- The table below shows the atomic radii of some elements in a group of the periodic table.
Element Atomic radius (nm) Ionic radius (nm)
W 0.112 0.031
X 0.160 0.065
Y 0.197 0.099
Z 0.215 0.113- Explain why the ionic radius is less than atomic radius of each element (1mk)
- Explain the variation in atomic radii down the group (1mk)
- Identify the most reactive element, give a reason (1mk)
- In a titration experiment 25cm3 of solution of sodium hydroxide containing 8 grams per litre was required for complete neutralization of 0.245g of dibasic acid.Calculate the relative molecular mass of the acid(Na=23, O=16, H=1) (3mks)
-
- What is drug and substance abuse? (1mk)
- Give four harmful effects of smoking tobacco on the Kenyan youths. (2mks)
- The table below shows results obtained from experiment carried out on salt solution W.
Experiment Result- A few drops of barium nitrate added to solution W No white precipitate/colourless solution
- A few drops of lead(II) nitrate added to solution W White precipitate
- Ammonia solution added dropwise until in excess White precipitate which dissolves into a colourless solution.
- Identify the cation and anion present in solution W (1mk)
- Write an ionic equation for the formation of white precipitate in experiment II (1mk)
- Write the formula of the ion responsible for the formation of the colourless solution in experiment III (1mk)
- Use the bond energies below to calculate the enthalpy change for the following reaction. (3mks)
N2(g) + 3H2(g) →2NH3(g) - Hexane and ethanol are miscible liquids. Describe how hexane can be obtained from the mixture of hexane and ethanol. (2mks)
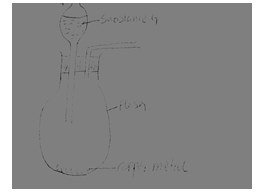
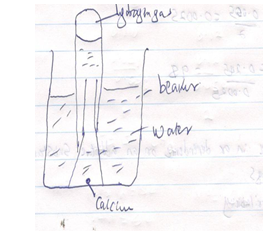
- When a piece of calcium metal is placed in cold water it sinks to the bottom and effervescence of a colourless gas that burns explosively is produced. Draw a well labeled diagram to illustrate how the gas produced above can be collected during the experiment. (2 mks)
- Write the discharge equations (heat equations) for the electrode reactions when molten sodium chloride is electrolysed using graphite electrodes.
- Anode ` (1mk)
- Cathode (1mk)
- In an experiment to determine the solubility of potassium chlorate in water at 30oc, the following results were obtained
Mass of dish =15.86g
Mass of dish + saturated solution at 30oc = 26.86g
Mass of dish + dry salt = 16.86g
Calculate the solubility of potassium chlorate at 30oc. (3mks) -
- What are isotopes (1mk)
- A certain element has three isotopes as shown in the table below
Isotopic mass % Abundance
28 92.2
29 4.7
30 3.1
Calculate the relative atomic mass of the element (2mks)
- Describe how a solid sample of lead(II) chloride can be prepared using the following reagents: dilute nitric(V) acid dilute hydrochloric acid and lead(II) carbonate (3mks)
- Below are pH values of unknown substances P, Q,R and S
Substance pH
P 7.0
Q 5.0
R 9.0
S 6.0
State the substance which is likely to be- Lemon juice (1mk)
- Sodium chloride solution (1mk)
- Calcium hydroxide solution (1mk)
- Why is it dangerous to run a motor car engine in a completely closed garage (1mk)
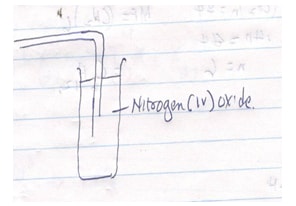
- The set up below was used to prepare nitrogen (IV) oxide gas.
- Complete the diagram to show how the gas was collected. (2mks)
- Write a balanced equation for the reaction that occurs in the flask (1mk)
- A fixed mass of a gas has a volume of 250cm3 at a temperature of 27oc and 750mmHg. Calculate the volume the gas would occupy at 42oc and 750mmHg pressure. (3mks)
- Give two reasons why dry ice is preferred for cooling instead of ordinary ice (2mks)
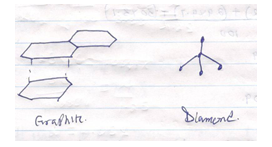
- Draw and name the two allotropes of carbon. (3mks)
- A hydrocarbon was burnt completely in excess oxygen; 2.64g of carbon (IV) oxide and 1.08g of water formed. The hydrocarbon had a molecular mass of 84. Determine its molecular formula. (C=12, H=1, O=16) (3mks)
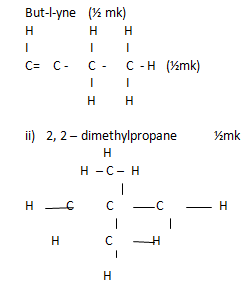
- Draw the structural formula and give the IUPAC name of the following hydrocarbon.
- HCCCH2CH3 (1mk)
- CH3C(CH3)2 CH3 (1mk)
- State and explain two observations you would make when iron nails are dipped and left in a solution of two molar copper (II) sulphate (2MCuSO4) in a beaker. (2mks)
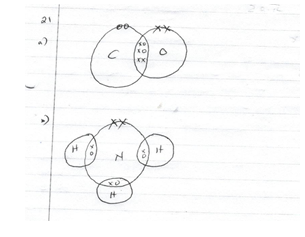
- Draw dot(.) and crosses(x) diagram to show the bonding in a molecule of
- Carbon(II) oxide (CO) (1 ½ mks)
- Ammonia (NH3) (1 ½ mks)
- Study the information given below carefully.The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements. T displaces X from an aqueous solution containing ions of X.H2 gas reduces hot oxide of S but not X. U liberates H2 gas from cold water but T does not.
- Arrange the elements in order of their increasing reactivity (2mks)
- Write an equation for the reaction between T and the ions of X2+ (T is a group II of periodic table) (1mk)
- The formula of a sulphate of titanium is Ti2(SO4)3. Write the formula of its phosphate (1mk)
-
- State Graham’s law of diffusion. (1mk)
- 60cm3 of oxygen diffuses through a membrane in 10 sec while 100cm3 of chlorine gas diffuses through the same membrane in 30 seconds. Given the density of oxygen as 1.25g/cm3, calculate the density of chlorine. (2mks)
- When a litmus solution was added to a solution of ammonia gas in methylbenzene there was no effect on the litmus solution on addition of water to the resulting mixture the litmus solution turned blue.Explain these observations. (3mks)
- Element P and Q have atomic numbers 13 and 8 respectively.
- Write down the electron arrangement of the ions
- P+ (1mk)
- Q- (1mk)
- Write down the formula of the compound formed between P and Q (1mk)
- Write down the electron arrangement of the ions
- When hydrogen peroxide is mixed with a little manganese (IV) oxide, a colourless gas is evolved.
- Identify the gas (1mk)
- What is the purpose of manganese (IV) oxide in the above reaction? (1mk)
- How is the gas in (a) above prepared in large scale (1mk)
- Hydrogen sulphide gas was bubbled into a test tube containing iron(III) chloride solution
- State the observations made (2 mks)
- Write an equation for the reaction that took place (1mk)
- In an experiment to prepare nitrogen, ammonium nitrite was gently heated in a flask.
- Write the equation for the reaction that took place in the flask (1mk)
- State one use of nitrogen (1mk)
- A hydrocarbon undergoes the process represented by the equation below to produce two other hydrocarbons.
C10H22 → X + C6H14- Name the process undergone by the hydrocarbon (1mk)
- State one condition necessary for the process. (1mk)
- To which homologous series does substance X belong? (1mk)
- Describe how the pH of anti-acid (actal) powder can be determined in the laboratory. (2mks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- The elements forms ions by losing electrons hence have less number of energy levels than corresponding atoms.
- Down the group, atomic radii with increase in the number of occupied energy levels.
- Element Z. It has largest atomic radius hence easily looses its outermost electrons.
- Z has a lower ionization energy and most electropositive
- Concentration of NaOH = 8/40 = 0.2M ½
Moles of NaOH = 0.2 x 25 = 0.005 mol ½
1000
Reacting mole ratio 2:1 ½
Moles of acid 0.005 = 0.0025 ½
2 ½
R.M.M of acid= 0.245 = 98 ½
=0.0025 -
- Over indulgence in or dependence on an addictive substance especially alcohol or drugs.
- - Anxiety and irritability
- Lung cancer
- Heart diseases
-Stained teeth/bad breathe
-Reduces fertility
- Respiratory diseases
-
- Zn2+ & Cl-
- Zn2+(aq) + 2OH-(aq) → Zn(OH)2(s)
- [Zn(NH3)4] 2+
- Bonds broken
944 + 3 x 436 = +2252KJ
Bonds formed
2(3 x388) = 232KJ
Heat of reaction = + 2252 – 2328 = -76KJ - Add water to the mixture; transfer the mixture to the separating funnel; shake well and allow to settle; water mixes with ethanol and forms lower layer while the upper layer is hexane. Draw out the lower and remain with hexane.
- Fractional distiration.
-
- 2 CL –(aq) →CL2(g) + 2e-
- 2 Na+ (aq) + 2e- → 2 Na(s)
- mass of saturated solution = 26.86 – 15.86 = 11.0g (½ mk each)
Mass of salt = 16.86 – 15.86 = 1g
Mass of water = 11 – 1= 10g
If 10g of water contains 1g of salt
100g of water = 1/10 x 100 = 10g/100g of water -
- Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same atomic number but different mass number.
- R.A.M. = (28 x 99.2) + (29x 4.7) + (30 x 3.1 1mk
100
= 2810.9
100
= 28.109 1 mk½ ½
- Add excess lead carbonate to dilute nitric(V) acid; filter to obtain lead(II) nitrate as filtrate. Add the filtrate to dilute hydrochloric acid; filter to obtain lead(II) chloride as residue; wash the residue with distilled water; dry between filter paper. ½
-
- Q
- P
- R
- Incomplete combustion of fuel leads to formation of carbon(II) oxide which is poisonous.
-
-
- 3 Cu(s) + 8 HNO3 (l) →Cu (N03)2(aq) + 2 N0 (g) + H2O(l)
-
- P1V1 = P2V2
T1 T2
=750 x 250 = 750 x V2 ( 1mk
300 315 = 262.5cm3 (1 mk) - Does not wet the container
Efficient coolant than water -
- Mass of C in Co2 12/44 x 2.64 = 0.710 (½ mk each)
Mass of H2 in H2O 12/18 x 1.08 = 0.12
Mass 0.710 0.12
Mole 0.059 0.12
0.059 0.059
Mole Ratio 1 2
EF = CH2
MF (CH2 )n = 84
MF = (CH2)6 ,
4n = 84
N = 6 ½mk = C6 H12 ½mk -
- Brown solid is deposited; blue solution changes to pale green solution; brown solid is due to copper; iron is more reactive and displaces copper. Blue solution changes to pale green due to iron (II) ions having displaced copper. Labeling - ½mk
-
Normal bonds - ½ mk
Dative bond - ½ mk -
- SXTU - first and last correct - 1 mk
all correct - 2 mks - T(s) + X2+(aq) → T2+(aq) + X(s)
- SXTU - first and last correct - 1 mk
- T3PO3-3 → TPO3
-
- Under the same conditions of temperature and pressure the rate of diffusion or a gas is inversely proportional to square root of its density.
- Rate of oxygen = 60/10 = 6cm3/sec (½ mk each)
Rate of Cl2 = 100/30 = 3.33cm3 /sec
RO2 =√x/1.25; 6/3.33 = √x/1.25
= 36/11.0884 = x/1.25
x= 4.058
- In methylbenzene ammonia does not ionize. In addition of water it ionizes and OH- are formed which are responsible for the colour change in the litmus.
-
-
- 2.8.2
- 2.7
- P2Q3
-
-
- Oxygen gas
- To speed up the reaction
- In fractional distillation of liquidified air.
-
- Brown iron (III) chloride solution turn green iron (II) chloride or yellow solid is deposited at the bottom of the test tube.
- H2S(g) + 2FeCl3(aq) → 2FeCl2(aq) + S(s) + 2HCl(aq)
-
- NH4NO2(s) →N2(s)+ 2H2O(l)
- -Manufacture of ammonia
-In food preservation
-Provide inert atmosphere in bulbs
-
- Cracking
- Heating / use of catalyst
- Alkene
- Add water to the powder and stir. Insert pH paper into the solution. Compare the colour formed against the colours given on the pH chart. Record the pH value of the colour that corresponds with the colour formed on the pH paper.
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 - 2019 KCSE CEKENA MOCK EXAMINATION (QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS).
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students