SECTION A
Answer all the questions in this section
-
- State three factors that contribute to growth of slums in urban centers. (3mk)
- List two types of settlement patterns in Kenya. (2mk)
-
- State three physical conditions that favour growing of maize in Kenya. (3mk)
- Give two problems facing maize farming in Kenya. (2mk)
-
- What is air pollution?(2mk)
- State three ways that Kenya has adopted to manage air pollution. (3mk)
-
- Differentiate between a national park and a game reserve. (2mk)
- State three effects of human encroachment into wildlife habitats. (3mk)
-
- Name two places where diamond mining is done in South Africa. (2mk)
- state three problems facing gold mining in South Africa. (3mk)
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other two questions from this section.
-
- The photograph below shows a crop cultivated under horticultural farming.

- identify the type of photograph shown above. (1mk)
- Using evidence from the photograph, identify two indicators that show the area receive high rainfall. (2mk)
- Draw a rectangle measuring 15 cm by 10 cm and on it sketch and show the main features.(4mk)
- State four reasons why growing of vegetables in green houses in Kenya would be preferred.(4mk)
- Explain four difficulties that the Kenyan farmer face in marketing horticultural produce.(8mks)
- Explain three similarities between horticultural farming in Kenya and Netherlands. (6mk)
- The photograph below shows a crop cultivated under horticultural farming.
-
- Differentiate between pelagic fishing and demersal fishing. (2mk)
- State four reasons why marine fisheries are not well developed in Kenya. (4mk)
- Explain three reasons why Lake Victoria is a major fishing ground in Kenya. (6mk)
- Give five ways in which fresh water fisheries in Kenya can be conserved. (5mk)
- Explain fourdifferences between fishing in Kenya and Japan. (8mk)
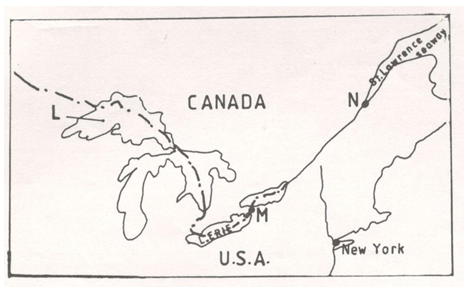
- The sketch map below shows the Great Lakes and the St. Lawrence sea way. Use it to answer question
- Name the lake marked (1mk)
- Name the waterfall marked (1mk)
- Name the sea port marked N. (1mk)
- List three objectives that led to the construction of the St. Lawrence sea way. (3mk)
- Explain four ways in which the St. Lawrence Sea way has benefited the economies of Canada and the USA. (8mk)
- State threecauses of the decline in use of letters as a mean of communication in Kenya. (3mk)
- Explain fourefforts made by the Government of Kenya to solve the problems facing communication in the country. (8mk)
-
-
- Name two places in Kenya where wind energy is being harnessed. (2mk)
- Give four reasons why Kenya has not been able to fully exploit her geothermal power potential. (4mk)
- Explain four benefits that would result from rural electrification in Kenya.(8mk)
- Apart from petroleum oil, name three other sources of non -renewable energy. (3mk)
- What is energy crisis. (2mk)
- Explain three effects that the increase in petroleum oil prices has had on the economy of Kenya.(6mk)
-
-
-
- Name two towns in Kenya with motor vehicle assemblyindustries. (2mks)
- State four ways in which Kenya has benefited from the motor vehicle assembly industries. (4mk)
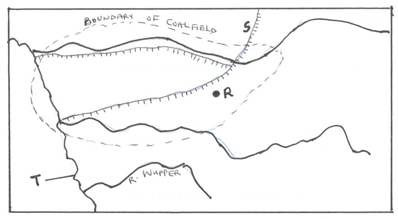
- The sketch map below shows the Ruhr Industrial region of Germany.
- Name the town marked R. (1mk)
- Name the canal marked (1mk)
- Name the river marked T. (1mk)
- Explain four factors that have led to the growth of the iron and steel industries in the Ruhr region of Germany. (8mk)
- Your class has decided to undertake a field study in a factory near your school.
- Give three reasons why it is important to seek permission from the school.(3mk)
- State two reasons why administering questionnaires may not be an appropriate method to collect data. (2mk)
- State three advantages of using statistical tables to record data. (3mk)
-

MARKING SCHEME
-
- State thee factors that contribute to growth of slums in urban centers.
- Low income due to unemployment or under employment
- Inadequate housing in urban centers
- High cost of land and houses in towns
- Poor urban planning
- High rate of rural urban migration
Any 3×1 mk = 3mk - List two types of settlement patterns in Kenya.
- Scattered/dispersed
- Nucleated/clustered
- Linear
- Radial
Any 2×1 mk =2mk
- State thee factors that contribute to growth of slums in urban centers.
-
- State three physical conditions that favour growing of maize in Kenya.
- Rainfall amount that vary between 300 – 1800 mm.
-Day temp between 180C - 300 C and night temp should not fall below 100 C.
- Deep well drained fertile loamy, clayey, sandy soils rich in nutrients.
- Gentle sloping undulating land to allow mechanization.
- Maize do well in altitude from the sea level to about 1800M.
Any 3×1mk = 3mk. - Give two problems facing maize farming in Kenya.
- Adverse weather conditions like drought, hail which destroy crop lowering yield.
- Diseases of maize like smut, leaf blight that destroy crop and lower yield/ cause death of crop.
- Pests like aphids, weevils that destroy crop lowering yield/ quality.
- Weeds like striga which lower yield of crop
- Price fluctuations in the market that kill farmer’s morale.
- High price of inputs like fertilizers which increase cost of production hence farmers use less of the inputs and lower yield.
- Inadequate storage facilities which make farmers to sell their produce at lower prices/ cause damage to crop due to poor storage.
Any 2 ×1 mrk = 2mk
- State three physical conditions that favour growing of maize in Kenya.
-
- What is air Pollution.
- This is the contamination of the atmosphere with harmful materials of solid or gaseous form that cause harm or injury to human health or property.
Mark as a block = 2mk - State three ways Kenya has adopted to manage air pollution.
- Enact regulations to punish those polluting the air.
- Installing filters in vehicles exhaust pipes to filter harmful emissions/ fumes
- Use of alternative means of transport like electric/ solar vehicles to cut on non- pollutants.
- Treatment of industrial fumes/ waste before releasing them into the atmosphere.
- Carry out campaigns to educate people on awareness and dangers of air pollution.
Any 3×1mk = 3mk
- What is air Pollution.
-
- Differentiate between a national park and a game reserve.
- A national park is an area set aside forpropagation, protection preservation of wildlife in their natural habitat in which hunting is prohibited while a game reserve is an area set aside for preservation ofwildlife but the local community is allowed limited access of grazing collection of firewood and are managed by the local authorities.
Mark as a block. (2mk) - State three effects of human encroachment into wildlife habitats.
- lead to killing or dying of animals.
- lead to some animals or plants becoming extinct.
- lead to enhanced wildlife human conflict
- may lead to migration of animals
- lead to reduction of wildlife habitat
- may lead to poaching of animals for their meat/skins/horns.
Any 3×1mark = 3mks.
- Differentiate between a national park and a game reserve.
-
- Name two places where diamond mining is done in South Africa.
- Kimberley - Pretoria - JagersFoutein - KoffieFoutein.
Any 2 ×1 mk = 2mk - State three problems facing gold mining in South Africa.
-Water shortage due to competition for water with other industries.
- High cost of mining due to increasing depth of mines
- Poor quality ore as a result of increasing depth of mines
- Over exploitation of gold which has led to the exhaustion/ closure of mines.
- High cost of labour due to competition of labour by other manufacturing industries.
- Accidents /death as a result of collapse/ suffocation in the mines.
Any 3×1 mk = 3mk
- Name two places where diamond mining is done in South Africa.
-
-
- identify the type of photograph shown above.

- Ground general view photograph.
1mk - Using evidence from the photograph, identify two indicators that show the area receive high rainfall.
- Presence of tall trees in the background.
- The crop being cultivated has luxuriant weeds between them.
- Presence of cabbages a crop that requires high rainfall.
- The ground has a continuous cover of crop/ plants.
Any 2×1mk = 2mk - Draw a rectangle measuring 15 CM by 10 CM and on it sketch and show the main features.
Mark - cabbages - trees - Electric power lines
- Kales - maize - Tree stump
- Well drawn rectangle *(must be drawn) 1mk
Any 3 features 3 ×1mk = 3mk (total 4mk)
- identify the type of photograph shown above.
- State four reasons why growing of vegetables in green houses in Kenya would be preferred.
- Cropsdoes not suffer from excessive rainfall/hailstones/strong winds.
- Crops are not affected by pests/diseases/ easy to control pests and diseases.
- Easy to grow crops through- out the year as external climate conditions are managed.
- Easy to control weeds
- Green house create uniform and constant climatic conditions.
- It is easy to control moisture amount available to the crop.
- Drought is controlled as crop can be watered.
Any 4×1 mk = 4mk - Explain four difficulties that the Kenyan farmer face in marketing horticultural produce.
- Impassable roads during rainy season create difficulties which lead to rotting of perishable produce/ deterioration of quality.
- Stringent quality standardsrequired in world market that lock off many farmers from selling/ increase cost of production/ lower profit margin.
- Fluctuating prices of produce in market that lower profit/ kill farmer’s morale.
- Inadequate/limited storage/preservation/refrigeration facilities which lead to loss /spoilage.
- Unhealthy competition from other countries that produce similar produce in the international market which cause loss of outlet for produce.
- High cost of freight which lower the profit margin.
- Poor marketing structures which encourage middlemen who exploit farmers / offer lower prices.
Difficulty = 4mk
Explanation = 4mk (total 8mk). - Explain three similarities between horticultural farming in Kenya and the Netherlands.
- In both countries the horticultural crops are sold locally and in the international market.
- In both countries the crops are grown in green houses.
- In both countriesthere is use of advanced technology/ scientific techniques in growing of crops.
- In both countries farming is carried out by large companies/ private organization who have invested heavily in farming.
- Both countries practice farming in areas with well drained fertile soils.
- Both countries have abundant labour to work in horticultural farms
- Both countries have varied climatic conditions favourable for different horticultural crops.
- In both countries farmers irrigate their farms/ artificially applies water to their crop.
*Accept other relevant points.
* Candidate must use words in their points to express similarities.
Each point 2mks (any 3×2 mk = 6mk)
-
-
- Differentiate between pelagic fishing and demersal fishing.
- Pelagic fishing is the exploitation of fish that live close to the surface of oceans/lakes/sea whiledemersal fishing is the exploitation of fish found deep in oceans/ at sea beds/bottom of water bodies.
Mark as block = 2mk - State four reasons why marine fisheries are not well developed in Kenya.
- The continental shelf is narrow hence not enough fishing ground.
- Kenya coast line is straight/ has few indentations/ not suitable for fish breeding.
- The ocean waters are warm and not suitable for growth of planktons.
- The demand for fish is low/ coastal people are poor and cannot afford to buy fish
- Fishermen are unable to buy fishing vessels for deep water fishing due to inadequate capital
- Stiff competitions from well developed countries/ with developed equipment hence inadequate market for Kenya’s fish.
-Fishermen have inadequate skills for deep sea fishing.
Any 4×1mk = 4mk -
- Explain three reasons why Lake Victoria is a major fishing ground in Kenya.
- The lake is shallow/ has an average depth of 84m thus allow penetration of sunlight for growth of planktons /feed for fish.
- Lake has several beaches/ inlets/ bays that provide good breeding grounds for fish/ harbor for landing of boats.
- People around the lake consume fish and provide market to the fish caught.
- Presence of fish processing factories at Kisumu/ Homa Bayensure proper preservation of fish thus encouraging fishing.
- Lake has a variety of fish species that are of economic value like the nile perch/tilapia/mud fish
- Presence of a developed network of roads/ railway/airport to encourage fish movement since it is perishable/ requires quick transport.
Reason = 3mk
Explanation = 3mk (total = 6mk) - Give five ways in which fresh water fisheries in Kenya can be conserved.
- Standardizing size of nets to ensure immature fish are not caught.
- restricting fishing to certain seasons to allow fish breeding.
- licensing fishermen to control their numbers/ control overfishing
- restrict disposal of effluents/pollutants/ untreated waste to ensure safety of waters.
- Employ marinepolice to patrol lake waters and control illegal fishing/ poaching of fish.
- control/ eradicate water weeds like hyacinth to protect water resources.
- restrict use of water bodies by controlling activities of those doing irrigation/ pumping water for industrial/ commercial use.
Any 5×1mk = 5mk
- Explain three reasons why Lake Victoria is a major fishing ground in Kenya.
- Explain four differences between fishing in Kenya and japan.
Kenya
Japan
- Poor technology/ inadequate capital that hamper deep sea fishing
- Advanced technology/ sophisticated vessels for fishing far and deep in the sea.
- Regular coastline/ inadequate sea inlets to provide sheltered areas for fish breeding.
- has indented coastline/ many islands/ which provide excellent fishing grounds.
- Warm Mozambique current that make water to be warm/unsuitable for growth of plankton
- Convergence of warm kurosiwo and cold OyaSiwo current result in upwelling/ abundant planktons.
- Limited market for fish/most communities do not have fish eating culture
- Large Japanese population/ surrounding nations offer market for fish.
- Has warm climatic conditions which limit growth of planktons/preservation of fish.
- has temperate climate/ cool climate ideal for growth of planktons.
- Has deep/ narrow continental shelf that limit growth of planktons/ limit fish in waters.
- Has broad shallow continental shelf that favour growth of planktons/ breeding of fish
- Land favour agriculture/ a small number of people engage in fishing.
- Country is rugged/ mountainous hinder agriculture/ people turn to sea for food.
Each point = 4×2 mk = 8mks*Difference must come out clearly.
- Differentiate between pelagic fishing and demersal fishing.
-
-
- Name the lake marked L
-Lake Superior
(1mk) - Name the waterfall marked M
- Niagara Falls
(1mk) - Name the sea port marked N.
- Quebec
(1mk)
- Name the lake marked L
-
- List three objectives that led to the construction of the St Lawrence sea way.
- Regulate the different water levels along the seawaythrough dredging/widening shallow sections
- Removal of rock outcrops/rapids/small islands.
- Regulate flow of river St. Lawrence by construction of dams.
- Promote growth of industries/trade between Canada and USA.
- Provide cheap route to transport bulky commodities - coal/wheat/iron and steel.
- Create employment opportunities along the sea way.
- Open the interior of Canada and USA to exploit the natural resources.
Any 3×1 mark = 3mks. - Explain four ways in which the St Lawrence Sea way has benefited the economies of Canada and the USA.
- Has provided a cheap means of transport for exports and imports hence promoting internal/international trade.
- Dams constructed along the route provide electricity for domestic/ industrial use.
- Has led to the growth of ports and towns like Duluth, Chicago/ Detroit which are focal points for economic activities.
- Features along the sea way like Niagara fall are tourist attractions which generate income to the countries.
- Creation of employment opportunities in the transport sector that help raise standards of living.
- Lakes and dams are sources of water for domestic/industrial use.
- Both countries earn revenue from the toll charged on vessels plying the route is used to better the economiesof both countries.
- The route has led to ease of movement of raw materials which has led to the growth of industries in the region.
Way = 4mk
Explanation = 4mk (Total 8mk)
- List three objectives that led to the construction of the St Lawrence sea way.
- State three causes of the decline in use of letters as a means of communication in Kenya.
-High cost of postage
- Loss of letters in the post office.
- Delay in delivery of letters.
- Emergence of other faster means of communication/ sms /internet/ whatsapp/ facebook/ skype.
tampering with letters.
Any 3×1 mk =3mk - Explain four efforts made by the Government of Kenya to solve the problems facing communication in the country.
- Liberalization of the communication sector which has led to modernization of communication systems/ encouraged a variety of providers of communication services.
- Installation of wireless telephones/ mobile telephones that has reduced vandalism associated with telephone facilities.
- Adoption of international languages like French/Germany/Chinese/English to reduce language barriers.
- Installation of satellites/radio boosters/television boosters in order to improve communication.
- Strengthening of regional trading blocs to create favourable conditions for improvement of communication with other member states.
- Liberalization of the economy to encourage more Kenyans access gadgets used in communication.
Any 4well explained points
Any 4×2mks = 8mks
-
-
-
- Name two places in Kenya where wind energy is being harnessed.
- Kinangop - Ngong Hills - Near L Turkana/Loiyangalani.
Any 2 ×1 mk = 2mk - Give four reasons why Kenya has not been able to fully exploit her geothermal power potential.
– Inadequate capital to fully develop more plants in existing geothermal sites/ other potential areas.
- Low level of technology in exploitation of geothermal power.
- Inadequate skills to explore/ harness energy sources.
- Danger of land subsidence as steam is tapped from within the earth crust.
-potential areas are located in remote areas/far off places from market for electricity.
Any 4×1 mark = 4mks
- Name two places in Kenya where wind energy is being harnessed.
- Explain four benefits that would result from rural electrification in Kenya.
- Promote establishment of industries in rural areas hence encouraging decentralization of industries.
- Reduce deforestation as households resort to use of electricity and cut on use of biomass which destroy environment.
- Help attract/ establishment of social amenities in rural areas thus reduce rural to urban migration.
- Stimulate investments in rural areaswhich would promote availabilityof opportunitiesto raisethe standards of living.
- Encourage development of horticulture by providing power for cold storage facilities for storage of perishable horticultural produce.
- Reduce the import bill/ foreign exchange used in the importation of petroleum oil as domestic homes switch to use of electricity.
Any 4Benefit = 4mk
Explanation = 4mk (Total = 8mk) - Apart from petroleum oil, name three other sources of non - renewable sources of energy.
- Coal - Natural gas - Thermal electricity - Nuclear energy.
Any 3×1 mk = 3mks -
- What is energy crisis.
- It is a situation where the demand for oil/ fossil fuel is higher than the supply hence leading to high oil/ energy prices.
Mark as block = 2mk - Explain three effects that the increase in petroleum oil prices has had on the economy of Kenya.
- Kenya would spend more foreign exchange on importation of oil at the expense of other sectors.
- Increasing cost of transport hence a rise in the cost of movement of people/goods /services.
- Increase in production cost hence increase in prices of commodities/ reduction in demand of goods and services.
-collapse of industries relying on petroleum oil by products/loss of employment/ redundancy.
- led to low economic growth thus leading to general poverty among the people.
- has led to the need to establish/ look for cheaper sources of energy to replace oil.
- has created awareness on the need to conserve energy sources.
- The country has started exploration for possibilities of striking its own oil resource to reduce or stop importation.
Any 3Effect = 3mks
Explanation = 3mks (total = 6mks)
- What is energy crisis.
-
-
-
- Name two towns in Kenya with motor vehicle assembly industries.
- Thika - Nairobi - Mombasa.
Any 2 ×1 mk = 2mk - State four ways in which Kenya has benefited from the motor vehicle assembly industries.
- Kenya saves foreign exchange that would have been used in importing the vehicles
- Country earn foreign exchange from exports of vehicles
- Creation of employment opportunities where people earn income to better standards of living.
- Promoted transport by availing vehicles to move people /goods.
- provided market for raw material produced by other industries locally.
Any 4×1 mk = 4mk
- Name two towns in Kenya with motor vehicle assembly industries.
- The sketch map below shows the Ruhr Industrial region of Germany.
- Name the town marked R.
- Dortmund
1mk - Name the canal marked S.
-Dortmund – Ems canal
1mk - Name the river marked T.
-River Rhine
1mk
- Name the town marked R.
- Explain four factors that have led to the growth of the iron and steel industries in the Ruhr region of Germany.
- Availability of iron/ coal/limestoneprovide raw materials needed in the industries.
- Availability of water from rivers Rhine/Ruhr/Lippe/Wupper/Emscher used for cooling machines/ industrial use.
- Presence of navigable rivers like Ruhr/Wupper, canals like Dortmund Ems/ Lippe/ Rhein - Herne to provide transport for bulky raw materials/ finished products.
- Presence of market for iron and steel from rich neighbouring countries of central Europe.
- Presence of Coal from the Ruhr/ imported petroleum provide power/ energy needed in the industries.
- Availability of highly skilledlabour necessary for industrialization favour growth of industries.
- Availability of capital as Germany is a wealthy country / presence of rich families that invest in iron and steel industries.
Any 4 Factor×1 = 4mk.
Explanation 4×1 = 4mk. (Total 8mk) - Your class has decided to undertake a field study in a factory near your school.
- Give three reasons why it is important to seek permission from the school.
- It is an official requirement.
- Enable administration arrange for transport/ lunch.
- Enable administration take care of disruption that may affect normal school programme.
- Enable administration provide essential tools for use in the study.
Any 3×1 mk = 3mk - State two reasons why administering questionnaires may not be an appropriate method to collect data.
- Information given could be biased/inaccurate
- Difficult to gauge accuracy of information given
- Some questions may not be answered
- When questions are not well understood can lead to inaccurate responses.
- Some questionnaires may not be sent back/ may be sent back unfilled
- Illiteracy/ language barriers limit use of method
- Expensive/ time consuming if it involves travelling
- Difficult to prepare good questionnaires.
- Some answers given are difficult to analyse.
Any 2×1 mrk = 2mk - State three advantages of using statistical tables to record data.
- Easy to extract data from a table
- Easy to read and interpret data in a table
- Save time/space as data is summarized
- Easy to compare data
- Easy to note data pattern/ changes.
- Suitable for presenting numerical data.
Any 3×1 mk = 3mk
- Give three reasons why it is important to seek permission from the school.
-
Download GEOGRAPHY PAPER 2 - 2019 LAINAKU JOINT MOCK EVALUATION EXAMINATION.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students