2mks)
-
-
- Carbon(IV) oxide (2mks)
Alcohol/Ethanol - Lactic acid (1mk)
- Carbon(IV) oxide (2mks)
-
- Genes located on the sex chromosomes and are transmitted together with those that determine sex.
- Albinism
Sickle –cell Anaemia
Colour blindness
Haemophilia - Sex in man is determined by sex- chromosomes. A male contain XY chromosomes while female contain XX chromosomes. The male produce sperms/gametes containing X-chromosome or Y-chromosome while female produce ova contain X – chromosome fertilizes the ovum, a girl result while if a sperm containing Y – chromosome fertilizes the ovum a boy results.
Or
-
- Cohension and adhesion,capillarity,root pressure,transpiration pull
- Walls are strengthened by deposition of lignin to ensure they do not collapseHollow and narrow lumen to aid capillarity.
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download BIOLOGY PAPER 1 - 2019 KCSE CEKENA MOCK EXAMINATION (QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS).
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students